DIについて。
「依存性の注入」と言われるもの。
依存とは
他のクラスを利用することを指す。
インターフェースにより、依存度合いを下げることができる(疎結合になる)。
//Badな例
//CarクラスとEngineAクラスが蜜結合
import java.util.*;
class EngineA{
public void boot(){
System.out.println("EngineA boot");
}
public void stop(){
System.out.println("EngineA stop");
}
}
class EngineB{
public void boot(){
System.out.println("EngineB boot");
}
public void stop(){
System.out.println("EngineB stop");
}
}
class Car{
private EngineA engineA;
public Car(EngineA engineA){
this.engineA = engineA;
}
public void engineStart(){
this.engineA.boot();
}
public void engineStop(){
this.engineA.stop();
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EngineA engineA = new EngineA();
Car car = new Car(engineA);//EngineBインスタンスを入れたい時は、Carクラス&利用クラス両方の修正が必要になる。
car.engineStart();
car.engineStop();
}
}
//Goodな例
//CarクラスとEngineAクラスが疎結合
//インターフェースにより結合度を下げる。
import java.util.*;
interface Engine{
public void boot();
public void stop();
}
class EngineA implements Engine{
public void boot(){
System.out.println("EngineA boot");
}
public void stop(){
System.out.println("EngineA stop");
}
}
class EngineB implements Engine{
public void boot(){
System.out.println("EngineB boot");
}
public void stop(){
System.out.println("EngineB stop");
}
}
class Car{
private Engine engine;
public Car(Engine engine){
this.engine = engine;
}
public void engineStart(){
this.engine.boot();
}
public void engineStop(){
this.engine.stop();
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Engine engine = new EngineA();
Car car = new Car(engine);//EngineBインスタンスに変える場合は、利用クラスも修正だけで済む。
car.engineStart();
car.engineStop();
}
}
注入とは
インターフェースの型にインスタンスを入れることを指す。
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Engine engineA = new EngineA();
Car car = new Car(engineA);
Engine engineB = new EngineB();
Car car = new Car(engineB);
}
}
ただし以下のようにEngineAをEngineA_Ver2に変えたい時は
利用クラスの実装も変えないといけなくなる。
インスタンス生成してる箇所が100箇所とかあると修正が大変になる。
class EngineA_ver2 implements Engine{
public void boot(){
System.out.println("EngineA_ver2 boot");
}
public void stop(){
System.out.println("EngineA_ver2 stop");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Engine engineA = new EngineA();
Engine engineA = new EngineA_ver2();
Car car = new Car(engineA);
}
}
ではどうするか。
Factoryを使う。
そうすることでインスタンスを入れ変えたい時は
Factoryを変えてあげるだけになる。
class EngineFactory{
public static Engine CreateEngineA(){
//return new EngineA();
new EngineA_ver2();
}
public static Engine CreateEngineB(){
return new EngineB();
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Engine engineA = EngineFactory.CreateEngineA();
Car car = new Car(engineA);
car.engineStop();
}
}
シングルトンにするなら以下のように実装する。
※他にも実装方法があるかもしれないがここでは触れない。
final class EngineFactory{
private static final Engine engineA = new EngineA();
private static final Engine engineB = new EngineB();
public static Engine CreateEngineA(){
return engineA;
}
public static Engine CreateEngineB(){
return engineB;
}
}
SpringのDIについて。
Springにはこの依存性注入(DI)の機能が備わっている。
「DIコンテナ」というものがその役割を担っている。
DIコンテナでDIされるクラスのインスタンス(Beanって言ったりするらしい)を管理しており、
これを必要に応じて注入してくれる。
<DIコンテナ>
---------------------
| |
| <Bean1> |
| ----- |
| | | |
| ----- |
| |
| <Bean2> |
| ----- |
| | | |
| ----- |
| |
---------------------
よくある使い方
Springで用意されてるアノテーション(@Controller、@RestController、@Service、@Repository などなど。)があるので、基本的にはそれを各クラスの用途(※)によって、付けることでBean対象とすることができ、使いたいときに@Autowiredを付けると注入してくれる。※例えばトランザクション処理を扱うクラスなら@Repositoryを付けるなど
package com.example.demo.web.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.demo.service.impl.HelloService;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private HelloService helloService;
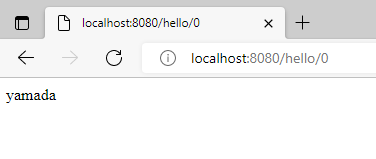
@GetMapping("/hello/{id:.+}")
public String hello(@PathVariable("id") int userId) {
return helloService.findOne(userId);
}
}
package com.example.demo.service.impl;
public interface HelloService {
public String findOne(int userId);
}
package com.example.demo.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.example.demo.persistence.repository.HelloRepository;
import com.example.demo.service.impl.HelloService;
@Service
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Autowired
private HelloRepository helloRepository;
public String findOne( int id) {
// 1 件 検索 実行
String str = helloRepository.findOne(id);
return str;
}
}
package com.example.demo.persistence.repository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class HelloRepository {
public String findOne( int id) {
//本当はここでDBから値取ってきたりする
String[] tbl = {"yamada","yoshida"};
String str = tbl[id];
return str;
}
}
独自で(?)Bean定義したいとき
2つやり方がある。
・コンポーネントスキャン
・メソッドによるBean定義
コンポーネントスキャン
①Bean化したい範囲を決める。(ここではdemo配下を指定)
package com.example.demo.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"demo"})
public class AppConfig {
}
package com.example.demo.service;
public interface FooService{
String method();
}
②Bean化したいクラスに「@Componet」を付ける
package com.example.demo.service.impl;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.example.demo.service.FooService;
@Component
public class FooServiceImpl implements FooService {
public String method() {
return "hello FooServiceImpl";
}
}
③Beanをセットしたい@Autowiredを付ける
package com.example.demo.web.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.demo.service.FooService;
@RestController
public class FooController {
@Autowired
private FooService fs;
@GetMapping("/foodi")
public String fooDi() {
return fs.method();
}
}
メソッドによるBean定義
ConfigクラスでBeanにしたいクラスのインスタンスを生成するメソッドを定義して、@Beanを付ける。
これがそのままBeanになる。メソッドの名前はなんでもいい。
package com.example.demo.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.example.demo.service.HogeService;
import com.example.demo.service.impl.HogeServiceImpl;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig2 {
@Bean
public HogeService getHogeService() {
return new HogeServiceImpl();
}
}
package com.example.demo.service;
public interface HogeService{
public String method();
}
package com.example.demo.service.impl;
import com.example.demo.service.HogeService;
public class HogeServiceImpl implements HogeService {
public HogeServiceImpl() {
}
public String method() {
return "hello HogeServiceImpl";
}
}
package com.example.demo.web.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.example.demo.service.HogeService;
@RestController
public class HogeController {
private HogeService hs;
@Autowired //アノテーションはコンストラクタが単一なら省略可能
public HogeController(HogeService hs) {
this.hs = hs;
}
@GetMapping("/hogedi")
public String hogeDi() {
return hs.method();
}
}
参考文献
https://www.amazon.co.jp/後悔しないためのSpring-Boot-入門書:Spring-解体新書(第2版)-Spring解体新書-ebook/dp/B08XPBPH9C
”4章 DI(依存性の注入)とは”
https://www.slideshare.net/masatoshitada7/spring-boot-jjug
”②Springのコア「DI」「コンテナ」「Bean」”