2次元凸包の求め方はいくつかありますが、今回は分割統治法による解法を紹介したいと思います。
別の解法としてはグラハム走査を使う方法あります。
点集合$P$の凸包$CF[P]$を求める基本方針は以下の通りです。
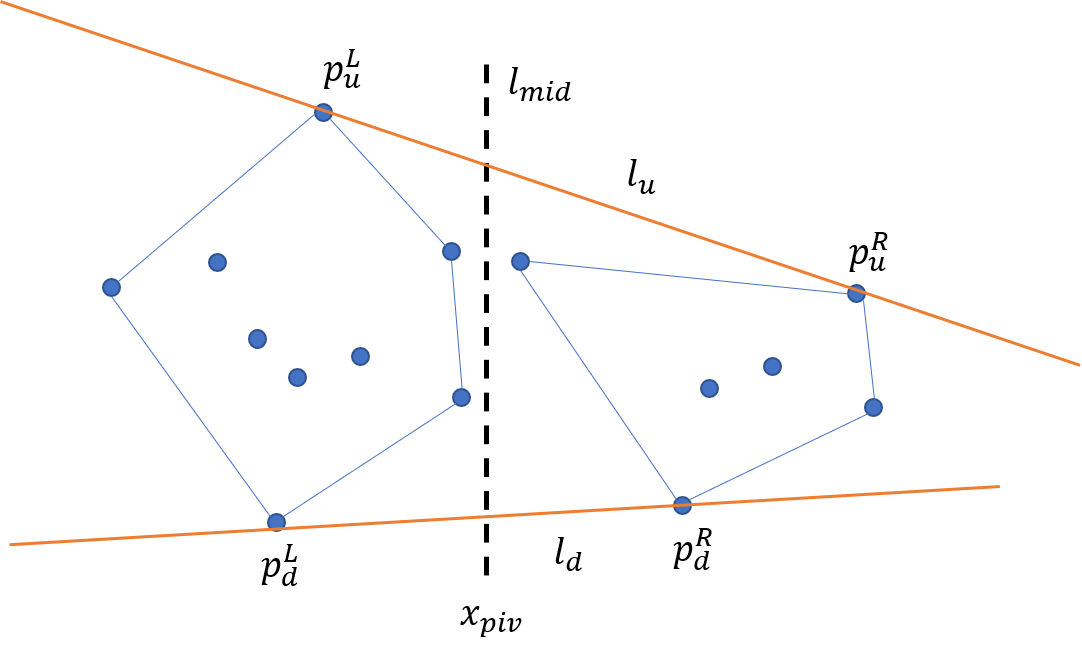
- y軸に平行な適当な線$x=x_{piv}$で点集合$P$を左右に分けます。
P_L = \{ p\in P \mid p_x < x_{piv} \} \\
P_R = \{ p\in P \mid p_x > x_{piv} \}
- 左右それぞれの凸包$CF[P_L]$、$CF[P_R]$を求めます。
- 左右の凸包を合成して全体の凸包を作ります:$merge(CF[P_L],CF[P_R])$
左右それぞれの凸包は今の3ステップで同様に求めることができます。また、点の数が3以下の場合の凸包はそれらの点すべてを使った三角形、線分、点のいずれかになります。
凸包の合成
凸包を合成する関数$merge$の中身を説明します。この合成は左右の凸包$C_L,C_R$に同時に接する接線を求めることで可能となります。
上図のように上部/下部の接線$l_u,l_d$を全体の凸包の新たな辺に加えて、その接点$p_{u/d}^{L},p_{u/d}^{R}$の間にある内側の点(つまり$l_{mid}$に近い点)は無視します。
上部接線になっているかどうかの判定は直線$p_lp_r$($p_l \in P_L$、$p_r \in P_R$)に対して他のすべての点が直線より下側にあるかどうかで判定します。下部接線は同様に選んだ2つの接点以外のすべての点が直線より上側にあるかどうかで判定します。ただ、全ての点を判定する必要はなく、凸包の性質から、辺でつながった外側の隣の点についてのみ判定すれば十分です。
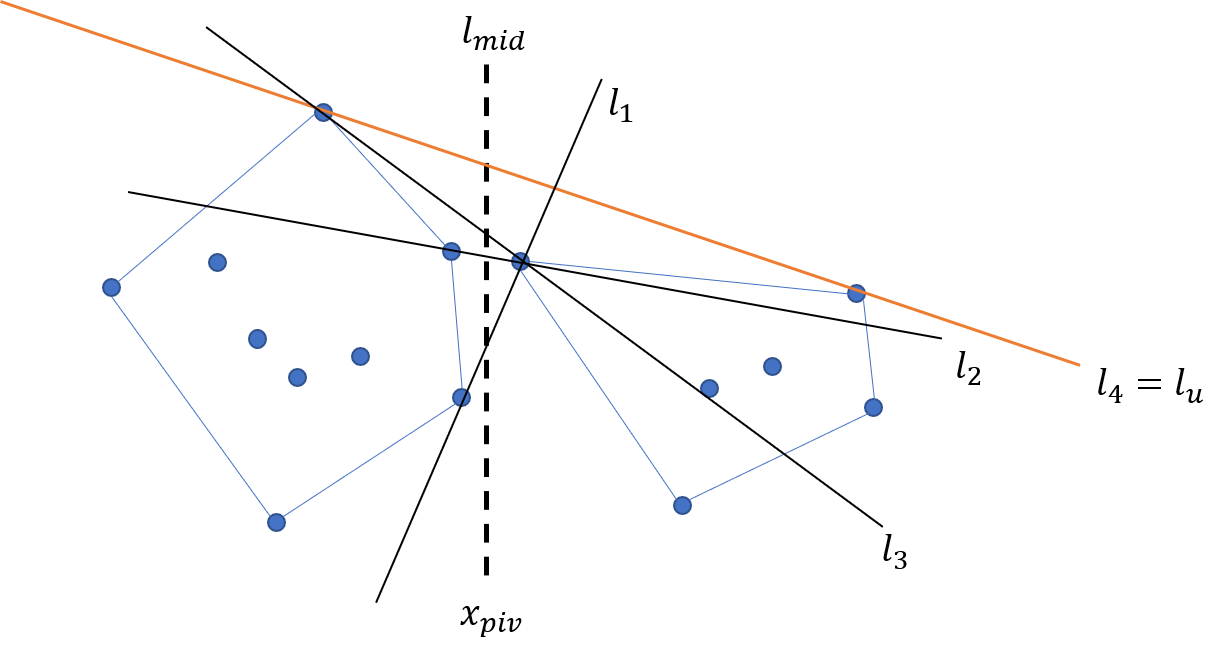
次に接点の選び方です。無視する点は内側の点なので、より内側の点を$p_l,p_r$として選べばその直線に対して無視される点はより外側の点を選んで無視される点に含まれます。そこで、$l_{mid}$に一番近い点から初めて、判定条件をクリアするまで凸包として隣の点を取りなおしていきます(この方法は凸包の辺が接する場合にも対応しています)。
図の例では例えば$l_1 \rightarrow l_2 \rightarrow l_3 \rightarrow l_4$のような順に更新されます。左側で判定条件を満たしていなければ左の点を、右側が満たしていなければ右の点を更新します。
実装
全体のコード
以上のプロセスを実装すると次のようになります。
# include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using P = pair<int,int>;
const int inf = numeric_limits<int>::max()/2;
////quick sort w.r.t. counter-clockwise
int signed_area( P p1, P p2, P p3 ){ // to chech relativistic position of 3 poins
P v1,v2;
v1.first = p2.first-p1.first; v1.second = p2.second-p1.second;
v2.first = p3.first-p1.first; v2.second = p3.second-p1.second;
return v1.first*v2.second - v1.second*v2.first; // calc area as z-component of v1 x v2
}
int partition (vector<P> &node, int l, int r, P p_minx) { // partation for quick sort
P pivot = node[r];
int i = (l - 1);
for (int j = l; j <= r - 1; j++)if ( signed_area( p_minx, node[j], pivot ) >= 0 ) {
i++;
iter_swap(node.begin()+i, node.begin()+j);
}
iter_swap(node.begin()+i+1, node.begin()+r);
return (i + 1);
}
void qsort_c_clockwise__init__( vector<P> &node, int l, int r, P p_minx) { // sort points counter-clockwise
if (l >= r) return;
int pivot = partition(node, l, r, p_minx);
qsort_c_clockwise__init__(node, l, pivot - 1,p_minx);
qsort_c_clockwise__init__(node, pivot + 1, r,p_minx);
return;
}
void qsort_c_clockwise( vector<P> &node) {
vector<P>::iterator itr_minx = min_element(node.begin(), node.end());
iter_swap( node.begin(), itr_minx );
qsort_c_clockwise__init__(node,0,node.size()-1,node[0]);
return;
}
/// difference of y from line(l,r)
int y_overline( P l, P r, P x ){
int an = r.first-l.first, ad = r.second-l.second;
int dy = x.second-l.second, dx = x.first-l.first;
return an*dy - ad*dx;
}
//get id's of contact points
//upper tangent: sgn=-1, lower tangent: sgn=+1,
pair<int,int> tangent(vector<P> pl, vector<P> pr, int sgn){
int il=0, ir=0, nl=pl.size(), nr=pr.size();
auto IDnext = [sgn]( int i, int n ){ return (i+sgn+n)%n; };
int yl = y_overline(pl[il], pr[ir], pl[IDnext(il,nl)] );
int yr = y_overline(pl[il], pr[ir], pr[IDnext(ir,nr)] );
bool judgeL = (sgn*yl<=0)and(nl>1), judgeR = (sgn*yr<=0)and(nr>1);
while( judgeL or judgeR ){
if( judgeL ) il = IDnext(il,nl);
else ir = IDnext(ir,nr);
yl = y_overline(pl[il], pr[ir], pl[IDnext(il,nl)] );
yr = y_overline(pl[il], pr[ir], pr[IDnext(ir,nr)] );
judgeL = (sgn*yl<=0)and(nl>1); judgeR = (sgn*yr<=0)and(nr>1);
}
return make_pair(il,ir);
}
//merge convex full
vector<P> merge(vector<P> pl, vector<P> pr){
qsort_c_clockwise(pr);
for( int i=0; i<pl.size(); ++i ) pl[i].first = -pl[i].first;
qsort_c_clockwise(pl);
for( int i=0; i<pl.size(); ++i ) pl[i].first = -pl[i].first;
pair<int,int> ilow = tangent(pl,pr,1);
pair<int,int> iup = tangent(pl,pr,-1);
//exception case: iup = 0
if(iup.first==0){
iup.first = pl.size();
if(ilow.first==0) --iup.first;
}
if(iup.second==0){
iup.second = pr.size();
if(ilow.second==0) --iup.second;
}
pl.push_back(pl[0]); pr.push_back(pr[0]);
vector<P> cvl{pl.begin()+ilow.first,pl.begin()+iup.first+1};
vector<P> cvr{pr.begin()+ilow.second,pr.begin()+iup.second+1};
cvl.insert(cvl.end(),cvr.rbegin(),cvr.rend());
return cvl;
}
//id of array p to devide
int id_div(vector<P> p){
int x_piv = (p[0].first + p[p.size()-1].first)/2;
P piv = make_pair(x_piv,-inf);
return lower_bound(p.begin(),p.end(),piv) - p.begin();
}
//construct convex full recursively
vector<P> conv_full(vector<P> p){
if(p.size()<3) return p;
sort(p.begin(),p.end());
if(p.size()==3){
// 3 points on the same line
if( y_overline(p[0], p[1], p[2])==0 ){
vector<P> cv{ p[0],p[2] };
return cv;
}
return p;
}
int i_piv = id_div(p);
vector<P> pl{p.begin(),p.begin()+i_piv};
vector<P> pr{p.begin()+i_piv,p.end()};
//exception: ex) x coord. of all points are same
if(pl.size()==0) return pr;
if(pr.size()==0) return pl;
return merge(conv_full(pl),conv_full(pr));
}
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<P> p(n);
for( int i=0; i<n; ++i ) cin >> p[i].first >> p[i].second;
vector<P> ans = conv_full(p);
for( P v : ans ) cout << v.first << " " << v.second << endl;
return 0;
}
各操作の説明
まず最初の部分は2次元平面上の点をxが最小の点$x_{min}$から見た仰角で反時計回りにクイックソートする操作です。ソート後の配列は$x_{min}$が先頭になります。
////quick sort w.r.t. counter-clockwise
int signed_area( P p1, P p2, P p3 ){ // to chech relativistic position of 3 poins
P v1,v2;
v1.first = p2.first-p1.first; v1.second = p2.second-p1.second;
v2.first = p3.first-p1.first; v2.second = p3.second-p1.second;
return v1.first*v2.second - v1.second*v2.first; // calc area as z-component of v1 x v2
}
int partition (vector<P> &node, int l, int r, P p_minx) { // partation for quick sort
P pivot = node[r];
int i = (l - 1);
for (int j = l; j <= r - 1; j++)if ( signed_area( p_minx, node[j], pivot ) >= 0 ) {
i++;
iter_swap(node.begin()+i, node.begin()+j);
}
iter_swap(node.begin()+i+1, node.begin()+r);
return (i + 1);
}
void qsort_c_clockwise__init__( vector<P> &node, int l, int r, P p_minx) { // sort points counter-clockwise
if (l >= r) return;
int pivot = partition(node, l, r, p_minx);
qsort_c_clockwise__init__(node, l, pivot - 1,p_minx);
qsort_c_clockwise__init__(node, pivot + 1, r,p_minx);
return;
}
void qsort_c_clockwise( vector<P> &node) {
vector<P>::iterator itr_minx = min_element(node.begin(), node.end());
iter_swap( node.begin(), itr_minx );
qsort_c_clockwise__init__(node,0,node.size()-1,node[0]);
return;
}
次のパートは凸包を統合する操作です。
まずは左右の凸包をそれぞれ反時計回りにソートします。ただ、基準の点を$x_{piv}$に最も近い点にしたいので、左の凸包については$x$を反転させてからソートします。次に上部/下部接線の接点のインデックス$i_{up},i_{low}$を求めれば$i_{low}$から$i_{up}$までの部分列が統合後の凸包にも使われる外側の点です。
/// difference of y from line(l,r)
int y_overline( P l, P r, P x ){
int an = r.first-l.first, ad = r.second-l.second;
int dy = x.second-l.second, dx = x.first-l.first;
return an*dy - ad*dx;
}
//get id's of contact points
//upper tangent: sgn=-1, lower tangent: sgn=+1,
pair<int,int> tangent(vector<P> pl, vector<P> pr, int sgn){
int il=0, ir=0, nl=pl.size(), nr=pr.size();
auto IDnext = [sgn]( int i, int n ){ return (i+sgn+n)%n; };
int yl = y_overline(pl[il], pr[ir], pl[IDnext(il,nl)] );
int yr = y_overline(pl[il], pr[ir], pr[IDnext(ir,nr)] );
bool judgeL = (sgn*yl<=0)and(nl>1), judgeR = (sgn*yr<=0)and(nr>1);
while( judgeL or judgeR ){
if( judgeL ) il = IDnext(il,nl);
else ir = IDnext(ir,nr);
yl = y_overline(pl[il], pr[ir], pl[IDnext(il,nl)] );
yr = y_overline(pl[il], pr[ir], pr[IDnext(ir,nr)] );
judgeL = (sgn*yl<=0)and(nl>1); judgeR = (sgn*yr<=0)and(nr>1);
}
return make_pair(il,ir);
}
//merge convex full
vector<P> merge(vector<P> pl, vector<P> pr){
qsort_c_clockwise(pr);
for( int i=0; i<pl.size(); ++i ) pl[i].first = -pl[i].first;
qsort_c_clockwise(pl);
for( int i=0; i<pl.size(); ++i ) pl[i].first = -pl[i].first;
pair<int,int> ilow = tangent(pl,pr,1);
pair<int,int> iup = tangent(pl,pr,-1);
//exception case: iup = 0
if(iup.first==0){
iup.first = pl.size();
if(ilow.first==0) --iup.first;
}
if(iup.second==0){
iup.second = pr.size();
if(ilow.second==0) --iup.second;
}
pl.push_back(pl[0]); pr.push_back(pr[0]);
vector<P> cvl{pl.begin()+ilow.first,pl.begin()+iup.first+1};
vector<P> cvr{pr.begin()+ilow.second,pr.begin()+iup.second+1};
cvl.insert(cvl.end(),cvr.rbegin(),cvr.rend());
return cvl;
}
最後のパートは点集合を真ん中で分けてそれぞれ凸包を求めたのちに統合する操作を再帰的に行います。
//id of array p to devide
int id_div(vector<P> p){
int x_piv = (p[0].first + p[p.size()-1].first)/2;
P piv = make_pair(x_piv,-inf);
return lower_bound(p.begin(),p.end(),piv) - p.begin();
}
//construct convex full recursively
vector<P> conv_full(vector<P> p){
if(p.size()<3) return p;
sort(p.begin(),p.end());
if(p.size()==3){
// 3 points on the same line
if( y_overline(p[0], p[1], p[2])==0 ){
vector<P> cv{ p[0],p[2] };
return cv;
}
return p;
}
int i_piv = id_div(p);
vector<P> pl{p.begin(),p.begin()+i_piv};
vector<P> pr{p.begin()+i_piv,p.end()};
//exception: ex) x coord. of all points are same
if(pl.size()==0) return pr;
if(pr.size()==0) return pl;
return merge(conv_full(pl),conv_full(pr));
}
実行結果
次の入力で試してみます。
10
1 -2
-1 2
-3 3
-6 -3
7 0
4 -9
5 6
-5 8
0 4
4 0
```
この点集合を図示すると次のようになります。

実行すると結果は以下のようになります。
```
-6 -3
-5 8
5 6
7 0
4 -9
```
これらの点を線で結んで図示すると確かに凸包になっています。

# 参考ページ
- http://www-ikn.ist.hokudai.ac.jp/~k-sekine/slides/convexhull.pdf