決定性有限オートマトン (DFA) の等価性判定を行うアルゴリズムを実装します.
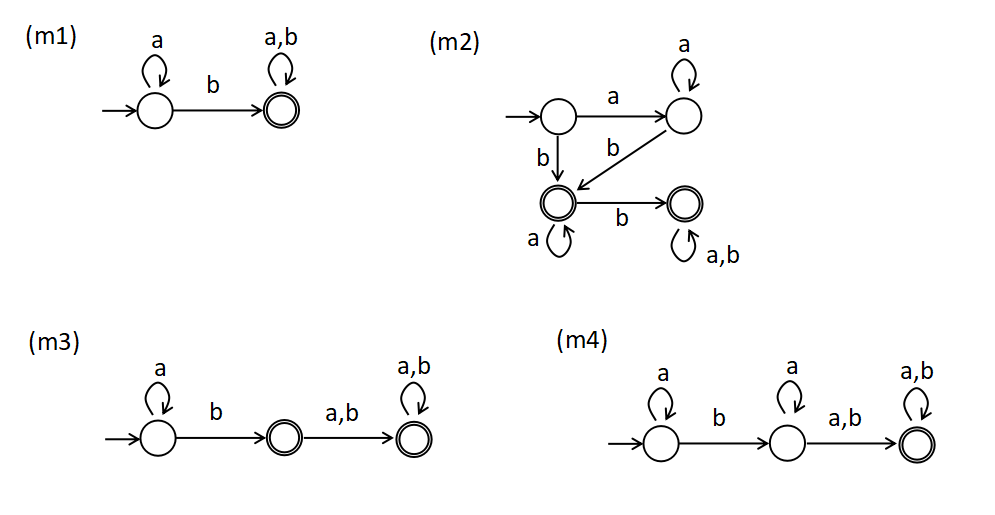
以上の (m1)~(m3) はすべてアルファベット $A={a, b}$ 上の文字列のうちで b を一度以上含む正規言語を表しているのに対して,(m4) は b を二度以上含む正規言語なので $m_1=m_2=m_3\ne m_4$ が成り立っている.
DFA が受理する文字列は一般に無限個あるので,すべて入力してチェックするわけにはいかない.
代わりに以下のような再帰アルゴリズムで判定可能 (比べるオートマトンを $m, M$ とする).
- m および M の初期状態 $(q, r)$ のペアを考える
- 各文字 $w\in A$ に関して $(q, r)$ の状態を m および M に関してそれぞれ進めて $(q_w, r_w)$ を得る
- $(q_w, r_w)$ はすでに調べた状態ペアの場合,この状態ペアはこれ以上深く調べない(枝刈り
- もし $(q_w, r_w)$ のどちらかが受理状態でもう一方がそうでないのならば m と M は等しくないと結論してOK(アルゴリズムの停止
- 上記のいずれでもない場合,$(q, r)\leftarrow (q_w, r_w)$ としてこの step 2 を再呼び出し
- すべて枝刈りされた場合,m と M は等しいと判定する
実装
import networkx as nx
class DFA:
def __init__(self, alphabet=['0','1']):
self.g = nx.DiGraph()
self.alphabet = alphabet
def add_state(self, delta, accept=False, state_name=None):
# delta = dict{char => state_id}
i = len(self.g.nodes())
if state_name is None:
state_name = "q%02d" % i
self.g.add_node(i, delta=delta, accept=accept, name=state_name)
def is_accepted(self, state):
return self.g.nodes[state]['accept']
def test(self, x):
'''test if x is accepted by this DFA'''
x = list(x)
cur_state = 0
for w in x:
cur_state = self._go(cur_state, w)
return self.g.nodes[cur_state]['accept']
def _go(self, state, w):
next_state = self.g.nodes[state]['delta'][w]
return next_state
def __eq_rec__(self, other, state_pair, seen_state_pair, counterexample):
for w in A:
counterexample += w
q0, r0 = state_pair
next_state_pair = (self._go(q0, w), other._go(r0, w))
q, r = next_state_pair
if next_state_pair in seen_state_pair:
continue
if self.is_accepted(q) != other.is_accepted(r):
self.counterexample = counterexample
other.counterexample = counterexample
return False
seen_state_pair.add(next_state_pair)
if not self.__eq_rec__(other, next_state_pair, seen_state_pair, counterexample):
return False
self.counterexample = None
other.counterexample = None
return True
def __eq__(self, other):
seen_state_pair = set()
state_pair = (0,0)
seen_state_pair.add(state_pair)
q, r = state_pair
if self.is_accepted(q) != other.is_accepted(r):
return False
counterexample = ''
return self.__eq_rec__(other, state_pair, seen_state_pair, counterexample)
if __name__ == '__main__':
A = ['a', 'b']
m1 = DFA(A)
m2 = DFA(A)
m3 = DFA(A)
m4 = DFA(A)
# Building m1:
# Firstly added state is assumed to be initial state
delta = {'a': 0, 'b': 1}
m1.add_state(delta)
delta = {'a': 1, 'b': 1}
m1.add_state(delta, accept=True)
#
x = 'abb'
if m1.test(x):
print("'%s' is accepted by m" % x)
else:
print("'%s' is rejected by m" % x)
x = 'abbab'
if m1.test(x):
print("'%s' is accepted by m" % x)
else:
print("'%s' is rejected by m" % x)
# Building m2:
delta = {'a': 2, 'b': 1}
m2.add_state(delta)
delta = {'a': 1, 'b': 3}
m2.add_state(delta, accept=True)
delta = {'a': 2, 'b': 1}
m2.add_state(delta)
delta = {'a': 3, 'b': 1}
m2.add_state(delta, accept=True)
# Building m3:
delta = {'a': 0, 'b': 1}
m3.add_state(delta)
delta = {'a': 2, 'b': 2}
m3.add_state(delta, accept=True)
delta = {'a': 2, 'b': 2}
m3.add_state(delta, accept=True)
# Building m4:
delta = {'a': 0, 'b': 1}
m4.add_state(delta)
delta = {'a': 2, 'b': 2}
m4.add_state(delta)
delta = {'a': 2, 'b': 2}
m4.add_state(delta, accept=True)
print("m1 == m1 ??", m1==m1)
print("m1 == m2 ??", m1==m2)
print("m1 == m3 ??", m1==m3)
print("m1 == m4 ??", m1==m4)
print("m2 == m3 ??", m2==m3)
print("m2 == m4 ??", m2==m4)
print("m3 == m4 ??", m3==m4)
print("m4 == m4 ??", m4==m4)
計算量
このアルゴリズムは同じ状態ペアを二度以上調べることがないので,呼び出される再帰の回数は $stateSize(m)\cdot stateSize(M)$ で上からバウンドされる.つまり必ず停止して,なおかつ DFA のサイズに関して多項式時間.計算量は $O(|A|\cdot stateSize(m)\cdot stateSize(M))$ となる (はずです)