axisとは
多次元の配列を扱うnumpyではaxis(軸)をきちんと理解しておくことが大切です。
例えば、配列の合計値を求めるnumpy.sum()を考えてみましょう。
単純なスカラーや1次元の配列ならば、軸を考えるまでもなく、全ての値を合計すればよいのですが、多次元配列の場合、どの軸に沿って合計すればいいかを意識する必要があります。
numpy.sum(a, axis)
numpyのsum()は第1引数aに配列を指定し、第2引数にはaxis(軸)を指定します。
このaxisに沿って、要素を足し合わせていくわけですね。
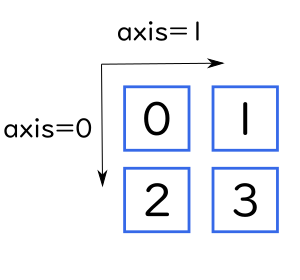
2次元配列のaxis
まずはわかりやすい2次元の配列を例にします。
2次元配列において、行方向はaxis=0、列方向はaxis=1となります。
Z = np.array([[0,1],
[2,3]])
print("axis=0 ->", sum(Z,0))
print("axis=1 ->", sum(Z,1))
実行結果
axis=0 -> [2 4]
axis=1 -> [1 5]
なお、axisに何も指定しないと、すべての要素の合計値(スカラー)になります。
Z = np.array([[0,1],
[2,3]])
print(sum(Z))
実行結果
6
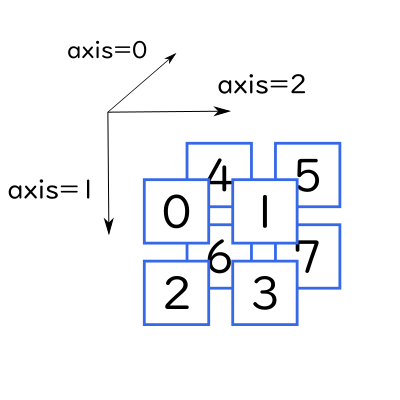
3次元配列のaxis
次に3次元配列を考えてみましょう。
3次元配列では、axis=0が奥行き方向、axis=1が行方向、axis=2が列方向になります。
Z = np.array([[[0,1],
[2,3]],
[[4,5],
[6,7]]])
print("axis=0")
print(sum(Z,0))
print("----")
print("axis=1")
print(sum(Z,1))
print("----")
print("axis=2")
print(sum(Z,2))
実行結果
axis=0
[[ 4 6]
[ 8 10]]
----
axis=1
[[ 2 4]
[10 12]]
----
axis=2
[[ 1 5]
[ 9 13]]
axis=-1は何を表すか
axis=-1とすると最後の軸方向を表します。つまり、3次元配列ならaxis=2、2次元配列ならaxis=1と同じです。
Z = np.array([[[0,1],
[2,3]],
[[4,5],
[6,7]]])
print("axis=2")
print(sum(Z,2))
print("----")
print("axis=-1")
print(sum(Z,-1))
実行結果
axis=2
[[ 1 5]
[ 9 13]]
----
axis=-1
[[ 1 5]
[ 9 13]]
同じ結果になりましたね。