torch.randn
torch.randn(*sizes, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False) → Tensor
Returns a tensor filled with random numbers from a normal distribution with mean 0 and variance 1 (also called the standard normal distribution).
The shape of the tensor is defined by the variable argument sizes.
- Parameters:
- sizes (int...) – a sequence of integers defining the shape of the output tensor. Can be a variable number of arguments or a collection like a list or tuple.
- out (Tensor, optional) – the output tensor
dtype (torch.dtype, optional) – the desired data type of returned tensor. Default: if None, uses a global default (see torch.set_default_tensor_type()). - layout (torch.layout, optional) – the desired layout of returned Tensor. Default: torch.strided.
- device (torch.device, optional) – the desired device of returned tensor. Default: if None, uses the current device for the default tensor type (see torch.set_default_tensor_type()). device will be the CPU for CPU tensor types and the current CUDA device for CUDA tensor types.
- requires_grad (bool, optional) – If autograd should record operations on the returned tensor. Default: False.
>>>torch.randn(4)
>>>tensor([-2.1436, 0.9966, 2.3426, -0.6366])
>>>torch.randn(2, 3)
>>>tensor([[ 1.5954, 2.8929, -1.0923],
[ 1.1719, -0.4709, -0.1996]])
torch.nn.Linear
torch.nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=True)[SOURCE]
Applies a linear transformation to the incoming data: y = xA^T + b
- Parameters:
- in_features – size of each input sample
out_features – size of each output sample - bias – If set to False, the layer will not learn an additive bias. Default: True
- in_features – size of each input sample
- Shape:
- Input: (N, *, \text{in_features})(N,∗,in_features) where *∗ means any number of additional dimensions
- Output: (N, *, \text{out_features})(N,∗,out_features) where all but the last dimension are the same shape as the input.
- Variables:
- weight – the learnable weights of the module of shape (\text{out_features}, \text{in_features})(out_features,in_features).
- bias – the learnable bias of the module of shape (\text{out_features})(out_features).
>>> m = nn.Linear(20, 30)
>>> input = torch.randn(128, 20)
>>> output = m(input)
>>> print(output.size())
torch.Size([128, 30])
nn.MSELoss
torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')[SOURCE]
Creates a criterion that measures the mean squared error (squared L2 norm) between each element in the input x and target y.
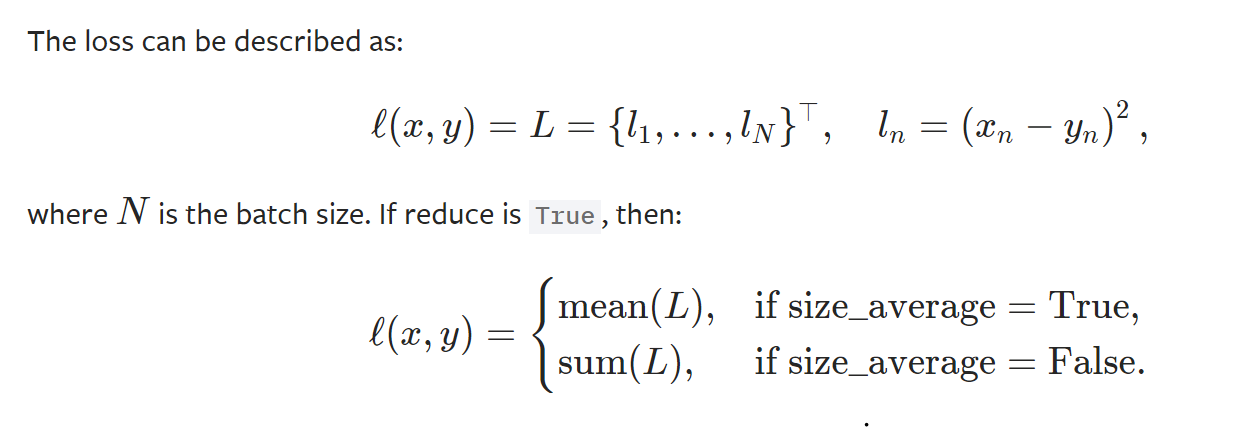
- parameters
- size_average(bool,optional)
- reduce(book.optional)
- reduction(string,optional)
- shape
- input:(N,*) where * means, any number of additional dimentions
- target:(N,*) same shape as the input
>>> loss = nn.MSELoss()
>>> input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
>>> target = torch.randn(3, 5)
>>> output = loss(input, target)
>>> output.backward()
torch.optim.SGD
torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=, momentum=0, dampening=0, weight_decay=0, nesterov=False)[SOURCE]
Implements stochastic gradient descent (optionally with momentum).
Nesterov momentum is based on the formula from On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning.
- Parameters:
- params (iterable) – iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining parameter groups
lr (float) – learning rate - momentum (float, optional) – momentum factor (default: 0)
- weight_decay (float, optional) – weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
- dampening (float, optional) – dampening for momentum (default: 0)
- nesterov (bool, optional) – enables Nesterov momentum (default: False)
- params (iterable) – iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining parameter groups
>>> optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9)
>>> optimizer.zero_grad()
>>> loss_fn(model(input), target).backward()
>>> optimizer.step()