凸包
凸包とは可算個の点集合$P$に対してその点を全て含むような最小の単体(平面の組み合わせでできる図形)です。
グラハム走査
グラハム走査は2次元空間において凸法を求めるアルゴリズムの1つです。一般に2次元の凸包は比較的容易に求めることができます(3次元以上はとても困難です)。
グラハム走査は以下の3ステップで構成されます。
- x座標が最小の点$p_{min}$を見つける
- $p_{min}$から見た仰角が小さい方から時計回りの順になるように各点をソートする。
- 3点ずつとってきて、それがへこんでいるか膨らんでいるかを比較する。
凸性の判定
凸であるかどうかは時計回り連続する3点$pi,p_{i+1},p_{i+2}$の角度関係を見ればいいです。それは外積
z=\vec{p_ip_{i+1}} \times \vec{p_ip_{i+2}}
と対応していて$z$が正ならば凸、0ならば一直線、負ならば凹となります。
$z \leq 0$ならば真ん中の点$p_{i+1}$を取り除けばよいです。
ソート済みなので、各点を時計回りに見ていけばよくて$O(N)$でチェックできます。
(僕のコードは念のため、1点削除するごとに最初からやり直しているので$O(N^2)$かかっていますが)
計算量
ソートがボトルネックになるので$O(N\log{N})$で計算できます。
実装
以上のプロセスを実装すると次のようになります。
// find convex hull of 2D points using Graham scan
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i,n) for ( int i=0; i< (n); ++i )
using namespace std;
using P = pair<int,int>;
P diff_pair( P p1, P p2 ){ // caculate difference of p1 from p2
int a = p1.first - p2.first;
int b = p1.second - p2.second;
return make_pair(a,b);
}
int signed_area( P p1, P p2, P p3 ){ // to chech relativistic position of 3 poins
P v1 = diff_pair( p2,p1 );
P v2 = diff_pair( p3,p1 );
return v1.first*v2.second - v1.second*v2.first; // calc area as z-component of v1 x v2
}
// partation for quick sort
int partition (vector<P> &node, int l, int r, P p_minx) {
P pivot = node[r];
int i = (l - 1);
for (int j = l; j <= r - 1; j++) {
// compare func : signed_area ~ Declination from p with min x
// signed_area < 0 => clockwise
if ( signed_area( p_minx, node[j], pivot ) >= 0 ) {
i++;
iter_swap(node.begin()+i, node.begin()+j);
}
}
iter_swap(node.begin()+i+1, node.begin()+r);
return (i + 1);
}
// sort points counter-clockwise
void qsort_c_clockwise( vector<P> &node, int l, int r, P p_minx) {
if (l < r) {
int pivot = partition(node, l, r, p_minx);
qsort_c_clockwise(node, l, pivot - 1,p_minx);
qsort_c_clockwise(node, pivot + 1, r,p_minx);
}
return;
}
void remove_concave( vector<P> &node ){
int max_step = node.size()*node.size()*node.size(); // all combination of triangle = nC3
int step = 0;
int i = 0;
while( i<node.size()-2 and step < max_step ){
int area = signed_area( node[i+1], node[i+2], node[i] );
// area < 0 => line graph of these points dents
// => remove concave point
// => check for new set again
if( area <= 0 ) {
node.erase( node.begin()+i+1 );
i=0;
}else{
++i;
}
++step;
}
return;
}
void graham_scan( vector<P> &node ){
// iterator of the node with min x components
vector<P>::iterator itr_minx = min_element(node.begin(), node.end(),
[](const P &l, const P &r) {
return r.first > l.first; });
// move min element to head
iter_swap( node.begin(), itr_minx );
qsort_c_clockwise ( node, 0, node.size()-1, node[0] );
remove_concave( node );
return;
}
int main(){
// input
int N;
cout << "# of points = "; cin >> N;
if( N<3 ){
cout << "N >= 3" << endl;
exit(1);
}
vector<P> node(N);
int x,y;
rep(i,N){
cin >> x >> y;
node[i] = make_pair(x,y);
}
graham_scan( node );
// output
cout << "nodes of the convex hull :" << endl;
for( P p : node ){
cout << p.first << " " << p.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
実行結果
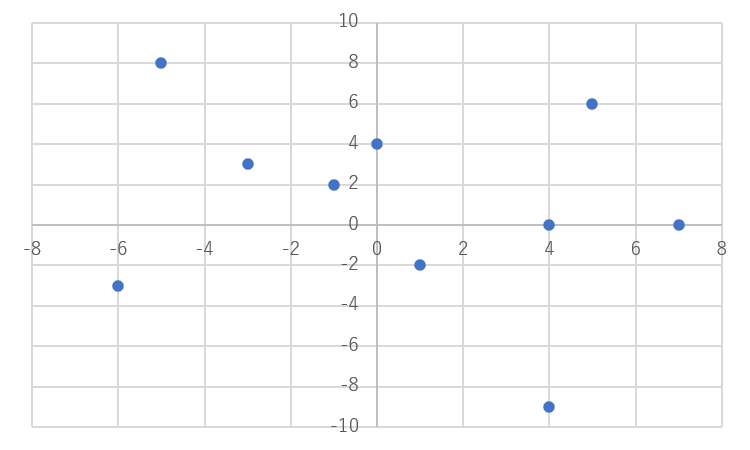
次の入力で試します。
10
1 -2
-1 2
-3 3
-6 -3
7 0
4 -9
5 6
-5 8
0 4
4 0
図示すると下図の通りです。
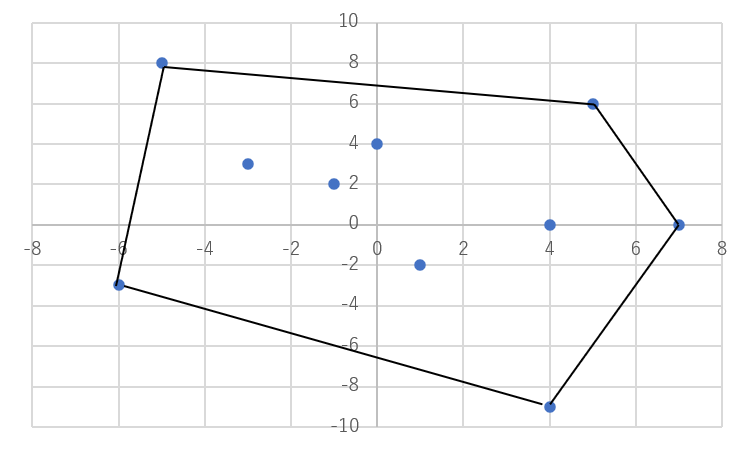
この入力に対して先のコードを実行すると、出力は次のようになります。
-6 -3
4 -9
7 0
5 6
-5 8
図示すると次図のようになり、確かに凸包となっています。
コメント
点の凸性の判定で$O(N^2)$かかりますが、より効率のいいやり方があればコメントしていただけると幸いです。
ちなみに分割統治法でも$O(N\log{N})$で計算できます。