はじめに
へー遺伝的アルゴリズムってやつがあるのか〜。011101010...これって特徴量選択に使えるのでは?と思ったら当たり前のようにやっている人がいました。先駆者の方のコードを参考に自分なりにまとめ直しました。n番煎じです。
参考
- 遺伝的アルゴリズムで特徴量選択(https://horomary.hatenablog.com/entry/2019/03/10/190919)
- 遺伝的アルゴリズムに入門するときに参考になったスライドとOneMax問題の実装(https://tech.mof-mof.co.jp/blog/ga-one-max-problem.html)
- Azunyan1111
/
OneMax(https://github.com/Azunyan1111/OneMax)
手順
遺伝的アルゴリズムの実装
遺伝的アルゴリズムの詳細はこちらが参考になります。この記事ではOneMax問題を例題にします。OneMax問題は、初期値として与えられた[0,1,0,1,1,1,0,...]という配列の要素をすべて1にする問題で、これを遺伝的アルゴリズムで解いてみます。
コードはこちらのgithubを参考にさせていただきました。遺伝的アルゴリズムに出てくる用語や変数の名前はこちらを参考にしました。簡単にまとめると、0または1をとるスカラー値を遺伝子(gene)、遺伝子を集めて配列[0,0,1,1,0,1,...]としたものを染色体(chromosome)、染色体を持った体?を個体(individual)としました。設計上は個体が属性として染色体を持つようにしています。個体の集合を集団(population)としました。アルゴリズムはエリート選択で、ルーレット選択はしていません。
遺伝的アルゴリズムに必要になる要素は下記です。
"""
著作 Azunyan https://github.com/Azunyan1111/OneMax
"""
"""
改変 Copyright 2020 ground0state All Rights Reserved.
"""
import random
import time
class Individual():
"""個体.
Parameters
----------
chromosome : list of {0 or 1}
染色体.
evaluation : float
評価.
"""
chromosome = None
evaluation = None
def __init__(self, chromosome, evaluation):
self.chromosome = chromosome
self.evaluation = evaluation
def create_individual(length):
"""引数で指定された桁のランダムな染色体を生成、格納した個体を返します.
Parameters
----------
length : int
染色体の長さ.
Returns
-------
individual : Individual
個体.
"""
individual = Individual([random.randint(0, 1) for i in range(length)], 0)
return individual
def evaluate_individual(individual):
"""評価関数.
Parameters
----------
individual : Individual
個体.
Returns
-------
eval : float
評価値.
"""
eval = sum(individual.chromosome)/len(individual.chromosome)
return eval
def extract_elites(population, num):
"""選択関数.
Parameters
----------
population : list of Individual
集団.
num : int
個体選択数.
Returns
-------
elites : list of Individual
選択処理をした集団.
"""
# 現行世代個体集団の評価を高い順番にソートする
sort_result = sorted(population, reverse=True, key=lambda individual: individual.evaluation)
# 一定の上位を抽出する
elites = sort_result[:num]
return elites
def crossover(individual1, individual2, chromosome_length):
"""交叉関数.
二点交叉を行います.
Parameters
----------
individual1 : Individual
交叉する個体1.
individual2 : Individual
交叉する個体2.
chromosome_length : int
染色体の長さ.
Returns
-------
offsprings : list of Individual
二つの孫.
"""
# 入れ替える二点の点を設定します
cross_one = random.randint(0, chromosome_length)
cross_second = random.randint(cross_one, chromosome_length)
# 遺伝子を取り出します
one = individual1.chromosome
second = individual2.chromosome
# 交叉させます
progeny_one = one[:cross_one] + second[cross_one:cross_second] + one[cross_second:]
progeny_second = second[:cross_one] + one[cross_one:cross_second] + second[cross_second:]
# 子孫
offsprings = [Individual(progeny_one, 0), Individual(progeny_second, 0)]
return offsprings
def create_next_generation(population, elites, offsprings):
"""世代交代処理を行います.
Parameters
----------
population : list of Individual
現行世代個体集団.
elites : list of Individual
現行世代エリート集団.
offsprings : list of Individual
現行世代子孫集団.
Returns
-------
next_generation_population : list of Individual
次世代個体集団.
"""
# 現行世代個体集団の評価を低い順番にソートする
next_generation_population = sorted(population, reverse=False, key=lambda individual: individual.evaluation)
# 追加するエリート集団と子孫集団の合計ぶんを取り除く
next_generation_population = next_generation_population[len(elites)+len(offsprings):]
# エリート集団と子孫集団を次世代集団を次世代へ追加します
next_generation_population.extend(elites)
next_generation_population.extend(offsprings)
return next_generation_population
def mutation(population, induvidual_mutation_probability, gene_mutation_probability):
"""突然変異関数.
Parameters
----------
population : list of Individual
集団.
induvidual_mutation_probability : float in [0, 1]
個体突然変異確率.
gene_mutation_probability : float in [0, 1]
遺伝子突然変異確率.
Returns
-------
new_population : list of Individual
突然変異処理した集団.
"""
new_population = []
for individual in population:
# 個体に対して一定の確率で突然変異が起きる
if induvidual_mutation_probability > random.random():
new_chromosome = []
for gene in individual.chromosome:
# 個体の遺伝子情報一つ一つに対して突然変異がおこる
if gene_mutation_probability > random.random():
new_chromosome.append(random.randint(0, 1))
else:
new_chromosome.append(gene)
individual.chromosome = new_chromosome
new_population.append(individual)
else:
new_population.append(individual)
return new_population
これらのクラスと関数を用いて、次のコードで実行します。
# 染色体の長さ
CHROMOSOME_LENGTH = 13
# 集団の大きさ
POPULATION_SIZE = 30
# エリート染色体選抜数
PICK_OUT_SIZE = 5
# 個体突然変異確率
INDIVIDUAL_MUTATION_PROBABILITY = 0.3
# 遺伝子突然変異確率
GENE_MUTATION_PROBABILITY = 0.1
# 繰り返す世代数
ITERATION = 10
# 現行世代の個体集団を初期化します
current_generation_population = [create_individual(CHROMOSOME_LENGTH) for i in range(POPULATION_SIZE)]
for count in range(ITERATION):
# 各ループの開始時刻
start = time.time()
# 現行世代個体集団の個体を評価
for individual in current_generation_population:
individual.evaluation = evaluate_individual(individual)
# エリート個体を選択します
elites = extract_elites(current_generation_population, PICK_OUT_SIZE)
# エリート遺伝子を交叉させ、リストに格納します
offsprings = []
for i in range(0, PICK_OUT_SIZE-1):
offsprings.extend(crossover(elites[i], elites[i+1], CHROMOSOME_LENGTH))
# 次世代個体集団を現行世代、エリート集団、子孫集団から作成します
next_generation_population = create_next_generation(current_generation_population, elites, offsprings)
# 次世代個体集団全ての個体に突然変異を施します。
next_generation_population = mutation(next_generation_population,
INDIVIDUAL_MUTATION_PROBABILITY,
GENE_MUTATION_PROBABILITY)
# 1世代の進化的計算終了。評価に移ります
# 各個体の評価値を配列化します。
fits = [individual.evaluation for individual in current_generation_population]
# 進化結果を評価します
min_val = min(fits)
max_val = max(fits)
avg_val = sum(fits) / len(fits)
# 現行世代の進化結果を出力します
print("-----第{}世代の結果-----".format(count+1))
print(" Min:{}".format(min_val))
print(" Max:{}".format(max_val))
print(" Avg:{}".format(avg_val))
# 現行世代と次世代を入れ替えます
current_generation_population = next_generation_population
# 時間計測
elapsed_time = time.time() - start
print (" {}/{} elapsed_time:{:.2f}".format(count+1, ITERATION, elapsed_time) + "[sec]")
# 最終結果出力
print("") # 改行
print("最も優れた個体は{}".format(elites[0].chromosome))
出力はつぎのようになります。
-----第1世代の結果-----
Min:0.23076923076923078
Max:0.8461538461538461
Avg:0.5384615384615384
1/10 elapsed_time:0.00[sec]
-----第2世代の結果-----
Min:0.46153846153846156
Max:0.8461538461538461
Avg:0.6692307692307694
2/10 elapsed_time:0.00[sec]
-----第3世代の結果-----
Min:0.6923076923076923
Max:0.9230769230769231
Avg:0.761538461538462
3/10 elapsed_time:0.00[sec]
-----第4世代の結果-----
Min:0.6923076923076923
Max:0.9230769230769231
Avg:0.8102564102564106
4/10 elapsed_time:0.00[sec]
-----第5世代の結果-----
Min:0.6923076923076923
Max:0.9230769230769231
Avg:0.8512820512820515
5/10 elapsed_time:0.00[sec]
-----第6世代の結果-----
Min:0.7692307692307693
Max:0.9230769230769231
Avg:0.848717948717949
6/10 elapsed_time:0.00[sec]
-----第7世代の結果-----
Min:0.7692307692307693
Max:0.9230769230769231
Avg:0.8948717948717951
7/10 elapsed_time:0.00[sec]
-----第8世代の結果-----
Min:0.6153846153846154
Max:0.9230769230769231
Avg:0.8974358974358977
8/10 elapsed_time:0.00[sec]
-----第9世代の結果-----
Min:0.7692307692307693
Max:0.9230769230769231
Avg:0.9000000000000002
9/10 elapsed_time:0.00[sec]
-----第10世代の結果-----
Min:0.8461538461538461
Max:1.0
Avg:0.9102564102564105
10/10 elapsed_time:0.00[sec]
最も優れた個体は[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
要素がすべて1の個体を得ることが出来ました。
遺伝的アルゴリズムで特徴量選択
こちらを参考にしてデータとモデルを準備しました。
データの準備は次のコードです。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# データセットのロード
X = pd.DataFrame(load_boston().data, columns=load_boston().feature_names)
y = load_boston().target
# 多項式特徴量を追加
poly = PolynomialFeatures(2)
poly.fit(X)
X_poly = pd.DataFrame(poly.transform(X), columns=poly.get_feature_names(input_features=X.columns))
# 標準化
sc = StandardScaler()
X_sc = pd.DataFrame(sc.fit_transform(X), columns=X.columns)
X_poly_sc = pd.DataFrame(sc.fit_transform(X_poly), columns=X_poly.columns)
特徴量が多いパターンを検証するために、PolynomialFeaturesを使って特徴量を増やしたものがX_poly_scです。
そのままのデータセットでのモデル。
from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeCV
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# そのままのデータセット
scores = []
for _ in range(30):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_sc, y, test_size=0.4)
model = RidgeCV()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
scores.append(model.score(X_test, y_test))
print(np.array(scores).mean()) # 0.70
多項式特徴量を追加したモデル。
from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeCV
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 多項式特徴量を追加した場合
scores = []
for _ in range(30):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_poly_sc, y, test_size=0.4)
model = RidgeCV()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
scores.append(model.score(X_test, y_test))
print(np.array(scores).mean()) # 0.82
さて、このモデルに対し遺伝的アルゴリズムで特徴量選択を行いましょう。改変するのはevaluate_individualメソッドです。個体の染色体をインプットとしてブール値に変換し、使用する列の指定を行います。その後モデルを用いて学習、スコアを算出しています。スコアを個体の評価値としてreturnしています。
def evaluate_individual(individual):
"""評価関数.
Parameters
----------
individual : Individual
個体.
Returns
-------
eval : float
評価値.
"""
use_cols = [bool(gene) for gene in individual.chromosome]
X_temp = X_sc.iloc[:, use_cols]
scores = []
for _ in range(30):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_temp, y, test_size=0.4)
model = RidgeCV()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
scores.append(model.score(X_test, y_test))
eval = float(np.array(scores).mean())
return eval
パラメータを下記のものに変えて実行してみました。
# 染色体の長さ
CHROMOSOME_LENGTH = 13
# 集団の大きさ
POPULATION_SIZE = 100
# エリート染色体選抜数
PICK_OUT_SIZE = 20
# 個体突然変異確率
INDIVIDUAL_MUTATION_PROBABILITY = 0.3
# 遺伝子突然変異確率
GENE_MUTATION_PROBABILITY = 0.1
# 繰り返す世代数
ITERATION = 10
結果は次のようになりました。
-----第1世代の結果-----
Min:0.245482696210891
Max:0.7062246093438559
Avg:0.5643638813331334
1/10 elapsed_time:13.21[sec]
-----第2世代の結果-----
Min:0.28765890628509017
Max:0.7175019664075553
Avg:0.6611343782899052
2/10 elapsed_time:14.07[sec]
-----第3世代の結果-----
Min:0.5958052127889627
Max:0.7343341487237112
Avg:0.6840346805288029
3/10 elapsed_time:14.39[sec]
-----第4世代の結果-----
Min:0.6011227398695212
Max:0.7265364514547696
Avg:0.694531099756538
4/10 elapsed_time:11.29[sec]
-----第5世代の結果-----
Min:0.6314510371602322
Max:0.7249977461594102
Avg:0.6938166370760438
5/10 elapsed_time:11.72[sec]
-----第6世代の結果-----
Min:0.6539907671434392
Max:0.7256998515926862
Avg:0.7042345770684423
6/10 elapsed_time:11.44[sec]
-----第7世代の結果-----
Min:0.6557998988298114
Max:0.7273580445493621
Avg:0.7009249865262361
7/10 elapsed_time:9.64[sec]
-----第8世代の結果-----
Min:0.6530159418050802
Max:0.7250968150681534
Avg:0.7044189020700958
8/10 elapsed_time:9.90[sec]
-----第9世代の結果-----
Min:0.6087336519329122
Max:0.7316442169584539
Avg:0.7008118423172378
9/10 elapsed_time:9.64[sec]
-----第10世代の結果-----
Min:0.6328245771251623
Max:0.7244970729879131
Avg:0.7034862249363725
10/10 elapsed_time:13.06[sec]
最も優れた個体は[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
スコアが0.72になっているので、より良い特徴量選択が出来ています。
クラス化
使い回せるようにクラス化しました。抽象クラスとして作成し、継承してevaluate_individualを実装します。
"""
著作 Azunyan https://github.com/Azunyan1111/OneMax
"""
"""
改変 Copyright 2020 ground0state All Rights Reserved.
"""
import random
import time
from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod
class Individual():
"""個体.
Parameters
----------
chromosome : list of {0 or 1}
染色体.
evaluation : float
評価.
"""
chromosome = None
evaluation = None
def __init__(self, chromosome, evaluation):
self.chromosome = chromosome
self.evaluation = evaluation
class GaSolver(metaclass=ABCMeta):
"""遺伝的アルゴリズムの抽象クラス.
染色体に対して、評価値を出力するメソッド「evaluate_individual」は要実装.
Parameters
----------
chromosome_length : int
染色体の長さ.
population_size : int
集団の大きさ.
pick_out_size : int
エリート染色体選抜数.
individual_mutation_probability : float
個体突然変異確率.
gene_mutation_probability : float
遺伝子突然変異確率.
iteration : int
繰り返す世代数.
"""
def __init__(self, chromosome_length, population_size, pick_out_size,
individual_mutation_probability=0.3, gene_mutation_probability=0.1, iteration=1, verbose=True):
self.chromosome_length = chromosome_length
self.population_size = population_size
self.pick_out_size = pick_out_size
self.individual_mutation_probability = individual_mutation_probability
self.gene_mutation_probability = gene_mutation_probability
self.iteration = iteration
self.verbose = verbose
self.history = None
def _create_individual(self, length):
"""引数で指定された桁のランダムな染色体を生成、格納した個体を返します.
Parameters
----------
length : int
染色体の長さ.
Returns
-------
individual : Individual
個体.
"""
individual = Individual([random.randint(0, 1) for i in range(length)], 0)
return individual
@abstractmethod
def evaluate_individual(self, individual, X, y):
"""評価関数.
Parameters
----------
individual : Individual
個体.
X : pandas.DataFrame
説明変数.
y : pandas.DataFrame
目的変数.
Returns
-------
eval : float
評価値.
"""
raise NotImplementedError()
def _extract_elites(self, population, num):
"""選択関数.
Parameters
----------
population : list of Individual
集団.
num : int
個体選択数.
Returns
-------
elites : list of Individual
選択処理をした集団.
"""
# 現行世代個体集団の評価を高い順番にソートする
sort_result = sorted(population, reverse=True, key=lambda individual: individual.evaluation)
# 一定の上位を抽出する
elites = sort_result[:num]
return elites
def _crossover(self, individual1, individual2, chromosome_length):
"""交叉関数.
二点交叉を行います.
Parameters
----------
individual1 : Individual
交叉する個体1.
individual2 : Individual
交叉する個体2.
chromosome_length : int
染色体の長さ.
Returns
-------
offsprings : list of Individual
二つの孫.
"""
# 入れ替える二点の点を設定します
cross_one = random.randint(0, chromosome_length)
cross_second = random.randint(cross_one, chromosome_length)
# 遺伝子を取り出します
one = individual1.chromosome
second = individual2.chromosome
# 交叉させます
progeny_one = one[:cross_one] + second[cross_one:cross_second] + one[cross_second:]
progeny_second = second[:cross_one] + one[cross_one:cross_second] + second[cross_second:]
# 子孫
offsprings = [Individual(progeny_one, 0), Individual(progeny_second, 0)]
return offsprings
def _create_next_generation(self, population, elites, offsprings):
"""世代交代処理を行います.
Parameters
----------
population : list of Individual
現行世代個体集団.
elites : list of Individual
現行世代エリート集団.
offsprings : list of Individual
現行世代子孫集団.
Returns
-------
next_generation_population : list of Individual
次世代個体集団.
"""
# 現行世代個体集団の評価を低い順番にソートする
next_generation_population = sorted(population, reverse=False, key=lambda individual: individual.evaluation)
# 追加するエリート集団と子孫集団の合計ぶんを取り除く
next_generation_population = next_generation_population[len(elites)+len(offsprings):]
# エリート集団と子孫集団を次世代集団を次世代へ追加します
next_generation_population.extend(elites)
next_generation_population.extend(offsprings)
return next_generation_population
def _mutation(self, population, induvidual__mutation_probability, gene__mutation_probability):
"""突然変異関数.
Parameters
----------
population : list of Individual
集団.
induvidual__mutation_probability : float in [0, 1]
個体突然変異確率.
gene__mutation_probability : float in [0, 1]
遺伝子突然変異確率.
Returns
-------
new_population : list of Individual
突然変異処理した集団.
"""
new_population = []
for individual in population:
# 個体に対して一定の確率で突然変異が起きる
if induvidual__mutation_probability > random.random():
new_chromosome = []
for gene in individual.chromosome:
# 個体の遺伝子情報一つ一つに対して突然変異がおこる
if gene__mutation_probability > random.random():
new_chromosome.append(random.randint(0, 1))
else:
new_chromosome.append(gene)
individual.chromosome = new_chromosome
new_population.append(individual)
else:
new_population.append(individual)
return new_population
def solve(self, X, y):
"""遺伝的アルゴリズムのメインクラス.
Returns
-------
list of {0 or 1}
最も優れた個体の染色体.
"""
self.history = {"Min":[], "Max":[], "Avg":[], "BestChromosome":[]}
# 現行世代の個体集団を初期化します
current_generation_population = [self._create_individual(self.chromosome_length) for i in range(self.population_size)]
# 現行世代個体集団の個体を評価
for individual in current_generation_population:
individual.evaluation = self.evaluate_individual(individual, X, y)
for count in range(self.iteration):
# 各ループの開始時刻
start = time.time()
# エリート個体を選択します
elites = self._extract_elites(current_generation_population, self.pick_out_size)
# エリート遺伝子を交叉させ、リストに格納します
offsprings = []
for i in range(0, self.pick_out_size-1):
offsprings.extend(self._crossover(elites[i], elites[i+1], self.chromosome_length))
# 次世代個体集団を現行世代、エリート集団、子孫集団から作成します
next_generation_population = self._create_next_generation(current_generation_population, elites, offsprings)
# 次世代個体集団全ての個体に突然変異を施します。
next_generation_population = self._mutation(next_generation_population,
self.individual_mutation_probability,
self.gene_mutation_probability)
# 現行世代個体集団の個体を評価
for individual in current_generation_population:
individual.evaluation = self.evaluate_individual(individual, X, y)
# 1世代の進化的計算終了。評価に移ります
# 各個体の評価値を配列化します。
fits = [individual.evaluation for individual in current_generation_population]
# 最も評価値のよい個体を取り出します
best_individual = self._extract_elites(current_generation_population, 1)
best_chromosome = best_individual[0].chromosome
# 進化結果を評価します
min_val = min(fits)
max_val = max(fits)
avg_val = sum(fits) / len(fits)
# 現行世代の進化結果を出力します
if self.verbose:
print("-----第{}世代の結果-----".format(count+1))
print(" Min:{}".format(min_val))
print(" Max:{}".format(max_val))
print(" Avg:{}".format(avg_val))
# history作成
self.history["Min"].append(min_val)
self.history["Max"].append(max_val)
self.history["Avg"].append(avg_val)
self.history["BestChromosome"].append(best_chromosome)
# 現行世代と次世代を入れ替えます
current_generation_population = next_generation_population
# 時間計測
elapsed_time = time.time() - start
print (" {}/{} elapsed_time:{:.2f}".format(count+1, self.iteration, elapsed_time) + "[sec]")
# 最終結果出力
if self.verbose:
print("") # 改行
print("最も優れた個体は{}".format(elites[0].chromosome))
return self.history
evaluate_individualに評価したい機械学習モデルを実装します。
from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeCV
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
class GaSolverImpl(GaSolver):
# override
def evaluate_individual(self, individual, X, y):
use_cols = [bool(gene) for gene in individual.chromosome]
X_temp = X.iloc[:, use_cols]
scores = []
for _ in range(30):
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_temp, y, test_size=0.4)
model = RidgeCV()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
scores.append(model.score(X_test, y_test))
eval = float(np.array(scores).mean())
return eval
実装クラスのインスタンスを生成して、データを渡して実行します。solveメソッドは履歴であるhistoryを返却します。
solver = GaSolverImpl(
chromosome_length = X_poly_sc.shape[1],
population_size = 50,
pick_out_size = 10,
individual_mutation_probability = 0.3,
gene_mutation_probability = 0.1,
iteration = 50,
verbose = True
)
history = solver.solve(X_poly_sc, y)
実行結果は次のようになります。
-----第1世代の結果-----
Min:0.7248417700796147
Max:0.8360838319205105
Avg:0.7927103625892467
1/50 elapsed_time:6.13[sec]
-----第2世代の結果-----
Min:0.7350424889460248
Max:0.8264758137896353
Avg:0.8114411035733131
2/50 elapsed_time:10.81[sec]
-----第3世代の結果-----
Min:0.7902116792529935
Max:0.8286229243915363
Avg:0.8125974889978004
3/50 elapsed_time:8.20[sec]
-----第4世代の結果-----
Min:0.773199874021567
Max:0.8312887517624212
Avg:0.810950812639705
4/50 elapsed_time:7.56[sec]
-----第5世代の結果-----
Min:0.768479730905661
Max:0.8386114466226944
Avg:0.8076230726252596
5/50 elapsed_time:8.13[sec]
-----第6世代の結果-----
Min:0.7797249579245809
Max:0.8319768049107215
Avg:0.8138790949911054
6/50 elapsed_time:9.00[sec]
-----第7世代の結果-----
Min:0.7971344524880782
Max:0.8333411281001641
Avg:0.8168863897838727
7/50 elapsed_time:7.56[sec]
-----第8世代の結果-----
Min:0.7709812458007903
Max:0.8316092177782253
Avg:0.8082876757394714
8/50 elapsed_time:7.96[sec]
-----第9世代の結果-----
Min:0.7459891729563418
Max:0.8322393628831635
Avg:0.8159389943969992
9/50 elapsed_time:8.77[sec]
-----第10世代の結果-----
Min:0.7538656919599587
Max:0.8254541549046537
Avg:0.8034195187548075
10/50 elapsed_time:8.99[sec]
-----第11世代の結果-----
Min:0.8046900766607942
Max:0.8379618406470278
Avg:0.8217659811828382
11/50 elapsed_time:8.60[sec]
-----第12世代の結果-----
Min:0.8020625272756005
Max:0.8356958927515973
Avg:0.8132506462797608
12/50 elapsed_time:8.31[sec]
-----第13世代の結果-----
Min:0.7442093041785434
Max:0.826166208838109
Avg:0.7693376466706999
13/50 elapsed_time:9.22[sec]
-----第14世代の結果-----
Min:0.80133807286147
Max:0.8264198880246336
Avg:0.8085481113173225
14/50 elapsed_time:8.08[sec]
-----第15世代の結果-----
Min:0.7316094852550766
Max:0.8139831643344952
Avg:0.7929373870389733
15/50 elapsed_time:8.92[sec]
-----第16世代の結果-----
Min:0.7955982071682629
Max:0.8210496822695305
Avg:0.8134173712784526
16/50 elapsed_time:9.72[sec]
-----第17世代の結果-----
Min:0.758489267352653
Max:0.826441026953439
Avg:0.7773437348210647
17/50 elapsed_time:8.58[sec]
-----第18世代の結果-----
Min:0.7687388062022248
Max:0.8211801466346264
Avg:0.7826663042340634
18/50 elapsed_time:6.94[sec]
-----第19世代の結果-----
Min:0.7429453738843712
Max:0.794799782442768
Avg:0.7525262014670999
19/50 elapsed_time:8.35[sec]
-----第20世代の結果-----
Min:0.7059056866516289
Max:0.8115968792777923
Avg:0.7941420197838582
20/50 elapsed_time:7.01[sec]
-----第21世代の結果-----
Min:0.7035195424104084
Max:0.8339769569079513
Avg:0.785429874209423
21/50 elapsed_time:8.84[sec]
-----第22世代の結果-----
Min:0.7605334574905934
Max:0.8178769887665864
Avg:0.7764313614722025
22/50 elapsed_time:8.89[sec]
-----第23世代の結果-----
Min:0.7622888571603964
Max:0.8125955330567856
Avg:0.7761008854264979
23/50 elapsed_time:8.47[sec]
-----第24世代の結果-----
Min:0.7325862134323571
Max:0.7781021993458462
Avg:0.76629374412332
24/50 elapsed_time:6.80[sec]
-----第25世代の結果-----
Min:0.7155008056263605
Max:0.7770200781667415
Avg:0.7679494414264083
25/50 elapsed_time:6.34[sec]
-----第26世代の結果-----
Min:0.7435193687961383
Max:0.8178098302473983
Avg:0.8025839605868198
26/50 elapsed_time:7.55[sec]
-----第27世代の結果-----
Min:0.757023831644299
Max:0.8134233524435134
Avg:0.7987707913780304
27/50 elapsed_time:8.24[sec]
-----第28世代の結果-----
Min:0.7731968991993663
Max:0.8307874217208041
Avg:0.7886999734804412
28/50 elapsed_time:6.93[sec]
-----第29世代の結果-----
Min:0.7918044164374493
Max:0.8258234982562584
Avg:0.8092356291245499
29/50 elapsed_time:6.45[sec]
-----第30世代の結果-----
Min:0.7742914329017841
Max:0.8170916314535998
Avg:0.8057764064558626
30/50 elapsed_time:6.46[sec]
-----第31世代の結果-----
Min:0.7900272740547029
Max:0.8252185280503214
Avg:0.8121724282164997
31/50 elapsed_time:6.87[sec]
-----第32世代の結果-----
Min:0.7668694386968217
Max:0.8231354707898234
Avg:0.8170271080711664
32/50 elapsed_time:7.61[sec]
-----第33世代の結果-----
Min:0.7721459013264073
Max:0.8365223852672053
Avg:0.82567433930934
33/50 elapsed_time:8.28[sec]
-----第34世代の結果-----
Min:0.802896605790934
Max:0.8367820565860135
Avg:0.8256706142219095
34/50 elapsed_time:7.94[sec]
-----第35世代の結果-----
Min:0.8188038196577934
Max:0.8388260026966802
Avg:0.8358101024561487
35/50 elapsed_time:7.64[sec]
-----第36世代の結果-----
Min:0.7887209549961678
Max:0.8386551764887261
Avg:0.8301462683188676
36/50 elapsed_time:8.13[sec]
-----第37世代の結果-----
Min:0.7862123272076996
Max:0.8405895787926129
Avg:0.8165090312639174
37/50 elapsed_time:7.54[sec]
-----第38世代の結果-----
Min:0.79041640507099
Max:0.8389789987982965
Avg:0.8075935438809548
38/50 elapsed_time:8.58[sec]
-----第39世代の結果-----
Min:0.7632897869020304
Max:0.8249959874282974
Avg:0.7783194384843993
39/50 elapsed_time:8.18[sec]
-----第40世代の結果-----
Min:0.7391820233337305
Max:0.8140492870179213
Avg:0.7954486450055553
40/50 elapsed_time:6.36[sec]
-----第41世代の結果-----
Min:0.7085099265464342
Max:0.7981244256568432
Avg:0.7831723305042879
41/50 elapsed_time:7.90[sec]
-----第42世代の結果-----
Min:0.7826056505944214
Max:0.8327777219420097
Avg:0.8064707164336307
42/50 elapsed_time:7.53[sec]
-----第43世代の結果-----
Min:0.7799209160785368
Max:0.8183673115100479
Avg:0.7992172395182555
43/50 elapsed_time:6.74[sec]
-----第44世代の結果-----
Min:0.756001056689909
Max:0.8338583079593664
Avg:0.8051445406627477
44/50 elapsed_time:6.31[sec]
-----第45世代の結果-----
Min:0.7755735607344747
Max:0.8283597660188781
Avg:0.7882919431369523
45/50 elapsed_time:6.52[sec]
-----第46世代の結果-----
Min:0.7766070559704219
Max:0.8165316562327392
Avg:0.8106111873738964
46/50 elapsed_time:7.22[sec]
-----第47世代の結果-----
Min:0.7780606007516856
Max:0.8084622225234689
Avg:0.7942400594914705
47/50 elapsed_time:9.72[sec]
-----第48世代の結果-----
Min:0.7745173603676726
Max:0.8363078519583506
Avg:0.8206202750563127
48/50 elapsed_time:10.67[sec]
-----第49世代の結果-----
Min:0.7800301936781145
Max:0.8368475790583294
Avg:0.8222375502197947
49/50 elapsed_time:7.54[sec]
-----第50世代の結果-----
Min:0.8077617917763787
Max:0.841354566380394
Avg:0.8147771424682558
50/50 elapsed_time:6.78[sec]
最も優れた個体は[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1]
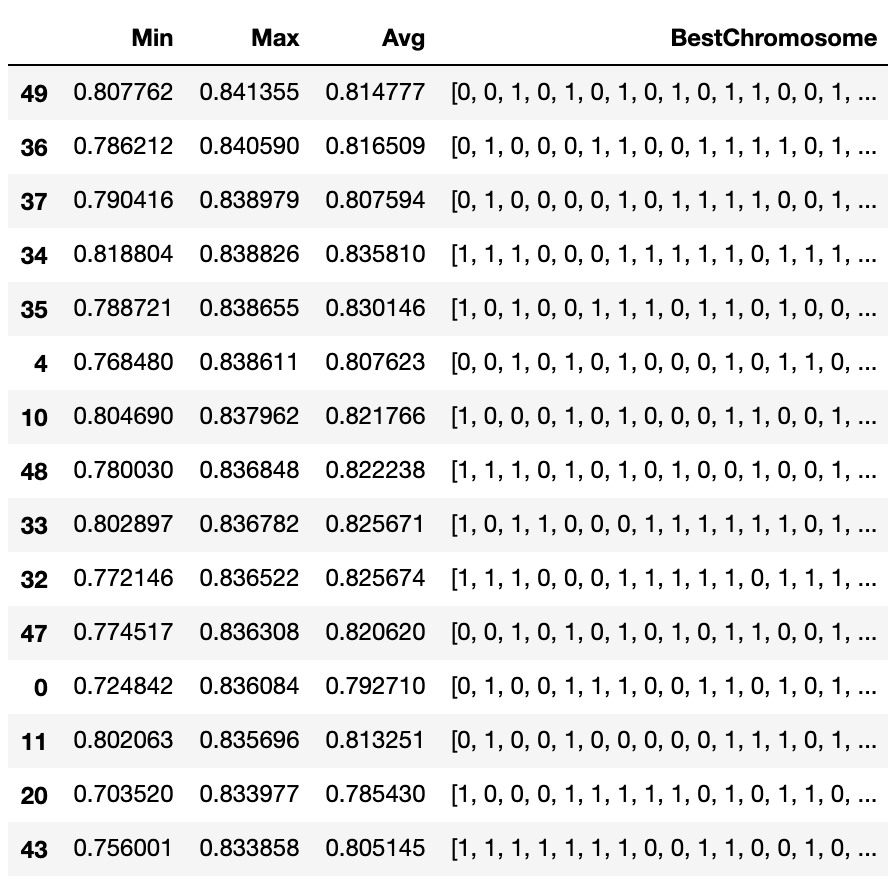
hisotryは次のようになります。
df = pd.DataFrame(history)

最終的に使用するカラムはMax列でソートして、上からいくつかを試してみて、ハイパーパラメータのサーチなども加味して採用すれば良いのではないでしょうか。
df.sort_values(["Max"], ascending=False)
おわりに
遺伝的アルゴリズムで特徴量選択をしてみました。遺伝的アルゴリズムにも種類があるようで、こちらのサイトで使用されているDEAPといったライブラリを使ってみるのもいいかもしれません。