はじめに
OpenGLとC言語を使って初音ミクの3Dモデルを表示するプログラムを作成に挑戦しています。今回は3Dモデルの読み込みと透視変換の実装に取り組みます。
過去の記事
プロジェクトの作成
前回と同じように新しいプロジェクトを作成し、プロパティシートを設定し、これまでに作成したソースコードをコピーしてプロジェクトに追加します。
OBJファイルの作成
ここでは3Dモデルのフォーマットとして、OBJファイルを採用したいと思います。
OBJファイルは単なるテキストファイルなので、手で書くこともできますが、面倒なのでここではMetasequoiaを使って生成したいと思います。
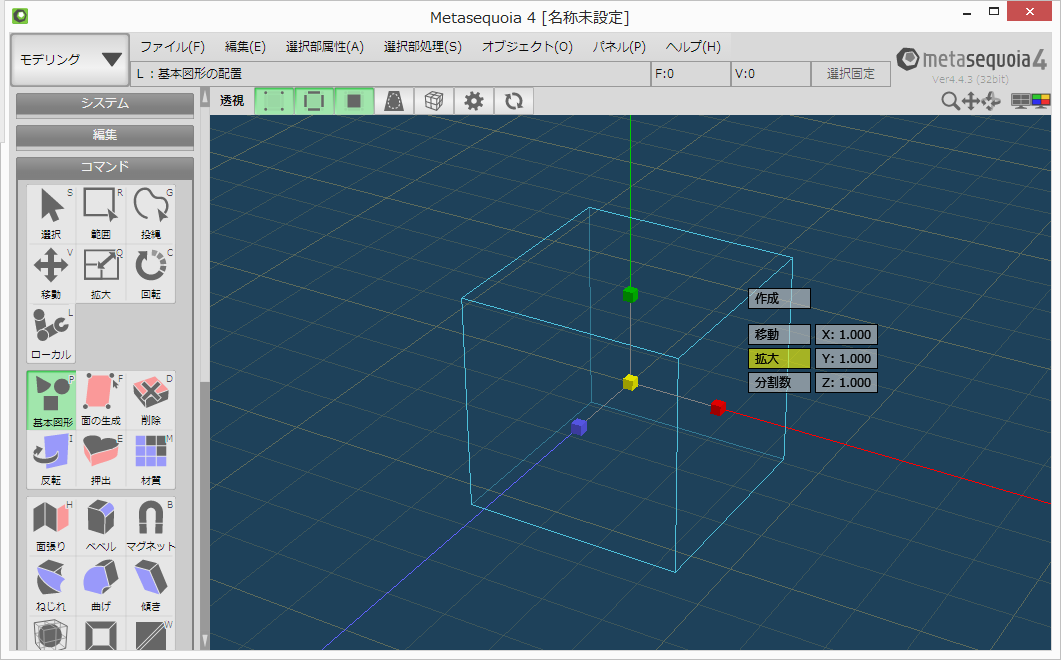
Metasequoiaを起動して、大きさが1.00の立方体を描画します。
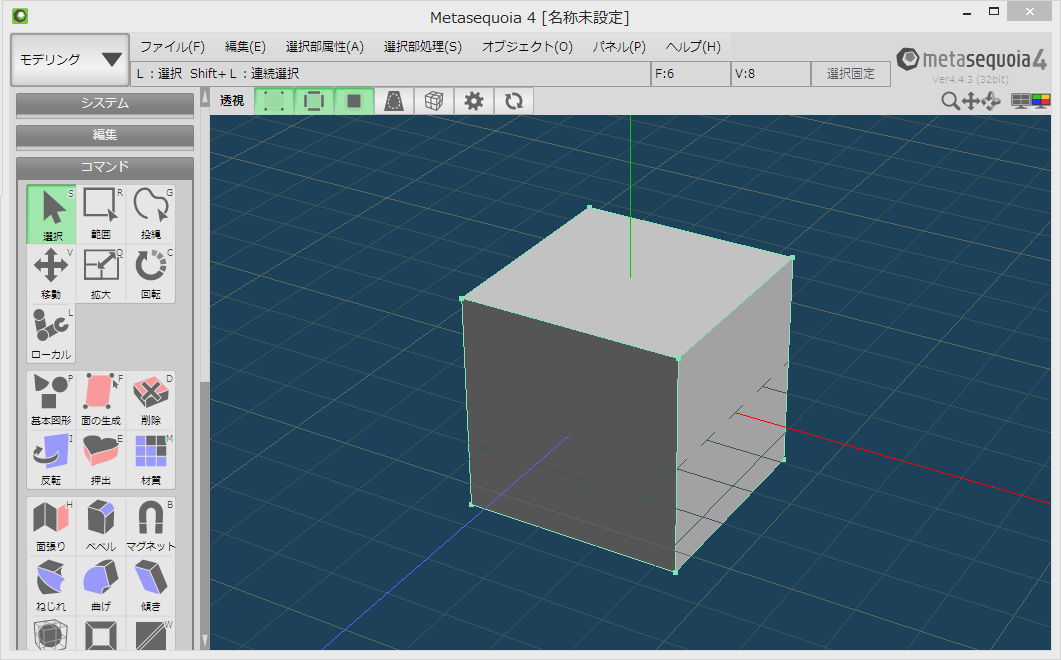
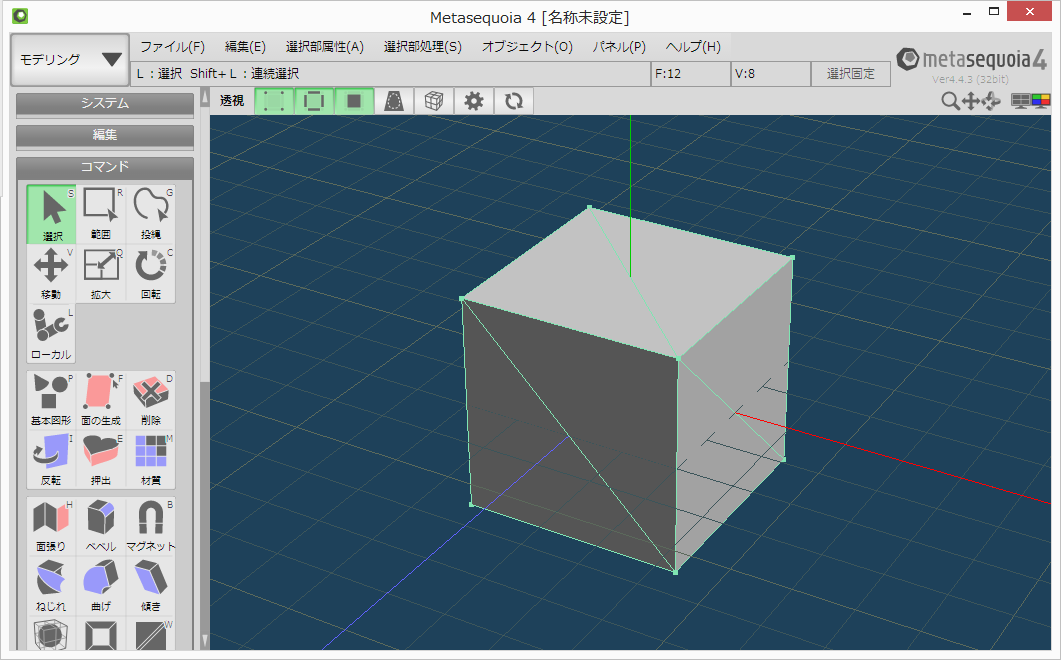
すべての頂点を選択して「選択部処理」→「面を三角形化」をクリックします。
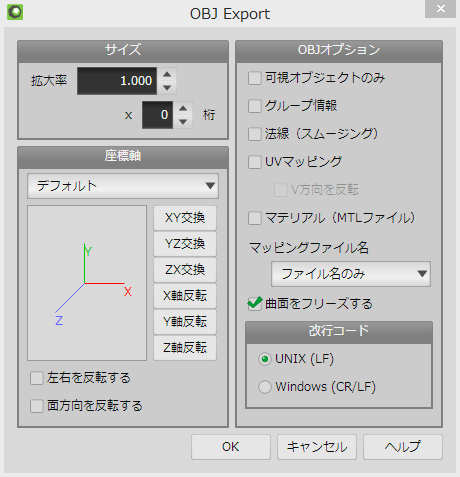
「ファイル」→「名前を付けて保存」をクリックし、ファイル名を「cube.obj」ファイルの種類を「Wavefront (*.obj)」にして保存をクリックします。保存場所はプロジェクトのフォルダとします。
以下のように設定して「OK」をクリックします。
作成されたOBJファイルを開くと以下のようになっています。
# Created by Metasequoia
v -0.500000 0.500000 0.500000
v -0.500000 -0.500000 0.500000
v 0.500000 0.500000 0.500000
v 0.500000 -0.500000 0.500000
v 0.500000 0.500000 -0.500000
v 0.500000 -0.500000 -0.500000
v -0.500000 0.500000 -0.500000
v -0.500000 -0.500000 -0.500000
# 8 vertices
f 4 3 1
f 2 4 1
f 6 5 3
f 4 6 3
f 8 7 5
f 6 8 5
f 2 1 7
f 8 2 7
f 3 5 7
f 1 3 7
f 6 4 2
f 8 6 2
# 12 elements
vで始まる行が頂点座標を表していて、fで始まる行はモデルを構成する三角形を表しています。
OBJファイルの読み込み
プロジェクトにObjLoader.hとObjLoader.cを追加して上で生成したようなOBJファイルを読み込む関数を定義します。
それぞれ以下のようになりました。
# ifndef OBJLOADER_H_INCLUDE
# define OBJLOADER_H_INCLUDE
/* モデルデータ */
typedef struct {
float *vertices;
int num_vertices;
} model;
/* OBJファイルの読み込み */
void load_obj(model *m, const char *file_name);
# endif
# include <stdio.h>
# include <stdlib.h>
# include "ObjLoader.h"
/* 初期バッファサイズ */
# define DEF_BUF_SIZE 2
/* 浮動小数点数バッファ */
typedef struct {
int buf_size;
int current_index;
float *buf;
} float_buffer;
/* 整数バッファ */
typedef struct {
int buf_size;
int current_index;
int *buf;
} int_buffer;
/* 頂点座標の読み込み */
void read_vertices(const char *line, float_buffer *vs);
/* インデックスの読み込み */
void read_indices(const char *line, int_buffer *fs);
/* モデルの作成 */
void create_model(model *m, float_buffer *vs, int_buffer *fs);
/* 浮動小数点数バッファの操作 */
float_buffer *alloc_float_buffer(void);
void free_float_buffer(float_buffer *fbuf);
void add_float(float_buffer *fbuf, float value);
float get_float(float_buffer *fbuf, int index);
/* 整数バッファの操作 */
int_buffer *alloc_int_buffer(void);
void free_int_buffer(int_buffer *ibuf);
void add_int(int_buffer *ibuf, int value);
int get_int(int_buffer *ibuf, int index);
/*==============================*
** OBJファイルの読み込み
**==============================*/
void load_obj(model *m, const char *file_name)
{
FILE *fp;
char line[1024];
float_buffer *vs;
int_buffer *fs;
fp = fopen(file_name, "r");
if (!fp) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot open %s.\n", file_name);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
vs = alloc_float_buffer();
fs = alloc_int_buffer();
while (!feof(fp)) {
fgets(line, sizeof(line), fp);
if (line[0] == 'v' && line[1] == ' ') {
read_vertices(line, vs);
}
else if (line[0] == 'f' && line[1] == ' ') {
read_indices(line, fs);
}
}
create_model(m, vs, fs);
free_float_buffer(vs);
free_int_buffer(fs);
fclose(fp);
}
/*------------------------------*
** 頂点座標の読み込み
**------------------------------*/
void read_vertices(const char *line, float_buffer *vs)
{
float x, y, z;
int count;
count = sscanf(line, "%*s%f%f%f", &x, &y, &z);
if (count == 3) {
add_float(vs, x);
add_float(vs, y);
add_float(vs, z);
}
}
/*------------------------------*
** インデックスの読み込み
**------------------------------*/
void read_indices(const char *line, int_buffer *fs)
{
int v1, v2, v3;
int count;
count = sscanf(line, "%*s%d%d%d", &v1, &v2, &v3);
if (count == 3) {
add_int(fs, v1);
add_int(fs, v2);
add_int(fs, v3);
}
}
/*------------------------------*
** モデルの作成
**------------------------------*/
void create_model(model *m, float_buffer *vs, int_buffer *fs)
{
int i, j;
m->num_vertices = fs->current_index * 3;
m->vertices = malloc(sizeof(float) * m->num_vertices);
if (!m->vertices) {
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation error.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for (i = 0; i < fs->current_index; i++) {
int idx = fs->buf[i] - 1;
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
m->vertices[i * 3 + j] = vs->buf[idx * 3 + j];
}
}
}
/*------------------------------*
** 浮動小数点数バッファの割り当て
**------------------------------*/
float_buffer *alloc_float_buffer(void)
{
float_buffer *fbuf;
fbuf = malloc(sizeof(float_buffer));
if (!fbuf) {
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation error.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
fbuf->buf_size = DEF_BUF_SIZE;
fbuf->current_index = 0;
fbuf->buf = malloc(sizeof(float) * fbuf->buf_size);
return fbuf;
}
/*------------------------------*
** 浮動小数点数バッファの解放
**------------------------------*/
void free_float_buffer(float_buffer *fbuf)
{
free(fbuf->buf);
free(fbuf);
}
/*------------------------------*
** バッファに浮動小数点数を追加
**------------------------------*/
void add_float(float_buffer *fbuf, float value)
{
fbuf->buf[fbuf->current_index] = value;
fbuf->current_index++;
if (fbuf->current_index >= fbuf->buf_size) {
fbuf->buf_size *= 2;
fbuf->buf = realloc(fbuf->buf, sizeof(float) * fbuf->buf_size);
if (!fbuf->buf) {
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation error.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
}
/*------------------------------*
** バッファから浮動小数点数を取り出し
**------------------------------*/
float get_float(float_buffer *fbuf, int index)
{
return fbuf->buf[index];
}
/*------------------------------*
** 整数バッファの割り当て
**------------------------------*/
int_buffer *alloc_int_buffer(void)
{
int_buffer *ibuf;
ibuf = malloc(sizeof(int_buffer));
if (!ibuf) {
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation error.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ibuf->buf_size = DEF_BUF_SIZE;
ibuf->current_index = 0;
ibuf->buf = malloc(sizeof(int) * ibuf->buf_size);
return ibuf;
}
/*------------------------------*
** 整数バッファの解放
**------------------------------*/
void free_int_buffer(int_buffer *ibuf)
{
free(ibuf->buf);
free(ibuf);
}
/*------------------------------*
** バッファに整数を追加
**------------------------------*/
void add_int(int_buffer *ibuf, int value)
{
ibuf->buf[ibuf->current_index] = value;
ibuf->current_index++;
if (ibuf->current_index >= ibuf->buf_size) {
ibuf->buf_size *= 2;
ibuf->buf = realloc(ibuf->buf, sizeof(int) * ibuf->buf_size);
if (!ibuf->buf) {
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation error.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
}
/*------------------------------*
** バッファから整数を取り出し
**------------------------------*/
int get_int(int_buffer *ibuf, int index)
{
return ibuf->buf[index];
}
実際に先ほど作成したcube.objを読み込んでみましょう。
Main.cを以下のように記述します。
# include <stdio.h>
# include <stdlib.h>
# include <GL/glew.h>
# include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
# include "Init.h"
# include "ShaderLoader.h"
# include "Matrix.h"
# include "ObjLoader.h"
int main(void)
{
GLFWwindow *window;
GLuint program;
model model;
GLuint position_buffer;
GLuint vertex_array;
const GLuint position_location = 0;
const GLuint position_bindindex = 0;
window = init(640, 480, "Step 03");
program = load_shader("Vertex.glsl", "Fragment.glsl");
load_obj(&model, "cube.obj");
glCreateBuffers(1, &position_buffer);
glNamedBufferData(position_buffer,
sizeof(float) * model.num_vertices,
model.vertices,
GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glCreateVertexArrays(1, &vertex_array);
glEnableVertexArrayAttrib(
vertex_array, position_location);
glVertexArrayAttribFormat(
vertex_array, position_location,
3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0);
glVertexArrayAttribBinding(
vertex_array, position_location,
position_bindindex);
glVertexArrayVertexBuffer(
vertex_array, position_bindindex,
position_buffer, 0, sizeof(GLfloat) * 3);
glClearColor(0.6, 0.8, 0.8, 1.0);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE);
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window)) {
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glBindVertexArray(vertex_array);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, model.num_vertices / 3);
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
glfwTerminate();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
頂点シェーダとフラグメントシェーダは以下のようになっています。
# version 450
layout (location = 0) in vec3 position;
void main()
{
gl_Position = vec4(position, 1.0);
}
# version 450
out vec4 out_color;
void main()
{
out_color = vec4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
}
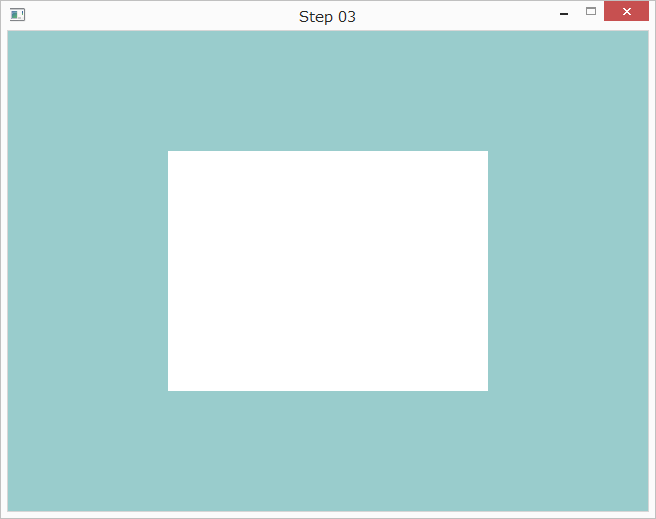
実行すると以下のように表示されます。
透視投影
3Dらしく表示するには、透視投影をする必要があります。これには行列計算をする必要があります。プロジェクトにMatrix.hとMatrix.cを追加して、ここに行列操作関数を実装します。
それぞれ以下のように実装しました。
# ifndef MATRIX_H_INCLUDE
# define MATRIX_H_INCLUDE
/* 行列の割り当て */
float *alloc_matrix(void);
/* 行列の解放 */
void free_matrix(float *mat);
/* 行列のクリア */
void clear_matrix(float *mat);
/* 単位行列の生成 */
void set_identity_matrix(float *mat);
/* 透視変換行列の生成 */
void set_perspective_matrix(float *mat,
float fov, float aspect, float near, float far);
/* 視野変換行列の生成 */
void set_lookat_matrix(float *mat,
float eye_x, float eye_y, float eye_z,
float center_x, float center_y, float center_z,
float up_x, float up_y, float up_z);
/* 行列の積 */
void multiply_matrix(float *result, float *mat1, float *mat2);
# endif
# include <stdio.h>
# include <stdlib.h>
# include <math.h>
/*==============================*
** 行列の割り当て
**==============================*/
float *alloc_matrix(void)
{
float *mat = malloc(sizeof(float) * 16);
if (!mat) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate memory.\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return mat;
}
/*==============================*
** 行列の解放
**==============================*/
void free_matrix(float *mat)
{
free(mat);
}
/*==============================*
** 行列のクリア
**==============================*/
void clear_matrix(float *mat)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
mat[i] = 0.0f;
}
}
/*==============================*
** 単位行列の生成
**==============================*/
void set_identity_matrix(float *mat)
{
int i;
clear_matrix(mat);
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
mat[i * 4 + i] = 1.0f;
}
}
/*==============================*
** 透視変換行列の生成
**==============================*/
void set_perspective_matrix(float *mat,
float fov, float aspect, float near, float far)
{
float f;
clear_matrix(mat);
f = 1.0f / tan(fov / 2.0f);
mat[0 * 4 + 0] = f / aspect;
mat[1 * 4 + 1] = f;
mat[2 * 4 + 2] = (far + near) / (near - far);
mat[2 * 4 + 3] = -1.0f;
mat[3 * 4 + 2] = (2.0f * far * near) / (near - far);
}
/*==============================*
** 視野変換行列の生成
**==============================*/
void set_lookat_matrix(float *mat,
float eye_x, float eye_y, float eye_z,
float center_x, float center_y, float center_z,
float up_x, float up_y, float up_z)
{
float tmp_x, tmp_y, tmp_z;
float d;
float f_x, f_y, f_z;
float s_x, s_y, s_z;
float u_x, u_y, u_z;
clear_matrix(mat);
tmp_x = center_x - eye_x;
tmp_y = center_y - eye_y;
tmp_z = center_z - eye_z;
d = sqrtf(tmp_x * tmp_x + tmp_y * tmp_y + tmp_z * tmp_z);
f_x = tmp_x / d;
f_y = tmp_y / d;
f_z = tmp_z / d;
tmp_x = f_y * up_z - f_z * up_y;
tmp_y = f_z * up_x - f_x * up_z;
tmp_z = f_x * up_y - f_y * up_x;
d = sqrtf(tmp_x * tmp_x + tmp_y * tmp_y + tmp_z * tmp_z);
s_x = tmp_x / d;
s_y = tmp_y / d;
s_z = tmp_z / d;
u_x = s_y * f_z - s_z * f_y;
u_y = s_z * f_x - s_x * f_z;
u_z = s_x * f_y - s_y * f_x;
mat[0 * 4 + 0] = s_x;
mat[1 * 4 + 0] = s_y;
mat[2 * 4 + 0] = s_z;
mat[0 * 4 + 1] = u_x;
mat[1 * 4 + 1] = u_y;
mat[2 * 4 + 1] = u_z;
mat[0 * 4 + 2] = -f_x;
mat[1 * 4 + 2] = -f_y;
mat[2 * 4 + 2] = -f_z;
mat[3 * 4 + 0] = -(s_x * eye_x + s_y * eye_y + s_z * eye_z);
mat[3 * 4 + 1] = -(u_x * eye_x + u_y * eye_y + u_z * eye_z);
mat[3 * 4 + 2] = f_x * eye_x + f_y * eye_y + f_z * eye_z;
mat[3 * 4 + 3] = 1.0f;
}
/*==============================*
** 行列の積
**==============================*/
void multiply_matrix(float *result, float *mat1, float *mat2)
{
int i, j, k;
clear_matrix(result);
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
for (k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
result[j * 4 + i] += mat1[k * 4 + i] * mat2[j * 4 + k];
}
}
}
}
mainに以下を追加して、MVP (Model View Projection) 行列を作ります。
GLuint mvp;
float *mat_proj, *mat_view, *mat_model;
float *mat_mvp;
float *mat_tmp;
mat_proj = alloc_matrix();
set_perspective_matrix(mat_proj,
45.0, 640.0f / 480.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);
mat_view = alloc_matrix();
set_lookat_matrix(mat_view,
4.0f, 3.0f, -3.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
mat_model = alloc_matrix();
set_identity_matrix(mat_model);
mat_tmp = alloc_matrix();
multiply_matrix(mat_tmp, mat_proj, mat_view);
mat_mvp = alloc_matrix();
multiply_matrix(mat_mvp, mat_tmp, mat_model);
free_matrix(mat_proj);
free_matrix(mat_view);
free_matrix(mat_model);
free_matrix(mat_tmp);
mvp = glGetUniformLocation(program, "mvp");
glUniformMatrix4fv(mvp, 1, GL_FALSE, mat_mvp);
頂点シェーダを以下のように書き替えます。
# version 450
layout (location = 0) in vec3 position;
uniform mat4 mvp;
void main()
{
gl_Position = mvp * vec4(position, 1.0);
}
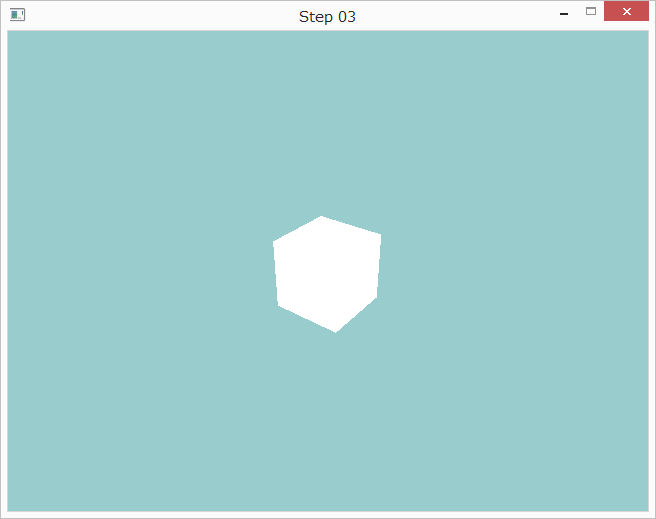
実行すると以下のように表示されます。