目次
Cypressとは?
概要
インストール方法
使用方法(起動・実行編)
使用方法(テストコード編)
まとめ
Cypressとは?
CypressOnRailsの導入を試みる前に、まずはCypressについて学びましょう。
Cypressは公式ドキュメントが充実しており親切にチュートリアルの動画も載せてくれてます。
この記事ではCypessとは?については省略しているので公式ドキュメントを参照ください。
概要
ざっくりまとめるとCypressの恩恵をRailsでも受けられるようになる、というgemですが
E2Eテストで陥りやすい「不安定なテスト」にならないよう以下のような仕組みが取られています。
- 各テストを行う前にdatabase_cleanerを使用する
- 各テストのデフォルトデータをseedで準備する
- factory_botを使用してデータのセットアップを行う
- 特定のテストに使用されるシナリオファイルを作成する
Rspecで使用しているテストデータを使い回しできることも、
既存のRailsアプリケーションへの導入が容易である要因の一つですね。
インストール方法
gemを導入してからテストの実行・テスト結果を確認するダッシュボードを開くところまでとても簡単に進められます。
gemファイルに追記
group :test, :development do
gem 'cypress-on-rails', '~> 1.0'
end
bundle installを行い、ターミナルで以下を実行
$ bin/rails g cypress_on_rails:install
# 他のフォルダで作成したいもしくはすでにcypressのフォルダがある場合
$ bin/rails g cypress_on_rails:install --cypress_folder=spec/cypress
# npmでインストールする場合
$ bin/rails g cypress_on_rails:install --install_cypress_with=npm
# すでにグローバルでインストールしている場合
$ bin/rails g cypress_on_rails:install --no-install-cypress
# すでにgenerateしたファイルをアップデートする場合
$ bin/rails g cypress_on_rails:update
下記のフォルダやディレクトリが作成されます

主要ファイルのデフォルトコードを添付しておきます
if defined?(CypressOnRails)
CypressOnRails.configure do |c|
c.cypress_folder = File.expand_path("#{__dir__}/../../cypress")
# WARNING!! CypressOnRails can execute arbitrary ruby code
# please use with extra caution if enabling on hosted servers or starting your local server on 0.0.0.0
c.use_middleware = !Rails.env.production?
c.logger = Rails.logger
end
# # if you compile your asssets on CI
# if ENV['CYPRESS'].present? && ENV['CI'].present?
# Rails.application.configure do
# config.assets.compile = false
# config.assets.unknown_asset_fallback = false
# end
# end
end
# This is loaded once before the first command is executed
begin
require 'database_cleaner-active_record'
rescue LoadError => e
puts e.message
begin
require 'database_cleaner'
rescue LoadError => e
puts e.message
end
end
begin
require 'factory_bot_rails'
rescue LoadError => e
puts e.message
begin
require 'factory_girl_rails'
rescue LoadError => e
puts e.message
end
end
require 'cypress_on_rails/smart_factory_wrapper'
factory = CypressOnRails::SimpleRailsFactory
factory = FactoryBot if defined?(FactoryBot)
factory = FactoryGirl if defined?(FactoryGirl)
CypressOnRails::SmartFactoryWrapper.configure(
always_reload: false,
factory: factory,
files: [
Rails.root.join('spec', 'factories.rb'),
Rails.root.join('spec', 'factories', '**', '*.rb')
]
)
// CypressOnRails: dont remove these command
Cypress.Commands.add('appCommands', function (body) {
Object.keys(body).forEach(key => body[key] === undefined ? delete body[key] : {});
const log = Cypress.log({ name: "APP", message: body, autoEnd: false })
return cy.request({
method: 'POST',
url: "/__cypress__/command",
body: JSON.stringify(body),
log: false,
failOnStatusCode: false
}).then((response) => {
log.end();
if (response.status !== 201) {
expect(response.body.message).to.be.empty
expect(response.status).to.be.equal(201)
}
return response.body
});
});
Cypress.Commands.add('app', function (name, command_options) {
return cy.appCommands({name: name, options: command_options}).then((body) => {
return body[0]
});
});
Cypress.Commands.add('appScenario', function (name, options = {}) {
return cy.app('scenarios/' + name, options)
});
Cypress.Commands.add('appEval', function (code) {
return cy.app('eval', code)
});
Cypress.Commands.add('appFactories', function (options) {
return cy.app('factory_bot', options)
});
Cypress.Commands.add('appFixtures', function (options) {
cy.app('activerecord_fixtures', options)
});
// CypressOnRails: end
// The next is optional
// beforeEach(() => {
// cy.app('clean') // have a look at cypress/app_commands/clean.rb
// });
// comment this out if you do not want to attempt to log additional info on test fail
Cypress.on('fail', (err, runnable) => {
// allow app to generate additional logging data
Cypress.$.ajax({
url: '/__cypress__/command',
data: JSON.stringify({name: 'log_fail', options: {error_message: err.message, runnable_full_title: runnable.fullTitle() }}),
async: false,
method: 'POST'
});
throw err;
});
database.ymlをアップデートする
テストを実行する度にdevelop環境のデータベースが汚れるのを防ぐにはdatabase.ymlを編集しましょう
development:
<<: *default
database: <%= ENV['CYPRESS'] ? 'my_db_test' : 'my_db_development' %>
test:
<<: *default
database: my_db_test
使用方法(起動・実行編)
ローカル環境で起動までを行なってみましょう
# railsをスタートさせる
$ bin/rails server -p 5017
# 別ウィンドウでcypressを起動する
$ yarn cypress open
# npmを使用する方はこちら
$ node_modules/.bin/cypress open
# spec/cypressにフォルダを変えた方はこちら
$ yarn cypress open --project ./spec
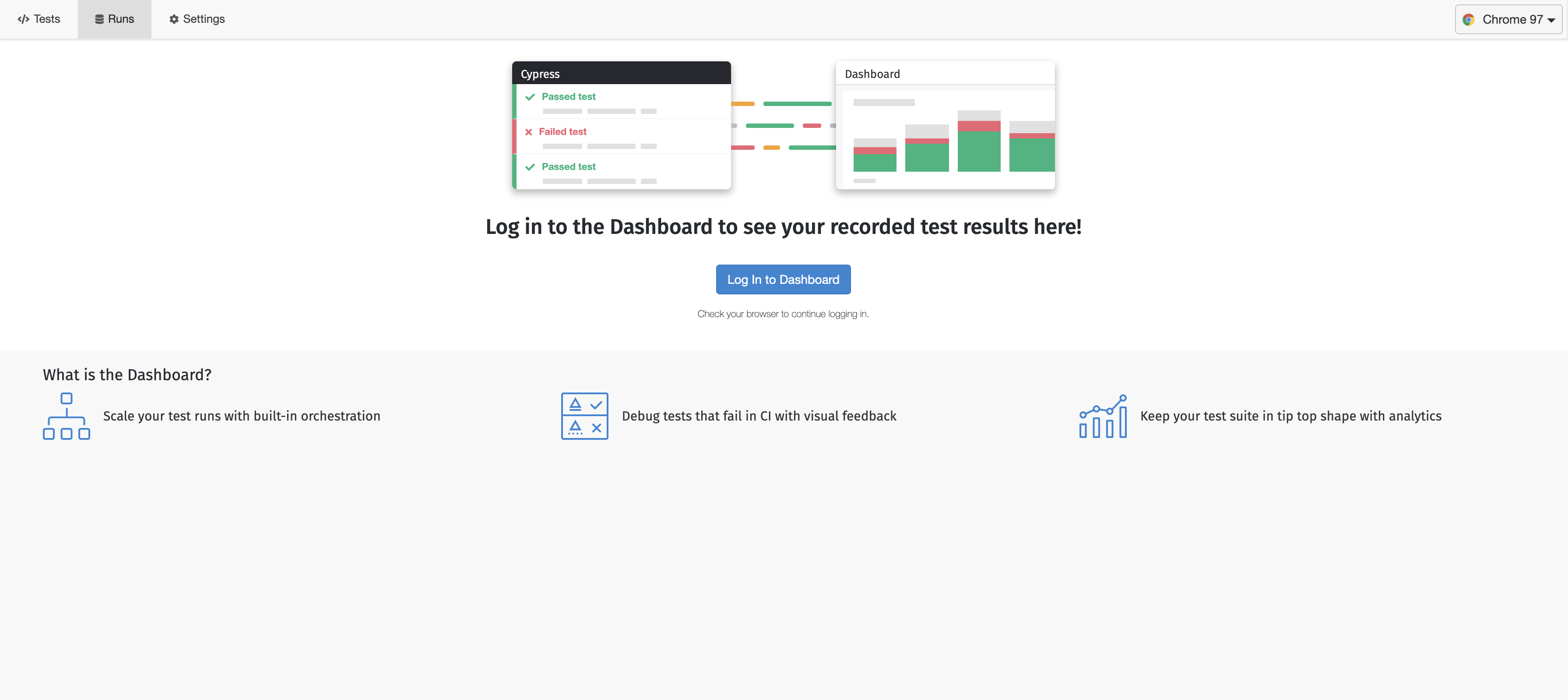
「Log In to DashBord」からログインすると、このようなページへリダイレクトします
GUIでテスト結果をデバックできるのは分かりやすいですね
実行
# railsを起動しバックグランドでサーバーを起動する
$ yarn run cypress run
# npmを使用する方はこちら
$ node_modules/.bin/cypress run
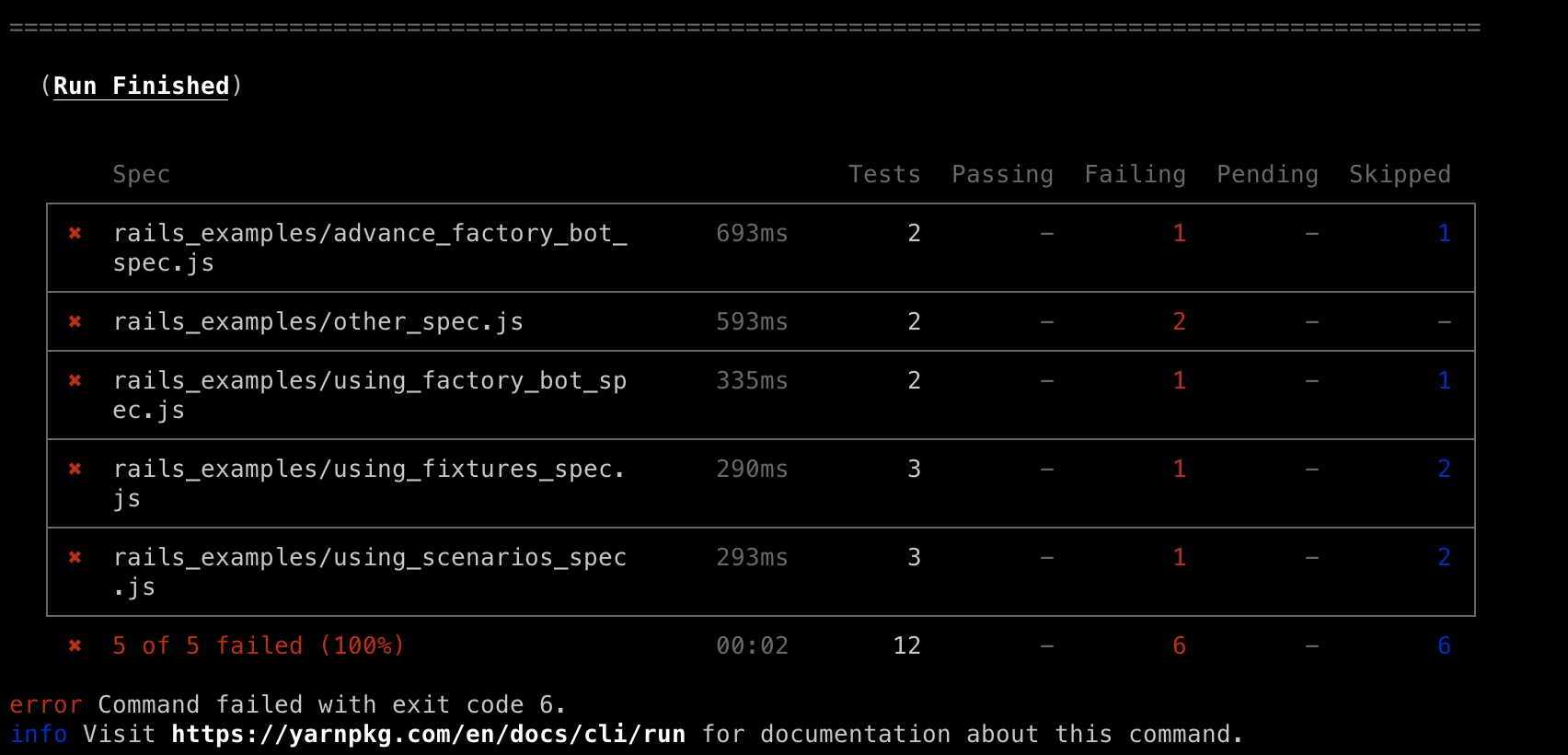
テスト結果はこのように表示されます(何も設定していないのでテスト落ちてます)
使用方法(テストコード編)
factory botの使用例
既存アプリケーションで作成していたfactory_botを直接実行することもできます
describe('My First Test', function() {
it('visit root', function() {
// バックエンドを呼び出し、アプリケーションの状態を準備する
cy.appFactories([
['create_list', 'post', 10],
['create', 'post', {title: 'Hello World'} ],
['create', 'post', 'with_comments', {title: 'Factory_bot Traits here'} ] # traitsを使う
])
// テスト対象のアプリケーションにアクセスする
cy.visit('/')
cy.contains("Hello World")
// アクセス結果
cy.appFactories([['create', 'invoice', { paid: false }]]).then((records) => {
cy.visit(`/invoices/${records[0].id}`);
});
})
})
テストフィクスチャーの使用例
activerecord_fixtures.rbはデフォルトで作成されるファイルです。
require "active_record/fixtures"
fixtures_dir = ActiveRecord::Tasks::DatabaseTasks.fixtures_path
fixture_files = Dir["#{fixtures_dir}/**/*.yml"].map { |f| f[(fixtures_dir.size + 1)..-5] }
logger.debug "loading fixtures: { dir: #{fixtures_dir}, files: #{fixture_files} }"
ActiveRecord::FixtureSet.reset_cache
ActiveRecord::FixtureSet.create_fixtures(fixtures_dir, fixture_files)
実際の使用してみましょう。
describe('My First Test', function() {
it('visit root', function() {
// This calls to the backend to prepare the application state
cy.appFixtures()
// Visit the application under test
cy.visit('/')
cy.contains("Hello World")
})
})
シナリオの使用例
シナリオとはテストで参照できる名前付きブロックです。
シナリオはspec/cypress/app_commands/scenariosディレクトリで定義してください。
Profile.create name: "Cypress Hill"
# factory_botがあればcypress_helperを使うことができます
CypressOnRails::SmartFactoryWrapper.create(:profile, name: "Cypress Hill")
次に、テストでシナリオを参照します。
describe('My First Test', function() {
it('visit root', function() {
// This calls to the backend to prepare the application state
cy.appScenario('basic')
cy.visit('/profiles')
cy.contains("Cypress Hill")
})
})
seedの使用例
spec/cypress/app_commandsディレクトリにファイルを作成してください
load "#{Rails.root}/db/seeds.rb"
次に、テストでcy.app('load_seed')を参照します。
describe('My First Test', function() {
beforeEach(() => { cy.app('load_seed') })
it('visit root', function() {
cy.visit('/')
cy.contains("Seeds")
})
})
まとめ
E2Eテストといえばseliniumが有名ですが、最近有名企業もseliniumからCypressに移行した話などが増えているみたいです。
フレームワークやラッパーの選定が面倒なseliniumに対してセットアップが容易なCypressは今後もシェアを広げていきそうです。

RailsアプリケーションだとSystem Specがありますが、CypressOnRailsも使いやすそうなので是非触ってみてください