はじめに
k-means法について勉強した内容をまとめました。
最もベーシックなクラスタリングアルゴリズムです。
参考
k-means法の理解に当たって下記を参考にさせていただきました。
- 言語処理のための機械学習入門 (自然言語処理シリーズ) 高村 大也 (著), 奥村 学 (監修) 出版社; コロナ社
- 機械学習のエッセンス 加藤公一(著) 出版社; SBクリエイティブ株式会社
k-means法概要
k-means法とは何か
k-means法は、まずデータを適当なクラスタに分けた後、クラスタの平均を用いてうまい具合にデータがわかれるように調整させていくアルゴリズムです。任意の指定のk個のクラスタを作成するアルゴリズムであることから、k-means法(k点平均法と呼ばれています。)
k-means法のアルゴリズム
k-mean法は具体的には下記のような工程を辿ります。
- 各点$x_{i}$に対してランダムにクラスタを割り振る
- 各クラスタに割り当てられた点について重心を計算する
- 各点について上記で計算された重心からの距離を計算し、距離が一番近いクラスタに割り当て直す。
- 2.と3.の工程を、割り当てられるクラスタが変化しなくなるまで行う
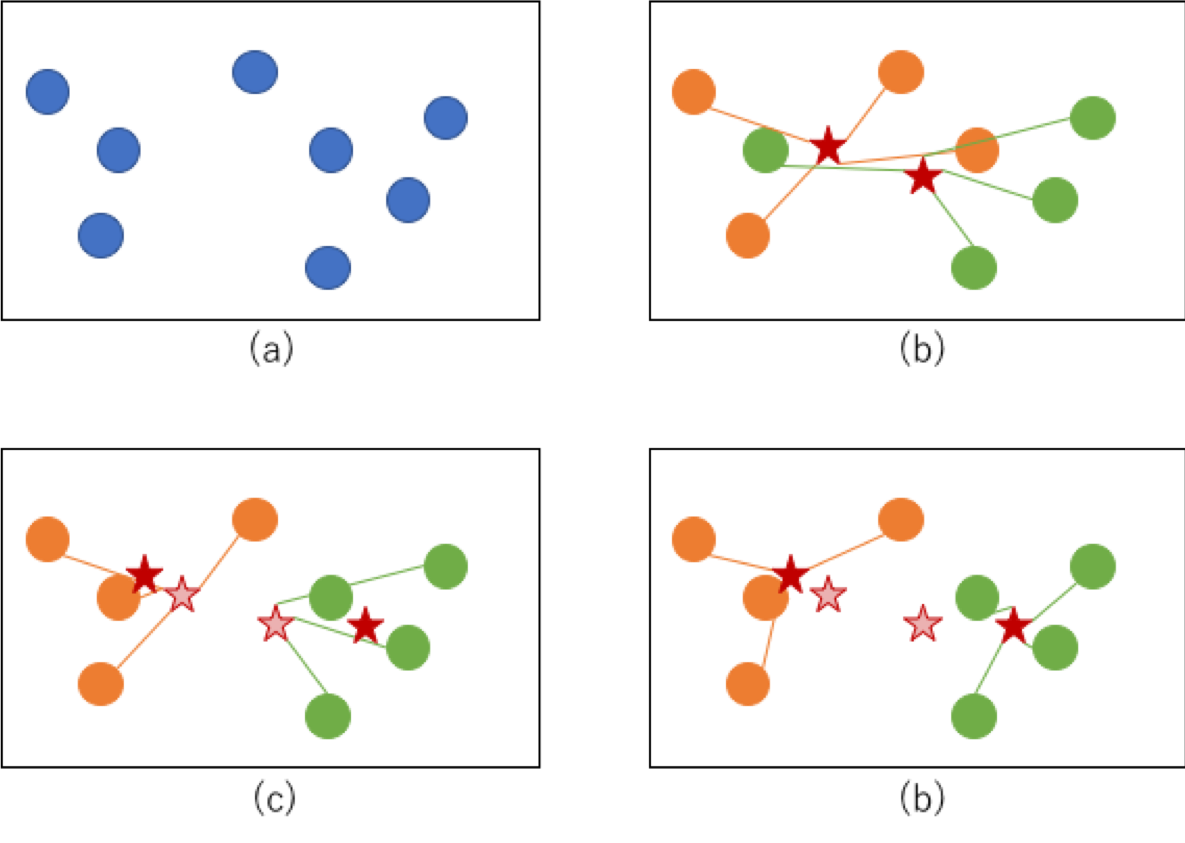
図で表現すると下記のように(a)→(b)→(c)→(d)のような順序を辿ってクラスタが収束していくイメージです。
(b)の段階でまず各点に適当にクラスタが割り振られ、その重心が計算されます(重心は赤星で図示)。(c)ではその重心との距離のもとに再度クラスタが割り当てられます。(新しい重心を赤星で図示、古い重心を薄い赤星で図示)。この工程を繰り返し(d)のようにクラスタが変化しないようなかたちに収束すれば完了です。
k-means法を実装する
ライブラリを用いないk-means法の実装
ライブラリを用いずk-means法を実装したものが下記になります。
機械学習のエッセンス記載のコードにメモ書きを記載しております。
import numpy as np
import itertools
class KMeans:
def __init__(self, n_clusters, max_iter = 1000, random_seed = 0):
self.n_clusters = n_clusters
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.random_state = np.random.RandomState(random_seed)
def fit(self, X):
#指定したクラスター数分のラベルを繰り返し作成するジェネレータを生成(0,1,2,0,1,2,0,1,2...みたいな感じ)
cycle = itertools.cycle(range(self.n_clusters))
#各データポイントに対してクラスタのラベルをランダムに割り振る
self.labels_ = np.fromiter(itertools.islice(cycle, X.shape[0]), dtype = np.int)
self.random_state.shuffle(self.labels_)
labels_prev = np.zeros(X.shape[0])
count = 0
self.cluster_centers_ = np.zeros((self.n_clusters, X.shape[1]))
#各データポイントが属しているクラスターが変化しなくなった、又は一定回数の繰り返しを越した場合は終了
while (not (self.labels_ == labels_prev).all() and count < self.max_iter):
#その時点での各クラスターの重心を計算する
for i in range(self.n_clusters):
XX = X[self.labels_ == i, :]
self.cluster_centers_[i, :] = XX.mean(axis = 0)
#各データポイントと各クラスターの重心間の距離を総当たりで計算する
dist = ((X[:, :, np.newaxis] - self.cluster_centers_.T[np.newaxis, :, :]) ** 2).sum(axis = 1)
#1つ前のクラスターラベルを覚えておく。1つ前のラベルとラベルが変化しなければプログラムは終了する。
labels_prev = self.labels_
#再計算した結果、最も距離の近いクラスターのラベルを割り振る
self.labels_ = dist.argmin(axis = 1)
count += 1
def predict(self, X):
dist = ((X[:, :, np.newaxis] - self.cluster_centers_.T[np.newaxis, :, :]) ** 2).sum(axis = 1)
labels = dist.argmin(axis = 1)
return labels
検証
こちらのアルゴリズムで本当にクラスタリングができているか検証したものが下記になります。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 適当なデータセットを作成する
np.random.seed(0)
points1 = np.random.randn(80, 2)
points2 = np.random.randn(80, 2) + np.array([4,0])
points3 = np.random.randn(80, 2) + np.array([5,8])
points = np.r_[points1, points2, points3]
np.random.shuffle(points)
# 3つのクラスタに分けるモデルを作成
model = KMeans(3)
model.fit(points)
print(model.labels_)
すると出力はこのような感じになります。
見事3つにラベルが振られていることがわかります。
[1 0 2 1 0 0 2 0 1 2 0 0 2 0 2 2 0 0 2 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 1 0 1 0 0 0 2 0 2 0
1 1 0 0 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 2 1 0 2 1 0 2 0 2 1 1 1 1 1 0 2 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 0
2 2 2 1 0 2 1 2 0 0 2 0 1 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 1 0 1
2 0 1 1 0 1 2 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 1 0 1 1 2 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 2 1 0 0 1 2 2 2 1 0 0
0 2 2 2 0 0 1 2 0 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 0 1 2 1 1 2 0 1 1 1 1 0 2 1 0 1 1
2 1 2 2 2 1 2 0 1 2 2 2 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 2 0 0 1 1 2 0 0 1 0 1 1 2 1
0 1 2 1 0 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 2 1 0 1 1 2]
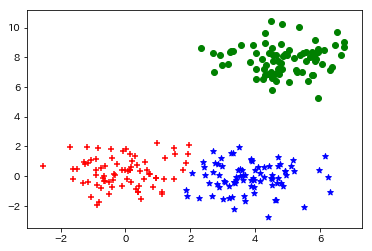
こちらをmatplotlibで図示してみます。
markers = ["+", "*", "o"]
color = ['r', 'b', 'g']
for i in range(3):
p = points[model.labels_ == i, :]
plt.scatter(p[:, 0], p[:, 1], marker = markers[i], color = color[i])
plt.show()
出力がこちら。概ね問題なくクラスタリングができていることがわかります。
Next
こちらのk-means法には最初のランダムのクラスタの割り振りによって精度が変わってしまうという問題点があります。その問題点の克服を試みている、k-means++の実装に挑戦したいと思います。