こちらの続きです。
導入
次はこちらをMLflowを使う形に魔改造してウォークスルーしてみます。
Travel Planner Agent概要
上記のノートブック上段部を邦訳して抜粋。
LangGraphを使った旅行プランナーの構築: チュートリアル
概要
このチュートリアルでは、LangGraphというライブラリを使用して、ユーザー入力を収集し、パーソナライズされた旅行プランを生成する会話型AIアプリケーションを構築する方法を紹介します。
動機
AIアプリケーションの分野では、複数ステップのプロセスで状態とフローを管理することが課題となります。LangGraphは、複雑な対話を処理しながら明確でモジュール化された構造を維持できるグラフベースのワークフローを作成する手段を提供します。この旅行プランナーは、LangGraphの機能を活用して有用でインタラクティブなアプリケーションを構築する実践的な例となります。
主要コンポーネント
- StateGraph: 旅行プランナーのフローを定義するアプリケーションのコア。
- PlannerState: プランニングプロセスの状態を表すカスタムタイプ。
- ノード関数: プランニングプロセスの個々のステップ(input_city、input_interests、create_itinerary)。
- LLM統合: 言語モデルを利用して最終的なプランを生成。
メソッドの詳細
旅行プランナーは、以下のシンプルな3ステップのプロセスに従います:
- 都市の入力:
- アプリケーションはユーザーに訪問したい都市を入力するよう促します。
- この情報は状態に保存されます。
- 興味の入力:
- ユーザーは旅行の興味を提供するよう求められます。
- これらの興味はリストとして状態に保存されます。
- プランの作成:
- 収集された都市と興味を使用して、アプリケーションは言語モデルを活用してパーソナライズされた日帰り旅行プランを生成します。
- 生成されたプランはユーザーに提示されます。
これらのステップ間のフローはLangGraphによって管理され、状態遷移が確実に正しい順序で実行されるようにします。
結論
このチュートリアルは、LangGraphを使用してシンプルで効果的な旅行プランナーを作成する方法を示しています。アプリケーションを相互接続されたノードのグラフとして構築することで、関心の分離が明確になり、ワークフローが容易に変更可能になります。このアプローチは、AI駆動の会話型インターフェースにおけるグラフベースのデザインの力と柔軟性を示し、より複雑なアプリケーションに拡張することができます。
旅行プランナーは、言語モデルを使用してより高度な状態管理アプリケーションを構築しようとする開発者にとっての出発点となります。状態管理、ユーザー入力処理、AIモデルとの統合などの重要な概念を、LangGraphが提供するフレームワーク内で説明しています。
ユーザに行きたい都市や興味のあることを入力させて、それを基に旅行プランを作るエージェントです。
応用すればプロジェクトの計画立案などもできるかもしれません。
若干特殊な作りとなっていて、inputを使って処理の途中にユーザ入力させて、処理途中にprintを使ってプラン過程を出力する処理となっています。
このあたり出力は最後にまとめるなど改善の余地があるのですが、今回はそのあたりの処理はオリジナルのままとしています。
それでは、mlflowにロギングしてDatabricks上で利用可能な形に実装してみます。
実装と実行
Databricks上でノートブックを作成し、LangChain/LangGraph関連とMlflow最新版をインストールします。なお、クラスタはサーバレスを利用しています。
%pip install -q -U langchain-core==0.3.13 langchain-databricks==0.1.1 langchain_community==0.3.3 langgraph==0.2.39
%pip install -q -U typing-extensions
%pip install -q -U "mlflow-skinny[databricks]>=2.17.1"
dbutils.library.restartPython()
前回同様、MLflowのカスタムチャットモデルとして、エージェントを実装します。
%%writefile "./travel_planning_agent.py"
import uuid
import re
from typing import List, Optional, Dict, TypedDict, Annotated
import mlflow
from mlflow.pyfunc import ChatModel
from mlflow.models import set_model
from mlflow.entities import SpanType
from mlflow.types.llm import (
ChatResponse,
ChatMessage,
ChatParams,
ChatChoice,
)
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
from langchain_databricks import ChatDatabricks
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, AIMessage
class PlannerState(TypedDict):
endpoint: str
params: dict
messages: Annotated[List[HumanMessage | AIMessage], "The messages in the conversation"]
city: str
interests: List[str]
itinerary: str
class TravelPlannerAgent(ChatModel):
def __init__(self):
self.models = {}
self.models_config = {}
self.app = None
def load_context(self, context):
self.models = context.model_config.get("models", {})
self.models_config = context.model_config
self.app = self.build_graph()
def predict(
self, context, messages: List[ChatMessage], params: Optional[ChatParams] = None
) -> ChatResponse:
with mlflow.start_span(name="TravelPlannerAgent", span_type=SpanType.AGENT) as root_span:
root_span.set_inputs(messages)
attributes = {**params.to_dict(), **self.models_config, **self.models}
root_span.set_attributes(attributes)
endpoint = self._get_model_endpoint("agent")
user_request = messages[-1].content
response = self.run_travel_planner(user_request, endpoint, params.to_dict())
output = ChatResponse(
choices=[
ChatChoice(
index=0,
message=ChatMessage(
role="assistant",
content=response.get("messages")[-1].content,
),
)
],
usage={},
model=endpoint,
)
root_span.set_outputs(output)
return output
def build_graph(self) -> StateGraph:
workflow = StateGraph(PlannerState)
workflow.add_node("input_city", self.input_city)
workflow.add_node("input_interests", self.input_interests)
workflow.add_node("create_itinerary", self.create_itinerary)
workflow.set_entry_point("input_city")
workflow.add_edge("input_city", "input_interests")
workflow.add_edge("input_interests", "create_itinerary")
workflow.add_edge("create_itinerary", END)
return workflow.compile()
def input_city(self, state: PlannerState) -> PlannerState:
print("Please enter the city you want to visit for your day trip:")
user_message = input("Your input: ")
return {
**state,
"city": user_message,
"messages": state['messages'] + [HumanMessage(content=user_message)],
}
def input_interests(self, state: PlannerState) -> PlannerState:
print(f"Please enter your interests for the trip to {state['city']} (comma-separated):")
user_message = input("Your input: ")
return {
**state,
"interests": [interest.strip() for interest in user_message.split(',')],
"messages": state['messages'] + [HumanMessage(content=user_message)],
}
def create_itinerary(self, state: PlannerState) -> PlannerState:
print(f"Creating an itinerary for {state['city']} based on interests: {', '.join(state['interests'])}...")
llm = ChatDatabricks(endpoint=state.get("endpoint"), **state.get("params"))
itinerary_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a helpful travel assistant. Create a day trip itinerary for {city} based on the user's interests: {interests}. Provide a brief, bulleted itinerary."),
("human", "Create an itinerary for my day trip."),
])
response = llm.invoke(itinerary_prompt.format_messages(city=state['city'], interests=", ".join(state['interests'])))
print("\nFinal Itinerary:")
print(response.content)
return {
**state,
"messages": state['messages'] + [AIMessage(content=response.content)],
"itinerary": response.content,
}
def run_travel_planner(self, user_request: str, endpoint:str, params: dict):
print(f"Initial Request: {user_request}\n")
state = {
"endpoint": endpoint,
"params": params,
"messages": [HumanMessage(content=user_request)],
"city": "",
"interests": [],
"itinerary": "",
}
return self.app.invoke(state)
def _get_model_endpoint(self, role: str) -> str:
"""
指定された役割のモデルエンドポイントを取得します。
Args:
role (str): モデルエンドポイントを取得する役割。
Returns:
str: モデルエンドポイント。
"""
role_config = self.models.get(role, {})
return role_config.get("endpoint")
set_model(TravelPlannerAgent())
大部分の処理はLangGraphのノード用メソッド定義です。
build_graphメソッド内でこれらのメソッドを利用してグラフを定義しています。
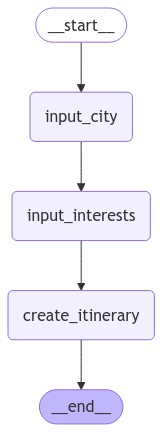
なお、グラフは以下のようになります。
訪問したい都市名の入力、興味事項の入力というノードのステップを経て、プランを作成するノードが実行されるシンプルなグラフとなっています。
次にカスタムチャットモデルをMLflowに保管・登録します。
モデル設定にLLMのエンドポイント名を指定していますが、前回同様Llama 3.2 3Bモデルを用いたMosaic AI Model Servingエンドポイントを指定しました。
import mlflow
# Databricks Unity Catalogを利用してモデル管理
mlflow.set_registry_uri("databricks-uc")
model_config = {
"models": {
"agent": {
"endpoint": "llama_v3_2_3b_instruct_endpoint",
},
},
}
input_example = {
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "I want to plan a day trip.",
}
]
}
registered_model_name = "training.llm.travel_planning_agent"
with mlflow.start_run():
model_info = mlflow.pyfunc.log_model(
"model",
python_model="travel_planning_agent.py",
model_config=model_config,
input_example=input_example,
registered_model_name=registered_model_name,
)
モデルが無事保管できたら、ロードして実際に使ってみます。
import mlflow
from mlflow import MlflowClient
from langchain_core.runnables.graph import MermaidDrawMethod
from IPython.display import display, Image
client = MlflowClient()
versions = [
mv.version for mv in client.search_model_versions(f"name='{registered_model_name}'")
]
agent = mlflow.pyfunc.load_model(f"models:/{registered_model_name}/{versions[0]}")
def display_graph():
display(
Image(
agent.get_raw_model().app.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png(
draw_method=MermaidDrawMethod.API,
)
)
)
def run_travel_planner(user_request:str):
result = agent.predict(
{
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_request}],
"temerature": 0.0,
"max_tokens": 1000,
}
)
run_travel_planner("I want to plan a day trip.")
Initial Request: I want to plan a day trip.
Please enter the city you want to visit for your day trip:
Your input:東京
Please enter your interests for the trip to 東京 (comma-separated):
Your input:食事,観光
Creating an itinerary for 東京 based on interests: 食事, 観光...
Final Itinerary:
Here's a suggested itinerary for a day trip to Tokyo based on your interests in food (食事) and sightseeing (観光):
**Day Trip Itinerary: Tokyo Food and Sightseeing**
**Stop 1: Tsukiji Outer Market (9:00 am - 10:30 am)**
* Start the day with a visit to the Tsukiji Outer Market, one of the world's largest fish markets
* Try some fresh sushi or sashimi for breakfast at one of the many restaurants in the market
* Explore the market stalls and try some other Japanese delicacies
**Stop 2: Asakusa Temple and Nakamise Shopping Street (11:00 am - 12:30 pm)**
* Take a short subway ride to Asakusa, one of the oldest districts in Tokyo
* Visit Senso-ji Temple, a famous Buddhist temple and one of the oldest in Japan
* Walk along Nakamise Shopping Street, a historic shopping street filled with traditional snacks and souvenirs
**Stop 3: Lunch at Shinjuku's Omoide Yokocho (1:00 pm - 2:30 pm)**
* Take a subway ride to Shinjuku and visit Omoide Yokocho, a small alley filled with tiny restaurants and bars
* Try some delicious yakitori (grilled chicken skewers) or tempura at one of the many restaurants in the area
**Stop 4: Shibuya Crossing and Takeshita Street (3:00 pm - 4:30 pm)**
* Take a subway ride to Shibuya and visit the famous Shibuya Crossing
* Walk down Takeshita Street, a fashionable shopping street filled with trendy boutiques and snacks
**Stop 5: Ichiran Shibuya Ramen (5:00 pm - 6:30 pm)**
* End the day with a visit to Ichiran Shibuya Ramen, a famous ramen chain known for its unique, rich tonkotsu broth
* Try a delicious bowl of ramen at this iconic restaurant
This itinerary should give you a good taste of Tokyo's food and sightseeing scene, but feel free to customize it to your interests and preferences!
日本語に翻訳すると以下の通り。
初期リクエスト:日帰り旅行を計画したい。
訪問したい都市を入力してください:
あなたの入力:東京
東京への旅行の興味を入力してください(カンマ区切り):
あなたの入力:食事,観光
興味:食事、観光に基づいて東京の日程を作成しています...
最終日程:
食事と観光に興味がある東京への日帰り旅行の提案日程はこちらです:
**日帰り旅行日程:東京 食事と観光**
**スポット1:築地場外市場(9:00 am - 10:30 am)**
* 世界最大級の魚市場の一つ、築地場外市場で一日をスタート
* 市場内の多くのレストランで新鮮な寿司や刺身の朝食を楽しむ
* 市場の屋台を探索し、他の日本の美味しいものを試す
**スポット2:浅草寺と仲見世通り(11:00 am - 12:30 pm)**
* 地下鉄で浅草へ短い旅、東京で最も古い地区の一つ
* 日本で最も古い仏教寺院の一つである浅草寺を訪れる
* 伝統的なお菓子やお土産でいっぱいの歴史的な仲見世通りを歩く
**スポット3:新宿の思い出横丁でランチ(1:00 pm - 2:30 pm)**
* 地下鉄で新宿へ移動し、小さなレストランやバーでいっぱいの思い出横丁を訪れる
* このエリアの多くのレストランで美味しい焼き鳥や天ぷらを試す
**スポット4:渋谷交差点と竹下通り(3:00 pm - 4:30 pm)**
* 地下鉄で渋谷へ移動し、有名な渋谷交差点を訪れる
* トレンディなブティックやスナックでいっぱいのファッショナブルな竹下通りを歩く
**スポット5:一蘭 渋谷ラーメン(5:00 pm - 6:30 pm)**
* 独特で濃厚な豚骨スープで知られる有名なラーメンチェーン、一蘭渋谷で一日を締めくくる
* この象徴的なレストランで美味しいラーメンを試す
この日程で東京の食事と観光シーンの良い味わいを得ることができますが、興味や好みに合わせて自由にカスタマイズしてください!
東京への旅行プランが出来ましたね。
まとめ
GenAI Agentsのチュートリアル:7. Travel Planning Agent をMLflowのカスタムモデルを使うように魔改造して実行してみました。
出力を処理途中にprintで行っていたり、ユーザからの入力をinputで行ったりしているため、このままではMosaic AI Model Servingのエンドポイントとしてはデプロイできないのですが、少し工夫すれば旅行プランニングエージェントをAPIとして公開することもできそうです。
(実際には旅行情報を検索するRAGシステムとして構築することが良いと思いますが)
プランニングという処理はエージェントと相性が良いと思っており、実務的な応答ができそうなチュートリアルだと思いました。
なぞって作ってみるだけでもアイディアがいろいろ出てくるものだなと実感します。