Android端末でLLMを動かす完全ガイド:MediaPipeによるオンデバイス推論
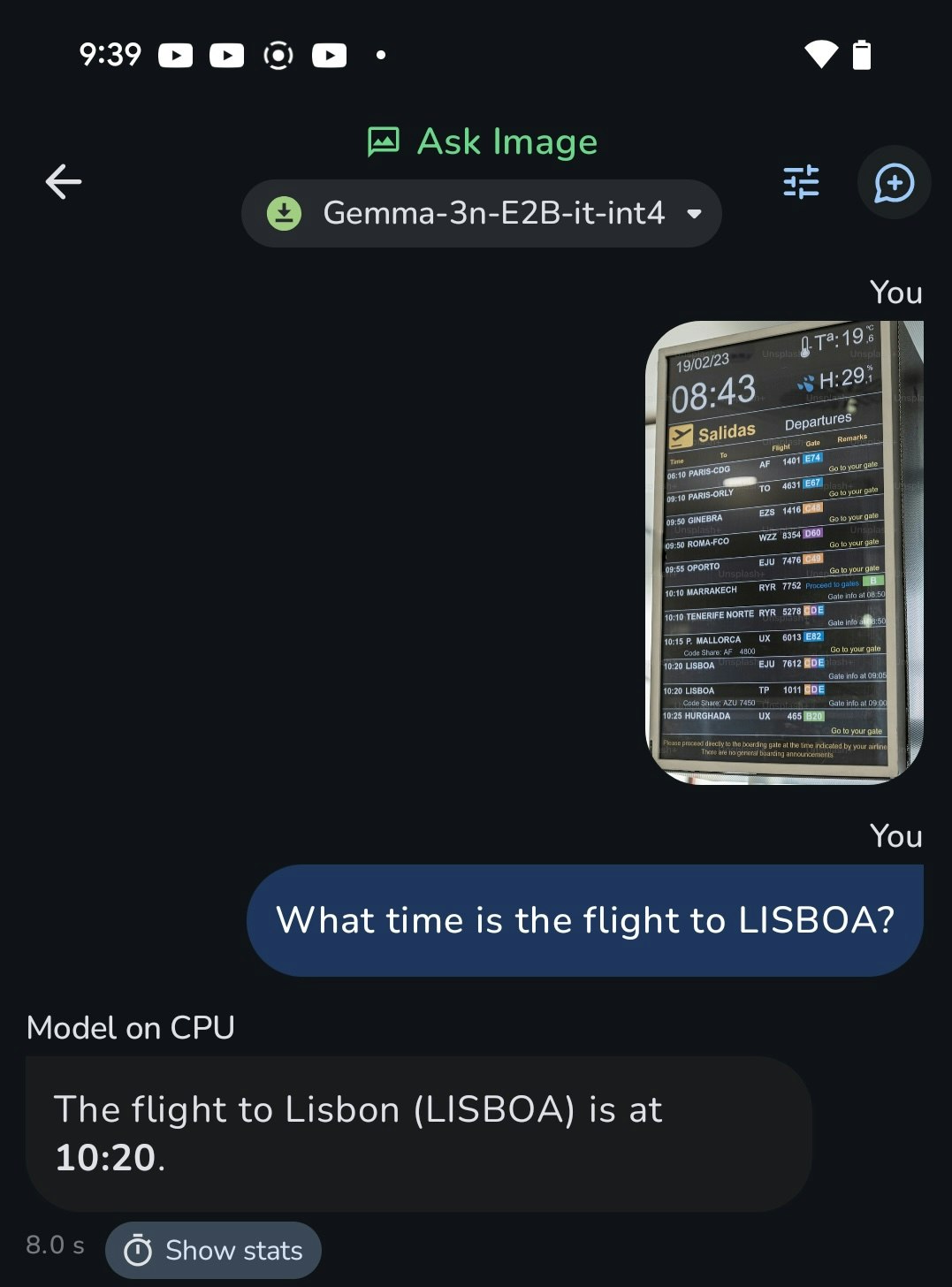
Google Pixel8a(iPhone SE的な廉価版端末)でWebサービスに引けをとらないスピードで動く

ちなみに日本語でも動きます。
↓手元で論文を要約したときの速度
| Processor | Prefill Speed | Decode Speed |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | 30.67token/s | 5.94token/s |
| GPU | 114.77token/s | 7.73token/s |
サンプルアプリは以下
はじめに
AndroidデバイスでLLM(大規模言語モデル)を直接実行できることをご存知ですか?
従来のクラウドAPIとは異なり、デバイス上で直接推論を行うオンデバイスLLMは、以下のメリットを提供します:
- 🔒 完全なプライバシー保護:データが端末から出ない
- ⚡ 低レイテンシ:ネットワーク通信なしで即座にレスポンス
- 💰 コスト削減:API料金不要
- 🌐 オフライン動作:インターネット接続不要
本ガイドでは、GoogleのMediaPipeフレームワークを使用して、Android端末でLLMを実装する方法を、基本的な実装から高度な機能まで段階的に解説します。
実用例:Google AI Edge Gallery
本ガイドでは、Googleが公開する「AI Edge Gallery」アプリを実例として参照しながら、実際のプロダクションレベルの実装方法を学びます。
📖 目次
- なぜオンデバイスLLMなのか
- MediaPipeによるLLM実装の基礎
- 最初の一歩:シンプルなLLMアプリ
- 画像入力対応:マルチモーダルLLM
- チャットアプリケーションの構築
- モデルの準備と変換
- 開発環境の構築とデプロイ
- プロダクション実装例:AI Edge Gallery
なぜオンデバイスLLMなのか
クラウドAPIとの比較
| 項目 | クラウドAPI | オンデバイスLLM |
|---|---|---|
| プライバシー | データを送信 | 完全にローカル |
| レスポンス時間 | ネットワーク依存 | 即座(50-200ms) |
| コスト | 従量課金 | 初期開発のみ |
| オフライン対応 | ❌ | ✅ |
| スケーラビリティ | 無制限 | デバイス性能に依存 |
| モデルサイズ | 制限なし | 1-5GB程度 |
技術的な実現可能性
2025年現在の状況:
- モデル軽量化技術:量子化により1-5GBでGPT-3.5相当の性能
- モバイル端末の性能向上:最新端末は8-16GBメモリ搭載
- 専用フレームワーク:MediaPipe、TensorFlow Lite等の最適化
適用シーンの例
- 個人情報を扱うアプリ:医療、金融、法務
- リアルタイム処理:ライブ翻訳、音声認識
- エンタープライズ:機密データを外部送信できない環境
- 教育・学習:オフライン学習アプリ
MediaPipeによるLLM実装の基礎
MediaPipeとは
GoogleのMediaPipeは、マルチモーダルAIタスクに最適化されたフレームワークです:
- 統一API:テキスト、画像、音声を同じインターフェースで処理
- ハードウェア最適化:GPU、NPU、CPUを自動選択
- ストリーミング対応:リアルタイムでの逐次出力
- プロダクション実績:YouTube、Google Assistant等で使用
アーキテクチャ概要
あなたのAndroidアプリ
↓
MediaPipe LLM API
↓
.taskファイル(専用モデル形式)
↓
ハードウェアアクセラレーション(GPU/CPU/NPU)
↓
ストリーミング出力
最初の一歩シンプルなLLMアプリ
環境準備
必要な依存関係:
dependencies {
implementation("com.google.mediapipe:tasks-genai:0.10.24")
implementation("androidx.compose.ui:ui:$compose_version")
}
最小限の実装
まずは、1つの関数でLLMを動かしてみましょう:
// シンプルな関数ベースの実装
import android.content.Context
import com.google.mediapipe.tasks.genai.llminference.LlmInference
import com.google.mediapipe.tasks.genai.llminference.LlmInferenceSession
fun simpleLlmExample(context: Context) {
// 1. 単一のメソッド内で完結する実装
val modelPath = "models/gemma-2b.task"
// 2. LLMエンジンの作成
val llmInference = LlmInference.createFromOptions(
context,
LlmInference.LlmInferenceOptions.builder()
.setModelPath(modelPath)
.setMaxTokens(256)
.build()
)
// 3. セッションの作成
val session = LlmInferenceSession.createFromOptions(
llmInference,
LlmInferenceSession.LlmInferenceSessionOptions.builder()
.setTopK(40)
.setTemperature(0.8f)
.build()
)
// 4. プロンプトを送信して結果を取得
session.addQueryChunk("Explain AI in one sentence.")
// 5. レスポンスを処理
session.generateResponseAsync { partialResult, done ->
print(partialResult) // コンソールに出力
if (done) {
println("\n--- Generation completed ---")
// 6. クリーンアップ
llmInference.close()
}
}
}
UI付きアプリケーション
実際のアプリで使えるComposeベースの実装:
// Composeでの使用例
@Composable
fun SimpleLlmChat() {
val context = LocalContext.current
var response by remember { mutableStateOf("") }
var isGenerating by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
Column(modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)) {
Button(
onClick = {
if (!isGenerating) {
isGenerating = true
response = ""
// インラインでLLMを使用
val llm = LlmInference.createFromOptions(
context,
LlmInference.LlmInferenceOptions.builder()
.setModelPath("models/gemma-2b.task")
.setMaxTokens(128)
.build()
)
val session = LlmInferenceSession.createFromOptions(
llm,
LlmInferenceSession.LlmInferenceSessionOptions.builder()
.setTemperature(0.7f)
.build()
)
session.addQueryChunk("Tell me a joke")
session.generateResponseAsync { partial, done ->
response += partial
if (done) {
isGenerating = false
llm.close()
}
}
}
},
enabled = !isGenerating
) {
Text(if (isGenerating) "Generating..." else "Generate Joke")
}
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(16.dp))
Text(
text = response,
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
)
}
}
再利用可能なクラス実装
プロダクション向けの構造化された実装:
// LlmMinimalExample.kt
import android.content.Context
import com.google.mediapipe.tasks.genai.llminference.LlmInference
import com.google.mediapipe.tasks.genai.llminference.LlmInferenceSession
class LlmMinimalExample(private val context: Context) {
private var llmInference: LlmInference? = null
private var session: LlmInferenceSession? = null
fun initialize(modelPath: String) {
// 1. LLM推論オプションの設定
val options = LlmInference.LlmInferenceOptions.builder()
.setModelPath(modelPath) // モデルファイルのパス
.setMaxTokens(512) // 最大トークン数
.setPreferredBackend(LlmInference.Backend.GPU) // GPU使用
.build()
// 2. LLM推論エンジンの作成
llmInference = LlmInference.createFromOptions(context, options)
// 3. セッションの作成
session = LlmInferenceSession.createFromOptions(
llmInference!!,
LlmInferenceSession.LlmInferenceSessionOptions.builder()
.setTopK(40)
.setTopP(0.95f)
.setTemperature(0.8f)
.build()
)
}
fun generateResponse(prompt: String, onResult: (String, Boolean) -> Unit) {
// 4. プロンプトを追加
session?.addQueryChunk(prompt)
// 5. 非同期でレスポンスを生成(ストリーミング)
session?.generateResponseAsync { partialResult, done ->
onResult(partialResult, done)
}
}
fun cleanup() {
// 6. リソースのクリーンアップ
llmInference?.close()
}
}
🔑 基本実装のポイント
-
.taskファイル:MediaPipe専用のモデル形式が必要 -
ストリーミング出力:
generateResponseAsyncでリアルタイム表示 -
メモリ管理:必ず
close()でリソース解放 - 非同期処理:UIをブロックしないよう必須
画像入力対応マルチモーダルLLM
Vision Language Modelとは
マルチモーダルLLMは、テキストと画像の両方を理解できるモデルです:
- 画像理解:写真の内容を詳細に説明
- 視覚的質問応答:画像について自然言語で質問可能
- OCR機能:画像内のテキストを読み取り
- シーン解析:複雑な場面の理解と説明
基本的な画像分析実装
// ImageLlmExample.kt
import android.content.Context
import android.graphics.Bitmap
import com.google.mediapipe.framework.image.BitmapImageBuilder
import com.google.mediapipe.tasks.genai.llminference.LlmInference
import com.google.mediapipe.tasks.genai.llminference.LlmInferenceSession
import com.google.mediapipe.tasks.genai.llminference.GraphOptions
class ImageLlmExample(private val context: Context) {
private var llmInference: LlmInference? = null
private var session: LlmInferenceSession? = null
fun initialize(modelPath: String) {
// 1. 画像対応モデル用のオプション設定
val options = LlmInference.LlmInferenceOptions.builder()
.setModelPath(modelPath)
.setMaxTokens(512)
.setMaxNumImages(1) // 画像入力を1枚まで許可
.setPreferredBackend(LlmInference.Backend.GPU)
.build()
llmInference = LlmInference.createFromOptions(context, options)
// 2. ビジョンモダリティを有効化したセッション
session = LlmInferenceSession.createFromOptions(
llmInference!!,
LlmInferenceSession.LlmInferenceSessionOptions.builder()
.setTopK(40)
.setTemperature(0.8f)
.setGraphOptions(
GraphOptions.builder()
.setEnableVisionModality(true) // ビジョン機能を有効化
.build()
)
.build()
)
}
fun analyzeImage(
image: Bitmap,
prompt: String,
onResult: (String, Boolean) -> Unit
) {
// 3. テキストプロンプトを追加(画像より先に追加する必要がある)
session?.addQueryChunk(prompt)
// 4. 画像を追加
val mpImage = BitmapImageBuilder(image).build()
session?.addImage(mpImage)
// 5. レスポンス生成
session?.generateResponseAsync { partialResult, done ->
onResult(partialResult, done)
}
}
fun cleanup() {
llmInference?.close()
}
}
シンプルな画像分析関数
// 画像を分析する単純な関数
fun analyzeImageSimple(
context: Context,
modelPath: String,
image: Bitmap,
question: String = "What do you see in this image?"
) {
// LLMエンジンの作成(画像対応)
val llm = LlmInference.createFromOptions(
context,
LlmInference.LlmInferenceOptions.builder()
.setModelPath(modelPath)
.setMaxTokens(256)
.setMaxNumImages(1)
.build()
)
// セッションの作成(ビジョンモダリティ有効)
val session = LlmInferenceSession.createFromOptions(
llm,
LlmInferenceSession.LlmInferenceSessionOptions.builder()
.setTemperature(0.7f)
.setGraphOptions(
GraphOptions.builder()
.setEnableVisionModality(true)
.build()
)
.build()
)
// プロンプトと画像を追加
session.addQueryChunk(question)
session.addImage(BitmapImageBuilder(image).build())
// 結果を出力
session.generateResponseAsync { partial, done ->
print(partial)
if (done) {
println("\n--- Analysis completed ---")
llm.close()
}
}
}
画像分析UIの完全実装
@Composable
fun ImageAnalysisScreen() {
val context = LocalContext.current
var selectedImage by remember { mutableStateOf<Bitmap?>(null) }
var analysisResult by remember { mutableStateOf("") }
var isAnalyzing by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
// 画像選択ランチャー
val launcher = rememberLauncherForActivityResult(
contract = ActivityResultContracts.GetContent()
) { uri: Uri? ->
uri?.let {
val bitmap = MediaStore.Images.Media.getBitmap(
context.contentResolver, it
)
selectedImage = bitmap
}
}
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp)
) {
// 画像選択ボタン
Button(
onClick = { launcher.launch("image/*") },
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
) {
Text("Select Image")
}
// 選択した画像の表示
selectedImage?.let { bitmap ->
Image(
bitmap = bitmap.asImageBitmap(),
contentDescription = "Selected image",
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.height(200.dp)
.padding(vertical = 8.dp)
)
// 分析ボタン
Button(
onClick = {
if (!isAnalyzing) {
isAnalyzing = true
analysisResult = ""
// インラインでLLM分析を実行
val llm = LlmInference.createFromOptions(
context,
LlmInference.LlmInferenceOptions.builder()
.setModelPath("models/gemma-3n-E2B-it-int4.task")
.setMaxTokens(256)
.setMaxNumImages(1)
.build()
)
val session = LlmInferenceSession.createFromOptions(
llm,
LlmInferenceSession.LlmInferenceSessionOptions.builder()
.setGraphOptions(
GraphOptions.builder()
.setEnableVisionModality(true)
.build()
)
.build()
)
session.addQueryChunk("Describe this image in detail.")
session.addImage(BitmapImageBuilder(bitmap).build())
session.generateResponseAsync { partial, done ->
analysisResult += partial
if (done) {
isAnalyzing = false
llm.close()
}
}
}
},
enabled = !isAnalyzing,
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
) {
Text(if (isAnalyzing) "Analyzing..." else "Analyze Image")
}
}
// 分析結果の表示
if (analysisResult.isNotEmpty()) {
Card(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(top = 16.dp)
) {
Text(
text = analysisResult,
modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)
)
}
}
}
}
🔑 マルチモーダル実装のポイント
-
対応モデルの確認:画像入力対応の
.taskファイルが必要 -
順序が重要:
addQueryChunk()→addImage()の順番を守る -
ビジョンモダリティの有効化:
setEnableVisionModality(true)必須 -
画像数制限:
setMaxNumImages()で同時処理可能な画像数を指定
チャットアプリケーションの構築
会話履歴管理の仕組み
AndroidでのLLMチャットアプリは、セッションベースの文脈管理が鍵となります:
-
MediaPipeの自動管理:
LlmInferenceSessionが会話履歴を自動保持 - 累積的なコンテキスト:新しい入力が既存の文脈に追加
- メモリ効率:不要になった古い履歴の自動削除
- リセット機能:セッション再作成で履歴クリア
基本的なチャット実装
AI Edge Galleryのアーキテクチャを参考にした実装:
// LlmChatModelHelper.kt より抜粋
data class LlmModelInstance(val engine: LlmInference, var session: LlmInferenceSession)
object LlmChatModelHelper {
fun initialize(
context: Context, model: Model, onDone: (String) -> Unit
) {
// モデル設定の取得
val maxTokens = model.getIntConfigValue(key = ConfigKey.MAX_TOKENS, defaultValue = DEFAULT_MAX_TOKEN)
val topK = model.getIntConfigValue(key = ConfigKey.TOPK, defaultValue = DEFAULT_TOPK)
val topP = model.getFloatConfigValue(key = ConfigKey.TOPP, defaultValue = DEFAULT_TOPP)
val temperature = model.getFloatConfigValue(key = ConfigKey.TEMPERATURE, defaultValue = DEFAULT_TEMPERATURE)
val accelerator = model.getStringConfigValue(key = ConfigKey.ACCELERATOR, defaultValue = Accelerator.GPU.label)
// バックエンドの選択(GPU/CPU)
val preferredBackend = when (accelerator) {
Accelerator.CPU.label -> LlmInference.Backend.CPU
Accelerator.GPU.label -> LlmInference.Backend.GPU
else -> LlmInference.Backend.GPU
}
// LlmInferenceのオプション設定
val options = LlmInference.LlmInferenceOptions.builder()
.setModelPath(model.getPath(context = context))
.setMaxTokens(maxTokens)
.setPreferredBackend(preferredBackend)
.setMaxNumImages(if (model.llmSupportImage) 1 else 0) // マルチモーダル対応
.build()
// インスタンスの作成
val llmInference = LlmInference.createFromOptions(context, options)
// セッションの作成
val session = LlmInferenceSession.createFromOptions(
llmInference,
LlmInferenceSession.LlmInferenceSessionOptions.builder()
.setTopK(topK)
.setTopP(topP)
.setTemperature(temperature)
.setGraphOptions(
GraphOptions.builder()
.setEnableVisionModality(model.llmSupportImage)
.build()
)
.build()
)
model.instance = LlmModelInstance(engine = llmInference, session = session)
}
推論実行とストリーミング処理
fun runInference(
model: Model,
input: String,
resultListener: ResultListener,
cleanUpListener: CleanUpListener,
image: Bitmap? = null,
) {
val instance = model.instance as LlmModelInstance
val session = instance.session
// テキストクエリの追加
session.addQueryChunk(input)
// 画像対応モデルの場合、画像を追加
if (image != null) {
session.addImage(BitmapImageBuilder(image).build())
}
// 非同期でレスポンスを生成(ストリーミング対応)
session.generateResponseAsync(resultListener)
}
セッション管理の詳細
// セッションのライフサイクル
object LlmChatModelHelper {
// 1. セッション作成(モデル初期化時)
fun initialize(context: Context, model: Model) {
val llmInference = LlmInference.createFromOptions(...)
val session = LlmInferenceSession.createFromOptions(...)
model.instance = LlmModelInstance(engine = llmInference, session = session)
}
// 2. メッセージ追加と推論
fun runInference(model: Model, input: String, image: Bitmap?) {
val session = (model.instance as LlmModelInstance).session
session.addQueryChunk(input) // 会話履歴に追加
if (image != null) {
session.addImage(BitmapImageBuilder(image).build())
}
session.generateResponseAsync(resultListener) // 全文脈を考慮して応答
}
// 3. セッションリセット
fun resetSession(model: Model) {
// 古いセッションを閉じて新規作成
session.close()
val newSession = LlmInferenceSession.createFromOptions(...)
instance.session = newSession
}
}
🔑 チャット機能開発のポイント
- 文脈の自動管理:MediaPipeが会話履歴を透過的に管理
- ストリーミング表示:ユーザー体験向上のため逐次出力必須
- メモリ制限の考慮:長い会話での自動的な履歴削除
- エラー処理:セッション障害時の自動復旧機能
モデルの準備と変換
対応モデル形式の理解
AndroidでのLLM実行には、MediaPipe専用の.taskファイルが必要です:
| 元形式 | 変換後 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| PyTorch (.pt) | .task | LLM推論 |
| ONNX (.onnx) | .task | LLM推論 |
| TensorFlow (.pb) | .tflite | 分類タスク |
| Hugging Face | .task | 事前変換済み |
事前変換済みモデルの活用
推奨入手先:
-
Hugging Face:
litert-communityタグ付きモデル - Kaggle Models: Gemmaシリーズ等のMediaPipe対応版
- Google AI Edge: 公式サンプルモデル
人気の画像対応モデル(2024年12月):
-
gemma-3n-E2B-it-int4.task(3.1GB)- Vision対応 -
gemma-3n-E4B-it-int4.task(4.4GB)- Vision対応、高性能
自前モデルの変換方法
MediaPipeでは、独自モデルを.task形式に変換するツールを提供:
1. 環境準備
pip install mediapipe
2. 基本的な変換スクリプト
from mediapipe.tasks.python.genai import bundler
# バンドル設定
config = bundler.BundleConfig(
tflite_model="model.tflite", # TFLiteモデルのパス
tokenizer_model="tokenizer.model", # SentencePieceトークナイザー
start_token="<s>", # 開始トークン
stop_tokens=["</s>"], # 終了トークンのリスト
output_filename="my_model.task", # 出力ファイル名
enable_bytes_to_unicode_mapping=True, # GPT-2スタイルのマッピング
# オプション設定
system_prompt="You are a helpful assistant.", # システムプロンプト
prompt_prefix="User: ", # プロンプトの接頭辞
prompt_suffix="\nAssistant: ", # プロンプトの接尾辞
)
# .taskファイルを作成
bundler.create_bundle(config)
3. 画像対応モデルの変換
config = bundler.BundleConfig(
# 基本設定は同じ
tflite_model="model.tflite",
tokenizer_model="tokenizer.model",
start_token="<s>",
stop_tokens=["</s>"],
output_filename="vision_model.task",
# ビジョン関連のモデルを追加
tflite_vision_encoder="vision_encoder.tflite", # ビジョンエンコーダー
tflite_vision_adapter="vision_adapter.tflite", # ビジョンアダプター
)
モデルサイズとパフォーマンスの最適化
量子化レベルの選択:
- int4: 最小サイズ(1-2GB)、やや精度低下
- int8: バランス型(2-4GB)、実用的な精度
- fp16: 高精度(4-8GB)、最新端末推奨
実機での性能目安:
| 端末クラス | 推奨モデルサイズ | 期待パフォーマンス |
|---|---|---|
| エントリー(4GB RAM) | 1-2GB | 5-10 tokens/sec |
| ミドル(8GB RAM) | 2-4GB | 10-20 tokens/sec |
| ハイエンド(12GB+ RAM) | 4-8GB | 20-50 tokens/sec |
開発環境の構築とデプロイ
開発環境のセットアップ
必要なツールとバージョン:
- Android Studio: Hedgehog以降
- JDK: 11以上(17推奨)
- Android SDK: API 35
- NDK: 25.1.8937393(C++使用時)
プロジェクトの初期設定
build.gradle.kts(アプリレベル):
dependencies {
// MediaPipe LLM
implementation("com.google.mediapipe:tasks-genai:0.10.24")
// UI (Compose)
implementation("androidx.compose.ui:ui:$compose_version")
implementation("androidx.activity:activity-compose:1.8.2")
// Image handling
implementation("androidx.compose.ui:ui-graphics:$compose_version")
}
AI Edge Galleryのビルド例
実際のプロダクションアプリを参考にしたい場合:
# 1. AI Edge Galleryをクローン
git clone https://github.com/google-ai-edge/gallery.git
cd gallery/Android/src
# 2. 依存関係のダウンロード
./gradlew build --refresh-dependencies
# 3. デバッグ版のビルド
./gradlew assembleDebug
# 4. 実機にインストール
./gradlew installDebug
パフォーマンス測定とプロファイリング
重要な指標:
- Time to First Token (TTFT): 最初のトークンまでの時間
- Tokens per Second: 生成速度
- Memory Usage: ピーク時メモリ使用量
- Battery Impact: バッテリー消費量
測定コード例:
// パフォーマンス測定
val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
var firstTokenTime = 0L
var tokenCount = 0
session.generateResponseAsync { partial, done ->
if (firstTokenTime == 0L) {
firstTokenTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime
Log.d("Performance", "TTFT: ${firstTokenTime}ms")
}
tokenCount++
if (done) {
val totalTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime
val tokensPerSecond = tokenCount * 1000.0 / totalTime
Log.d("Performance", "Speed: $tokensPerSecond tokens/sec")
}
}
プロダクション実装例AI Edge Gallery
プロダクションレベルの機能
1. モデル管理システム
{External Storage}/models/
├── {model_name}/
│ ├── model.task
│ ├── config.json
│ └── metadata.json
2. パフォーマンス最適化
- GPU/CPU/NPUの自動選択
- メモリ使用量の動的監視
- バックグラウンド処理の制御
3. エラー処理とフォールバック
- モデル読み込み失敗時の自動復旧
- メモリ不足時の軽量モデルへの切り替え
- ネットワークエラー時のローカルモデル使用
UI/UXのベストプラクティス
リアルタイム応答表示:
- ストリーミング出力でタイピング効果
- プログレスインジケーターでの処理状況表示
- レスポンス時間の可視化
ユーザビリティ配慮:
- モデル切り替えの簡便性
- 設定パラメータの直感的な調整
- エラー状況の分かりやすい説明
C++レベルでの最適化実装
AI Edge Galleryでは、Kotlin/Javaに加えてC++レベルでの最適化も活用:
// llm_minimal_example.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "mediapipe/tasks/cc/genai/inference/c/llm_inference_engine.h"
// コールバック関数:レスポンスをストリーミング出力
void async_callback(void* context, LlmResponseContext* response_context) {
std::cout << response_context->response_array[0] << std::flush;
LlmInferenceEngine_CloseResponseContext(response_context);
}
int main() {
// 1. モデル設定
const LlmModelSettings model_settings = {
.model_path = "path/to/gemma-2b.task", // モデルファイルのパス
.cache_dir = "./cache", // キャッシュディレクトリ
.max_num_tokens = 512, // 最大トークン数
.preferred_backend = kLlmPreferredBackendGpu // GPU使用
};
// 2. エンジン作成
void* engine = nullptr;
char* error_msg = nullptr;
if (LlmInferenceEngine_CreateEngine(&model_settings, &engine, &error_msg)) {
std::cerr << "Engine creation failed: " << error_msg << std::endl;
free(error_msg);
return 1;
}
// 3. セッション設定と作成
const LlmSessionConfig session_config = {
.topk = 40,
.topp = 0.95f,
.temperature = 0.8f,
.random_seed = 42
};
void* session = nullptr;
if (LlmInferenceEngine_CreateSession(engine, &session_config, &session, &error_msg)) {
std::cerr << "Session creation failed: " << error_msg << std::endl;
free(error_msg);
return 1;
}
// 4. プロンプト追加
char prompt[] = "What is machine learning?";
if (LlmInferenceEngine_Session_AddQueryChunk(session, prompt, &error_msg)) {
std::cerr << "Failed to add prompt: " << error_msg << std::endl;
free(error_msg);
return 1;
}
// 5. 非同期推論実行
std::cout << "Response: ";
if (LlmInferenceEngine_Session_PredictAsync(session, nullptr, &error_msg, async_callback)) {
std::cerr << "Prediction failed: " << error_msg << std::endl;
free(error_msg);
return 1;
}
// 6. クリーンアップ
LlmInferenceEngine_Session_Delete(session);
LlmInferenceEngine_Engine_Delete(engine);
return 0;
}
まとめ:AndroidでのLLM開発の未来
技術的達成点
AndroidでのオンデバイスLLMは、2024年時点で以下を実現しています:
- 🚀 実用的な性能: 最新端末で20-50 tokens/sec
- 📱 モバイル最適化: 1-5GBのコンパクトモデル
- 🔒 完全なプライバシー: データの外部送信不要
- 🌐 オフライン動作: ネットワーク接続不要
開発エコシステム
- MediaPipe: 統一APIでの簡単な実装
- 豊富なモデル: Hugging Face、Kaggleでの事前変換済みモデル
- プロダクション実例: AI Edge Galleryによるベストプラクティス
- クロスプラットフォーム: Android、iOS、デスクトップ対応
今後の発展方向
- 性能向上: NPU活用による更なる高速化
- モデル軽量化: より小さなモデルでの高性能実現
- マルチモーダル拡張: 音声、動画への対応拡大
- 開発者体験: より簡単な実装とデバッグツール
AndroidでのLLM開発は、プライバシーを重視する現代のアプリケーション開発において、重要な選択肢となっています。本ガイドを参考に、ぜひあなた自身のAIアプリケーションを構築してみてください!
🐣
フリーランスエンジニアです。
お仕事のご相談こちらまで
rockyshikoku@gmail.com
Core MLを使ったアプリを作っています。
機械学習関連の情報を発信しています。