はじめに
javaでApache POIを使用して結合せるに罫線とセットする。
例
空のテンプレートからE2とE3を結合して、文字セット、罫線セットをする
(結果イメージ)
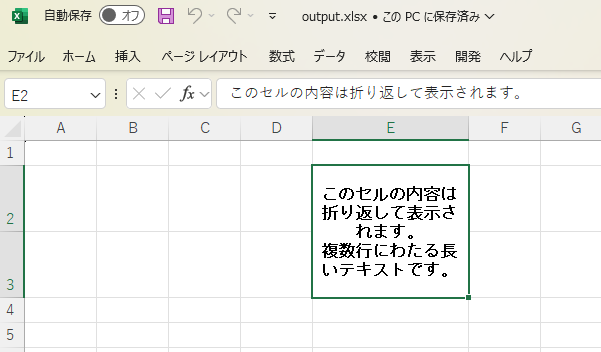
処理流れ
・セルを結合
・各セルセット
まず行を取得、または作成
次に行より列をセットしセルの場所を特定
・そこに文字を設定、今回だとE2に文字をセット
・スタイルはworkbookのcreateCellStyleメソッドよりセット
・フォントはworkbookのcreateFontメソッドよりセットし、styleにセットする
・それぞれのセルにスタイル適用
結合セルを扱う場合でも、結合がない通常のセルと同様に、範囲内のすべてのセルに対してスタイルを適用する(今回だとE2とE3にそれぞれ)
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.util.CellRangeAddress;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExcelMergeAndBorder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String templatePath = "template.xlsx"; // テンプレートファイルのパス
String outputPath = "output.xlsx"; // 出力ファイルのパス
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(templatePath);
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis)) {
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 既存の結合範囲を確認し、解除
for (int i = 0; i < sheet.getNumMergedRegions(); i++) {
CellRangeAddress mergedRegion = sheet.getMergedRegion(i);
if (mergedRegion.isInRange(1, 4) || mergedRegion.isInRange(2, 4)) { // E2, E3を含むか
sheet.removeMergedRegion(i);
i--; // 削除後はインデックスを調整
}
}
// E2とE3を縦に結合
CellRangeAddress cellRangeAddress = new CellRangeAddress(1, 2, 4, 4); // 行と列は0ベース
sheet.addMergedRegion(cellRangeAddress);
// 必要な行を取得または作成
Row row2 = sheet.getRow(1);
if (row2 == null) {
row2 = sheet.createRow(1);
}
Row row3 = sheet.getRow(2);
if (row3 == null) {
row3 = sheet.createRow(2);
}
// E2セルを取得または作成
Cell cell = row2.getCell(4); // E2セル
if (cell == null) {
cell = row2.createCell(4);
}
// 値をセット
String cellValue = "このセルの内容は折り返して表示されます。\n複数行にわたる長いテキストです。";
cell.setCellValue(cellValue);
// 罫線とスタイルの設定
XSSFCellStyle style = (XSSFCellStyle) workbook.createCellStyle();
style.setBorderTop(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setBorderBottom(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setBorderLeft(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setBorderRight(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
style.setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignment.CENTER);
style.setWrapText(true); // 折り返して表示を設定
// フォント設定
Font font = workbook.createFont();
font.setFontName("MS Gothic");
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12);
font.setBold(true);
style.setFont(font);
// スタイルを結合されたセル全体に適用
for (int row = 1; row <= 2; row++) { // E2, E3
Row currentRow = sheet.getRow(row);
if (currentRow == null) {
currentRow = sheet.createRow(row);
}
Cell currentCell = currentRow.getCell(4); // E列
if (currentCell == null) {
currentCell = currentRow.createCell(4);
}
currentCell.setCellStyle(style); // スタイルを適用
}
// 列幅の設定(E列 = 4番目の列)
sheet.setColumnWidth(4, 5000); // 列幅を調整
// 行の高さを設定
row2.setHeightInPoints(50); // E2の行の高さを調整
row3.setHeightInPoints(50); // E3の行の高さを調整
// ファイルを書き出し
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outputPath)) {
workbook.write(fos);
}
System.out.println("Excelファイルが正常に出力されました: " + outputPath);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
わかりやすく
Apache POIを使用したコードはクラスやメソッドの階層が深く、直感的に理解しにくい場合があります。特に、セル結合、スタイル設定、値の設定がそれぞれ異なるメソッドや処理フローを必要とするため、コードが複雑になりがちです。
以下に、コードを整理して可読性を向上させる方法を示します。
1. メソッドに分割して処理を整理
コードを単一のメインメソッドに詰め込むのではなく、以下のように処理を分割して再利用可能にすると、理解しやすくなります。
修正版コード(メソッド分割)
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.util.CellRangeAddress;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExcelMergeAndBorder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String templatePath = "template.xlsx"; // テンプレートファイルのパス
String outputPath = "output.xlsx"; // 出力ファイルのパス
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(templatePath);
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis)) {
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// セル結合処理
mergeCells(sheet, 1, 2, 4);
// スタイル作成
CellStyle style = createCellStyle(workbook);
// 結合範囲にスタイルと値を適用
applyStyleAndValue(sheet, 1, 2, 4, style, "このセルの内容は折り返して表示されます。\n複数行にわたる長いテキストです。");
// ファイル出力
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outputPath)) {
workbook.write(fos);
}
System.out.println("Excelファイルが正常に出力されました: " + outputPath);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// セル結合処理
private static void mergeCells(Sheet sheet, int startRow, int endRow, int colIndex) {
// 既存の結合範囲を解除(重複回避)
for (int i = 0; i < sheet.getNumMergedRegions(); i++) {
CellRangeAddress mergedRegion = sheet.getMergedRegion(i);
if (mergedRegion.isInRange(startRow, colIndex) || mergedRegion.isInRange(endRow, colIndex)) {
sheet.removeMergedRegion(i);
i--; // 削除後インデックスを調整
}
}
// セルを結合
CellRangeAddress cellRangeAddress = new CellRangeAddress(startRow, endRow, colIndex, colIndex);
sheet.addMergedRegion(cellRangeAddress);
}
// スタイル作成
private static CellStyle createCellStyle(Workbook workbook) {
XSSFCellStyle style = (XSSFCellStyle) workbook.createCellStyle();
style.setBorderTop(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setBorderBottom(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setBorderLeft(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setBorderRight(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
style.setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignment.CENTER);
style.setWrapText(true); // 折り返して表示を設定
// フォント設定
Font font = workbook.createFont();
font.setFontName("MS Gothic");
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12);
font.setBold(true);
style.setFont(font);
return style;
}
// 結合範囲にスタイルと値を適用
private static void applyStyleAndValue(Sheet sheet, int startRow, int endRow, int colIndex, CellStyle style, String value) {
// 結合範囲内のセルにスタイル適用
for (int rowIndex = startRow; rowIndex <= endRow; rowIndex++) {
Row row = sheet.getRow(rowIndex);
if (row == null) {
row = sheet.createRow(rowIndex);
}
Cell cell = row.getCell(colIndex);
if (cell == null) {
cell = row.createCell(colIndex);
}
cell.setCellStyle(style); // スタイルを適用
}
// 先頭セルに値を設定
Row mainRow = sheet.getRow(startRow);
if (mainRow != null) {
Cell mainCell = mainRow.getCell(colIndex);
if (mainCell != null) {
mainCell.setCellValue(value);
}
}
}
}
コードの改善点
-
役割ごとにメソッド分割
-
mergeCells: セル結合の処理を1つのメソッドにまとめました。 -
createCellStyle: スタイル設定の処理を切り出しました。 -
applyStyleAndValue: 結合範囲にスタイルを適用し、値を設定する処理を分けました。
-
-
冗長な処理を簡略化
- メイン処理が短くなり、全体の流れが明確になりました。
-
再利用性の向上
- 結合範囲やスタイルの設定が変更になっても、特定のメソッドのみ修正すれば済むようになりました。
期待される効果
- メインの処理が短くなり、全体の流れが見やすくなります。
- 各メソッドが独立しているため、個別にテストしやすくなります。
- メソッドの役割が明確になり、コードの再利用が容易になります。
実行結果
コードを実行すると、E2:E3が正しく結合され、罫線と折り返し表示が適用され、値が設定されます。
(全体表示等まで考慮に入れていません)
追記
Apache POIを使用してテンプレートからExcelファイルを読み込み、ページ設定やフォント、配置などの設定を確認する方法を記載します。特に、ページ向きや余白設定、印刷の方向などはSheetオブジェクトのPrintSetupを通じて確認できます。
以下に、ページ向きやその他の設定を確認する例を示します。
ページ設定を確認する例
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExcelTemplateReader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String templatePath = "template.xlsx"; // テンプレートのパスを指定してください
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(templatePath);
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis)) {
// シートを取得
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); // 0番目のシートを取得
// ページ設定の確認
System.out.println("ページ向き: " + (printSetup.getLandscape() ? "横" : "縦"));
// 余白設定の確認
System.out.println("左余白: " + sheet.getMargin(Sheet.LeftMargin));
System.out.println("右余白: " + sheet.getMargin(Sheet.RightMargin));
System.out.println("上余白: " + sheet.getMargin(Sheet.TopMargin));
System.out.println("下余白: " + sheet.getMargin(Sheet.BottomMargin));
// スケーリング設定の確認
System.out.println("スケーリング (%): " + printSetup.getScale());
// 用紙サイズの確認
System.out.println("用紙サイズ: " + printSetup.getPaperSize());
// フォントや配置の確認 (1つのセルを例に)
Row row = sheet.getRow(0); // 1行目を取得
if (row != null) {
Cell cell = row.getCell(0); // 1列目を取得
if (cell != null) {
CellStyle cellStyle = cell.getCellStyle();
Font font = workbook.getFontAt(cellStyle.getFontIndex());
System.out.println("フォント名: " + font.getFontName());
System.out.println("フォントサイズ: " + font.getFontHeightInPoints());
System.out.println("横位置: " + cellStyle.getAlignment());
System.out.println("縦位置: " + cellStyle.getVerticalAlignment());
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
主なポイント
-
ページ向き:
PrintSetupオブジェクトのgetLandscape()メソッドでページ向き(横または縦)を確認できます。 -
余白設定:
Sheet.getMargin()メソッドで余白を確認できます。 -
フォントと配置: セルのスタイル (
CellStyle) からフォントや配置を取得できます。
ページ向きの設定を修正する例
ページ向きが意図した設定と異なる場合、以下のように修正可能です。
// ページ向きを横に設定
printSetup.setLandscape(true);
これをテンプレートの読み込み後に設定することで、正しいページ向きで出力できます。
セルの書式保持
package com.example.POIExample2;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.util.CellRangeAddress;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileInputStream templateFile = new FileInputStream("template.xlsx");
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(templateFile)) {
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 2行目AからE列の結合セル設定
int sourceRowIndex = 1; // 2行目 (インデックスは0から始まる)
int sourceStartCol = 0; // A列 (インデックスは0から始まる)
int sourceEndCol = 4; // E列 (インデックスは0から始まる)
Row sourceRow = sheet.getRow(sourceRowIndex);
if (sourceRow != null) {
// 結合セル範囲を作成
CellRangeAddress range = new CellRangeAddress(sourceRowIndex, sourceRowIndex, sourceStartCol, sourceEndCol);
// 既存の結合セル範囲をチェック
boolean isAlreadyMerged = false;
for (int i = 0; i < sheet.getNumMergedRegions(); i++) {
CellRangeAddress existingRange = sheet.getMergedRegion(i);
if (existingRange.equals(range)) {
isAlreadyMerged = true;
break;
}
}
if (!isAlreadyMerged) {
sheet.addMergedRegion(range);
}
// 左上セルの値を設定
Cell sourceCell = sourceRow.getCell(sourceStartCol);
if (sourceCell == null) {
sourceCell = sourceRow.createCell(sourceStartCol);
}
sourceCell.setCellValue("Sample Text");
// 左上セルのスタイルをコピーして適用
CellStyle sourceStyle = sourceCell.getCellStyle();
for (int col = sourceStartCol; col <= sourceEndCol; col++) {
Cell targetCell = sourceRow.getCell(col);
if (targetCell == null) {
targetCell = sourceRow.createCell(col);
}
targetCell.setCellStyle(sourceStyle);
}
}
// ファイル出力
try (FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("output.xlsx")) {
workbook.write(outputStream);
}
System.out.println("結合セルに値をセットし、書式設定を引き継ぎました。");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
セルスタイルやフォントのコピー
private static CellStyle copyCellStyle(CellStyle originalStyle, XSSFWorkbook templateWorkbook, XSSFWorkbook newWorkbook) {
CellStyle newStyle = newWorkbook.createCellStyle();
// 各種プロパティのコピー
newStyle.setAlignment(originalStyle.getAlignment());
newStyle.setVerticalAlignment(originalStyle.getVerticalAlignment());
newStyle.setBorderTop(originalStyle.getBorderTop());
newStyle.setBorderBottom(originalStyle.getBorderBottom());
newStyle.setBorderLeft(originalStyle.getBorderLeft());
newStyle.setBorderRight(originalStyle.getBorderRight());
newStyle.setTopBorderColor(originalStyle.getTopBorderColor());
newStyle.setBottomBorderColor(originalStyle.getBottomBorderColor());
newStyle.setLeftBorderColor(originalStyle.getLeftBorderColor());
newStyle.setRightBorderColor(originalStyle.getRightBorderColor());
newStyle.setWrapText(originalStyle.getWrapText());
newStyle.setFillForegroundColor(originalStyle.getFillForegroundColor());
newStyle.setFillBackgroundColor(originalStyle.getFillBackgroundColor());
newStyle.setFillPattern(originalStyle.getFillPattern());
newStyle.setRotation(originalStyle.getRotation());
newStyle.setIndention(originalStyle.getIndention());
newStyle.setDataFormat(originalStyle.getDataFormat());
newStyle.setShrinkToFit(originalStyle.getShrinkToFit());
// フォントのコピー
Font originalFont = templateWorkbook.getFontAt(originalStyle.getFontIndexAsInt());
Font newFont = newWorkbook.createFont();
newFont.setFontName(originalFont.getFontName());
newFont.setFontHeight(originalFont.getFontHeight());
newFont.setBold(originalFont.getBold());
newFont.setItalic(originalFont.getItalic());
newFont.setColor(originalFont.getColor());
newFont.setUnderline(originalFont.getUnderline());
newFont.setStrikeout(originalFont.getStrikeout());
newStyle.setFont(newFont);
return newStyle;
}