What is Crossplane?
Crossplane is an open source Kubernetes add-on that enables platform teams to assemble infrastructure from multiple vendors, and expose higher level self-service APIs for application teams to consume, without having to write any code.
Crossplane provides the way to manage cloud resources as YAML files. With Crossplane, we can define custom resource definition (XRD) to manage cloud services. It is like an orchestration for cloud services!
Crossplane supports infrastructure from all the major cloud providers.
- AWS
- GCP
- Azure
- etc…
Why Crossplane?
-
Declarative infrastructure configuration
-
Unify application and infrastructure configuration and deployment
-
Crossplane provides a consistent API across a diverse set of vendors, resources, and abstractions
-
Don’t need to learn about HCL (HashiCorp Configuration Language) for Terraform
-
With Argo CD, we might be able to see what kinds of cloud resources are created
Concepts
Composite resource (XR)
A composite resource (XR) is a special kind of custom resource. It composes one or more managed resources into a higher-level infrastructure unit.
We can consider composite resources as resources that are composed of one or more cloud resources.
Composite resource definition (XRD)
A composite resource definition is a file that describes composite resources as YAML.
Composite resource claim (XRC)
This is for a resource declare that an application requires a particular kind of infrastructure, as well as specifying how to configure it.
Composition
This specifies which resources a composite resource will be composed of, and how they should be configured.
Configuration
The name of packages that contain composite resources definitions and compositions
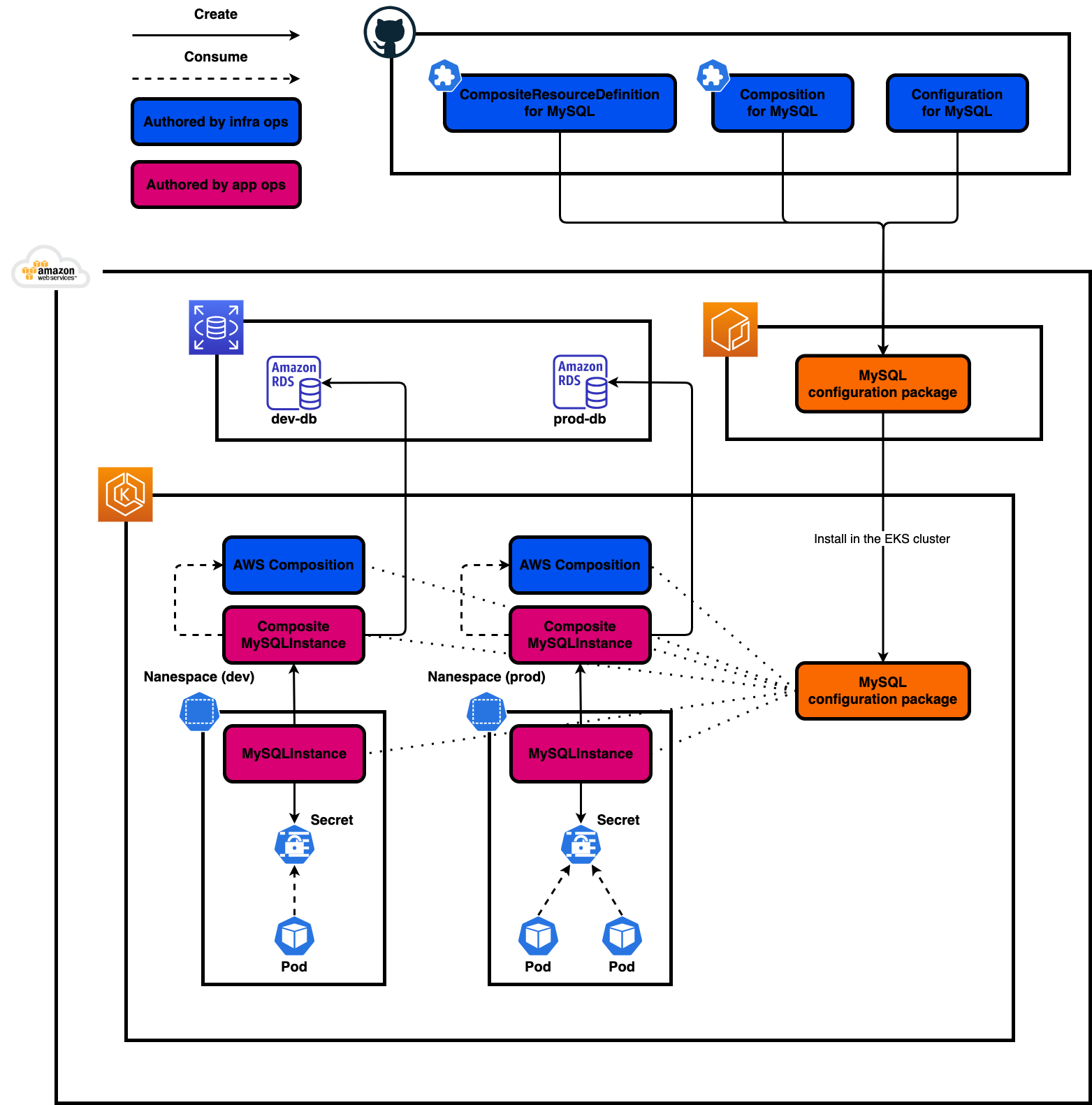
Whole architecture
The following figure shows how we can create RDS instances for different namespaces with Crossplane.
- Define composite resource definition, composition, and configuration as YAML files
- Upload these YAML files as a configuration package on ECR (This configuration package satisfies OCI, so we can use Docker Hub as OCI registry)
- Install the configuration package in EKS cluster
- With a composite resource claim, we can make a request to create an RDS instance with the desired spec
- Based on the request, desired RDS instance is created
Example for creating RDS instance
Suppose that we need to create a database named my-db for development purpose.
- AWS (RDS)
- Postgres (version 9.6)
-
db.t2.smallfor volume type - 20GB is allocated (← only this value is configurable)
I show you the YAML files to create an RDS instance with the above specs.
Composite resource definition and Composite resource claim
> bat definition.yaml
───────┬──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
│ File: definition.yaml
───────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 │ ---
2 │ apiVersion: apiextensions.crossplane.io/v1
3 │ kind: CompositeResourceDefinition
4 │ metadata:
5 │ name: compositepostgresqlinstances.database.example.org
6 │ spec:
7 │ group: database.example.org
8 │ names:
9 │ kind: CompositePostgreSQLInstance
10 │ plural: compositepostgresqlinstances
11 │ claimNames:
12 │ kind: PostgreSQLInstance
13 │ plural: postgresqlinstances
14 │ connectionSecretKeys:
15 │ - username
16 │ - password
17 │ - endpoint
18 │ - port
19 │ versions:
20 │ - name: v1alpha1
21 │ served: true
22 │ referenceable: true
23 │ schema:
24 │ openAPIV3Schema:
25 │ type: object
26 │ properties:
27 │ spec:
28 │ type: object
29 │ properties:
30 │ parameters:
31 │ type: object
32 │ properties:
33 │ storageGB:
34 │ type: integer
35 │ required:
36 │ - storageGB
37 │ required:
38 │ - parameters
───────┴──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Composition
> bat composition.yaml
───────┬──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
│ File: composition.yaml
───────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 │ ---
2 │ apiVersion: apiextensions.crossplane.io/v1
3 │ kind: Composition
4 │ metadata:
5 │ name: compositepostgresqlinstances.aws.database.example.org
6 │ labels:
7 │ provider: aws
8 │ guide: quickstart
9 │ vpc: default
10 │ spec:
11 │ writeConnectionSecretsToNamespace: crossplane-system
12 │ compositeTypeRef:
13 │ apiVersion: database.example.org/v1alpha1
14 │ kind: CompositePostgreSQLInstance
15 │ resources:
16 │ - name: rdsinstance
17 │ base:
18 │ apiVersion: database.aws.crossplane.io/v1beta1
19 │ kind: RDSInstance
20 │ spec:
21 │ forProvider:
22 │ region: ap-northeast-1
23 │ dbInstanceClass: db.t2.small
24 │ masterUsername: masteruser
25 │ engine: postgres
26 │ engineVersion: "9.6"
27 │ skipFinalSnapshotBeforeDeletion: true
28 │ publiclyAccessible: true
29 │ writeConnectionSecretToRef:
30 │ namespace: crossplane-system
31 │ patches:
32 │ - fromFieldPath: "metadata.uid"
33 │ toFieldPath: "spec.writeConnectionSecretToRef.name"
34 │ transforms:
35 │ - type: string
36 │ string:
37 │ fmt: "%s-postgresql"
38 │ - fromFieldPath: "spec.parameters.storageGB"
39 │ toFieldPath: "spec.forProvider.allocatedStorage"
40 │ connectionDetails:
41 │ - fromConnectionSecretKey: username
42 │ - fromConnectionSecretKey: password
43 │ - fromConnectionSecretKey: endpoint
44 │ - fromConnectionSecretKey: port
───────┴──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Metadata for configuration
> bat crossplane.yaml
───────┬──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
│ File: crossplane.yaml
───────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 │ apiVersion: meta.pkg.crossplane.io/v1alpha1
2 │ kind: Configuration
3 │ metadata:
4 │ name: customized-getting-started-with-aws
5 │ annotations:
6 │ guide: quickstart
7 │ provider: aws
8 │ vpc: default
9 │ spec:
10 │ crossplane:
11 │ version: ">=v1.0.0-0"
12 │ dependsOn:
13 │ - provider: crossplane/provider-aws
14 │ version: ">=v0.14.0"
───────┴──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Demo!
百聞は一見にしかず! (Seeing is believing!)
Let’s create an RDS instance with the above YAML files.
I’ve already packaged them as my custom configuration and uploaded them on my private Docker Hub (Link: https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/kanata333/customized-getting-started-with-aws).
Let’s start by installing Crossplane!
Configuration for Kubernetes
I use minikube and use containerd as the container runtime.
> minikube version
minikube version: v1.18.1
commit: 09ee84d530de4a92f00f1c5dbc34cead092b95bc
> kubectl version --short
Client Version: v1.20.4-dirty
Server Version: v1.20.2
> kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
minikube Ready control-plane,master 39d v1.20.2 192.168.49.2 <none> Ubuntu 20.04.1 LTS 4.19.121-linuxkit containerd://1.4.3
Install Crossplane
> kubectl create namespace crossplane-system
namespace/crossplane-system created
> helm repo add crossplane-stable https://charts.crossplane.io/stable
"crossplane-stable" has been added to your repositories
> helm repo update
Hang tight while we grab the latest from your chart repositories...
...Successfully got an update from the "crossplane-stable" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "prometheus-community" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "grafana" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "stable" chart repository
...Successfully got an update from the "bitnami" chart repository
Update Complete. ⎈Happy Helming!⎈
> helm install crossplane --namespace crossplane-system crossplane-stable/crossplane
NAME: crossplane
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Mar 23 16:41:50 2021
NAMESPACE: crossplane-system
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
Release: crossplane
Chart Name: crossplane
Chart Description: Crossplane is an open source Kubernetes add-on that extends any cluster with the ability to provision and manage cloud infrastructure, services, and applications using kubectl, GitOps, or any tool that works with the Kubernetes API.
Chart Version: 1.1.0
Chart Application Version: 1.1.0
Kube Version: v1.20.2
Check Crossplane status
> helm list -n crossplane-system
NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
crossplane crossplane-system 1 2021-03-23 16:41:50.018674 +0900 JST deployed crossplane-1.1.0 1.1.0
> kubectl get all -n crossplane-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/crossplane-54dd944978-dtz58 1/1 Running 0 53s
pod/crossplane-rbac-manager-549c7c6dc9-6kdn9 1/1 Running 0 53s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/crossplane 1/1 1 1 53s
deployment.apps/crossplane-rbac-manager 1/1 1 1 53s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/crossplane-54dd944978 1 1 1 53s
replicaset.apps/crossplane-rbac-manager-549c7c6dc9 1 1 1 53s
Install Crossplane CLI
> curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/crossplane/crossplane/master/install.sh | sh
kubectl plugin downloaded successfully! Run the following commands to finish installing it:
sudo mv kubectl-crossplane /usr/local/bin
kubectl crossplane --help
Visit https://crossplane.io to get started. 🚀
Have a nice day! 👋
> sudo mv kubectl-crossplane /usr/local/bin
Password:
> kubectl crossplane --help
Usage: kubectl crossplane <command>
A command line tool for interacting with Crossplane.
Flags:
-h, --help Show context-sensitive help.
-v, --version Print version and quit.
Commands:
build configuration
Build a Configuration package.
build provider
Build a Provider package.
install configuration <package> [<name>]
Install a Configuration package.
install provider <package> [<name>]
Install a Provider package.
push configuration <tag>
Push a Configuration package.
push provider <tag>
Push a Provider package.
Run "kubectl crossplane <command> --help" for more information on a command.
Install configuration package
> kubectl crossplane install configuration kanata333/customized-getting-started-with-aws:v1.1.0
configuration.pkg.crossplane.io/kanata333-customized-getting-started-with-aws created
> kubectl get pkg
NAME INSTALLED HEALTHY PACKAGE AGE
provider.pkg.crossplane.io/crossplane-provider-aws True True crossplane/provider-aws:v0.17.0 3d6h
NAME INSTALLED HEALTHY PACKAGE AGE
configuration.pkg.crossplane.io/kanata333-customized-getting-started-with-aws True True kanata333/customized-getting-started-with-aws:v1.1.0 23m
Get AWS account key file
> AWS_PROFILE=<your profile> && echo -e "[default]\naws_access_key_id = $(aws configure get aws_access_key_id --profile $AWS_PROFILE)\naws_secret_access_key = $(aws configure get aws_secret_access_key --profile $AWS_PROFILE)" > creds.conf
Create a provider secret
> kubectl create secret generic aws-creds -n crossplane-system --from-file=creds=./creds.conf
secret/aws-creds created
Configure the provider
> kubectl get secret -n crossplane-system
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
aws-creds Opaque 1 2m43s
crossplane-provider-aws-4ebd5d8c7cb7-token-bb5gg kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 7m1s
crossplane-token-m88wf kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 15m
default-token-z6rrf kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 16m
rbac-manager-token-wh682 kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 15m
sh.helm.release.v1.crossplane.v1 helm.sh/release.v1 1 15m
> curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/crossplane/crossplane/release-1.1/docs/snippets/configure/aws/providerconfig.yaml
---
apiVersion: aws.crossplane.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: Secret
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: aws-creds
key: creds
> kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/crossplane/crossplane/release-1.1/docs/snippets/configure/aws/providerconfig.yaml
providerconfig.aws.crossplane.io/default created
> kubectl get providerconfig
NAME AGE
default 30s
Provision infrastructure
> bat rds_my-db.yaml
───────┬───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
│ File: rds_my-db.yaml
───────┼───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 │ apiVersion: database.example.org/v1alpha1
2 │ kind: PostgreSQLInstance
3 │ metadata:
4 │ name: my-db
5 │ namespace: default
6 │ spec:
7 │ parameters:
8 │ storageGB: 20
9 │ compositionSelector:
10 │ matchLabels:
11 │ provider: aws
12 │ vpc: default
13 │ writeConnectionSecretToRef:
14 │ name: db-conn
───────┴───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
> kubectl apply -f rds_my-db.yaml
postgresqlinstance.database.example.org/my-db created
> kubectl get postgresqlinstance my-db
NAME READY CONNECTION-SECRET AGE
my-db True db-conn 9m34s
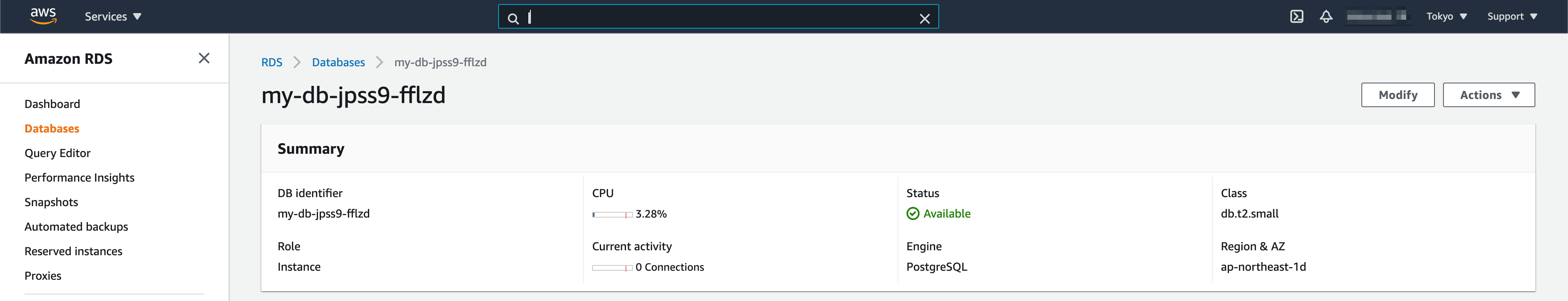
Check the result in AWS console
The desired RDS instance is created!