はじめに
CVPR2019 main conference から以下の論文
[1] Z. Zhang, et. al. "PPGNet: Learning Point-Pair Graph for Line Segment Detection"
のまとめ
コード:
https://github.com/svip-lab/PPGNet
著者らはpytorchで実装しているので、今回tensorflowで実装してみた。
概要
- 画像から線分をセグメントするモデル
- まずモデルからheatmapの形で頂点を推定する
- その後モデルから推定した隣接行列で頂点と頂点を対応づけ、線分とする
以下の図([1]Figure 3 より抜粋)のように画像内の線を推定する

アーキテクチャ
アーキテクチャの全体像は以下の[1]Figure 2。
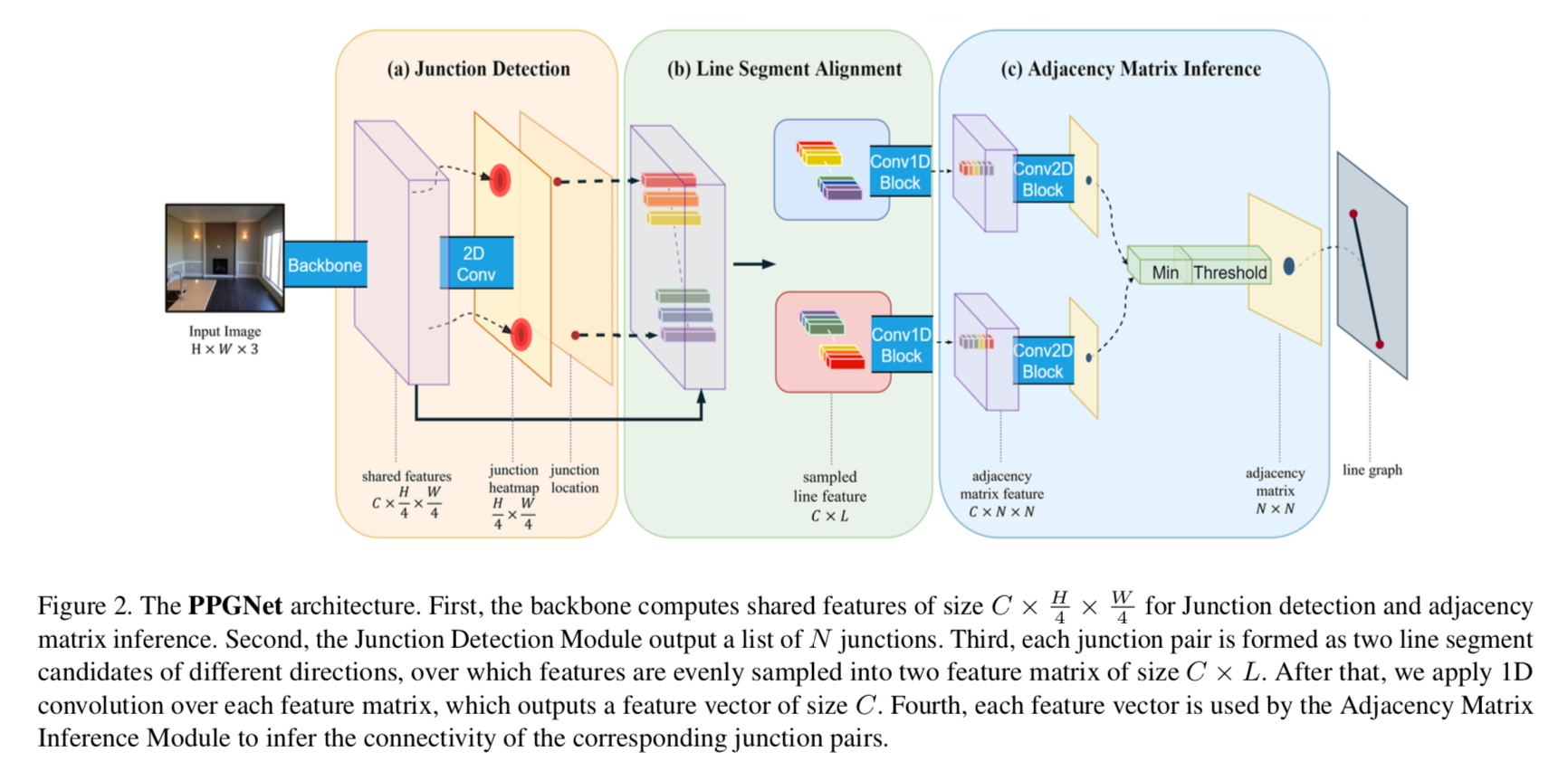
おおまかに
-
- Backbone network・・・特徴量を抽出する
- a) Junction Detection・・・頂点のヒートマップを推定
- b) Line Segment Alignment・・・線の候補ごとに特徴量を求める
- c) Adjacency Matrix Inference・・・線を決定
にわかれる。
0) Backbone network
ここでは入力画像を入力し、特徴量を抽出する。論文ではResNetでencodeし、それをdecodeして入力画像の縦横1/4のサイズにscale up したものを用いている。

a) Junction Detection
ここではヒートマップを出力し、頂点の位置を求める。

この図で一番左は $C \times \frac{H}{4} \times \frac{W}{4}$ の厚みの特徴量。これを2D Convで畳み込んで、 $1 \times \frac{H}{4} \times \frac{W}{4}$ ?のheatmapにしたものが真ん中。
それに1)8近傍のピークを選ぶ処理でピークを算出し、さらに 2)non-maximum suppressionで同じと思われる頂点を1つに絞る。そうして絞られた位置が図中右のjunction location。
b) Line Segment Alignment
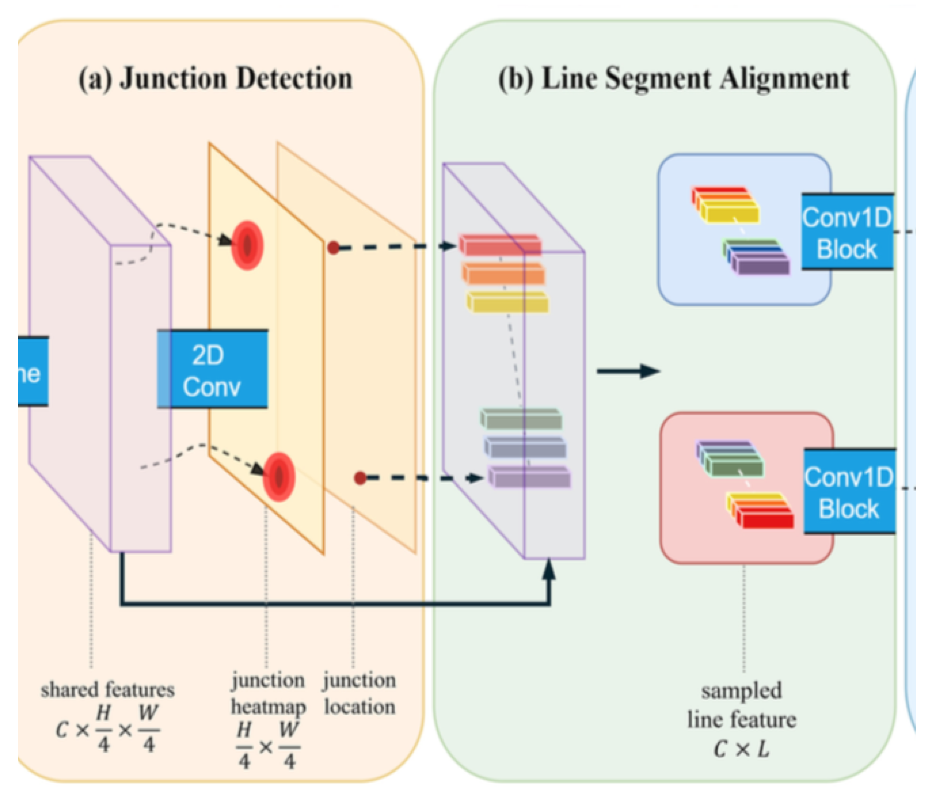
junction locationにおける特徴量を抽出したものが (b) Line Segment Aliginment における一番左の部分。
次に、任意の2頂点に対して、その両者を結ぶ位置は直線を考える。
(b)Line Segment Alignment の左側の図のように、直線上の点から、等間隔にL個(灰色の部分)サンプリングすると、$C \times L$ のベクトルが出来上がる。
これを全ての頂点のペアに対して行うと、頂点の組み合わせの個数(頂点が $N$ 個なら組み合わせは自分自身も含めて $N \times N$ 個)だけこのベクトルが算出される。
論文では $L=64$ を用いている。
Adjacency Matrix Inference
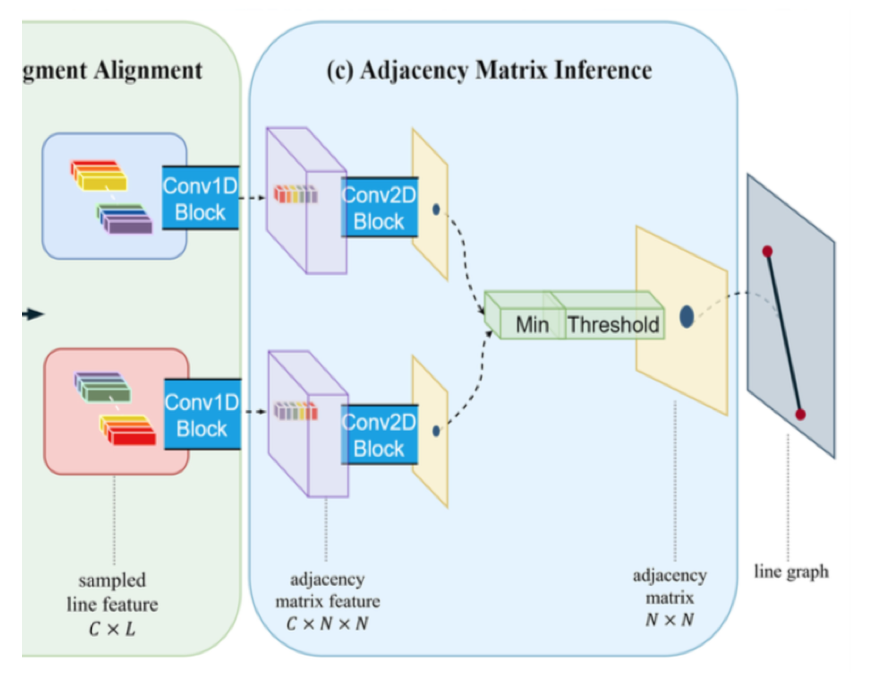
まず図の左側・・・Line Segment Alignmentで求めた $C \times L$ のline feature $N \times N$ 個のそれぞれに対して 1次元convで畳み込み、$C$ の大きさのベクトルにする。これが$N \times N$ 個あるので、整列すると $C \times N \times N$ のadjacency matrix featureになる。
このmatrixに対して畳み込む。 -> ここがよくわからない。conv2Dとなっているので、$N \times N$ のmatrixに対して畳み込むのだろうが、そうすると matrixの $i$ 列(もしくは行)目要素に対応する直線とmatrixの $i+1$ 列(もしくは行)目要素に対応する直線になんらかの関係性を想定していると考えられる。それは何?
とにかく、このようにして $N \times N$ のマトリクスが出来上がる。最後にsigmoidをかけて、マトリクスの各要素が確率を表すようにする。
次にこのマトリクスの $(i,j)$ と $(j,i)$ とは一致するので、小さい方を選択する。(図中の Min と書かれたブロック。
最後に、確率が閾値を下回るものをはじく。(図中のThresholdと書かれたブロック)
のこったマトリクスの要素が直線の存在を示す。
loss
lossは2種類。(a)Junction Detection で用いたheatmapに関するものと、(c) Adjacency Matrix Inference に関するもの。
いずれもpixel wiseなbinary entropyで求める。
\begin{eqnarray}
\mathcal{L} &=& \lambda_{junc} \mathcal{L}_{junc} + \lambda_{adj} \mathcal{L}_{adj} \\
\mathcal{L}_{junc} &=& -\sum_i \tilde{H}_i \log H_i + (1 - \tilde{H}_i ) \log (1 - H_i)\\
\mathcal{L}_{adj} &=& -\sum_i \tilde{A}_i \log A_i + (1 - \tilde{A}_i ) \log (1 - A_i)\\
\end{eqnarray}
掛け率は $\lambda_{junc} = \lambda_{adj} = 1$ を使用。
実装例
以下、tensorflowを用いたミニマムサイズでの実装例
0) Backbone network
論文ではencodeにResNetを用い、それをdecodeしているが、今回はミニマムのためResNet-v2-50を1/4サイズにencodeして代用する。
また、最後にheatmapを作成するための処理が論文からは不明なので、 $1 \times 1 conv$ で次元削減し、1channelにする。
class Backbone(object):
def __init__(self, input_channel, base_channel, model_name='resnet_v2_50'):
self.INPUT_CHANNEL = input_channel
self.BASE_CHANNEL = base_channel
self.MODEL_NAME = model_name
assert self.MODEL_NAME == 'resnet_v2_50', "model name is not resnet_v2_50"
self.FIRST_CONV_FILTER_SIZE = 7
self.BLOCK_FILTER_SIZE = 3
self.BLOCK_STRIDE = 1
def cal_input_num(self, input_num):
stddev = math.sqrt(2 / (input_num))
return stddev
def model(self, x, is_training=True):
with tf.name_scope("resnet_v2_50"):
with tf.name_scope("conv1"): # in_size x in_size x 3 -> in_size /2 x in_size /2 x base_chan
stdd_init = self.cal_input_num(
self.INPUT_CHANNEL * self.FIRST_CONV_FILTER_SIZE * self.FIRST_CONV_FILTER_SIZE)
conv1_W = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([self.FIRST_CONV_FILTER_SIZE, self.FIRST_CONV_FILTER_SIZE,
self.INPUT_CHANNEL, self.BASE_CHANNEL]
, mean=0.0, stddev=stdd_init),
dtype=tf.float32, name='weights')
conv1_b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.BASE_CHANNEL]), dtype=tf.float32, name='biases')
conv_init = tf.nn.conv2d(x, conv1_W, [1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME") + conv1_b
conv_init_relu = tf.nn.relu(conv_init)
with tf.name_scope("block1"): # in_size /2 x in_size /2 x 3 -> in_size /4 x in_size /4 x base_chan*2,
with tf.name_scope("unit_1"):
b1_u1 = self._add_Bottle_Neck(conv_init_relu, self.BASE_CHANNEL, self.BASE_CHANNEL,
self.BASE_CHANNEL * 4, self.BLOCK_FILTER_SIZE, self.BLOCK_STRIDE,
is_training=is_training)
with tf.name_scope("unit_2"):
b1_u2 = self._add_Bottle_Neck(b1_u1, self.BASE_CHANNEL * 4, self.BASE_CHANNEL,
self.BASE_CHANNEL * 4, self.BLOCK_FILTER_SIZE, self.BLOCK_STRIDE,
is_training=is_training)
with tf.name_scope("unit_3"):
b1_u3 = self._add_Bottle_Neck(b1_u2, self.BASE_CHANNEL * 4, self.BASE_CHANNEL,
self.BASE_CHANNEL * 4, self.BLOCK_FILTER_SIZE, 2,
is_training=is_training)
with tf.name_scope("block2"): # in_size /2 x in_size /2 x 3 -> in_size /4 x in_size /4 x base_chan*4
with tf.name_scope("unit_1"):
b2_u1 = self._add_Bottle_Neck(b1_u3, self.BASE_CHANNEL * 4, self.BASE_CHANNEL * 2,
self.BASE_CHANNEL * 8, self.BLOCK_FILTER_SIZE, self.BLOCK_STRIDE,
is_training=is_training)
with tf.name_scope("unit_2"):
b2_u2 = self._add_Bottle_Neck(b2_u1, self.BASE_CHANNEL * 8, self.BASE_CHANNEL * 2,
self.BASE_CHANNEL * 8, self.BLOCK_FILTER_SIZE, self.BLOCK_STRIDE,
is_training=is_training)
with tf.name_scope("unit_3"):
feature = self._add_Bottle_Neck(b2_u2, self.BASE_CHANNEL * 8, self.BASE_CHANNEL * 2,
self.BASE_CHANNEL * 8, self.BLOCK_FILTER_SIZE, self.BLOCK_STRIDE,
is_training=is_training)
self.backbone_trainable_vars = tf.trainable_variables()
self.backbone_all_vars = tf.all_variables()
with tf.name_scope("make_heatmap"):
stdd_hm = self.cal_input_num(
self.BASE_CHANNEL * 8 * 1 * 1)
conv_hp_w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([1, 1, self.BASE_CHANNEL * 8, 1], mean=0.0, stddev=stdd_hm),
dtype=tf.float32, name='weights')
conv_hp_b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self.BASE_CHANNEL]), dtype=tf.float32, name='biases')
conv_hp = tf.nn.conv2d(feature, conv_hp_w, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME") + conv_hp_b
heatmap = tf.nn.sigmoid(conv_hp)
return feature, heatmap
def batch_norm_train(self, inputs, pop_mean, pop_var, beta, scale, decay=0.99):
batch_mean, batch_var = tf.nn.moments(inputs, [0, 1, 2])
train_mean = tf.assign(pop_mean, pop_mean * decay + batch_mean * (1 - decay))
train_var = tf.assign(pop_var, pop_var * decay + batch_var * (1 - decay))
with tf.control_dependencies([train_mean, train_var]):
return tf.nn.batch_normalization(inputs, batch_mean, batch_var, beta, scale, 1e-4)
def batch_norm_wrapper(self, inputs, decay=0.99, is_training=True):
beta = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([inputs.get_shape()[-1]]), dtype=tf.float32, name='beta')
scale = tf.Variable(tf.ones([inputs.get_shape()[-1]]), dtype=tf.float32, name='gamma')
pop_mean = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([inputs.get_shape()[-1]]), trainable=False, name='moving_mean')
pop_var = tf.Variable(tf.ones([inputs.get_shape()[-1]]), trainable=False, name='moving_variance')
# tf.cond(c, func1, func2)
result = tf.cond(is_training, lambda: self.batch_norm_train(inputs, pop_mean, pop_var, beta, scale, decay),
lambda: tf.nn.batch_normalization(inputs, pop_mean, pop_var, beta, scale, 1e-4))
return result
def _add_Bottle_Neck(self, sequence, in_filter_count, hidden_filter_count, out_filter_count, filter_size,
last_stride,
is_training=True): # there is conv in short cut
with tf.name_scope("bottleneck_v2"):
preact = self._Base_Unit_PreAct(sequence, in_filter_count, "preact", is_training=is_training)
conv1 = self._Base_Unit(preact, in_filter_count, hidden_filter_count, 1, 1, "conv1",
batchNorm_relu_nonBias_flag=True, is_training=is_training)
conv2 = self._Base_Unit(conv1, hidden_filter_count, hidden_filter_count, 3, 1, "conv2",
batchNorm_relu_nonBias_flag=True, is_training=is_training)
conv3 = self._Base_Unit(conv2, hidden_filter_count, out_filter_count, 1, last_stride, "conv3",
batchNorm_relu_nonBias_flag=False, is_training=is_training)
if in_filter_count != out_filter_count:
preact = self._conv_in_shortcut(preact, in_filter_count, out_filter_count, 1, 1)
elif last_stride == 2:
preact = self._pool_in_shortcut(preact, in_filter_count, stride=2)
add = tf.add(conv3, preact)
return add
def _Base_Unit(self, sequence, in_filter_count, out_filter_count, filter_size, stride, name,
batchNorm_relu_nonBias_flag=True, is_training=True):
with tf.name_scope(name):
stdd = self.cal_input_num(filter_size * filter_size * in_filter_count)
convW = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([filter_size, filter_size, in_filter_count, out_filter_count]
, mean=0.0, stddev=stdd), dtype=tf.float32,
name='weights')
if batchNorm_relu_nonBias_flag:
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(sequence, convW, [1, stride, stride, 1], padding="SAME")
with tf.name_scope("BatchNorm"):
conv = self.batch_norm_wrapper(conv, is_training=is_training)
conv = tf.nn.relu(conv)
else:
convb = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([out_filter_count]), dtype=tf.float32, name='biases')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(sequence, convW, [1, stride, stride, 1], padding="SAME") + convb
return conv
def _Base_Unit_deconv(self, sequence, in_filter_count, out_filter_count, filter_size, stride, name,
batchNorm_relu_nonBias_flag=True, is_training=True):
with tf.name_scope('deconv'):
stdd = self.cal_input_num(filter_size * filter_size * out_filter_count)
deconvW = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([filter_size, filter_size, out_filter_count, in_filter_count]
, mean=0.0, stddev=stdd), dtype=tf.float32,
name='weights')
temp_batch_size_0 = tf.shape(sequence)[0]
temp_batch_size_1 = tf.shape(sequence)[1]
temp_batch_size_2 = tf.shape(sequence)[2]
temp_batch_size_3 = tf.shape(sequence)[3]
output_shape = tf.stack(
[temp_batch_size_0, temp_batch_size_1 * 2, temp_batch_size_2 * 2, out_filter_count])
if batchNorm_relu_nonBias_flag:
deconv = tf.nn.conv2d_transpose(sequence, deconvW, output_shape=output_shape,
strides=[1, stride, stride, 1],
padding="SAME")
with tf.name_scope("BatchNorm"):
deconv = self.batch_norm_wrapper(deconv, is_training=is_training)
else:
deconvb = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([out_filter_count]), dtype=tf.float32, name='biases')
deconv = tf.nn.conv2d_transpose(sequence, deconvW, output_shape=output_shape,
strides=[1, stride, stride, 1],
padding="SAME") + deconvb
relu = tf.nn.relu(deconv)
return relu
def _Base_Unit_PreAct(self, sequence, in_filter_count, name, is_training=True):
with tf.name_scope(name):
sequence = self.batch_norm_wrapper(sequence, is_training=is_training)
relu = tf.nn.relu(sequence)
return relu
def _conv_in_shortcut(self, sequence, in_filter_count, out_filter_count, filter_size, stride):
with tf.name_scope('shortcut'):
stdd = self.cal_input_num(filter_size * filter_size * in_filter_count)
convW = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([filter_size, filter_size, in_filter_count, out_filter_count]
, mean=0.0, stddev=stdd,), dtype=tf.float32,
name='weights')
convb = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([out_filter_count]), dtype=tf.float32, name='biases')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(sequence, convW, [1, stride, stride, 1], padding="SAME") + convb
return conv
def _pool_in_shortcut(self, sequence, filter_size, stride):
with tf.name_scope('shortcut'):
pool = tf.nn.max_pool(sequence, [1, filter_size, filter_size, 1], [1, stride, stride, 1], padding="SAME")
return pool
実験と結果
書きかけ