やりたいこと
ポリオミノパズルとは,正方形を連結させた多角形のブロックを指定の枠にぴったり並べていくパズルです.

目標は,ブロックの数$N$(上図だと5)と枠の形を入力として,パズルを自動的に生成することです.
アプローチ
今回は,「最初に各マスを$N$色からランダムに塗り,それを並べ替えてブロックを形作っていく」という方法を採ります.
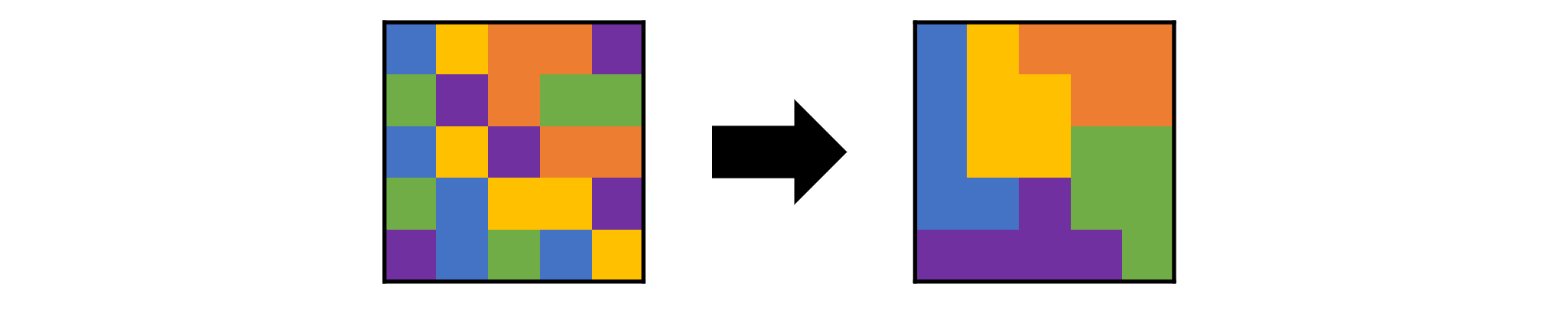
処理の流れは以下のようにします.
- 各マスをランダムに塗る
- 2つのマスを選ぶ
- それらのマスを入れ替えて盤面が「より良い状態」になるなら,入れ替える
- 2に戻って繰り返す
盤面の「良い状態」
盤面を以下の式で評価することにします.
Evaluation = \sum_{c \in S} cost(c)\\
cost(c) = \sum_{c* \in S_c} distance(c,c*)
ここで$S$は盤面のマスの集合,$S_c$は$c$と同色のマスの集合を表します.
$distance$は$c$から$c*$まで距離(または移動コスト)です.1マスで距離1ですが,cと同色の連結しているマスがあれば,その間は距離0とします.
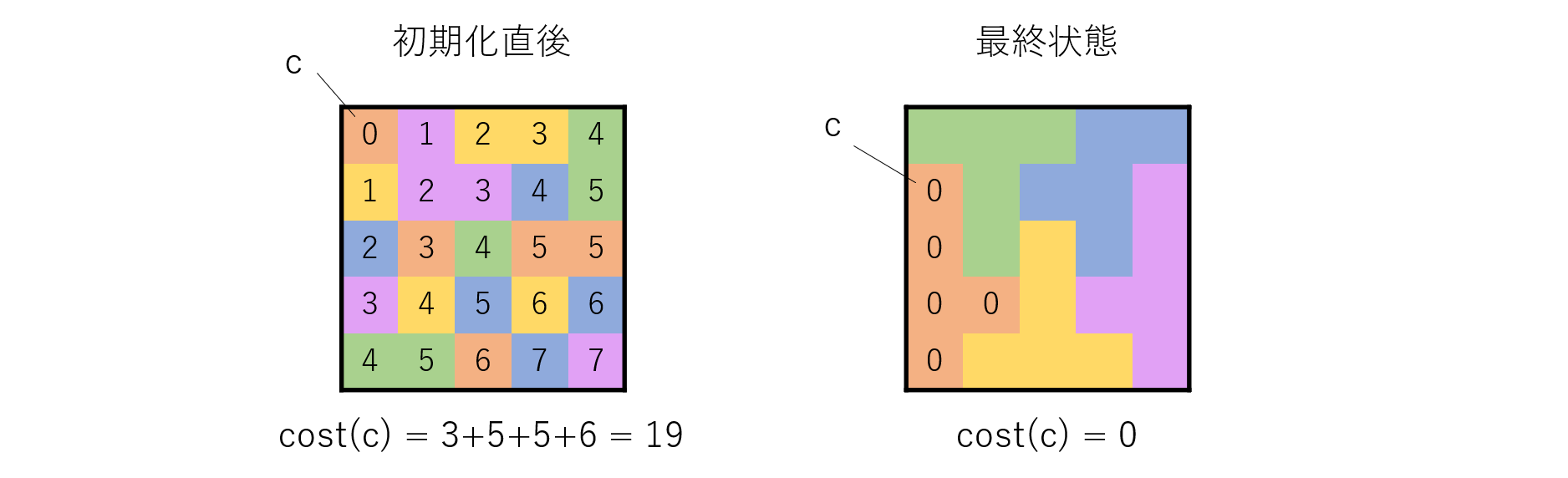
最終的に同じ色のマスが全て連結している盤面にできれば,それでパズルが生成できたことになります.そのとき,この評価式は0になります.評価式の値が小さいほど「より良い盤面」です.
盤面が完成しないパターン
評価関数が局所解にハマり,盤面が完成しない場合があります.例えば以下の盤面.
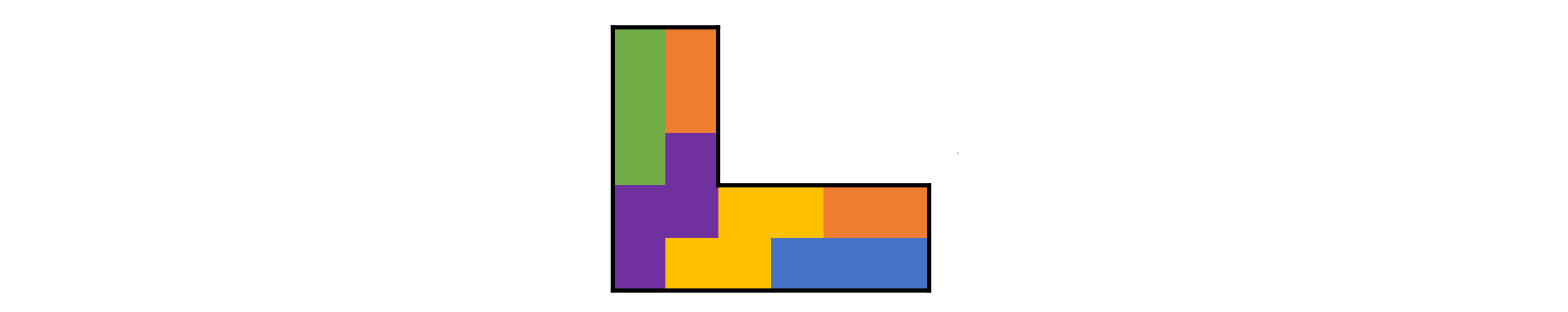
オレンジのブロックが2つに分かれてしまっていますが,どの2マスを選んでもこれ以上評価関数は改善しません.枠の形が複雑だとか,ブロック数が多い場合に発生しやすい気がします.
マスの入れ替えを何手か先まで考慮する探索アルゴリズムを書くか,局所解にハマったら盤面を初期化してもう一度実行しなおす手もあります.
実装
C++で実装しました.
以下に一部抜粋します.
盤面の初期化
盤面に色の初期値を設定します.今回は各ブロックのサイズができるだけ均等になるように各色の個数を設定しています(count++ * blockNum / boardSizeの部分).少し書き換えれば各色の個数を配列として入力するようにもできます.
int blockNum = 5;
void initBoard(vector<vector<int>>& board) {
vector<int> colors(boardSize);
int count = 0;
generate(colors.begin(), colors.end(), [&count]() {return count++ * blockNum / boardSize;});
random_device seed_gen;
mt19937 engine(seed_gen());
shuffle(colors.begin(), colors.end(), engine);
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; i++) {
auto pos = positions[i];
board[pos.first][pos.second] = colors[i];
}
}
盤面の更新
「マスを2つ選んで,より良くなるなら入れ替える」の部分です.今回は完全ランダムに選んでいますが,$cost(c)$の大きいマスを優先的に選ぶなどすると収束が早まると思います.
bool nextStep(vector<vector<int>>& board) {
random_device seed_gen;
mt19937 engine(seed_gen());
uniform_int_distribution<int> randPos(0, boardSize-1);
pair<int,int> pos1, pos2;
while(1) {
pos1 = positions[randPos(engine)];
pos2 = positions[randPos(engine)];
if (board[pos1.first][pos1.second] != board[pos2.first][pos2.second]) break;
}
auto temp_board = board;
swapCell(temp_board, pos1, pos2);
int eval = evaluateBoard(temp_board);
if (eval < evaluateBoard(board)) {
board = temp_board;
if (eval == 0) return true;
}
return false;
}
void swapCell(vector<vector<int>>& board, pair<int,int> pos1, pair<int,int> pos2) {
int color = board[pos1.first][pos1.second];
board[pos1.first][pos1.second] = board[pos2.first][pos2.second];
board[pos2.first][pos2.second] = color;
}
盤面の評価
評価式の計算です.$cost(c)$は01-BFSで計算しています.計算量的には入れ替えたマスと同色の部分のみ再計算するようにしたほうがベターです.
int evaluateBoard(const vector<vector<int>>& board) {
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i< boardSize; i++) {
ret += calcCost(board, positions[i]);
}
return ret;
}
int calcCost(const vector<vector<int>>& board, pair<int,int> target) {
deque<pair<int,pair<int,int>>> deq;
map<pair<int,int>, bool> checked;
int ret = 0;
int color = board[target.first][target.second];
deq.emplace_front(make_pair(0, target));
while(deq.size() != 0) {
auto p = deq.front();
deq.pop_front();
pair<int,int> pos = p.second;
int cost = p.first;
if (checked[pos]) continue;
checked[pos] = true;
if (board[pos.first][pos.second] == color) ret += cost;
static const vector<pair<int,int>> offset = { {0,1}, {1,0}, {0,-1}, {-1,0} };
for (auto o : offset) {
pair<int, int> nxt = { pos.first + o.first, pos.second + o.second };
if (nxt.first >= 0 && nxt.first < board.size() &&
nxt.second >= 0 && nxt.second < board[nxt.first].size() &&
board[nxt.first][nxt.second] >= 0) {
if (board[pos.first][pos.second] == color && board[nxt.first][nxt.second] == color) {
deq.emplace_front(make_pair(cost, nxt));
}
else deq.emplace_back(make_pair(cost + 1, nxt));
}
}
}
return ret;
}
盤面の可視化
現在の盤面の状態をコンソールに出力します.
void showBoard(const vector<vector<int>>& board, int val) {
cout << val << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < board.size(); i++) {
cout << toSymbols(board[i]) << endl;
}
cout << "\033["+to_string(board.size()+1)+"A\r";
}
string toSymbols(vector<int> row) {
static const vector<string> symbol = {"+", "*", "^"};
static const vector<string> color = {"\u001b[31m", "\u001b[32m", "\u001b[34m", "\u001b[33m", "\u001b[35m", "\u001b[36m"};
string ret = "";
for (int i = 0; i < row.size(); i++) {
if (row[i] < 0) ret += " ";
else ret += color[row[i] % 6] + symbol[row[i] / 6] + "\u001b[0m";
}
return ret;
}
void returnCursor(const vector<vector<int>>& board) {
cout << "\033["+to_string(board.size()+1)+"B\r";
}