やりたいこと
Raspi4の起動時に室温と湿度をひたすら記録する
必要なもの
H/W
使用したH/Wは以下のとおり
- Raspberry Pi 4
- HDC1000
S/W
- Python 3.6.1 | packaged by rpi | (default, Apr 20 2017, 19:35:19)
- Linux raspi4 4.19.97-v7l+ #1294 SMP Thu Jan 30 13:21:14 GMT 2020 armv7l GNU/Linux
各種設定
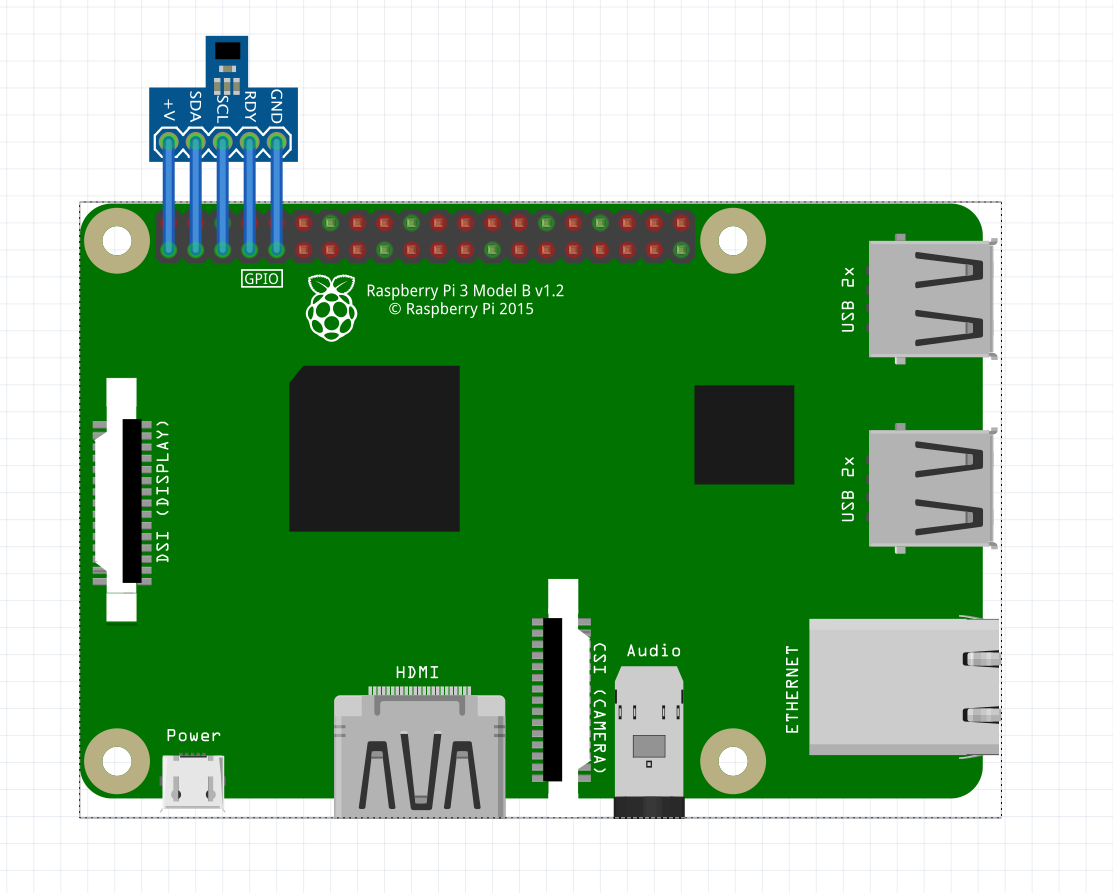
HDC1000の接続
ラズパイ4のパーツを見つけられませんでした。
HDC1000の設定
/boot/config.txt
i2c関連の設定部分
dtparam=i2c_arm=on
/etc/modules
モジュール関連の設定
i2c-dev
i2c-bcm2835
HDC1000の設定の確認
sh
$ lsmod | grep i2c
i2c_bcm2835 16384 0
i2c_dev 20480 0
sh
$ dmesg | grep i2c
[ 2.153160] i2c /dev entries driver
sh
$ i2cdetect -l
i2c-1 i2c bcm2835 I2C adapter I2C adapter
$ i2cdetect -y 1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
40: 40 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
動作確認
サンプルプログラムです。
python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import smbus
import time
# Get I2C bus
bus = smbus.SMBus(1)
# HDC1000 address, 0x40(64)
# Select configuration register, 0x02(02)
# 0x30(48) Temperature, Humidity enabled, Resolultion = 14-bits, Heater on
bus.write_byte_data(0x40, 0x02, 0x30)
# HDC1000 address, 0x40(64)
# Send temp measurement command, 0x00(00)
bus.write_byte(0x40, 0x00)
time.sleep(0.2)
# HDC1000 address, 0x40(64)
# Read data back, 2 bytes
# temp MSB, temp LSB
data0 = bus.read_byte(0x40)
data1 = bus.read_byte(0x40)
# Convert the data
temp = (data0 * 256.000) + data1
cTemp = (temp / 65536.000) * 165.000 - 40.000
# HDC1000 address, 0x40(64)
# Send humidity measurement command, 0x01(01)
bus.write_byte(0x40, 0x01)
time.sleep(0.2)
# HDC1000 address, 0x40(64)
# Read data back, 2 bytes
# humidity MSB, humidity LSB
data0 = bus.read_byte(0x40)
data1 = bus.read_byte(0x40)
# Convert the data
humidity = (data0 * 256.000) + data1
humidity = (humidity / 65536.000) * 100.000
print('Humid.:' + str(humidity) + '%')
print('Temp. :' + str(cTemp) + '℃ ')
実行すると以下のようになります。
$ python HDC1000.py
Humid.:41.96014404296875%
Temp. :22.763748168945312℃
記録用プログラム
記録用のプログラムは、こんな感じにしました。
python
# !/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import smbus
import time
import datetime
import csv
import pathlib
import os
file_name = 'th_data.csv'
header_data = 'date_time,temperature\n'
def read_temp():
# Get I2C bus
bus = smbus.SMBus(1)
# HDC1000 address, 0x40(64)
# Select configuration register, 0x02(02)
# 0x30(48) Temperature, Humidity enabled, Resolultion = 14-bits, Heater on
bus.write_byte_data(0x40, 0x02, 0x30)
# HDC1000 address, 0x40(64)
# Send temp measurement command, 0x00(00)
bus.write_byte(0x40, 0x00)
time.sleep(0.2)
# HDC1000 address, 0x40(64)
# Read data back, 2 bytes
# temp MSB, temp LSB
data0 = bus.read_byte(0x40)
data1 = bus.read_byte(0x40)
# Convert the data
temp = (data0 * 256.000) + data1
cTemp = (temp / 65536.000) * 165.000 - 40.000
return cTemp
def read_humid():
# Get I2C bus
bus = smbus.SMBus(1)
# HDC1000 address, 0x40(64)
# Select configuration register, 0x02(02)
# 0x30(48) Temperature, Humidity enabled, Resolultion = 14-bits, Heater on
bus.write_byte_data(0x40, 0x02, 0x30)
# HDC1000 address, 0x40(64)
# Send humidity measurement command, 0x01(01)
bus.write_byte(0x40, 0x01)
time.sleep(0.2)
# HDC1000 address, 0x40(64)
# Read data back, 2 bytes
# humidity MSB, humidity LSB
data0 = bus.read_byte(0x40)
data1 = bus.read_byte(0x40)
# Convert the data
humidity = (data0 * 256.000) + data1
humidity = (humidity / 65536.000) * 100.000
return humidity
def file_check():
global file_name
file_name = pathlib.Path(file_name)
if os.path.exists(file_name):
print('Data File exists!')
else:
file_name.touch()
def header():
global file_name
with open(file_name) as f:
line = f.readline()
if 'date' in line:
print('Header exists!')
else:
with open(file_name) as f:
lines = f.readlines()
lines.insert(0, header_data)
f.close()
with open(file_name, mode='w') as f:
f.writelines(lines)
def main():
global file_name
file_check()
header()
while True:
now = datetime.datetime.now()
temp = read_temp()
humid = read_humid()
# print(now.strftime('%Y%m%d-%H:%M:%S'), '{:.3f}'.format(temp), '{:.3f}'.format(humid))
save_data = [now.strftime('%Y%m%d-%H:%M:%S'), '{:.3f}'.format(temp), '{:.3f}'.format(humid)]
with open(file_name,'a',newline='') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f, lineterminator='\r\n')
writer.writerow(save_data)
time.sleep(10)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
systemdの設定と自動起動の設定
/etc/systemd/system/thlogger.service
thloggerというサービス名にしました。
[Unit]
Description=TH_Logger
After=syslog.target
[Service]
User = pi
PIDFile=/var/run/thlogger.pid
WorkingDirectory=/home/pi/Jupyter/data
ExecStart=/home/pi/berryconda3/bin/python /home/pi/works/HDC1000/TH_logger.py
ExecStop=/bin/kill $MAINPID
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
Restart=always
RestartSec=10s
[Install]
WantedBy = multi-user.target
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl start thlogger
起動ログを確認(/var/log/system)し
$ sudo systemctl status thlogger.service -l
● thlogger.service - TH_Logger
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/thlogger.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2020-04-10 13:09:16 JST; 18min ago
Main PID: 352 (python)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4915)
Memory: 9.1M
CGroup: /system.slice/thlogger.service
└─352 /home/pi/berryconda3/bin/python /home/pi/works/HDC1000/TH_logger.py
4月 10 13:09:16 raspi4 systemd[1]: Started TH_Logger.
問題なければ、起動時に実行するようにします。
$ sudo systemctl enable thlogger
自動起動しないようにする
サービスの状況の確認
$ sudo systemctl status thplogger.service
● thplogger.service - THP_Logger
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/thplogger.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2021-01-29 16:57:13 JST; 4s ago
Main PID: 7244 (python)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4248)
CGroup: /system.slice/thplogger.service
└─7244 /usr/bin/python /home/pi/share/pi4_works/thp_logger/THP_logger.py
1月 29 16:57:13 raspi4 systemd[1]: Started THP_Logger.
稼働していることを確認して、サービスを停止します。
$ sudo systemctl status thplogger.service
● thplogger.service - THP_Logger
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/thplogger.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead) since Fri 2021-01-29 16:58:42 JST; 1s ago
Process: 7244 ExecStart=/usr/bin/python /home/pi/share/pi4_works/thp_logger/THP_logger.py (code=killed, signal=TERM)
Process: 7339 ExecStop=/bin/kill $MAINPID (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 7244 (code=killed, signal=TERM)
1月 29 16:57:13 raspi4 systemd[1]: Started THP_Logger.
1月 29 16:58:42 raspi4 systemd[1]: Stopping THP_Logger...
1月 29 16:58:42 raspi4 systemd[1]: thplogger.service: Main process exited, code=killed, status=15/TERM
1月 29 16:58:42 raspi4 systemd[1]: thplogger.service: Succeeded.
1月 29 16:58:42 raspi4 systemd[1]: Stopped THP_Logger.
自動起動しないようにします。
$ sudo systemctl disable thplogger.service
Removed /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/thplogger.service.