はじめに
今回はOpen Interpreterの紹介になります.すでに様々な方がOpen Interpreterについて紹介されていますが,自分の勉強のためにまとめたので共有しようと思います.機能としてはCode Interpreter(現在はAdvanced data analysis)のオープンソース版のようなものとなっており,画像生成,動画の編集,データ分析,資料作成などのプログラミングやAPIを使ってできることをほぼ全て行うことができます.
また,この記事では実際にどのようなことが出力されるか分かるように出力結果をそのまま貼り付けています.より凄さを実感していただけると思います.
目次
1. Open Interpreter
プログラミングやAPIを使えばできるほぼ全てのことを実行できる対話型のOSSです.ファイルのアップロードなどもできるためCode Interpreterなどに比べさらに多くのことに利用することが可能となっています.
ライセンス:MIT(商用利用可能)
リポジトリ:https://github.com/KillianLucas/open-interpreter
公式サイト:
以下のコマンドでインストールします.
!pip install open-interpreter
※注意点:Open Interpreterでは必要なライブラリをいくつもインストールしていくので,ColabやDocker環境などで実行することをお勧めします.
2. 使い方(Python)
すぐに試したい方は以下のColabのリンクから実行してみてください
以下のコマンドでimportするだけですぐに使えます.
またOpen Interpreterがコードを実行する際に毎回実行して良いか確認をしてきます.二行目のコードを実行しておくことでこれを防ぐことができます.
import interpreter
interpreter.auto_run = True
# 以下のような設定をすることでGPT-3.5-turboを使うこともできる.
interpreter.model = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
以下のようなコードを実行すると対話形式で操作できます.
interpreter.chat()
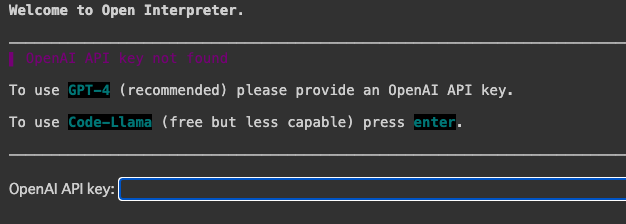
初回実行時に以下のようにOpenAI API keyの入力が求められます.
GPT-4を使う場合はOpenAIのAPI Keyを入力し,無料のCode-Llamaを使う場合はEnterを押します.
今回は以下のような指示を与え機械学習モデルの精度比較を行ってもらいます.
また日本語で出力するように指示をすると全て日本語で回答してくれます.
text = """
SeabornのTitanicデータセットを使いLightGBM,XGBoost,CatBoostおよび3つのモデルのアンサンブルした場合で
どれが最も精度が良いか検証してください.検証する際は4foldのクロスバリデーションの結果の平均値としてください.
全て日本語で対応してください.
"""
# return_massagesは出力結果のデータを変数として保持するため引数
# 出力結果はmassagesにも保存される
messages = interpreter.chat(text, return_messages=True)
- 実行結果
途中でエラーが出ていますが,エラーの原因も自分で分析して最終的な結論を導けています.今回の結果ではCatBoostが最も精度が良いという結論を導いています.
(出力が長いため一部省略していますがなるべくそのままの状態で載せています)
了解しました。以下の手順で進めていきます。
1 必要なライブラリをインストールします。これには、seaborn(データセットの取得)、pandas(データの操作)、numpy
cikit-learn(クロスバリデーションと精度評価)、lightgbm、xgboost、catboost(各モデル)が含まれます。
2 SeabornからTitanicデータセットを読み込みます。
3 データの前処理を行います。これには、カテゴリ変数のエンコーディングと欠損値の処理が含まれます。
4 LightGBM、XGBoost、CatBoostの各モデルを訓練し、4-foldクロスバリデーションを用いて評価します。
5 3つのモデルをアンサンブルし、同様に評価します。
6 各モデルの精度を比較し、最も精度が高いモデルを報告します。
まず、必要なライブラリをインストールします。
pip install seaborn pandas numpy scikit-learn lightgbm xgboost catboost
ライブラリのインストールが完了しました。次に、SeabornからTitanicデータセットを読み込みます。
import seaborn as sns
# Load Titanic dataset
df = sns.load_dataset('titanic')
df.head()
survived pclass sex age ... deck embark_town alive alone
0 0 3 male 22.0 ... NaN Southampton no False
1 1 1 female 38.0 ... C Cherbourg yes False
2 1 3 female 26.0 ... NaN Southampton yes True
3 1 1 female 35.0 ... C Southampton yes False
4 0 3 male 35.0 ... NaN Southampton no True
[5 rows x 15 columns]
Titanicデータセットを読み込むことができました。このデータセットには、乗客の生存(survived)、客室クラス(pclass
(sex)、年齢(age)、兄弟・配偶者の数(sibsp)、親・子供の数(parch)、運賃(fare)、乗船港(embarked)、デッ(deck)、
乗船地(embark_town)、生存状態(alive)、単独乗船(alone)などの情報が含まれています。次に、データの前処理を
行います。具体的には、カテゴリ変数をエンコーディングし、欠損値を処理します。今回は、生存ved)を目的変数とし、
それ以外の特徴量を説明変数とします。また、alive列はsurvived列と同じ情報を持っているため、これを削除します。
さらに、deck列は欠損値が多いため、これも削除します。
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
df = df.drop(['alive', 'deck'], axis=1)
# Fill missing values
df['age'] = df['age'].fillna(df['age'].mean())
df['embark_town'] = df['embark_town'].fillna(df['embark_town'].mode()[0])
df['embarked'] = df['embarked'].fillna(df['embarked'].mode()[0])
# Encode categorical variables
le = LabelEncoder()
for col in ['sex', 'embarked', 'embark_town']:
df[col] = le.fit_transform(df[col])
# Convert boolean to int
df['alone'] = df['alone'].astype(int)
# Show the preprocessed dataframe
df.head()
survived pclass sex age ... who adult_male embark_town alone
0 0 3 1 22.0 ... man True 2 0
1 1 1 0 38.0 ... woman False 0 0
2 1 3 0 26.0 ... woman False 2 1
3 1 1 0 35.0 ... woman False 2 0
4 0 3 1 35.0 ... man True 2 1
[5 rows x 13 columns]
データの前処理が完了しました。次に、LightGBM、XGBoost、CatBoostの各モデルを訓練し、4-foldクロスバリデーションを
用いて評価します。まずはLightGBMから始めます。
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier
# Define the model
model_lgbm = LGBMClassifier(random_state=0)
# Perform 4-fold cross validation
scores_lgbm = cross_val_score(model_lgbm, df.drop('survived', axis=1), df['survived'], cv=4)
# Calculate the mean score
mean_score_lgbm = scores_lgbm.mean()
mean_score_lgbm
Output truncated. Showing the last 2000 characters.
4 fits failed with the following error:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/sklearn/model_selection/_validation.py", line 686, in
_fit_and_score
......
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages/lightgbm/basic.py", line 661, in _check_for_bad_pandas_dtypes
raise ValueError('pandas dtypes must be int, float or bool.\n'
ValueError: pandas dtypes must be int, float or bool.
Fields with bad pandas dtypes: who: object
エラーが発生しました。エラーメッセージを見ると、モデルの訓練中に問題が発生したようです。エラーの原因を特定するため
に、データセットの詳細を確認します。
df.info()
<class pandas.core.frame.DataFrame>
RangeIndex: 891 entries, 0 to 890
Data columns (total 13 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 survived 891 non-null int64
1 pclass 891 non-null int64
2 sex 891 non-null int64
3 age 891 non-null float64
4 sibsp 891 non-null int64
5 parch 891 non-null int64
6 fare 891 non-null float64
7 embarked 891 non-null int64
8 class 891 non-null category
9 who 891 non-null object
10 adult_male 891 non-null bool
11 embark_town 891 non-null int64
12 alone 891 non-null int64
dtypes: bool(1), category(1), float64(2), int64(8), object(1)
memory usage: 78.6+ KB
データセットの情報を確認したところ、'class'と'who'の2つの列がエンコーディングされていないことがわかりました。
これらの列もエンコーディングして、再度モデルの訓練を試みます。
for col in ['class', 'who']:
df[col] = le.fit_transform(df[col])
# Convert boolean to int
df['adult_male'] = df['adult_male'].astype(int)
# Show the preprocessed dataframe
df.head()
survived pclass sex age ... who adult_male embark_town alone
0 0 3 1 22.0 ... 1 1 2 0
1 1 1 0 38.0 ... 2 0 0 0
2 1 3 0 26.0 ... 2 0 2 1
3 1 1 0 35.0 ... 2 0 2 0
4 0 3 1 35.0 ... 1 1 2 1
[5 rows x 13 columns]
全てのカテゴリ変数がエンコーディングされ、欠損値も処理されました。再度、LightGBMモデルの訓練と評価を行います。
scores_lgbm = cross_val_score(model_lgbm, df.drop('survived', axis=1), df['survived'], cv=4)
mean_score_lgbm = scores_lgbm.mean()
mean_score_lgbm
Output truncated. Showing the last 2000 characters.
positive gain, best gain: -inf
[LightGBM] [Warning] No further splits with positive gain, best gain: -inf
[LightGBM] [Warning] No further splits with positive gain, best gain: -inf
[LightGBM] [Warning] No further splits with positive gain, best gain: -inf
[LightGBM] [Warning] No further splits with positive gain, best gain: -inf
0.8181634549347554
LightGBMモデルの4-foldクロスバリデーションの平均スコアは約0.818です。
次に、XGBoostモデルの訓練と評価を行います。
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
# Define the model
model_xgb = XGBClassifier(random_state=0)
# Perform 4-fold cross validation
scores_xgb = cross_val_score(model_xgb, df.drop('survived', axis=1), df['survived'], cv=4)
# Calculate the mean score
mean_score_xgb = scores_xgb.mean()
mean_score_xgb
0.8058366662626752
XGBoostモデルの4-foldクロスバリデーションの平均スコアは約0.806です。
次に、CatBoostモデルの訓練と評価を行います。
from catboost import CatBoostClassifier
# Define the model
model_cat = CatBoostClassifier(random_state=0, verbose=0)
# Perform 4-fold cross validation
scores_cat = cross_val_score(model_cat, df.drop('survived', axis=1), df['survived'], cv=4)
# Calculate the mean score
mean_score_cat = scores_cat.mean()
mean_score_cat
0.8305306427503737
CatBoostモデルの4-foldクロスバリデーションの平均スコアは約0.831です。
最後に、これら3つのモデルをアンサンブルし、同様に評価します。アンサンブルは、複数のモデルの予測を組み合わせること
で、一般的にはより良い予測精度を達成することができます。ここでは、単純な投票アンサンブル(ハード投票)を使用します。
それぞれのモデルが投票を行い、最も得票数が多かったクラスが最終的な予測となります。
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier
# Define the ensemble model
model_ensemble = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('lgbm', model_lgbm), ('xgb', model_xgb), ('cat', model_cat)],
voting='hard')
# Perform 4-fold cross validation
scores_ensemble = cross_val_score(model_ensemble, df.drop('survived', axis=1),df['survived'], cv=4)
# Calculate the mean score
mean_score_ensemble = scores_ensemble.mean()
mean_score_ensemble
Output truncated. Showing the last 2000 characters.
positive gain, best gain: -inf
[LightGBM] [Warning] No further splits with positive gain, best gain: -inf
[LightGBM] [Warning] No further splits with positive gain, best gain: -inf
[LightGBM] [Warning] No further splits with positive gain, best gain: -inf
[LightGBM] [Warning] No further splits with positive gain, best gain: -inf
0.8204258069728922
アンサンブルモデルの4-foldクロスバリデーションの平均スコアは約0.820です。
以上の結果から、LightGBM、XGBoost、CatBoost、アンサンブルの4つのモデルの中で、最も高い精度を示し
たのはCatBoostモデルであることがわかりました。したがって、Titanicデータセットに対する予測モデルとして
は、CatBoostが最も高いそうです。
会話をリセットする際は以下のコードを実行します.
interpreter.reset()
3. 使い方(Terminal)
基本的な使い方はPython上での実行と同じです.
以下のコマンドで開始します.
interpreter
ここでも,以下のようにOpenAIのKeyを入力してGPT-4を使うか,無料でCode-Llamaを使うか選択します.
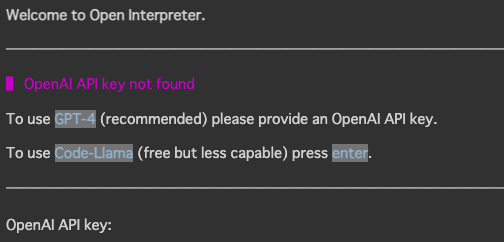
また以下のように入力するとGPT-3.5-turboを使うことができます.
interpreter --fast
4. その他
他には以下のような使い方ができるようです.
- Hugging Faceのモデル
- Azure OpenAIとの連携
また,公式のNotebookには動画編集やドキュメント作成などの様々な実行例が載っています.ぜひ参考にしてみてください.
5. おわりに
今回はOpen Interpreterの紹介でした.出力結果としては人間が雑にプログラムを書いて実装したような結果が得られましたが,この点に関してはより詳細な命令を与えることで正確でかつ狙い通りの結果を得ることができると思いました.プログラマーやデータサイエンティストの生産性が上がりそうでこれからの発展が非常に楽しみです.