普段BtoBのお堅めWebアプリを作っているエンジニアがスイカゲームに魅了されてしまい、
ChatGPTをお供にスイカゲームっぽいものを作ってみたというお話です。
背景
私は普段、BtoBの割と堅めのWebアプリケーションを作っていて、
業務の中でJavaScriptと戯れる機会がそれなりにあるのですが、
業務アプリ以外で、JavaScriptのアクションゲームっぽいものをつくってみたいな~
と常々思ってました。
ただ、何から手を付けていいかわからなかったので、今まで未着だったのですが、
ちょうどよい機会なのでChatGPTに聞きながらスイカゲーム風の何かの製作に挑戦してみることにしました。
題材を考える
何かものづくりをするときは、モチベーションが欲しいですよね。
私は猫が好きなので、猫関連グッズをモチーフとした「ネコゲーム」を作って
猫たちと戯れたいと思います。
何はともあれ、素材をつくろう
プログラムを書く前に素材を用意してモチベを高めます。
猫に関連が深いアイテムと言えば、やはりエビのけりけりですよね。
野良猫なので耳が欠けています。

猫と言えば鈴。

まずはiPadで色々と絵をかきました。
ChatGPTにジャブを打ってみる
ここからはプログラムを作成していきますが、どこから手を付けたらよいかわからないので
ChatGPTに丸投げしてみます。
自分:
JavaScriptで以下のゲームを作成してください。
・上から果物が落下してくるゲーム
・矢印キーで左右に移動し、スペースキーで果物が落下する。
・果物を2つくっつけると、次の果物に進化する。(進化の段階は5段階で定義してください。)
・落下した果物は物理法則にしたがってバウンドしたり移動したりする
ChatGPT:
こちらが、指定された要件に基づいたフルーツ進化ゲームのためのJavaScriptコードです。このゲームでは、上から落ちてくる果物を矢印キーで左右に動かすプレイヤーがキャッチし、スペースキーを押すことで新しい果物を落下させます。果物が2つくっつくと、次の進化段階に進みます。ゲームは5段階の進化を含みます。
HTMLとJavaScriptを組み合わせたコードを以下に示します。このコードをHTMLファイルに貼り付け、ブラウザで実行することでゲームをプレイできます。
作成されたプログラム(クリックで展開)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Fruit Evolution Game</title>
<style>
canvas { background: #eee; display: block; margin: 0 auto; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="gameCanvas"></canvas>
<script>
// ゲームの設定と変数
const canvas = document.getElementById("gameCanvas");
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
canvas.width = 800;
canvas.height = 600;
const fruitSymbols = ["🍎", "🍐", "🍊", "🍋", "🍌"]; // 進化段階のシンボル
const fruitSize = 40; // フルーツのサイズ
let fruits = []; // 落ちるフルーツを格納する配列
let player = { x: canvas.width / 2, y: canvas.height - 50, width: 100, height: 20 }; // プレイヤー
let gravity = 0.5; // 重力
let gameSpeed = 5; // ゲームの速度、フルーツの落下速度を制御
// フルーツオブジェクトのコンストラクタ
function Fruit(x, y, symbolIndex) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.symbolIndex = symbolIndex;
this.velY = 0;
}
// キャンバスにフルーツを描画
Fruit.prototype.draw = function() {
ctx.font = fruitSize + "px Arial";
ctx.fillText(fruitSymbols[this.symbolIndex], this.x, this.y);
this.y += this.velY;
this.velY += gravity;
// プレイヤーとの衝突をチェック
if (this.y + fruitSize > player.y && this.x > player.x && this.x < player.x + player.width) {
this.y = player.y - fruitSize;
this.velY = 0;
checkForEvolution(this);
}
// キャンバスの底をチェック
if (this.y + fruitSize > canvas.height) {
this.y = canvas.height - fruitSize;
this.velY = -this.velY * 0.7; // バウンド効果
}
};
// フルーツの進化をチェック
function checkForEvolution(fruit) {
fruits.forEach(otherFruit => {
if (otherFruit !== fruit && otherFruit.x === fruit.x && otherFruit.y === fruit.y) {
fruit.symbolIndex++;
fruits.splice(fruits.indexOf(otherFruit), 1); // 他のフルーツを削除
}
});
if (fruit.symbolIndex >= fruitSymbols.length) {
fruit.symbolIndex = 0; // 最大段階に達したら最初の段階にリセット
}
}
// プレイヤーを描画
function drawPlayer() {
ctx.fillRect(player.x, player.y, player.width, player.height);
}
// ゲームループ
function update() {
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
fruits.forEach(fruit => fruit.draw());
drawPlayer();
requestAnimationFrame(update);
}
// プレイヤーの動きを制御
document.addEventListener("keydown", function(event) {
if (event.key === "ArrowLeft") player.x -= gameSpeed;
if (event.key === "ArrowRight") player.x += gameSpeed;
if (event.key === "Spacebar" || event.key === " ") {
fruits.push(new Fruit(Math.random() * canvas.width, 0, Math.floor(Math.random() * fruitSymbols.length)));
}
});
update(); // ゲームループを開始
</script>
</body>
</html>
動かしてみる
・・・
なかなか斬新なゲームができてしまいました。なんか文字化けしてるし。
スイカゲームの定義をChatGPTに伝えてみる
さすがに要件が雑過ぎたかもしれません。
もう少し具体的に伝えてみます。
自分:
JavaScriptで以下のゲームを作成してください。
・上から果物が落下してくるゲームです。
・次に落ちる果物が画面上部に表示されます。
・次に落ちる果物は矢印キーで左右に移動させることができ、スペースキーで果物が落下します。
・同じ果物を2つくっつけると、次の果物に進化します。(進化の段階は5段階で定義してください。)
・落下した果物は物理法則にしたがってバウンドしたり移動したりします。
・画像は用意できないので果物はアルファベットで表現してください。
ChatGPT:
このゲームの実装にはHTML、CSS、およびJavaScriptを使用します。HTMLでゲームの基本的な構造を作成し、CSSでスタイルを設定した後、JavaScriptでゲームのロジックを実装します。以下は、このゲームを作成するための基本的なステップです。
HTMLのセットアップ:
ゲーム領域と次に落ちる果物を表示する領域を作成します。
CSSでのスタイリング:
ゲーム領域と果物を視覚的に表示するためのスタイルを設定します。
JavaScriptでのゲームロジック:
果物の落下、操作、衝突判定、進化のロジックを実装します。
果物の表現:
画像がないため、果物をアルファベット(例: A, B, C, D, E)で表現します。
進化の段階:
5段階の進化を定義します(例: A + A = B, B + B = C, 以降同様)。
キーボードイベントの処理:
矢印キーで果物を移動し、スペースキーで果物を落下させます。
ここでは、このゲームの基本的な枠組みをコードで示します。ただし、全ての機能を完全に実装するにはかなりのコーディング作業が必要です。以下は簡単なスタートポイントです。
~~(中略)~~
このコードは、ゲームの基本的な構造と、キーボードイベントの取り扱いを示しています。実際の果物の動き、衝突判定、進化のロジックなどはさらに詳細なコーディングが必要です。また、ゲームの物理的な挙動(バウンドなど)を実装するためには、物理エンジンの使用も検討することができます。
なるほど、物理エンジンを使うとよさそう
さすがにちょっと複雑すぎたのか、ChatGPTは枠組みしか作ってくれませんでしたが、
物理エンジンを使ったほうが良さそうだということが分かりました。
たしかに物理演算を1から実装するなんて不可能なので、ライブラリを使ったほうが良さそうですね。
物理エンジンの選定
というわけで、適当な物理エンジンを見つけてきます。
今回はMatter.jsというライブラリを使ってみることにしました。
(このデモがスイカゲームの挙動そっくりだったので採用しました。)
Matter.jsでネコゲームを実装
まずはシンプルに物体落下の動作を作成
まずは、Matter.jsを使うとどのような実装になるのかをつかむため、シンプルに聞いてみます。
私:
matter.jsを使用して、落ち物ゲームを作りたいです。
スペースを押すとオブジェクトが落ちてきて、2つオブジェクトがくっつくと一つの大きなオブジェクトになるソースコードを書いてください。
ChatGPT:
Matter.jsを使って、スペースキーを押すとオブジェクトが落ちてきて、2つのオブジェクトがくっついたら一つの大きなオブジェクトになるゲームのソースコードを作成します。このコードは、Matter.jsの基本的な機能を使用して、オブジェクトの生成、重力のシミュレーション、衝突の検出と反応を行います。
まず、Matter.jsライブラリをプロジェクトに追加する必要があります。HTMLファイルの
セクションに以下のスクリプトタグを追加してください:
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/matter-js/0.14.2/matter.min.js"></script>
次に、以下のJavaScriptコードを使用します。このコードは、スペースキーを押すことで新しいオブジェクトを生成し、2つのオブジェクトが衝突するとそれらを結合して大きなオブジェクトを作成します。
JavaScript(クリックで展開)
// Matter.js のモジュールを取り込む
const { Engine, Render, World, Bodies, Body, Events } = Matter;
// エンジンとレンダラーを作成
const engine = Engine.create();
const render = Render.create({
element: document.body,
engine: engine
});
// 2つのオブジェクトが衝突した時に呼ばれる関数
function mergeBodies(pair) {
const bodyA = pair.bodyA;
const bodyB = pair.bodyB;
// 新しいオブジェクトのプロパティを計算
const newX = (bodyA.position.x + bodyB.position.x) / 2;
const newY = (bodyA.position.y + bodyB.position.y) / 2;
const newRadius = Math.sqrt(bodyA.circleRadius * bodyA.circleRadius + bodyB.circleRadius * bodyB.circleRadius);
// 古いオブジェクトをワールドから削除
World.remove(engine.world, [bodyA, bodyB]);
// 新しいオブジェクトを作成してワールドに追加
const newBody = Bodies.circle(newX, newY, newRadius);
World.add(engine.world, newBody);
}
// オブジェクトが衝突した時にイベントリスナーを設定
Events.on(engine, 'collisionStart', event => {
const pairs = event.pairs;
pairs.forEach(pair => {
if (pair.bodyA.label === 'fallingObject' && pair.bodyB.label === 'fallingObject') {
mergeBodies(pair);
}
});
});
// スペースキーが押された時に新しいオブジェクトを作成
window.addEventListener('keydown', event => {
if (event.code === 'Space') {
const radius = 30;
const x = Math.random() * render.options.width;
const fallingBody = Bodies.circle(x, -radius, radius, { label: 'fallingObject' });
World.add(engine.world, fallingBody);
}
});
// レンダラーとエンジンを実行
Render.run(render);
Engine.run(engine);
実装してみる
上記を参考に、以下のようにHTMLとJavaScriptファイルを作りました。
index.html
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/matter-js/0.14.2/matter.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
<script src="./script.js"></script>
</html>
script.js
// Matter.js のモジュールを取り込む
const { Engine, Render, World, Bodies, Body, Events } = Matter;
// エンジンとレンダラーを作成
const engine = Engine.create();
const render = Render.create({
element: document.body,
engine: engine
});
// 2つのオブジェクトが衝突した時に呼ばれる関数
function mergeBodies(pair) {
const bodyA = pair.bodyA;
const bodyB = pair.bodyB;
// 新しいオブジェクトのプロパティを計算
const newX = (bodyA.position.x + bodyB.position.x) / 2;
const newY = (bodyA.position.y + bodyB.position.y) / 2;
const newRadius = Math.sqrt(bodyA.circleRadius * bodyA.circleRadius + bodyB.circleRadius * bodyB.circleRadius);
// 古いオブジェクトをワールドから削除
World.remove(engine.world, [bodyA, bodyB]);
// 新しいオブジェクトを作成してワールドに追加
const newBody = Bodies.circle(newX, newY, newRadius);
World.add(engine.world, newBody);
}
// オブジェクトが衝突した時にイベントリスナーを設定
Events.on(engine, 'collisionStart', event => {
const pairs = event.pairs;
pairs.forEach(pair => {
if (pair.bodyA.label === 'fallingObject' && pair.bodyB.label === 'fallingObject') {
mergeBodies(pair);
}
});
});
// スペースキーが押された時に新しいオブジェクトを作成
window.addEventListener('keydown', event => {
if (event.code === 'Space') {
const radius = 30;
const x = Math.random() * render.options.width;
const fallingBody = Bodies.circle(x, -radius, radius, { label: 'fallingObject' });
World.add(engine.world, fallingBody);
}
});
// レンダラーとエンジンを実行
Render.run(render);
Engine.run(engine);
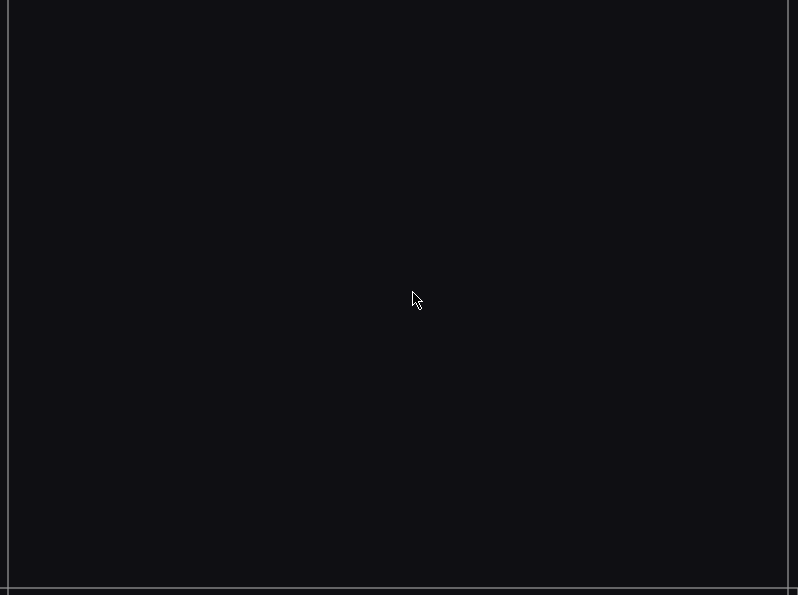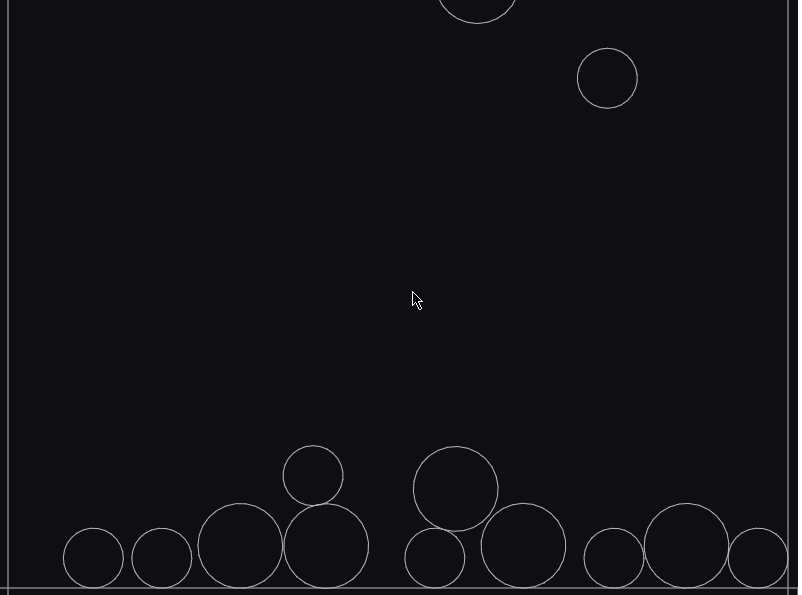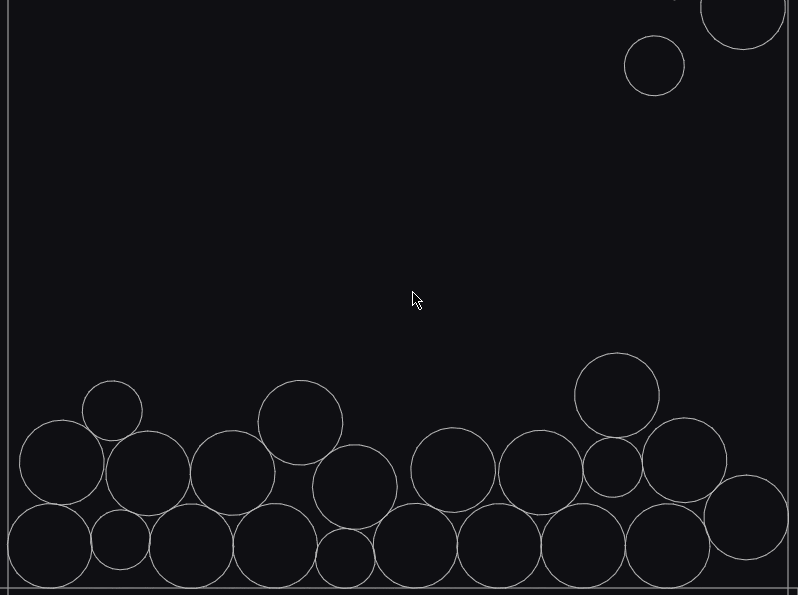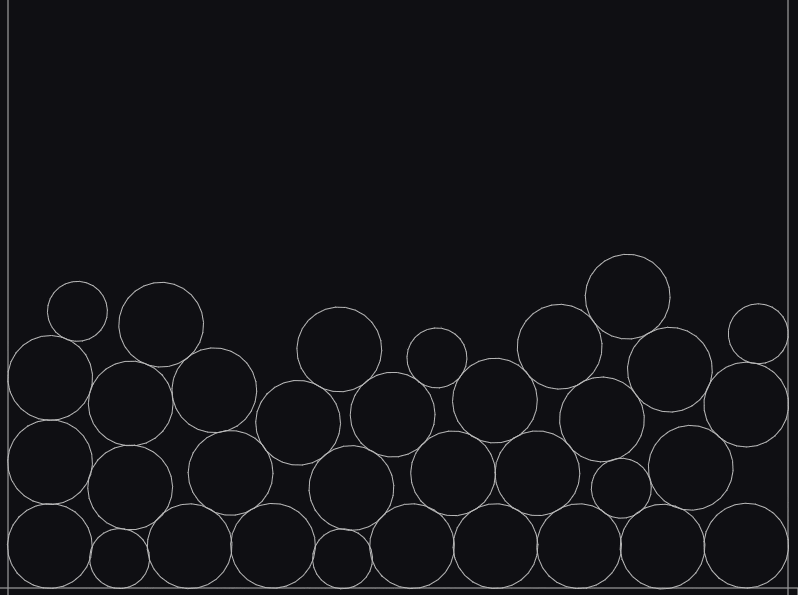
動かしてみる
おっと、床がありませんね。
確かに床をつけるのはお願いしていなかったかもしれません。(トホホ)
床をつけてもらいましょう。
Matter.jsで床をつくるには…?
私:
ゲームを動かしてみましたが、床が無いので物体が落ち続けてしまうようです。
床と壁を作ってくれませんか?
ChatGPT:
もちろんです。床と壁を追加することで、落下する物体が画面内に留まるようにします。以下のコードを先ほどのスクリプトに追加してください。これにより、画面の下部に床が、両側に壁が設置されます。
// 画面の幅と高さを取得
const width = render.options.width;
const height = render.options.height;
// 床と壁を作成
const ground = Bodies.rectangle(width / 2, height, width, 20, { isStatic: true });
const leftWall = Bodies.rectangle(0, height / 2, 20, height, { isStatic: true });
const rightWall = Bodies.rectangle(width, height / 2, 20, height, { isStatic: true });
// 床と壁をワールドに追加
World.add(engine.world, [ground, leftWall, rightWall]);
Worldにオブジェクトを追加して壁を作るんですね。
言われたとおりに追加してみましょう。
// Matter.js のモジュールを取り込む
const { Engine, Render, World, Bodies, Body, Events } = Matter;
// エンジンとレンダラーを作成
const engine = Engine.create();
const render = Render.create({
element: document.body,
engine: engine
});
+ // 画面の幅と高さを取得
+ const width = render.options.width;
+ const height = render.options.height;
+ // 床と壁を作成
+ const ground = Bodies.rectangle(width / 2, height, width, 20, { isStatic: true });
+ const leftWall = Bodies.rectangle(0, height / 2, 20, height, { isStatic: true });
+ const rightWall = Bodies.rectangle(width, height / 2, 20, height, { isStatic: true });
+ // 床と壁をワールドに追加
+ World.add(engine.world, [ground, leftWall, rightWall]);
// 2つのオブジェクトが衝突した時に呼ばれる関数
function mergeBodies(pair) {
const bodyA = pair.bodyA;
const bodyB = pair.bodyB;
// 新しいオブジェクトのプロパティを計算
const newX = (bodyA.position.x + bodyB.position.x) / 2;
const newY = (bodyA.position.y + bodyB.position.y) / 2;
const newRadius = Math.sqrt(bodyA.circleRadius * bodyA.circleRadius + bodyB.circleRadius * bodyB.circleRadius);
// 古いオブジェクトをワールドから削除
World.remove(engine.world, [bodyA, bodyB]);
// 新しいオブジェクトを作成してワールドに追加
const newBody = Bodies.circle(newX, newY, newRadius);
World.add(engine.world, newBody);
}
// オブジェクトが衝突した時にイベントリスナーを設定
Events.on(engine, 'collisionStart', event => {
const pairs = event.pairs;
pairs.forEach(pair => {
if (pair.bodyA.label === 'fallingObject' && pair.bodyB.label === 'fallingObject') {
mergeBodies(pair);
}
});
});
// スペースキーが押された時に新しいオブジェクトを作成
window.addEventListener('keydown', event => {
if (event.code === 'Space') {
const radius = 30;
const x = Math.random() * render.options.width;
const fallingBody = Bodies.circle(x, -radius, radius, { label: 'fallingObject' });
World.add(engine.world, fallingBody);
}
});
// レンダラーとエンジンを実行
Render.run(render);
Engine.run(engine);
動かしてみる
ほええええ!!!!
スイカゲームができてしまった・・・(早とちり)
もう少しスイカゲームに近づけたいので、
次に落ちる果物を矢印キーで左右に移動させて、スペースキーで落とせるようにしてみます。
オブジェクトをキーボード操作できるように
ChatGPTにソースコードの改修を頼むときは、可能な限り現在のソースコードを提供してあげるとうまく処理してくれる気がします。それと、なぜかコードの一部を省略したがるので、コードを省略しないようにお願いしています。
私:
現在のソースコードに以下の機能を追加してください。
・初期状態として、次に落とすオブジェクトが画面の上部に表示されるようにする。
・次に落とすオブジェクトは矢印キーで左右に移動できるようにする。
・スペースキーを押下すると、移動した場所を起点にオブジェクトが落下する。
修正後のソースコードは省略することなくすべて示してください。
なお、現在のソースコードは以下の通りです。
~~(コードは省略)~~
ChatGPT:
次に落とすオブジェクトを画面上部に表示し、矢印キーで左右に移動できるようにし、スペースキーでその位置から落下させる機能を追加します。以下が修正後の完全なソースコードです:
生成されたソースコード(クリックで展開)
// Matter.js のモジュールを取り込む
const { Engine, Render, World, Bodies, Body, Events } = Matter;
// エンジンとレンダラーを作成
const engine = Engine.create();
const render = Render.create({
element: document.body,
engine: engine
});
// 画面の幅と高さを取得
const width = render.options.width;
const height = render.options.height;
// 床と壁を作成
const ground = Bodies.rectangle(width / 2, height, width, 20, { isStatic: true });
const leftWall = Bodies.rectangle(0, height / 2, 20, height, { isStatic: true });
const rightWall = Bodies.rectangle(width, height / 2, 20, height, { isStatic: true });
// 床と壁をワールドに追加
World.add(engine.world, [ground, leftWall, rightWall]);
// 2つのオブジェクトが衝突した時に呼ばれる関数
function mergeBodies(pair) {
const bodyA = pair.bodyA;
const bodyB = pair.bodyB;
// 新しいオブジェクトのプロパティを計算
const newX = (bodyA.position.x + bodyB.position.x) / 2;
const newY = (bodyA.position.y + bodyB.position.y) / 2;
const newRadius = Math.sqrt(bodyA.circleRadius * bodyA.circleRadius + bodyB.circleRadius * bodyB.circleRadius);
// 古いオブジェクトをワールドから削除
World.remove(engine.world, [bodyA, bodyB]);
// 新しいオブジェクトを作成してワールドに追加
const newBody = Bodies.circle(newX, newY, newRadius, { label: 'fallingObject' });
World.add(engine.world, newBody);
}
// オブジェクトが衝突した時にイベントリスナーを設定
Events.on(engine, 'collisionStart', event => {
const pairs = event.pairs;
pairs.forEach(pair => {
if (pair.bodyA.label === 'fallingObject' && pair.bodyB.label === 'fallingObject') {
mergeBodies(pair);
}
});
});
// 次に落とすオブジェクトの初期設定
let nextObject = Bodies.circle(width / 2, 30, 30, { label: 'fallingObject', isStatic: true });
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
// キーボード入力に応じてオブジェクトを操作
window.addEventListener('keydown', event => {
if (event.code === 'Space') {
// スペースキーでオブジェクトを落下
Body.setStatic(nextObject, false);
nextObject = Bodies.circle(width / 2, 30, 30, { label: 'fallingObject', isStatic: true });
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
} else if (event.code === 'ArrowLeft') {
// 左矢印キーでオブジェクトを左に移動
Body.translate(nextObject, { x: -20, y: 0 });
} else if (event.code === 'ArrowRight') {
// 右矢印キーでオブジェクトを右に移動
Body.translate(nextObject, { x: 20, y: 0 });
}
});
// レンダラーとエンジンを実行
Render.run(render);
Engine.run(engine);
このコードでは、画面上部に次に落とすオブジェクトを表示し、矢印キーで左右に移動できるようになります。スペースキーを押すと、そのオブジェクトが落下し、新たなオブジェクトが上部に生成されます。これにより、よりインタラクティブなゲーム体験を提供できます。
動かしてみる
たまに次に落ちるオブジェクトが出なかったりしますが、
ほぼほぼスイカゲームに近づいてきました。
ChatGPTだけでここまでやってくれるとは、本当にすごい時代になったものです。
つぎは、オブジェクトを画像に置き換えてみることにします。
オブジェクトに画像が表示されるようにする
私:
次に落ちるオブジェクトは、現在のところただの図形ですが
これを画像に置き換えることはできますか
ChatGPT:
はい、Matter.jsでは画像を使ってオブジェクトを描画することができます。これを行うには、Bodies.rectangle や Bodies.circle などの関数を使用して物理オブジェクトを作成し、その render プロパティに sprite を設定します。sprite には画像のパスと、画像のサイズを指定します。
まず、使用したい画像ファイルをプロジェクトに追加してください。次に、以下の変更をソースコードに適用します。ここでは例として、画像を使用して円形のオブジェクトを作成する方法を示します。
// 次に落とすオブジェクトを画像で作成する関数
function createFallingObject(x, y, radius) {
const object = Bodies.circle(x, y, radius, {
label: 'fallingObject',
isStatic: true,
render: {
sprite: {
texture: 'path/to/your/image.png', // 画像のパスを指定
xScale: radius * 2 / 100, // 画像のスケールを調整
yScale: radius * 2 / 100
}
}
});
return object;
}
// 初期の落下オブジェクトを作成
nextObject = createFallingObject(width / 2, 30, 30);
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
// キーボード入力の処理(変更なし)
window.addEventListener('keydown', event => {
// ...
});
// その他の部分(変更なし)
// ...
なるほど、どうやらtextureを指定すればいいようです。 言われたとおりに実装してみます。
まずはエビのけりけりを表示するようにしてみます。
+ // 次に落とすオブジェクトを画像で作成する関数
+ function createFallingObject(x, y, radius) {
+ const object = Bodies.circle(x, y, radius, {
+ label: 'fallingObject',
+ isStatic: true,
+ render: {
+ sprite: {
+ texture: "/img/ebi.png", // 画像のパスを指定
+ xScale: radius * 2 / 100, // 画像のスケールを調整
+ yScale: radius * 2 / 100
+ }
+ }
+ });
+ return object;
+ }
-// 次に落とすオブジェクトの初期設定
+// 初期の落下オブジェクトを作成
-let nextObject = Bodies.circle(width / 2, 30, 30, { label: 'fallingObject', isStatic: true });
+let nextObject = createFallingObject(width / 2, 30, 30);
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
// キーボード入力に応じてオブジェクトを操作
window.addEventListener('keydown', event => {
if (event.code === 'Space') {
// スペースキーでオブジェクトを落下
Body.setStatic(nextObject, false);
- nextObject = Bodies.circle(width / 2, 30, 30, { label: 'fallingObject', isStatic: true });
+ nextObject = createFallingObject(width / 2, 30, 30);
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
} else if (event.code === 'ArrowLeft') {
// 左矢印キーでオブジェクトを左に移動
Body.translate(nextObject, { x: -20, y: 0 });
} else if (event.code === 'ArrowRight') {
// 右矢印キーでオブジェクトを右に移動
Body.translate(nextObject, { x: 20, y: 0 });
}
});
動かしてみる
なぜか画像が表示されない
ググってみましょう。
ここに書いてある通り、ワイヤフレームモードがONになっていると画像が表示されないようです。
Render.createのoptionsにwireframes: falseを渡してみましょう。
// エンジンとレンダラーを作成
const engine = Engine.create();
const render = Render.create({
element: document.body,
engine: engine,
+ options: {wireframes: false}
});
画像が表示されるようになったのでエビのけりけりリベンジ
エビのけりけりが出るようになりました!!!!!
あまりにもかわいすぎる。
ここで一旦バグ修正
なんとなくベースができたような気がするので、
ここで少しバグを直しておきます。
現時点で挙動がおかしいそうなところは以下の通り。
- スペースキーを連続で押せてしまう。
- 落下中にオブジェクトを動かせてしまう。
なんとなくソースコードを眺めてたら自力で直せそうなので、
以下のように直してみました。
オブジェクトが落下しているかどうかを判定するフラグをいれ
オブジェクトが落下開始してから2秒後までスペースキーを押せなくしています。
また、落下中は左右キーを押せなくしてみました。
// 初期の落下オブジェクトを作成
let nextObject = createFallingObject(width / 2, 30, 30);
// オブジェクトが落下中かどうか
let isFalling = false;
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
// キーボード入力に応じてオブジェクトを操作
window.addEventListener('keydown', event => {
if (event.code === 'Space') {
// スペースキーでオブジェクトを落下
isFalling = true;
Body.setStatic(nextObject, false);
window.setTimeout(() => {
nextObject = createFallingObject(width / 2, 30, 30);
isFalling = false;
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
}, 2000)
} else if (event.code === 'ArrowLeft' && !isFalling) {
// 左矢印キーでオブジェクトを左に移動
Body.translate(nextObject, { x: -20, y: 0 });
} else if (event.code === 'ArrowRight' && !isFalling) {
// 右矢印キーでオブジェクトを右に移動
Body.translate(nextObject, { x: 20, y: 0 });
}
});
次に落下するオブジェクトをランダムにする
ベースができてきたので、落下するオブジェクトをランダムに指定できるようにします。
私:
既存のソースコードをベースに、以下の機能を実装してください。
・次に落下するオブジェクト(nextObject)は、複数のオブジェクトの中からランダムに選ばれるようにする。
・落下するオブジェクトの定義として、以下を指定できるようにする。
・画像パス
・サイズ
・オブジェクトの識別子
既存のソースコードは以下です。
~~(省略)~~
ChatGPT:
次に落下するオブジェクト(nextObject)が複数のオブジェクトの中からランダムに選ばれるように機能を追加するために、まずオブジェクトの定義を配列で管理し、その中からランダムに選択するようにします。各オブジェクトは画像パス、サイズ、識別子を持つようにします。
// オブジェクトの定義の配列
const objectDefinitions = [
{
texture: "/img/object1.png",
size: 30,
label: "object1"
},
{
texture: "/img/object2.png",
size: 40,
label: "object2"
},
// 他のオブジェクトの定義を追加...
];
// 次に落とすオブジェクトをランダムに選択して作成する関数
function createRandomFallingObject(x, y) {
const randomIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * objectDefinitions.length);
const objectDef = objectDefinitions[randomIndex];
const object = Bodies.circle(x, y, objectDef.size, {
label: objectDef.label,
isStatic: true,
render: {
sprite: {
texture: objectDef.texture,
xScale: objectDef.size * 2 / 100,
yScale: objectDef.size * 2 / 100
}
}
});
return object;
}
// 初期の落下オブジェクトをランダムに作成
let nextObject = createRandomFallingObject(width / 2, 30);
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
// キーボード入力に応じてオブジェクトを操作(変更なし)
window.addEventListener('keydown', event => {
// ...
});
// レンダラーとエンジンを実行(変更なし)
Render.run(render);
Engine.run(engine);
この変更により、ゲームはobjectDefinitions配列内のオブジェクト定義からランダムにオブジェクトを選択し、それを次に落下するオブジェクトとして画面上に表示します。各オブジェクト定義は、それぞれ独自の画像パス、サイズ、識別子を持ちます。これにより、ゲームにバリエーションと予測不可能性が加わり、より面白くなります。
さっそくソースコードに反映してみます。 また、ゲーム内のオブジェクトは円で描画しているので、素材の方も円で囲っておきます。
// Matter.js のモジュールを取り込む
const { Engine, Render, World, Bodies, Body, Events } = Matter;
// オブジェクトの定義の配列
+ const objectDefinitions = [
+ {
+ texture: "/img/ebi_circle.png",
+ size: 30,
+ label: "ebi_circle"
+ }
+ ];
+ // 次に落とすオブジェクトをランダムに選択して作成する関数
+ function createRandomFallingObject(x, y) {
+ const randomIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * objectDefinitions.length);
+ const objectDef = objectDefinitions[randomIndex];
+
+ const object = Bodies.circle(x, y, objectDef.size, {
+ label: objectDef.label,
+ isStatic: true,
+ render: {
+ sprite: {
+ texture: objectDef.texture,
+ xScale: objectDef.size * 2 / 100,
+ yScale: objectDef.size * 2 / 100
+ }
+ }
+ });
+ return object;
+ }
// エンジンとレンダラーを作成
const engine = Engine.create();
const render = Render.create({
element: document.body,
engine: engine,
options: { wireframes: false }
});
// 画面の幅と高さを取得
const width = render.options.width;
const height = render.options.height;
// 床と壁を作成
const ground = Bodies.rectangle(width / 2, height, width, 20, { isStatic: true });
const leftWall = Bodies.rectangle(0, height / 2, 20, height, { isStatic: true });
const rightWall = Bodies.rectangle(width, height / 2, 20, height, { isStatic: true });
// 床と壁をワールドに追加
World.add(engine.world, [ground, leftWall, rightWall]);
// 2つのオブジェクトが衝突した時に呼ばれる関数
function mergeBodies(pair) {
const bodyA = pair.bodyA;
const bodyB = pair.bodyB;
// 新しいオブジェクトのプロパティを計算
const newX = (bodyA.position.x + bodyB.position.x) / 2;
const newY = (bodyA.position.y + bodyB.position.y) / 2;
const newRadius = Math.sqrt(bodyA.circleRadius * bodyA.circleRadius + bodyB.circleRadius * bodyB.circleRadius);
// 古いオブジェクトをワールドから削除
World.remove(engine.world, [bodyA, bodyB]);
// 新しいオブジェクトを作成してワールドに追加
const newBody = Bodies.circle(newX, newY, newRadius, { label: 'fallingObject' });
World.add(engine.world, newBody);
}
// オブジェクトが衝突した時にイベントリスナーを設定
Events.on(engine, 'collisionStart', event => {
const pairs = event.pairs;
pairs.forEach(pair => {
if (pair.bodyA.label === 'fallingObject' && pair.bodyB.label === 'fallingObject') {
mergeBodies(pair);
}
});
});
- // 次に落とすオブジェクトを画像で作成する関数
- function createFallingObject(x, y, radius) {
- const object = Bodies.circle(x, y, radius, {
- label: 'fallingObject',
- isStatic: true,
- render: {
- sprite: {
- texture: "/img/ebi.png", // 画像のパスを指定
- xScale: radius * 2 / 100, // 画像のスケールを調整
- yScale: radius * 2 / 100
- }
- }
- });
- return object;
- }
// 初期の落下オブジェクトを作成
- let nextObject = createFallingObject(width / 2, 30, 30);
+ let nextObject = createRandomFallingObject(width / 2, 30);
// オブジェクトが落下中かどうか
let isFalling = false;
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
// キーボード入力に応じてオブジェクトを操作
window.addEventListener('keydown', event => {
if (event.code === 'Space') {
// スペースキーでオブジェクトを落下
isFalling = true;
Body.setStatic(nextObject, false);
window.setTimeout(() => {
- nextObject = createFallingObject(width / 2, 30, 30);
+ nextObject = createRandomFallingObject(width / 2, 30);
isFalling = false;
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
}, 2000)
} else if (event.code === 'ArrowLeft' && !isFalling) {
// 左矢印キーでオブジェクトを左に移動
Body.translate(nextObject, { x: -20, y: 0 });
} else if (event.code === 'ArrowRight' && !isFalling) {
// 右矢印キーでオブジェクトを右に移動
Body.translate(nextObject, { x: 20, y: 0 });
}
});
// レンダラーとエンジンを実行
Render.run(render);
Engine.run(engine);
動かしてみる
さて、動かしてみましょう。
エビがでかすぎる!!!!!!
なんだかスケール調整を工夫しないといけない気がしますね。
ちょっと聞いてみましょう。
オブジェクトのサイズと画像のサイズが同じになるように
私:
画像のサイズとオブジェクトサイズを一致させるにはどうしたらよいでしょうか。
画像のサイズをobjectDefinitionsに定義して、objectDefinitionsのsizeに応じてスケールを調整したいです。
ChatGPT:
画画像の実際のサイズとMatter.jsでのオブジェクトのサイズを一致させるには、画像の元のサイズを知っておく必要があります。その上で、Matter.jsのオブジェクトサイズ(半径や幅・高さ)に合わせて、スケールを調整します。
まず、objectDefinitionsに各オブジェクトの画像の元のサイズを含めるようにします。その後、このサイズを基にして、Matter.jsのオブジェクトサイズに合わせたスケールを計算します。
以下は、オブジェクト定義に画像の元のサイズを含め、それをもとにスケールを計算する方法です:
// オブジェクトの定義の配列(画像の元のサイズを含む)
const objectDefinitions = [
{
texture: "/img/object1.png",
size: 30,
label: "object1",
originalWidth: 100, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 100 // 画像の元の高さ
},
{
texture: "/img/object2.png",
size: 40,
label: "object2",
originalWidth: 120,
originalHeight: 120
},
// 他のオブジェクトの定義を追加...
];
// 次に落とすオブジェクトをランダムに選択して作成する関数
function createRandomFallingObject(x, y) {
const randomIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * objectDefinitions.length);
const objectDef = objectDefinitions[randomIndex];
// スケールを計算(オブジェクトのサイズに合わせる)
const scale = objectDef.size * 2 / Math.max(objectDef.originalWidth, objectDef.originalHeight);
const object = Bodies.circle(x, y, objectDef.size, {
label: objectDef.label,
isStatic: true,
render: {
sprite: {
texture: objectDef.texture,
xScale: scale,
yScale: scale
}
}
});
return object;
}
// 初期の落下オブジェクトをランダムに作成
let nextObject = createRandomFallingObject(width / 2, 30);
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
// キーボード入力に応じてオブジェクトを操作(その他のコードは変更なし)
// ...
なるほど、言われたとおりに実装してみます。
// オブジェクトの定義の配列
const objectDefinitions = [
{
texture: "/img/ebi_circle.png",
size: 60,
label: "ebi_circle",
+ originalWidth: 792, // 画像の元の幅
+ originalHeight: 792 // 画像の元の高さ
}
];
// 次に落とすオブジェクトをランダムに選択して作成する関数
function createRandomFallingObject(x, y) {
const randomIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * objectDefinitions.length);
const objectDef = objectDefinitions[randomIndex];
// スケールを計算(オブジェクトのサイズに合わせる)
+ const scale = objectDef.size * 2 / Math.max(objectDef.originalWidth, objectDef.originalHeight);
const object = Bodies.circle(x, y, objectDef.size, {
label: objectDef.label,
isStatic: true,
render: {
sprite: {
texture: objectDef.texture,
- xScale: objectDef.size * 2 / 100,
+ xScale: scale,
- yScale: objectDef.size * 2 / 100
+ yScale: scale
}
}
});
return object;
}
動かしてみる
動かしてみましょう!
エビのサイズが調整されていい感じになりましたね!
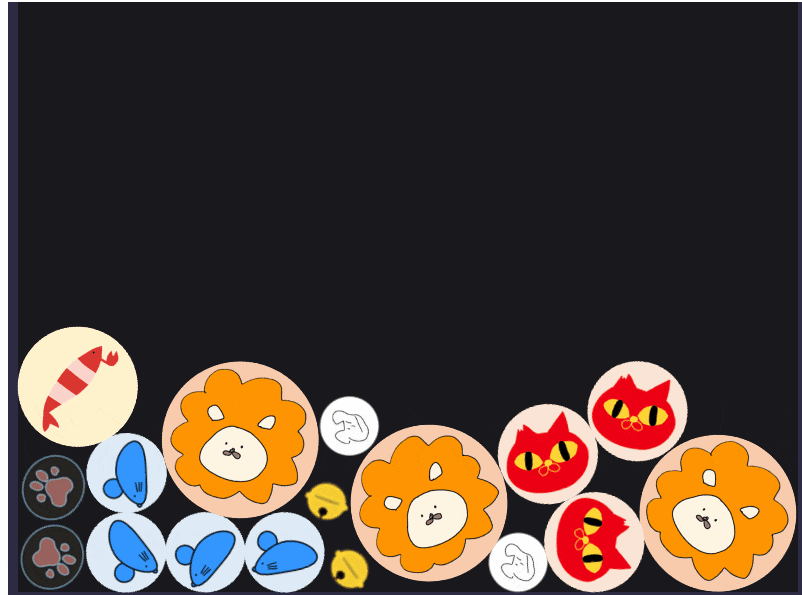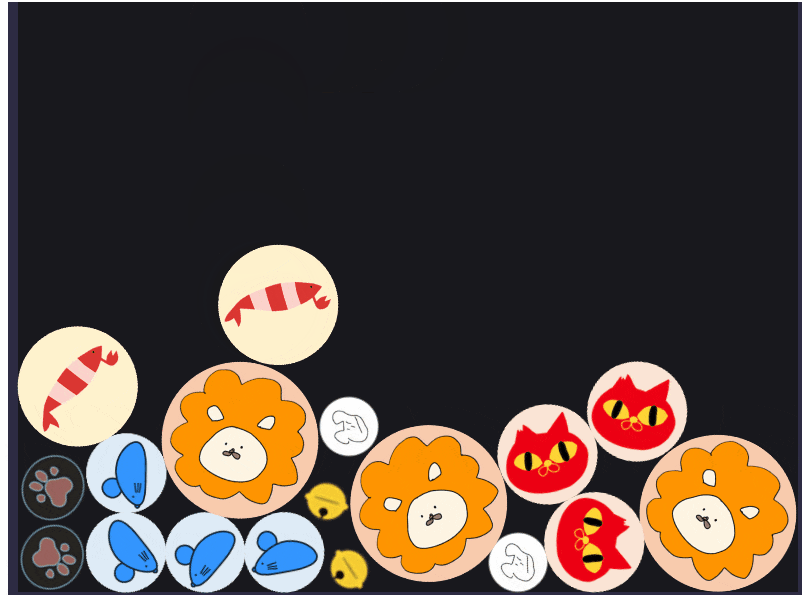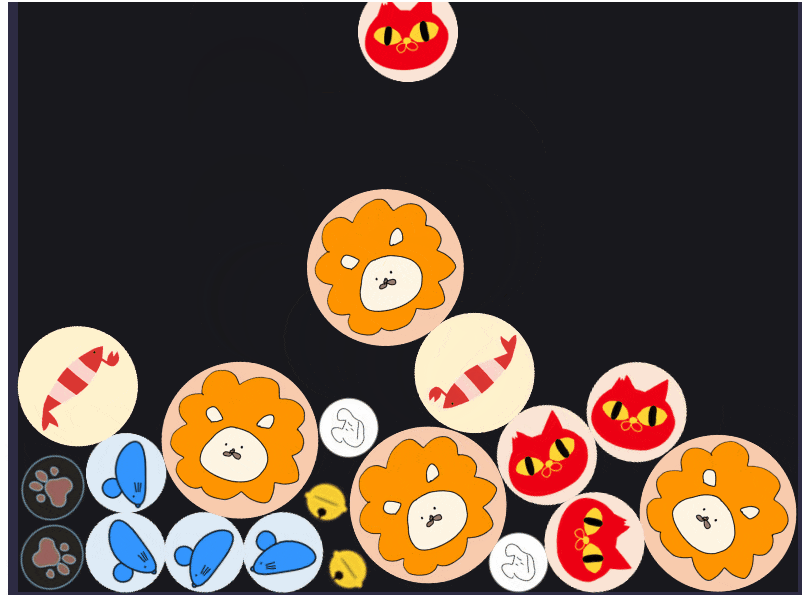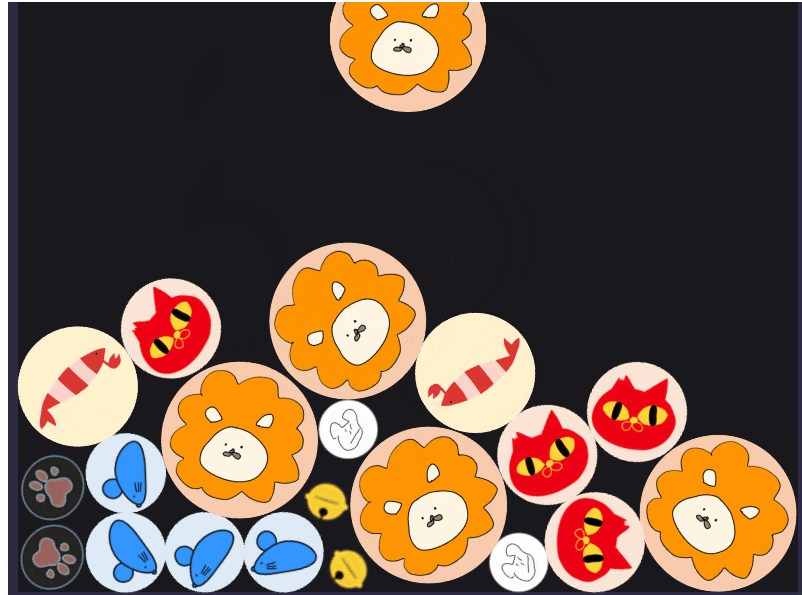
ほかの素材も定義に加えて画面をにぎやかにしてみます。
随分とにぎやかになりました。
(素材の統一性が無いのが気になりますが一旦よしとしましょう。)
つぎのステップに進みます。
同じ種類のオブジェクトがぶつかったときに次のオブジェクトに進化するようにしてみる
スイカゲームでは同じ種類のオブジェクトがぶつかると、
進化して次のオブジェクトに変わります。
この動作を実装してみましょう。
私:
既存のコードに以下の機能を付け加えてください。
・同一labelのオブジェクトが衝突したときに、次のオブジェクトに進化する。
・次のオブジェクトとは、objectDefinitions配列において衝突したオブジェクトの次の要素のオブジェクトと定義。
・次のオブジェクトの出現場所は、衝突先オブジェクトがあった位置とする。
ChatGPT:
指定された機能を実装するためには、衝突時の処理を変更し、次のオブジェクトに進化するようにする必要があります。衝突したオブジェクトが同じlabelを持っている場合、objectDefinitions配列の中で次の要素にあたるオブジェクトを作成し、衝突した位置に表示します。
以下の変更を行います:
- mergeBodies関数を変更して、同じlabelのオブジェクトが衝突した場合に、次のオブジェクトに進化するようにします。
- objectDefinitions内のオブジェクトを検索し、次のオブジェクトを見つけるためのヘルパー関数を作成します。
// 次のオブジェクトを取得する関数
function getNextObjectDefinition(label) {
for (let i = 0; i < objectDefinitions.length; i++) {
if (objectDefinitions[i].label === label) {
// 次のオブジェクトを配列から取得
return objectDefinitions[(i + 1) % objectDefinitions.length];
}
}
return null;
}
// 2つのオブジェクトが衝突した時に呼ばれる関数
function mergeBodies(pair) {
const bodyA = pair.bodyA;
const bodyB = pair.bodyB;
// 同じラベルのオブジェクトが衝突した場合
if (bodyA.label === bodyB.label) {
const nextObjectDef = getNextObjectDefinition(bodyA.label);
if (nextObjectDef) {
const newX = (bodyA.position.x + bodyB.position.x) / 2;
const newY = (bodyA.position.y + bodyB.position.y) / 2;
// スケールを計算(オブジェクトのサイズに合わせる)
const scale = nextObjectDef.size * 2 / Math.max(nextObjectDef.originalWidth, nextObjectDef.originalHeight);
const newBody = Bodies.circle(newX, newY, nextObjectDef.size, {
label: nextObjectDef.label,
render: {
sprite: {
texture: nextObjectDef.texture,
xScale: scale,
yScale: scale
}
}
});
World.remove(engine.world, [bodyA, bodyB]);
World.add(engine.world, newBody);
}
}
}
// イベントリスナーおよびその他のコードは変更なし...
提案してもらったコードを参考に、以下のように実装をしてみました。
次のオブジェクトを検索する関数を追加しました。
※objectDefinitions配列の最後の要素の場合は、進化するものが無いのでそのままにするように工夫。
// 次のオブジェクトを取得する関数
function getNextObjectDefinition(label) {
for (let i = 0; i < objectDefinitions.length; i++) {
if (objectDefinitions[i].label === label) {
// 次のオブジェクトを配列から取得
if (i === objectDefinitions.length-1) {
return null;
}
return objectDefinitions[(i + 1) % objectDefinitions.length];
}
}
return null;
}
オブジェクトを進化させるようにmergeBodiesを修正
// 2つのオブジェクトが衝突した時に呼ばれる関数
function mergeBodies(pair) {
const bodyA = pair.bodyA;
const bodyB = pair.bodyB;
// 同じラベルのオブジェクトが衝突した場合
if (bodyA.label === bodyB.label) {
const nextObjectDef = getNextObjectDefinition(bodyA.label);
if (nextObjectDef) {
const newX = (bodyA.position.x + bodyB.position.x) / 2;
const newY = (bodyA.position.y + bodyB.position.y) / 2;
// スケールを計算(オブジェクトのサイズに合わせる)
const scale = nextObjectDef.size * 2 / Math.max(nextObjectDef.originalWidth, nextObjectDef.originalHeight);
const newBody = Bodies.circle(newX, newY, nextObjectDef.size, {
label: nextObjectDef.label,
render: {
sprite: {
texture: nextObjectDef.texture,
xScale: scale,
yScale: scale
}
}
});
World.remove(engine.world, [bodyA, bodyB]);
World.add(engine.world, newBody);
}
}
}
オブジェクト衝突検知のイベントで、
2つオブジェクトのラベルが同じ場合に、mergeBodiesを呼び出すように修正
// オブジェクトが衝突した時にイベントリスナーを設定
Events.on(engine, 'collisionStart', event => {
const pairs = event.pairs;
pairs.forEach(pair => {
if (pair.bodyA.label === pair.bodyB.label) {
mergeBodies(pair);
}
});
});
動かしてみる
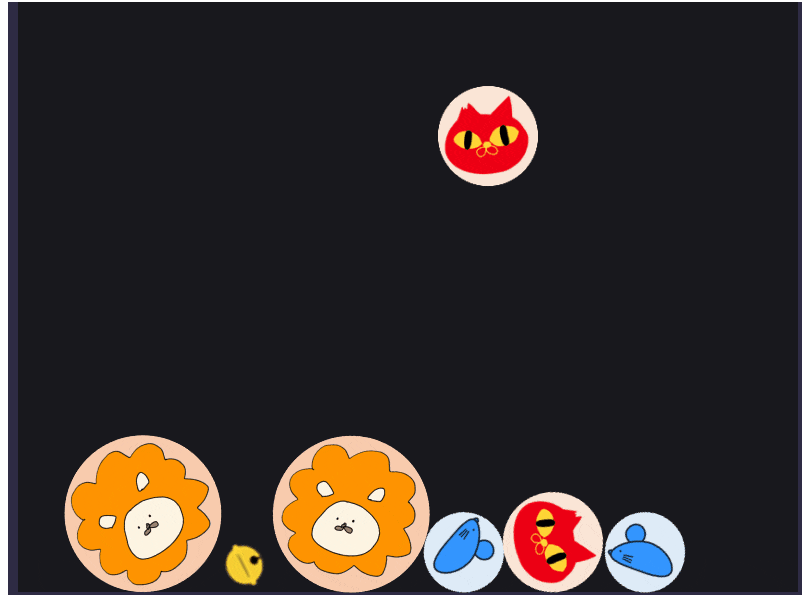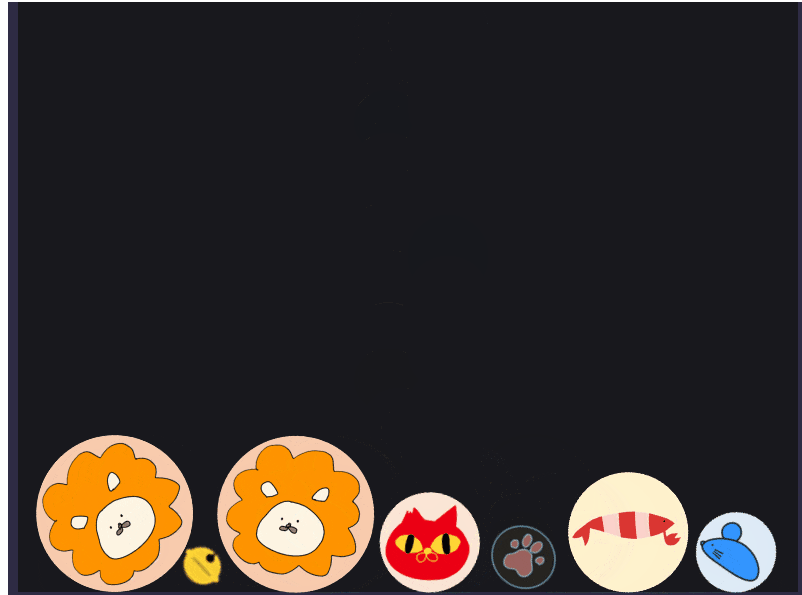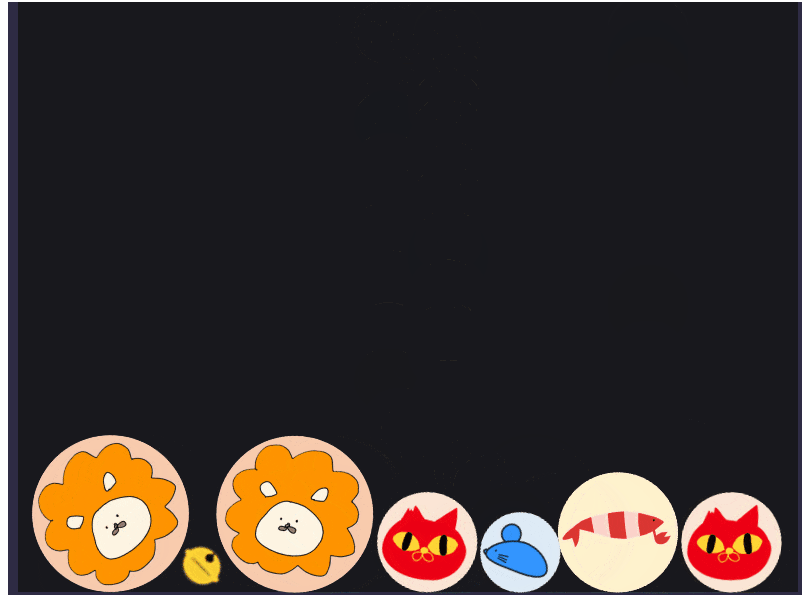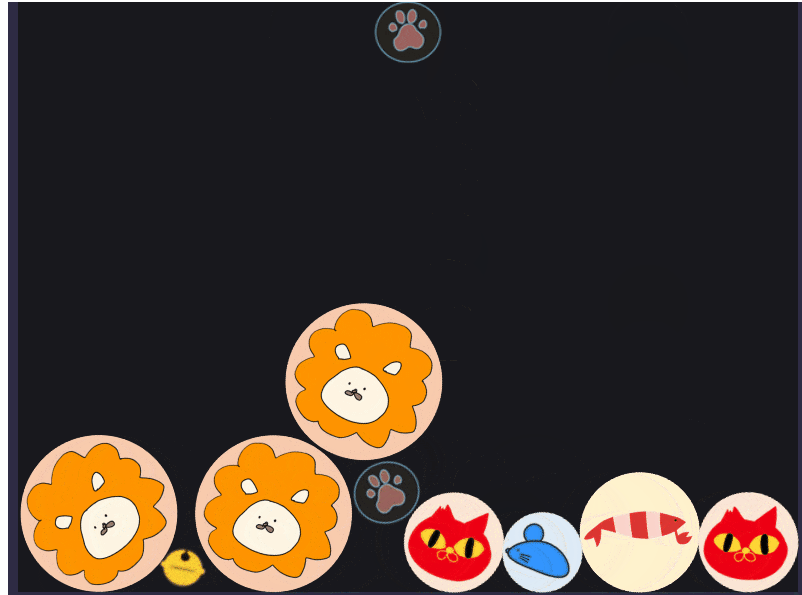
これを動かしてみると、いい感じにオブジェクトが進化するようになりました。
また、ライオンは最後の進化オブジェクトなのでぶつけても進化しないようになっています!
スコアリング機能を付けてみる
(なんだかまだ素材が足りない気はしますが)
一旦ゲームとして仕上げるためにスコアリング機能を付けておきましょう。
本家のスイカゲームのスコア付け方法がちょっとわからないのですが、
今回は簡易的に、生み出したオブジェクトでスコアが加算されるようにしてみます。
ここからは手元でできそうなので、ChatGPTに聞かずにトライしてみます。
まず、スコアを保持する変数を用意して、objectDefinitionsの各要素にスコアを持たせます。
let total_score = 0
// オブジェクトの定義の配列
const objectDefinitions = [
{
texture: "/img/suzu_circle.png",
size: 25,
label: "suzu_circle",
originalWidth: 32, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 32, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 10
},
{
texture: "/img/kanineko_circle.png",
size: 30,
label: "kanineko_circle",
originalWidth: 182, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 182, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 20
},
{
texture: "/img/nikukyu_circle.png",
size: 35,
label: "nikukyu_circle",
originalWidth: 58, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 52, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 30
},
{
texture: "/img/mouse_circle.png",
size: 40,
label: "mouse_circle",
originalWidth: 333, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 333, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 40
},
{
texture: "/img/neko_circle.png",
size: 50,
label: "neko_circle",
originalWidth: 429, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 429, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 50
},
{
texture: "/img/ebi_circle.png",
size: 60,
label: "ebi_circle",
originalWidth: 792, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 792, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 60
},
{
texture: "/img/lion_circle.png",
size: 80,
label: "lion_circle",
originalWidth: 574, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 586, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 70
},
];
続いて、mergeBodies内で進化後のオブジェクトが見つかったときにスコアが加算されるようにします。
// 2つのオブジェクトが衝突した時に呼ばれる関数
function mergeBodies(pair) {
const bodyA = pair.bodyA;
const bodyB = pair.bodyB;
// 同じラベルのオブジェクトが衝突した場合
if (bodyA.label === bodyB.label) {
const nextObjectDef = getNextObjectDefinition(bodyA.label);
if (nextObjectDef) {
+ total_score += nextObjectDef.score
+ $('#score').html(total_score.toString())
const newX = (bodyA.position.x + bodyB.position.x) / 2;
const newY = (bodyA.position.y + bodyB.position.y) / 2;
// スケールを計算(オブジェクトのサイズに合わせる)
const scale = nextObjectDef.size * 2 / Math.max(nextObjectDef.originalWidth, nextObjectDef.originalHeight);
const newBody = Bodies.circle(newX, newY, nextObjectDef.size, {
label: nextObjectDef.label,
render: {
sprite: {
texture: nextObjectDef.texture,
xScale: scale,
yScale: scale
}
}
});
World.remove(engine.world, [bodyA, bodyB]);
World.add(engine.world, newBody);
}
}
}
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/matter-js/0.14.2/matter.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
+ <div>score:<p id="score">0</p></div>
</body>
<script src="./script_collision.js"></script>
+ <script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script>
</html>
動かしてみる
動かしてみます。
画面の上部にスコアがでるようになって、少しゲームっぽくなりました!
このあとの展望
ざっくり形になったので、細かい実装を入れていきたいところなのですが
時間が足りなくなってしまったのでまたの機会にしたいと思います。
このあとは以下の要素を入れることでネコゲームを完成にもっていけそうです。
- ゲームオーバーの要素を入れる
- 次に振ってくるオブジェクトを制限する
- コンボによるスコアリングの倍率をつける
- ランキング機能を付ける
- 素材をふやす
まとめ
駆け足でしたが、アクションゲームを一度も作ったことがないエンジニアでも、それらしいものが作れるということが分かり感動です。
動くものを作るとやっぱり楽しいですね。
そして、ChatGPTが優秀過ぎて最高の相棒だな~と再認識しました。
普段とは違うモノづくりをたまにやってみるとなかなか楽しいので、
皆様もぜひ!
参考(ソースコード)
最終的に以下のソースコードになりました。
ChatGPTの提供コードをほとんどそのまま使っているので、
すこし散らかっている部分もありますがご了承ください。
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/matter-js/0.14.2/matter.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div>score:<p id="score">0</p></div>
</body>
<script src="./script.js"></script>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script>
</html>
// Matter.js のモジュールを取り込む
const { Engine, Render, World, Bodies, Body, Events } = Matter;
let total_score = 0
// オブジェクトの定義の配列
const objectDefinitions = [
{
texture: "/img/suzu_circle.png",
size: 25,
label: "suzu_circle",
originalWidth: 32, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 32, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 10
},
{
texture: "/img/kanineko_circle.png",
size: 30,
label: "kanineko_circle",
originalWidth: 182, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 182, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 20
},
{
texture: "/img/nikukyu_circle.png",
size: 35,
label: "nikukyu_circle",
originalWidth: 58, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 52, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 30
},
{
texture: "/img/mouse_circle.png",
size: 40,
label: "mouse_circle",
originalWidth: 333, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 333, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 40
},
{
texture: "/img/neko_circle.png",
size: 50,
label: "neko_circle",
originalWidth: 429, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 429, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 50
},
{
texture: "/img/ebi_circle.png",
size: 60,
label: "ebi_circle",
originalWidth: 792, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 792, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 60
},
{
texture: "/img/lion_circle.png",
size: 80,
label: "lion_circle",
originalWidth: 574, // 画像の元の幅
originalHeight: 586, // 画像の元の高さ
score: 70
},
];
// 次に落とすオブジェクトをランダムに選択して作成する関数
function createRandomFallingObject(x, y) {
const randomIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * objectDefinitions.length);
const objectDef = objectDefinitions[randomIndex];
// スケールを計算(オブジェクトのサイズに合わせる)
const scale = objectDef.size * 2 / Math.max(objectDef.originalWidth, objectDef.originalHeight);
const object = Bodies.circle(x, y, objectDef.size, {
label: objectDef.label,
isStatic: true,
render: {
sprite: {
texture: objectDef.texture,
xScale: scale,
yScale: scale
}
}
});
return object;
}
// 次のオブジェクトを取得する関数
function getNextObjectDefinition(label) {
for (let i = 0; i < objectDefinitions.length; i++) {
if (objectDefinitions[i].label === label) {
// 次のオブジェクトを配列から取得
if (i === objectDefinitions.length-1) {
return null;
}
return objectDefinitions[(i + 1) % objectDefinitions.length];
}
}
return null;
}
// エンジンとレンダラーを作成
const engine = Engine.create();
const render = Render.create({
element: document.body,
engine: engine,
options: { wireframes: false }
});
// 画面の幅と高さを取得
const width = render.options.width;
const height = render.options.height;
// 床と壁を作成
const ground = Bodies.rectangle(width / 2, height, width, 20, { isStatic: true });
const leftWall = Bodies.rectangle(0, height / 2, 20, height, { isStatic: true });
const rightWall = Bodies.rectangle(width, height / 2, 20, height, { isStatic: true });
// 床と壁をワールドに追加
World.add(engine.world, [ground, leftWall, rightWall]);
// 2つのオブジェクトが衝突した時に呼ばれる関数
function mergeBodies(pair) {
const bodyA = pair.bodyA;
const bodyB = pair.bodyB;
// 同じラベルのオブジェクトが衝突した場合
if (bodyA.label === bodyB.label) {
const nextObjectDef = getNextObjectDefinition(bodyA.label);
if (nextObjectDef) {
total_score += nextObjectDef.score;
$('#score').html(total_score.toString())
const newX = (bodyA.position.x + bodyB.position.x) / 2;
const newY = (bodyA.position.y + bodyB.position.y) / 2;
// スケールを計算(オブジェクトのサイズに合わせる)
const scale = nextObjectDef.size * 2 / Math.max(nextObjectDef.originalWidth, nextObjectDef.originalHeight);
const newBody = Bodies.circle(newX, newY, nextObjectDef.size, {
label: nextObjectDef.label,
render: {
sprite: {
texture: nextObjectDef.texture,
xScale: scale,
yScale: scale
}
}
});
World.remove(engine.world, [bodyA, bodyB]);
World.add(engine.world, newBody);
}
}
}
// オブジェクトが衝突した時にイベントリスナーを設定
Events.on(engine, 'collisionStart', event => {
const pairs = event.pairs;
pairs.forEach(pair => {
if (pair.bodyA.label === pair.bodyB.label) {
mergeBodies(pair);
}
});
});
// 初期の落下オブジェクトを作成
let nextObject = createRandomFallingObject(width / 2, 30);
// オブジェクトが落下中かどうか
let isFalling = false;
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
// キーボード入力に応じてオブジェクトを操作
window.addEventListener('keydown', event => {
if (event.code === 'Space') {
// スペースキーでオブジェクトを落下
isFalling = true;
Body.setStatic(nextObject, false);
window.setTimeout(() => {
nextObject = createRandomFallingObject(width / 2, 30);
isFalling = false;
World.add(engine.world, nextObject);
}, 2000)
} else if (event.code === 'ArrowLeft' && !isFalling) {
// 左矢印キーでオブジェクトを左に移動
Body.translate(nextObject, { x: -20, y: 0 });
} else if (event.code === 'ArrowRight' && !isFalling) {
// 右矢印キーでオブジェクトを右に移動
Body.translate(nextObject, { x: 20, y: 0 });
}
});
// レンダラーとエンジンを実行
Render.run(render);
Engine.run(engine);