今までの内容は以下の通り
-
Twitter APIを使って自動でTweetする(1)
Request Tokenの取得 -
Twitter APIを使って自動でTweetする(2)
AWSのAPI GatewayとLambdaへのデプロイ -
Twitter APIを使って自動でTweetする(3)
Vueを使ったTwitterの認証・認可の取得 -
Twitter APIを使って自動でTweetする(4)
AWS S3のホスティングでコンテンツの公開 -
Twitter APIを使って自動でTweetする(5)
Access Tokenの取得
今回は、取得したAccess Tokenを使って定期的にTweetする仕組みを作る。まず、Access TokenをDynamoDBに保存する。そして、CloudWatch Eventを使って定期的にLambdaを実行して、DynamoDBからAccess Tokenを取得してTweetする。
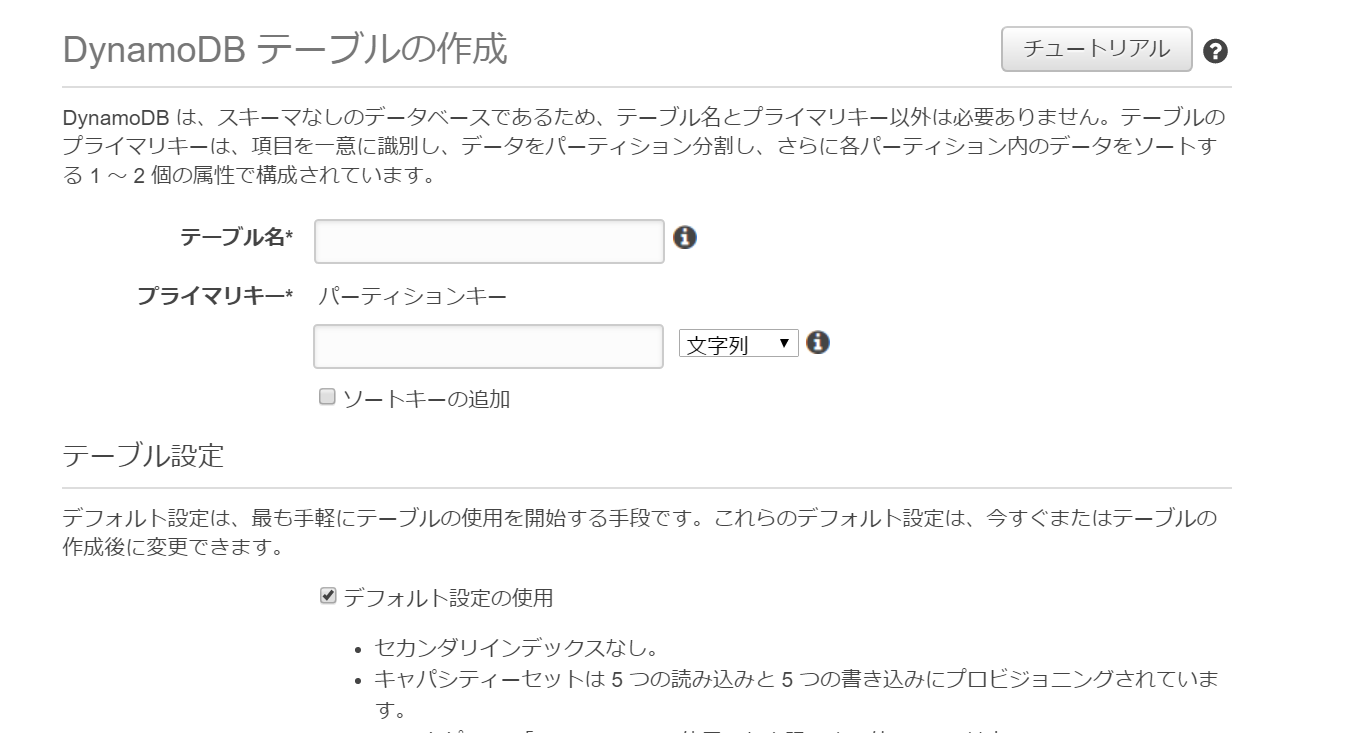
DynamoDB Tableの作成
DynamoDBコンソールにアクセスし、テーブルを作成する。テーブル名は「token-table」、プライマリーキーは「id」として、「作成」をクリックする。
DynamoDBアクセス用Lambda Layerの作成
DynamoDBにtokenを保存したり、保存したtokenを取得するために、DynamoDBにアクセスする関数を作成し、Layerに登録する。Layerに登録することで複数のLambda関数からLayerを使ってDynamoDBにアクセスすることができる。以下はDynamoDBへアクセスするためのコード。Layerの使い方については「Twitter APIを使って自動でTweetする(5)」を参照してほしい。
import boto3
class TokenTable:
parition_name = 'id'
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = dynamodb.Table('token-table')
@classmethod
def register(cls, data):
cls.table.put_item(Item=data)
@classmethod
def get_item(cls, id):
response = cls.table.get_item(
Key={
'id': id
}
)
return response.get('Item')
また、LambdaからDynamoDBにアクセスするためにLambdaに権限を追加する必要がある。
DynamoDBにアクセスする必要のあるget_access_token関数を開き、「IAMコンソールでget_access_token-xxxxロールを表示します。」をクリックする。
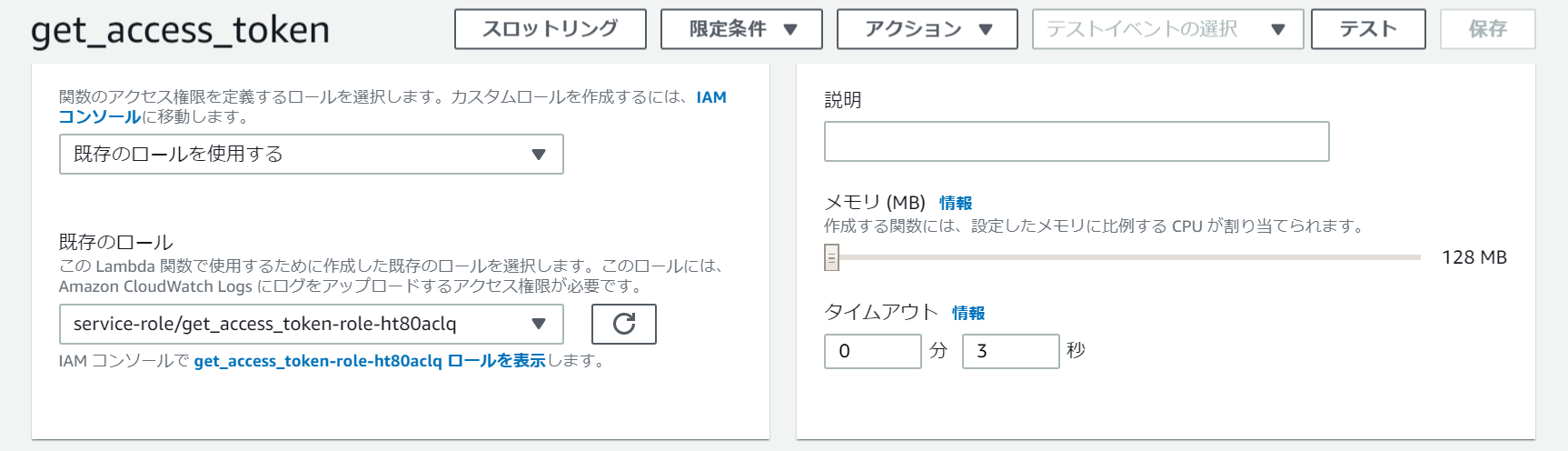
「インラインポリシーの追加」をクリックする。
「JSON」タブをクリックする。
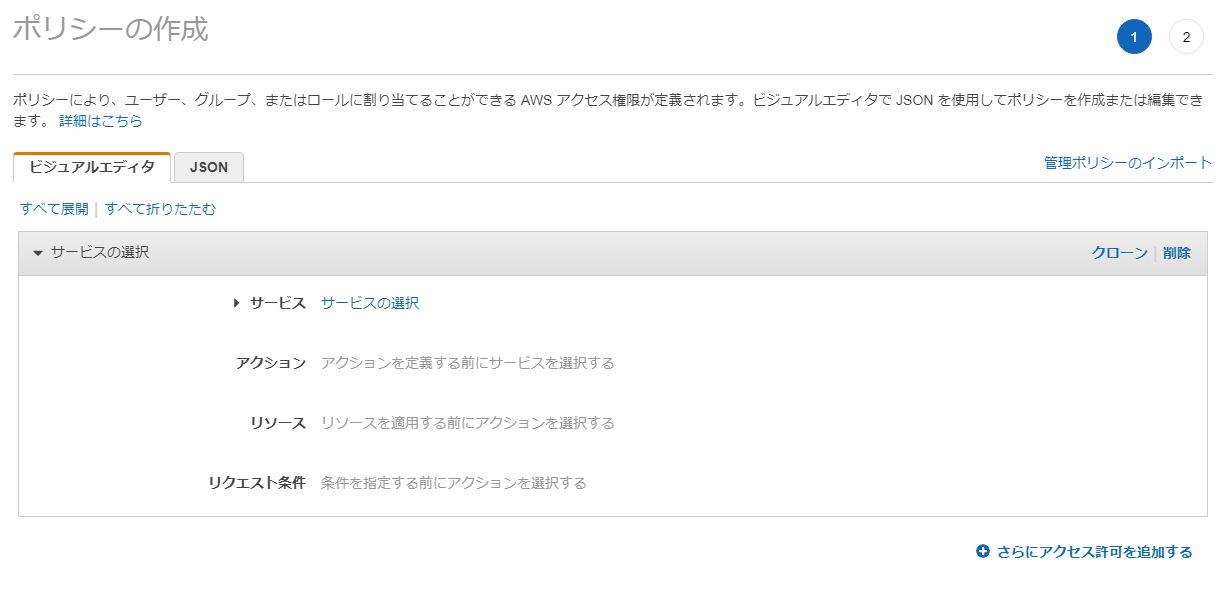
インラインポリシーをJSON形式で入力する。
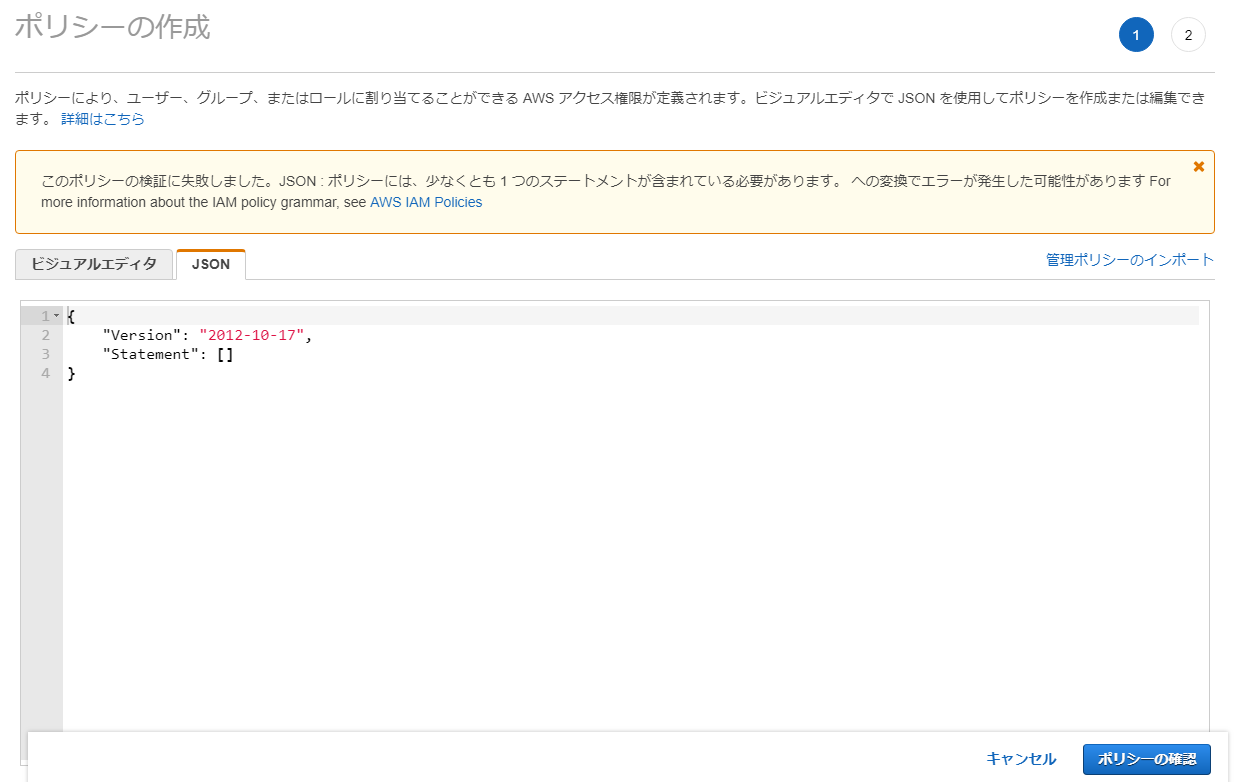
ポリシーは以下のように入力し、「ポリシーの確認」をクリックする。
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "dynamodb:*",
"Resource": "arn:aws:dynamodb:*:*:table/token-table"
}
]
}
ポリシー名を入力し、「ポリシーの作成」をクリックする。
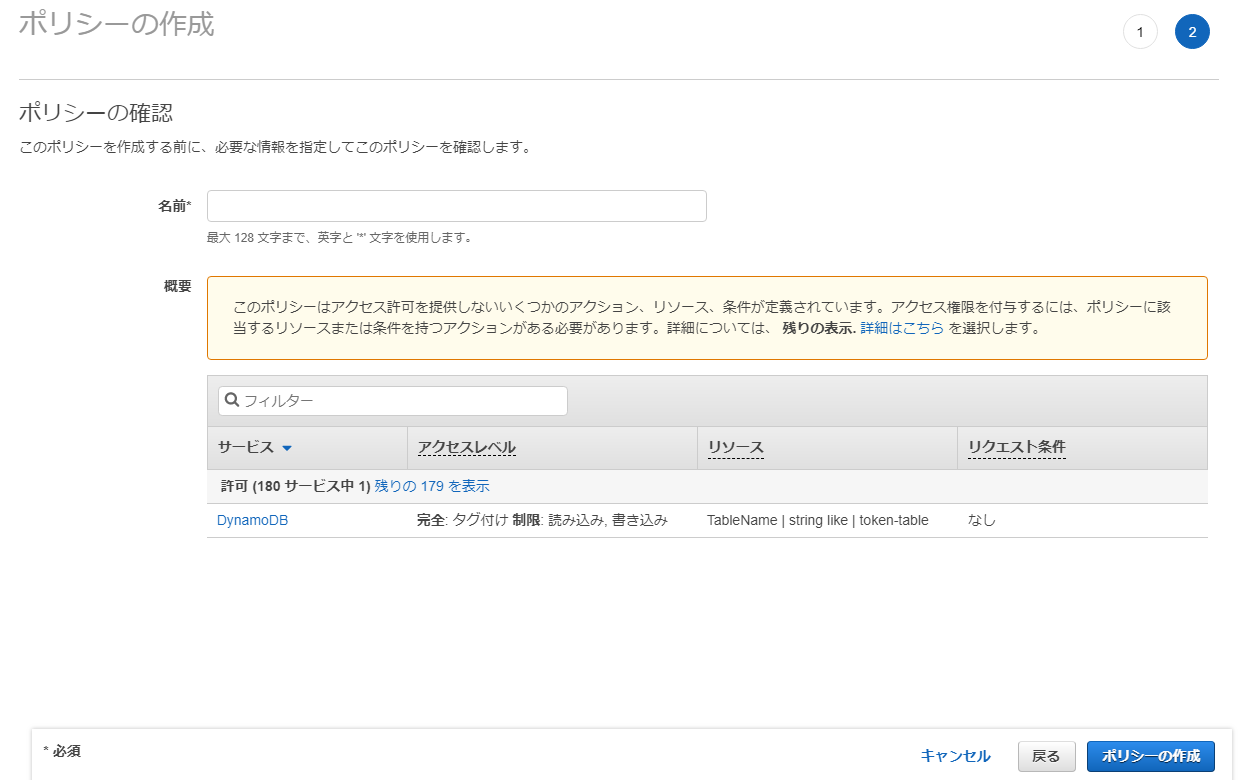
次に、get_access_token関数を以下のように修正し、取得したAccess TokenをDynamoDBのtoken-tableに保存するように変更する。
import os
import urllib.parse
import requests
import utilities
from dynamodb import TokenTable
REQUEST_URL = 'https://api.twitter.com/oauth/access_token'
REQUEST_METHOD = 'POST'
API_KEY = os.environ.get('API_KEY')
API_SECRET = os.environ.get('API_SECRET')
TOKEN_SECRET = ''
SIGNATURE_METHOD = 'HMAC-SHA1'
class GetAccessToken:
def __init__(self, event, context):
self.oauth_token = event.get('queryStringParameters').get('oauth_token')
self.oauth_verifier = event.get('queryStringParameters').get('oauth_verifier')
def _create_authorization_params(self):
authorization_params = {}
authorization_params['oauth_timestamp'] = utilities.create_timestamp()
authorization_params['oauth_consumer_key'] = urllib.parse.quote(API_KEY, safe='')
authorization_params['oauth_nonce'] = utilities.create_nonce()
authorization_params['oauth_signature_method'] = SIGNATURE_METHOD
authorization_params['oauth_version'] = '1.0'
authorization_params['oauth_token'] = self.oauth_token
authorization_params['oauth_verifier'] = self.oauth_verifier
authorization_params['oauth_signature'] = utilities.create_signature(utilities.create_base_string(authorization_params), REQUEST_METHOD, REQUEST_URL, API_SECRET, TOKEN_SECRET)
return authorization_params
def _create_authorization_header(self):
authorization_header_val = 'OAuth '
params = self._create_authorization_params()
authorization_header_val += utilities.convert_dict(params)
return {'Authorization': authorization_header_val}
def _parse_response(self, response):
response_dict = {
(response.text.split('&')[0]).split('=')[0]: (response.text.split('&')[0]).split('=')[1],
(response.text.split('&')[1]).split('=')[0]: (response.text.split('&')[1]).split('=')[1],
(response.text.split('&')[2]).split('=')[0]: (response.text.split('&')[2]).split('=')[1],
(response.text.split('&')[3]).split('=')[0]: (response.text.split('&')[3]).split('=')[1]
}
data = {
'id': response_dict['user_id'],
'token': response_dict['oauth_token'],
'secret': response_dict['oauth_token_secret'],
'name': response_dict['screen_name']
}
return data
def _register_id(self, data):
token_table = TokenTable()
token_table.register(data)
def _execute(self):
headers = self._create_authorization_header()
response = requests.post(REQUEST_URL, headers=headers)
data = self._parse_response(response)
self._register_id(data)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
get_access_token = GetAccessToken(event, context)
get_access_token._execute()
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'headers': {'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*'},
'body': 'Registration Success!'
}
これで、Access TokenをDynamoDBに保存されるようになった。あとは、このAccess Tokenを使ってTweetする関数を作成し、CloudWatch Eventを使って定期的にそのLambdaを実行すれば自動でTweetすることができる。
Tweetする関数のコードは以下のように作成した。環境変数、ロール、レイヤーはget_access_tokenの関数と同様に設定している。
また、token-tableにアクセスする際のパーティションキーであるidの値を今回は決め打ちで設定している。この値は自身のtoken-tableを確認し、保存されているidに書き換えて使う必要がある。
import os
import urllib.parse
import requests
import utilities
from dynamodb import TokenTable
REQUEST_METHOD = 'POST'
API_KEY = os.environ.get('API_KEY')
API_SECRET = os.environ.get('API_SECRET')
SIGNATURE_METHOD = 'HMAC-SHA1'
TWEET_URL = 'https://api.twitter.com/1.1/statuses/update.json'
class AutoTweet:
def __init__(self, event, context):
pass
def get_token(self, id):
token_table = TokenTable()
res = TokenTable.get_item(id)
return {'token': res.get('token'), 'secret': res.get('secret')}
def _create_authorization_params_for_tweet(self, token, token_secret, message):
signature_params = {}
signature_params['status'] = urllib.parse.quote(message, safe='')
authorization_params = {}
authorization_params['status'] = urllib.parse.quote(message, safe='')
authorization_params['oauth_timestamp'] = utilities.create_timestamp()
authorization_params['oauth_consumer_key'] = urllib.parse.quote(API_KEY, safe='')
authorization_params['oauth_nonce'] = utilities.create_nonce()
authorization_params['oauth_version'] = '1.0'
authorization_params['oauth_signature_method'] = SIGNATURE_METHOD
authorization_params['oauth_token'] = token
signature_params.update(authorization_params)
authorization_params['oauth_signature'] = utilities.create_signature(utilities.create_base_string(signature_params), REQUEST_METHOD, TWEET_URL, API_SECRET, token_secret)
return authorization_params
def _create_authorization_header_for_tweet(self, token, token_secret, message):
authorization_header_val = 'OAuth '
params = self._create_authorization_params_for_tweet(token, token_secret, message)
authorization_header_val += utilities.convert_dict(params)
return {'Authorization': authorization_header_val}
def _tweet(self, token, token_secret, message):
ENDPOINT = TWEET_URL + '?status=' + urllib.parse.quote(message, safe='')
headers = self._create_authorization_header_for_tweet(token, token_secret, message)
return requests.post(ENDPOINT, headers=headers)
def _execute(self):
id = '1132669739304513536'
token_info = self.get_token(id)
return self._tweet(token_info['token'], token_info['secret'], 'Hello, this is auto tweet test:' + utilities.create_timestamp())
def lambda_handler(event, context):
auto_tweet = AutoTweet(event, context)
try:
auto_tweet._execute()
except Exception as e:
raise e
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'headers': {'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*'},
'body': 'success!'
}
最後に、CloudWatch Eventの設定をする。
まず、CloudWatchコンソールにアクセスし、イベントのルールからルール作成をクリックする。
イベントソースでスケジュールを選択し、適当な値を設定してターゲットで作成したLambda関数を選択して、「設定の詳細」をクリックする。
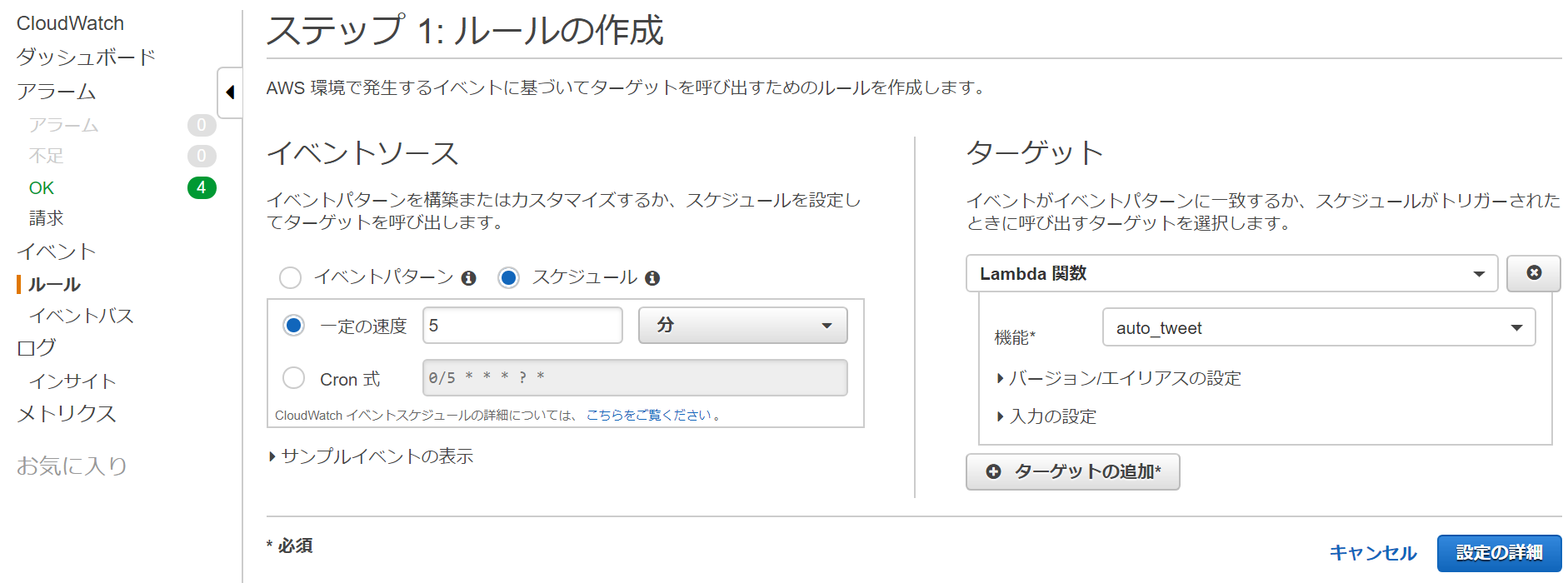
名前を入力し、状態を「有効」にして「ルールの作成」をクリックする。
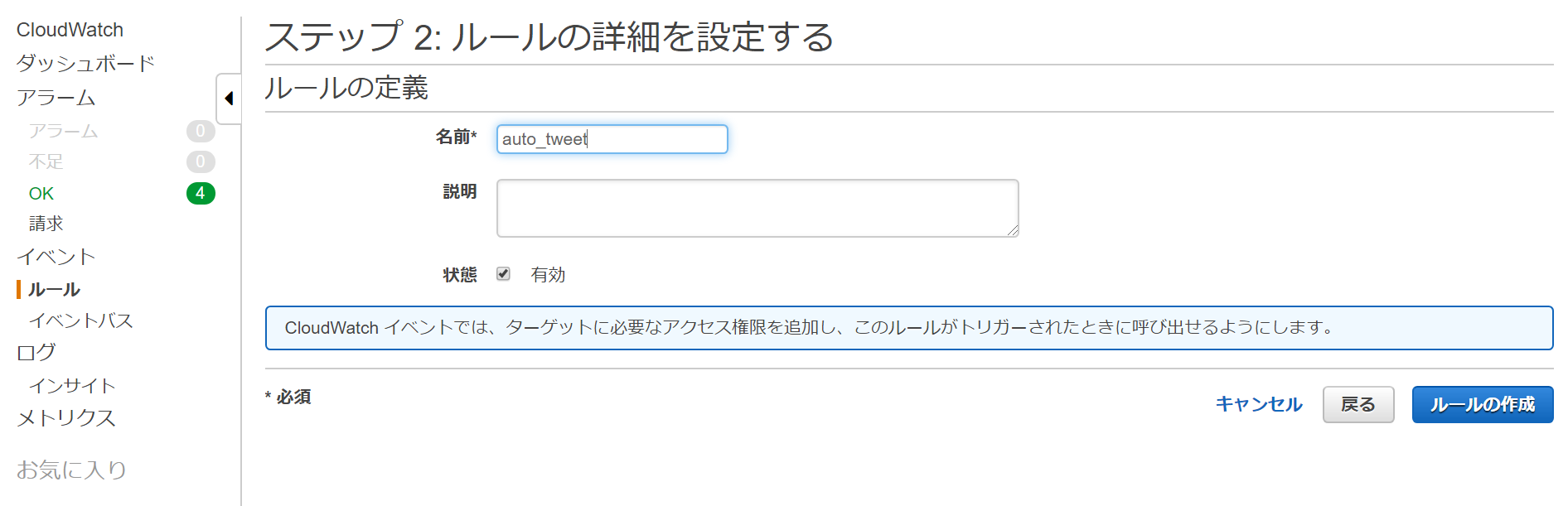
これで、「Twitter APIを使って自動でTweetする(3)」で作成したVueアプリからログインをすると、そのログインしたTwitterのアカウント(実際は、上記で指定したidに紐づくアカウント)で定期的にTweetされるようになる。
次回はフロントエンドを追加して、汎用的に使えるようにする予定。
前回までの投稿は以下
Twitter APIを使って自動でTweetする(1)
Twitter APIを使って自動でTweetする(2)
Twitter APIを使って自動でTweetする(3)
Twitter APIを使って自動でTweetする(4)
Twitter APIを使って自動でTweetする(5)