コード:https://github.com/mo49/firebase_test
Firebase console
Googleアカウントでログイン
https://console.firebase.google.com/
Firebase CLI
以下を参考に、プロジェクト作成までを行う
https://firebase.google.com/docs/cli/?hl=ja
プロジェクト自体はFirebase consoleで作っておいたほうがシンプル
(CLIではプロジェクトを選択するだけにする)
ローカルで起動させる
$ firebase serve
データベースのルール変更
親の階層のルールが子へとカスケードされる書き方
{
"rules": {
".read": "true",
"message": {
".write": "auth != null"
},
"info": {
".write": "true"
}
}
}
「データベース/messageの書き込みには認証が必要」
「データベース/infoの書き込みには認証が不要」という設定
書き込み・読み込み
書き込み
const databaseRef = firebase.database().ref();
// set
databaseRef.set()
読み込み
パスデータの変更をvalueイベントでリッスンする
// on
databaseRef.on('value',snapshot => {
console.log(snapshot.val());
})
// once(1回のみ)
databaseRef.once('value').then(snapshot => {})
参考
https://firebase.google.com/docs/database/web/read-and-write
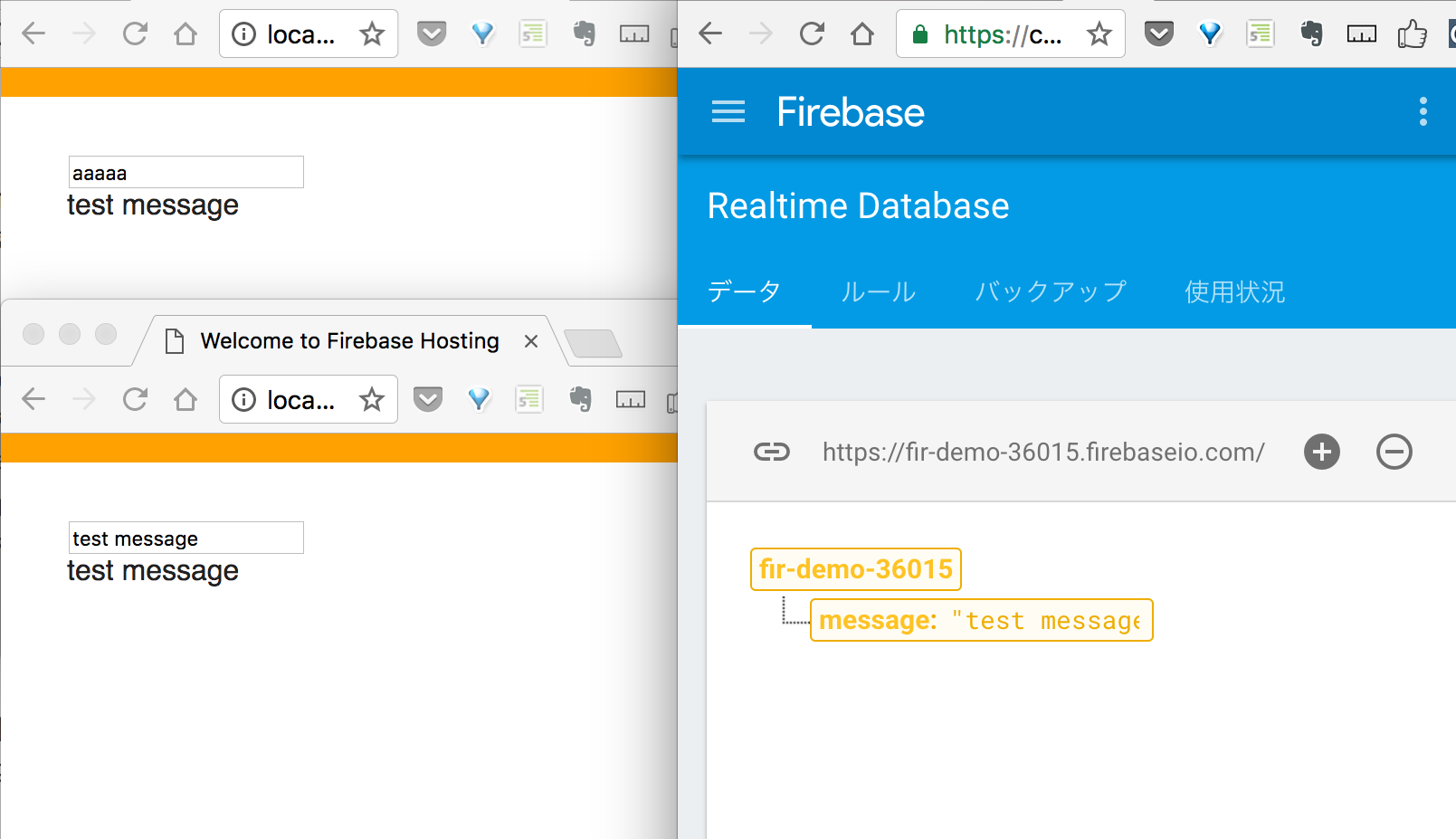
リアルタイムにテキストの変更を反映する
const $input = document.querySelector('#input')
const $output = document.querySelector('#output')
const db = firebase.database();
// データベース/messageへの参照を作成
const messageRef = db.ref('/message');
// write
$input.addEventListener('input', e => {
messageRef.set(e.target.value);
})
// read
messageRef.on('value',snapshot => {
$output.textContent = snapshot.val();
})
Firebase consoleの「Database > データ」にリアルタイム反映される
認証
サインイン・サインアウト
// どの認証手段を使うか
const provider = new firebase.auth.GoogleAuthProvider();
$signin.addEventListener('click', () => {
// 指定したproviderのサインイン画面に飛ぶ
firebase.auth().signInWithRedirect(provider);
})
ここではGoogleアカウントで認証
https://firebase.google.com/docs/auth/web/google-signin?hl=ja
^ 他アカウントでの認証も載っているので参考に!
$signout.addEventListener('click', () => {
firebase.auth().signOut().then(() => {
location.reload()
})
})
変更をリッスン
firebase.auth().onAuthStateChanged(user => {
if (user) {
const $profile = document.querySelector('#profile')
$profile.innerHTML = `
<div>uid: ${user['uid']}</div>
<div>displayName: ${user['displayName']}</div>
<div>email: ${user['email']}</div>
<img src="${user['photoURL']}" width="100">
`
} else {
// 認証していない場合は自動的に認証画面へ
// firebase.auth().signInWithRedirect(provider);
}
})
データの操作
child
以下の3つは同じ意味。childを使うとシンプルになるよという話。
(以降、infoRefを使用)
const infoRef = db.ref('/info');
infoRef.child('user01').set({
name: 'user01',
})
const infoRef = db.ref('/info');
infoRef.set({
user01: {
name: 'user01',
}
})
const infoRef = db.ref('/info/user01');
infoRef.set({
name: 'user01',
})
更新 | update
set:書き込む
update:変更があれば更新
// それぞれのメソッドでpromiseが返ってくるので、
// thenで処理をつなぐこともできる
infoRef.update()
.then((value) => {
console.log('更新完了');
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log(err.message);
})
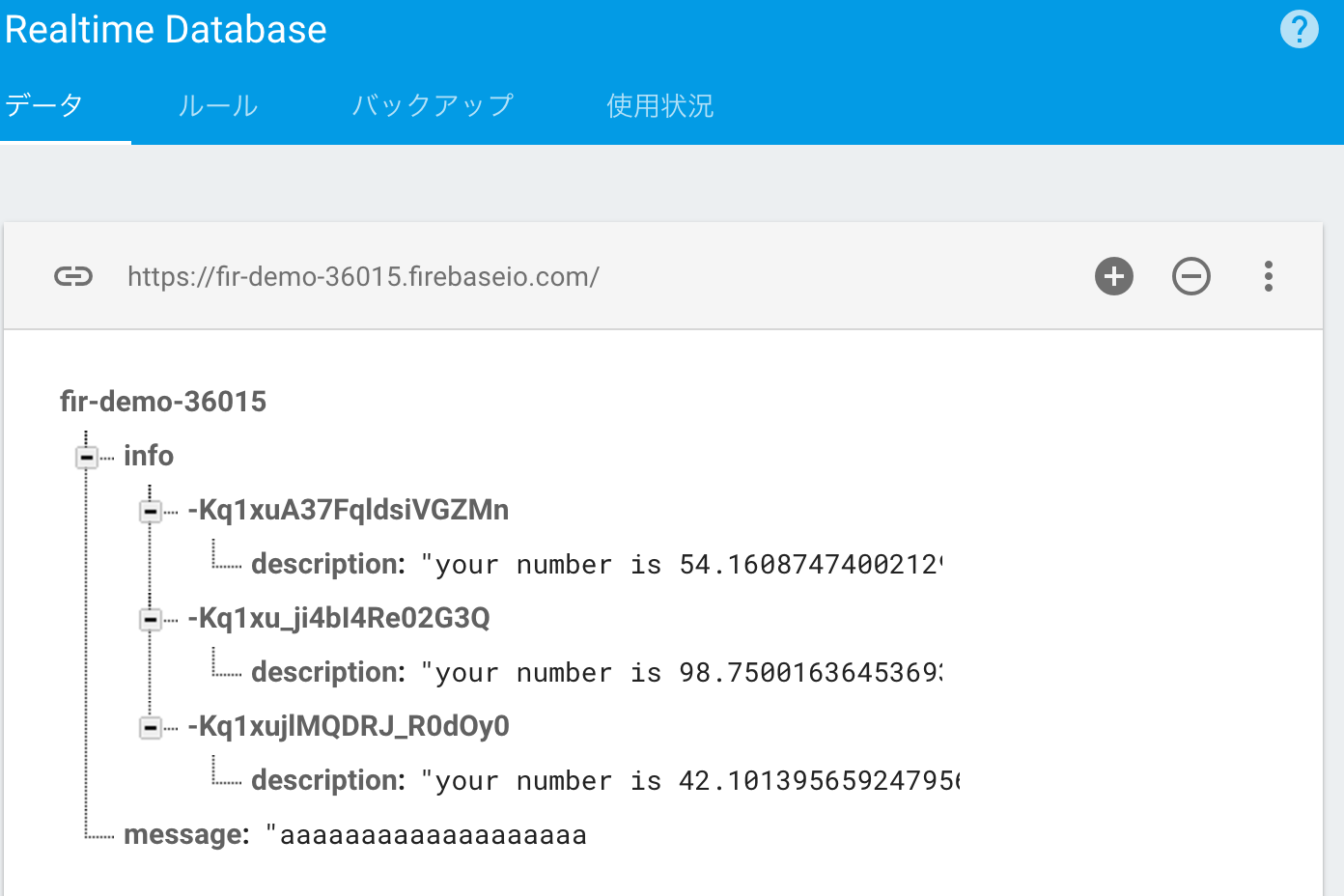
追加 | push
重複することのないユニークなキーを生成するので、
何度クリックしても別データとして追加されていく
$push.addEventListener('click', () => {
infoRef.push({
description: `your number is ` + Math.random() * 100,
})
})
削除 | remove
infoRef.remove();
infoRef.set(null);
デプロイ
$ firebase deploy