記事の概要
Openposeの骨格データを作ることに憤りを感じたため、こちらの記事を参考に、動画から骨格データを取得する方法を調べました。
参照した記事では、骨格データを動画に反映させるプログラムだったので、PNGとして出力するプログラムを個別に作成しています。
注意として、今回のプログラムはCPUで動作します。
GPUでの動作方法については、時間がある時に調査します。
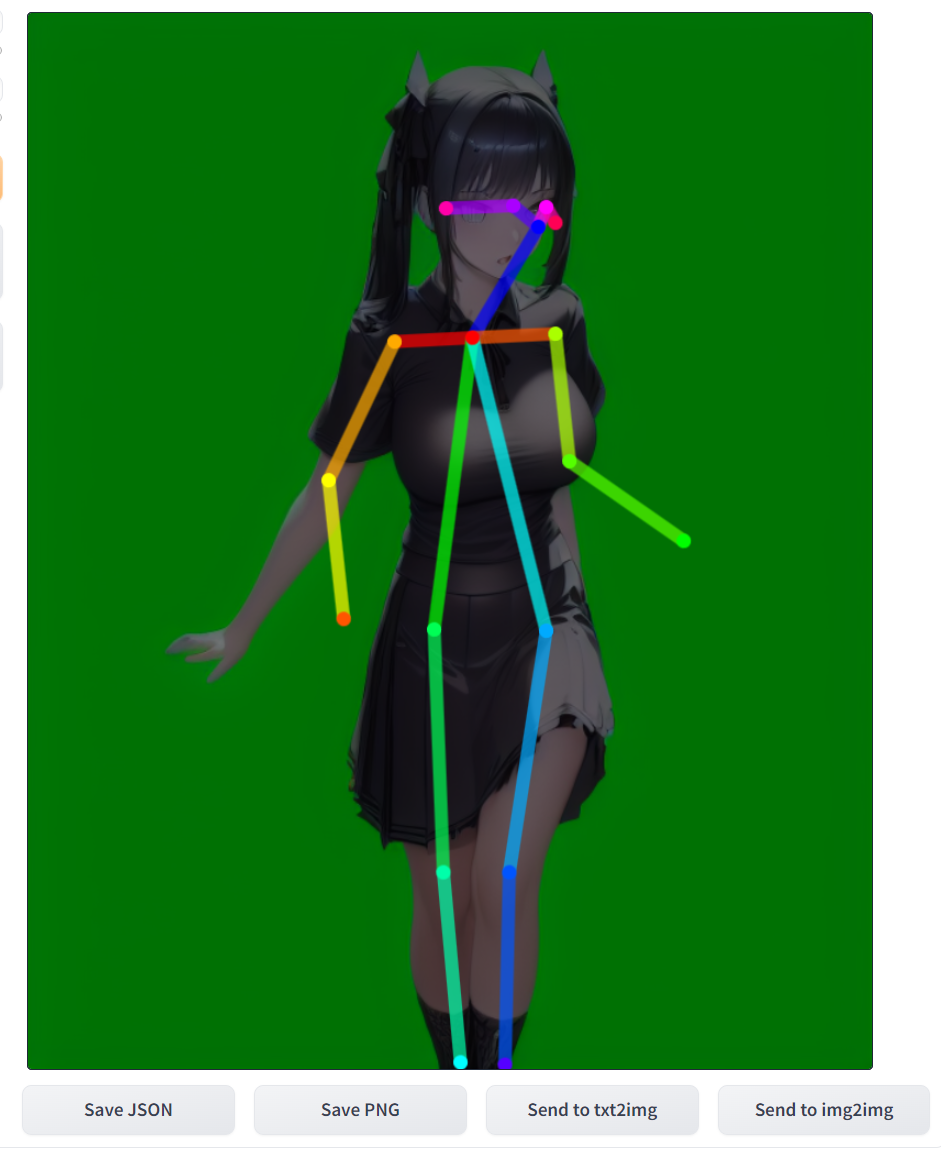
↑↑↑ Stable Diffusion WebU Iで頑張って骨格形成してみたけど挫折。。。
環境
OS:Windows 11
GPU:GeForce RTX 4090
CPU:i9-13900KF
memory:64G
python:3.10.10
pytorch:2.0.1
CUDA:11.8
cuDNN:8.8
環境構築
①Gitからソースをダウンロード
構築する想定のフォルダで、コマンドプロンプトを起動し、以下のコマンドを実行します。
git clone https://github.com/spmallick/learnopencv.git
②不足ドキュメントを補完
「OpenPose>pose>coco」フォルダに、「pose_iter_440000.caffemodel」が格納されていないので、以下のサイトからダウンロードし、ファイルを配置する。
③独自実装のプログラムを格納
「OpenPose-Multi-Person」フォルダに、「pose_estimation.py」というファイル名で、以下のプログラムを格納する。
import cv2
import numpy as np
import argparse
import os
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Run keypoint detection')
parser.add_argument("--device", default="cpu", help="Device to inference on")
parser.add_argument("--video_file", default="sample.mp4", help="Input Video")
args = parser.parse_args()
input_source = args.video_file
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(input_source)
protoFile = "pose/coco/pose_deploy_linevec.prototxt"
weightsFile = "pose/coco/pose_iter_440000.caffemodel"
nPoints = 18
keypointsMapping = ['Nose', 'Neck', 'R-Sho', 'R-Elb', 'R-Wr', 'L-Sho', 'L-Elb', 'L-Wr', 'R-Hip', 'R-Knee', 'R-Ank', 'L-Hip', 'L-Knee', 'L-Ank', 'R-Eye', 'L-Eye', 'R-Ear', 'L-Ear']
POSE_PAIRS = [[1,2], [1,5], [2,3], [3,4], [5,6], [6,7], [1,8], [8,9], [9,10], [1,11], [11,12], [12,13], [1,0], [0,14], [14,16], [0,15], [15,17], [2,17], [5,16] ]
mapIdx = [[31,32], [39,40], [33,34], [35,36], [41,42], [43,44], [19,20], [21,22], [23,24], [25,26], [27,28], [29,30], [47,48], [49,50], [53,54], [51,52], [55,56], [37,38], [45,46]]
colors = [ [0,100,255], [0,100,255], [0,255,255], [0,100,255], [0,255,255], [0,100,255], [0,255,0], [255,200,100], [255,0,255], [0,255,0], [255,200,100], [255,0,255], [0,0,255], [255,0,0], [200,200,0], [255,0,0], [200,200,0], [0,0,0]]
# 以降の関数定義 (getKeypoints, getValidPairs, getPersonwiseKeypoints) は変更なし
def getKeypoints(probMap, threshold=0.1):
mapSmooth = cv2.GaussianBlur(probMap,(3,3),0,0)
mapMask = np.uint8(mapSmooth>threshold)
keypoints = []
#find the blobs
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(mapMask, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
#for each blob find the maxima
for cnt in contours:
blobMask = np.zeros(mapMask.shape)
blobMask = cv2.fillConvexPoly(blobMask, cnt, 1)
maskedProbMap = mapSmooth * blobMask
_, maxVal, _, maxLoc = cv2.minMaxLoc(maskedProbMap)
keypoints.append(maxLoc + (probMap[maxLoc[1], maxLoc[0]],))
return keypoints
# Find valid connections between the different joints of a all persons present
def getValidPairs(output):
valid_pairs = []
invalid_pairs = []
n_interp_samples = 10
paf_score_th = 0.1
conf_th = 0.7
# loop for every POSE_PAIR
for k in range(len(mapIdx)):
# A->B constitute a limb
pafA = output[0, mapIdx[k][0], :, :]
pafB = output[0, mapIdx[k][1], :, :]
pafA = cv2.resize(pafA, (frameWidth, frameHeight))
pafB = cv2.resize(pafB, (frameWidth, frameHeight))
# Find the keypoints for the first and second limb
candA = detected_keypoints[POSE_PAIRS[k][0]]
candB = detected_keypoints[POSE_PAIRS[k][1]]
nA = len(candA)
nB = len(candB)
# If keypoints for the joint-pair is detected
# check every joint in candA with every joint in candB
# Calculate the distance vector between the two joints
# Find the PAF values at a set of interpolated points between the joints
# Use the above formula to compute a score to mark the connection valid
if( nA != 0 and nB != 0):
valid_pair = np.zeros((0,3))
for i in range(nA):
max_j=-1
maxScore = -1
found = 0
for j in range(nB):
# Find d_ij
d_ij = np.subtract(candB[j][:2], candA[i][:2])
norm = np.linalg.norm(d_ij)
if norm:
d_ij = d_ij / norm
else:
continue
# Find p(u)
interp_coord = list(zip(np.linspace(candA[i][0], candB[j][0], num=n_interp_samples),
np.linspace(candA[i][1], candB[j][1], num=n_interp_samples)))
# Find L(p(u))
paf_interp = []
for k in range(len(interp_coord)):
paf_interp.append([pafA[int(round(interp_coord[k][1])), int(round(interp_coord[k][0]))],
pafB[int(round(interp_coord[k][1])), int(round(interp_coord[k][0]))] ])
# Find E
paf_scores = np.dot(paf_interp, d_ij)
avg_paf_score = sum(paf_scores)/len(paf_scores)
# Check if the connection is valid
# If the fraction of interpolated vectors aligned with PAF is higher then threshold -> Valid Pair
if ( len(np.where(paf_scores > paf_score_th)[0]) / n_interp_samples ) > conf_th :
if avg_paf_score > maxScore:
max_j = j
maxScore = avg_paf_score
found = 1
# Append the connection to the list
if found:
valid_pair = np.append(valid_pair, [[candA[i][3], candB[max_j][3], maxScore]], axis=0)
# Append the detected connections to the global list
valid_pairs.append(valid_pair)
else: # If no keypoints are detected
print("No Connection : k = {}".format(k))
invalid_pairs.append(k)
valid_pairs.append([])
return valid_pairs, invalid_pairs
# This function creates a list of keypoints belonging to each person
# For each detected valid pair, it assigns the joint(s) to a person
def getPersonwiseKeypoints(valid_pairs, invalid_pairs):
# the last number in each row is the overall score
personwiseKeypoints = -1 * np.ones((0, 19))
for k in range(len(mapIdx)):
if k not in invalid_pairs:
partAs = valid_pairs[k][:,0]
partBs = valid_pairs[k][:,1]
indexA, indexB = np.array(POSE_PAIRS[k])
for i in range(len(valid_pairs[k])):
found = 0
person_idx = -1
for j in range(len(personwiseKeypoints)):
if personwiseKeypoints[j][indexA] == partAs[i]:
person_idx = j
found = 1
break
if found:
personwiseKeypoints[person_idx][indexB] = partBs[i]
personwiseKeypoints[person_idx][-1] += keypoints_list[partBs[i].astype(int), 2] + valid_pairs[k][i][2]
# if find no partA in the subset, create a new subset
elif not found and k < 17:
row = -1 * np.ones(19)
row[indexA] = partAs[i]
row[indexB] = partBs[i]
# add the keypoint_scores for the two keypoints and the paf_score
row[-1] = sum(keypoints_list[valid_pairs[k][i,:2].astype(int), 2]) + valid_pairs[k][i][2]
personwiseKeypoints = np.vstack([personwiseKeypoints, row])
return personwiseKeypoints
# フレームごとの出力ディレクトリ
os.makedirs('output_frames', exist_ok=True)
hasFrame, frame = cap.read()
frameWidth = frame.shape[1]
frameHeight = frame.shape[0]
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter('output_pose.avi', cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('M','J','P','G'), int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)), (frameWidth, frameHeight))
frameCount = 0
while cv2.waitKey(1) < 0:
t = cv2.getTickCount()
hasFrame, frame = cap.read()
if not hasFrame:
break
frameWidth = frame.shape[1]
frameHeight = frame.shape[0]
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(protoFile, weightsFile)
if args.device == "cpu":
net.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CPU)
else:
net.setPreferableBackend(cv2.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_CUDA)
net.setPreferableTarget(cv2.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CUDA)
inHeight = 368
inWidth = int((inHeight/frameHeight)*frameWidth)
inpBlob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 1.0 / 255, (inWidth, inHeight), (0, 0, 0), swapRB=False, crop=False)
net.setInput(inpBlob)
output = net.forward()
detected_keypoints = []
keypoints_list = np.zeros((0,3))
keypoint_id = 0
threshold = 0.1
for part in range(nPoints):
probMap = output[0,part,:,:]
probMap = cv2.resize(probMap, (frameWidth, frameHeight))
keypoints = getKeypoints(probMap, threshold)
keypoints_with_id = []
for i in range(len(keypoints)):
keypoints_with_id.append(keypoints[i] + (keypoint_id,))
keypoints_list = np.vstack([keypoints_list, keypoints[i]])
keypoint_id += 1
detected_keypoints.append(keypoints_with_id)
valid_pairs, invalid_pairs = getValidPairs(output)
personwiseKeypoints = getPersonwiseKeypoints(valid_pairs, invalid_pairs)
# ポーズのみを描画するフレームを作成
pose_frame = np.zeros((frameHeight, frameWidth, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
for i in range(17):
for n in range(len(personwiseKeypoints)):
index = personwiseKeypoints[n][np.array(POSE_PAIRS[i])]
if -1 in index:
continue
B = np.int32(keypoints_list[index.astype(int), 0])
A = np.int32(keypoints_list[index.astype(int), 1])
cv2.line(pose_frame, (B[0], A[0]), (B[1], A[1]), colors[i], 3, cv2.LINE_AA)
# ビデオとして保存
vid_writer.write(pose_frame)
# PNGファイルとして保存
cv2.imwrite(f'output_frames/frame_{frameCount:04d}.png', pose_frame)
frameCount += 1
vid_writer.release()
cap.release()
④動画ファイルを格納
mp4ファイルを「OpenPose-Multi-Person」に格納する。
※試すだけであれば、参考記事のmp4ファイルを格納するで問題ないです。
⑤プログラムの実行
以下のコマンドを実行する。(ファイル名が異なる場合は、「sample.mp4」の文字列を変更してください。)
python pose_estimation.py --video_file sample.mp4
⑥ログの確認
問題なく処理が進んでいる場合は、以下のようなログが出力されるはずです。

⑦出力ファイルの確認
「OpenPose-Multi-Person>output_frames」にPNGファイルが出力されているはずです。
