はじめに
インターンのコーディング面接をJavaScriptで受けることになったので、その対策としてAtCoder に登録したら次にやること ~これだけ解けば十分闘える!過去問精選 10 問~を解いてみました。あんまり解説を見ずに自力で解いたので、綺麗なアルゴリズムじゃないのでご了承ください!他に良い解法があったらぜひコメントお願いします!
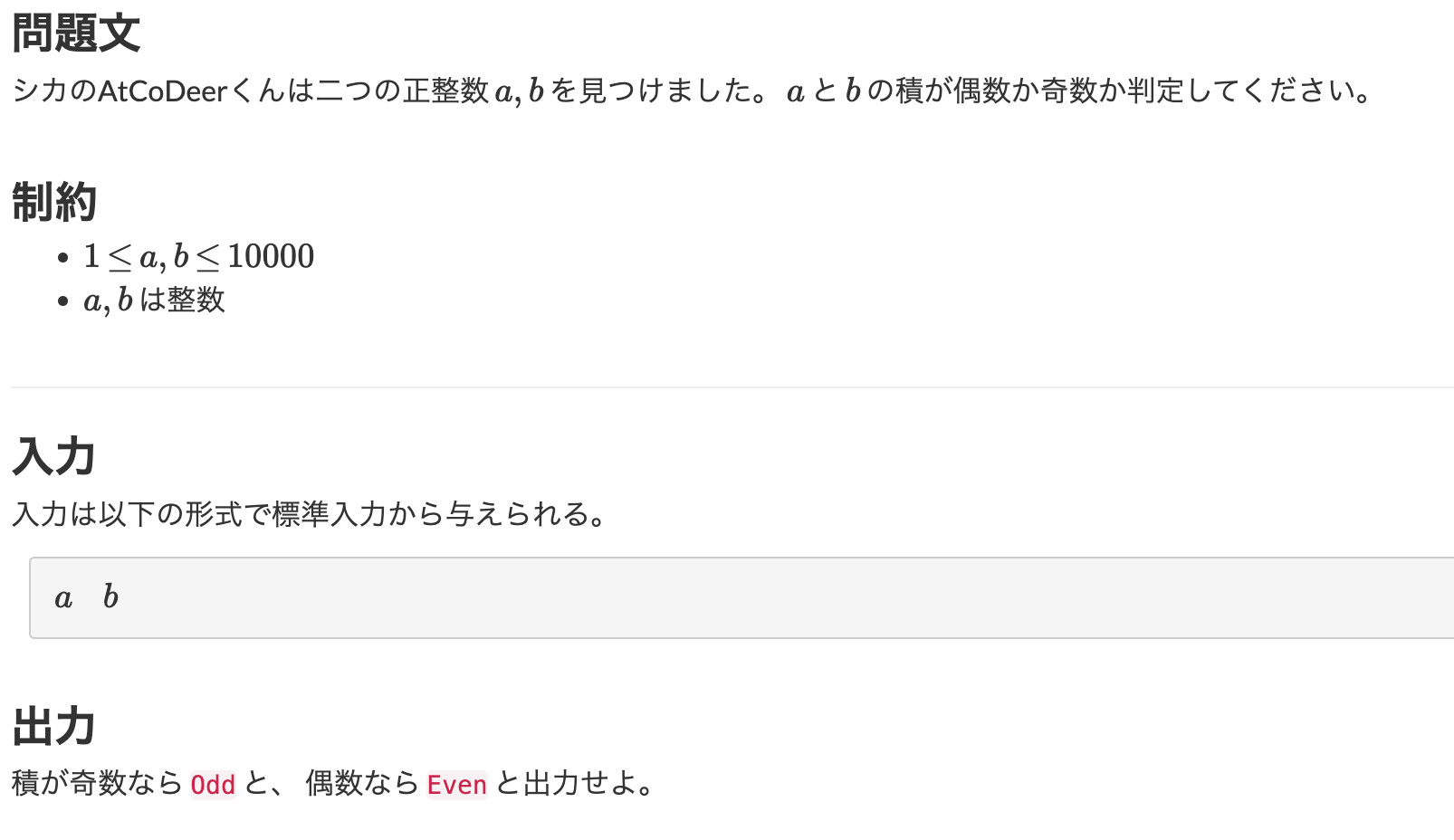
【1問目】ABC086A - Product
const main = input => {
input = input.split(" ");
a = parseInt(input[0], 10);
b = parseInt(input[1], 10);
if(a % 2 == 0 || b % 2 == 0){
console.log("Even");
}
else{
console.log("Odd");
}
}
main(require('fs').readFileSync('/dev/stdin', 'utf8'));
特に言うことないです。
【2問目】ABC081A - Placing Marbles
const main = (input) => {
count = 0;
if (input[0] == "1") count++;
if (input[1] == "1") count++;
if (input[2] == "1") count++;
console.log(count);
};
main(require("fs").readFileSync("/dev/stdin", "utf8"));
入力を文字列のまま処理
入力に整数が出てくると脳死でキャストしそうになるが、この場合完全に無駄なので文字列のまま処理。for文でも書けるけど、入力が定数オーダーの場合はかえってこんな感じでもいいなと感じた。3つしかないし、いいよね。
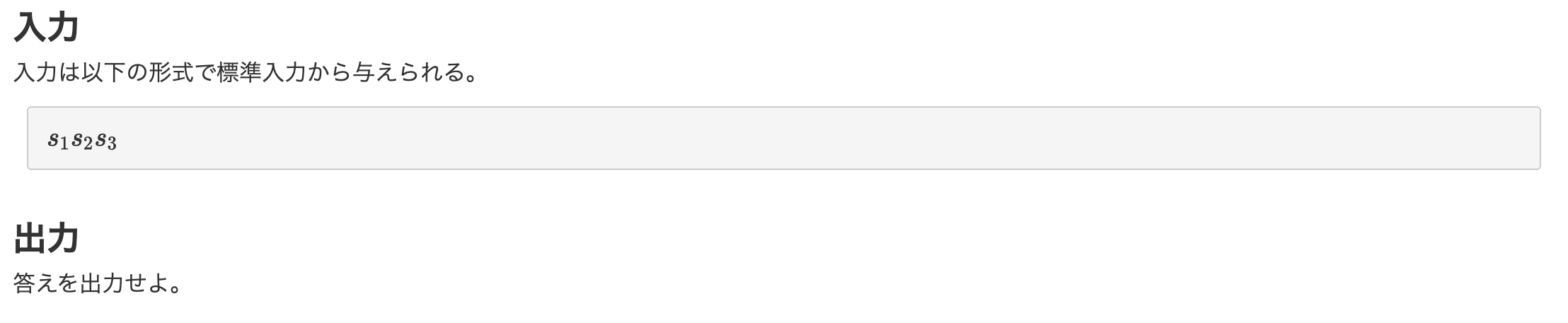
【3問目】ABC081B - Shift only
const main = (input) => {
input = input.split("\n");
numbers = input[1].split(" ");
count = 0;
while (numbers.every((num) => num % 2 == 0)) {
numbers = numbers.map((num) => num / 2);
count++;
}
console.log(count);
};
main(require("fs").readFileSync("/dev/stdin", "utf8"));
every関数
array.every(callback function)と書くことで、配列の全ての要素がコールバック関数の条件を満たすときのみtrueを返し、それ以外はfalseを返すメソッド。これを使って、配列の全ての要素が偶数の時のみ2で割る操作を繰り替えす、といった感じ。
map関数
array.map(callback function)と書くことで、配列の全ての要素に対して順番にコールバック関数の処理を実行し、実行後の要素からなる新しい配列を返すメソッド。
foreachではダメなのか
ダメでした。 map関数の部分を、numbers.foreach(num => num / 2)としたところ、実行時間制限超過エラーが出てダメでした。不思議ですね。
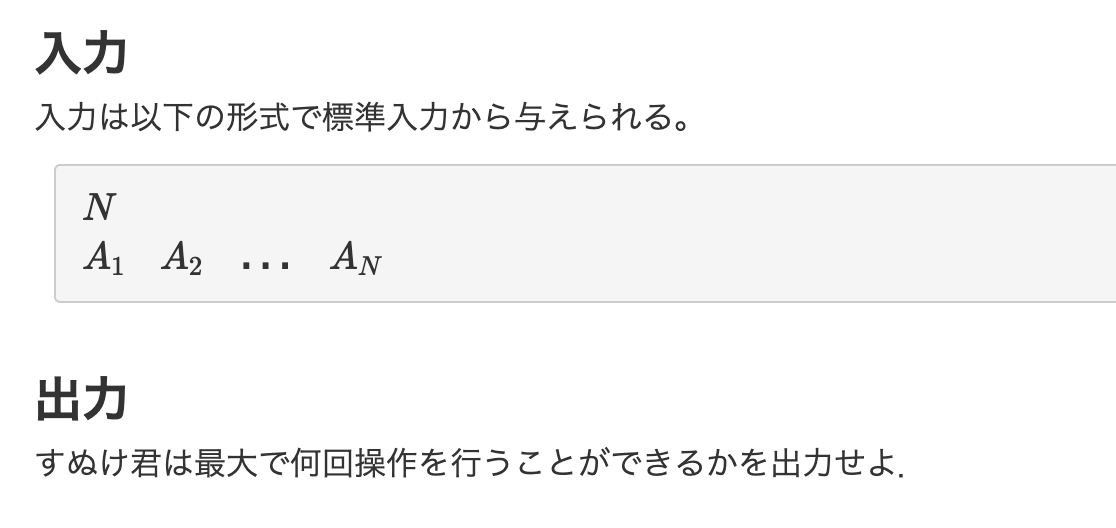
【4問目】ABC087B - Coins
const main = (input) => {
input = input.split("\n");
a = parseInt(input[0]);
b = parseInt(input[1]);
c = parseInt(input[2]);
x = parseInt(input[3]);
count = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= a; i++) {
for (j = 0; j <= b; j++) {
for (k = 0; k <= c; k++) {
if (500 * i + 100 * j + 50 * k == x) {
count++;
}
}
}
}
console.log(count);
};
main(require("fs").readFileSync("/dev/stdin", "utf8"));
全探索
気合いの全探索。入力によって実行時間が爆発する可能性がありそうだけど、提出したら通ったのでOK。
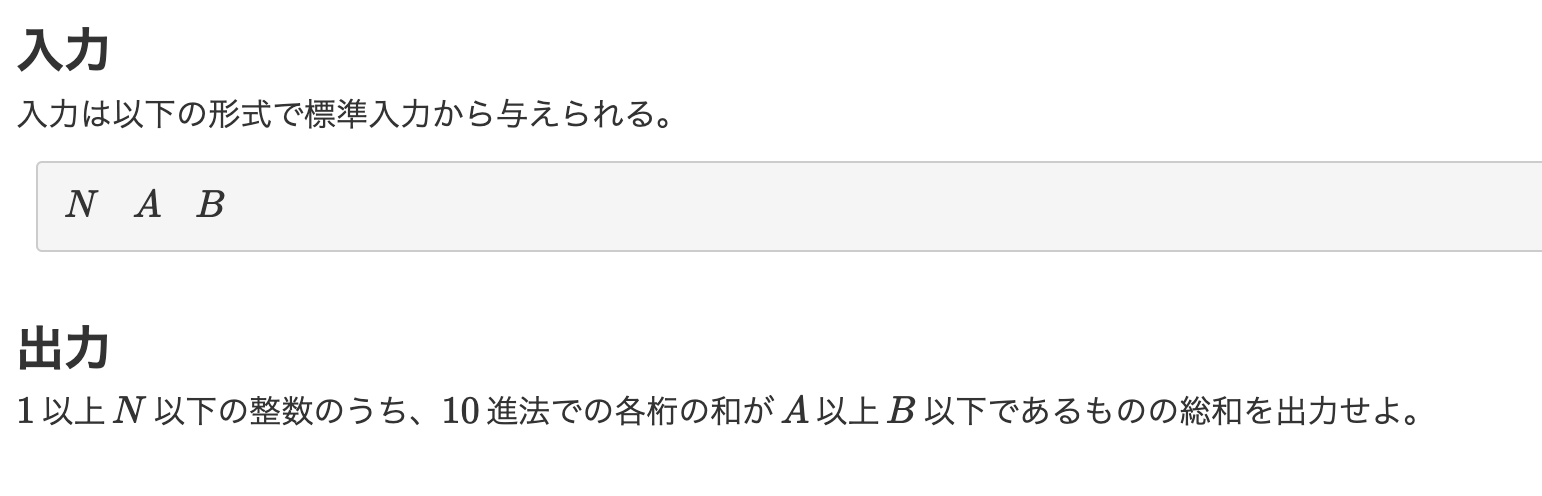
【5問目】ABC083B - Some Sums
const main = (input) => {
input = input.split(" ");
n = parseInt(input[0]);
a = parseInt(input[1]);
b = parseInt(input[2]);
total = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
num = i.toString();
sum = 0;
for (digit of num) {
sum += parseInt(digit);
}
if (a <= sum && sum <= b) {
total += i;
}
}
console.log(total);
};
main(require("fs").readFileSync("/dev/stdin", "utf8"));
for(element of array)構文
文字列型へのキャストtoString()
【6問目】ABC088B - Card Game for Two
const main = (input) => {
input = input.split("\n");
n = parseInt(input[0]);
cards = input[1].split(" ");
sumAlice = 0;
sumBob = 0;
cards = cards.map((card) => parseInt(card));
cards.sort((a, b) => b - a);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
sumAlice += cards[i];
} else {
sumBob += cards[i];
}
}
console.log(sumAlice - sumBob);
};
main(require("fs").readFileSync("/dev/stdin", "utf8"));
array.sort()
配列のインデックスによる条件分岐
【7問目】ABC085B - Kagami Mochi
const main = (input) => {
input = input.trim().split("\n");
input.shift();
numbers = input;
numSet = new Set(numbers);
console.log(numSet.size);
};
main(require("fs").readFileSync("/dev/stdin", "utf8"));
標準入力を最初にtrim()する
Set(集合)で重複要素を排除する
【8問目】ABC085C - Otoshidama
const main = (input) => {
input = input.trim().split(" ");
n = parseInt(input[0]);
y = parseInt(input[1]);
findloop: for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j <= n - i; j++) {
k = n - i - j;
total = 10000 * i + 5000 * j + 1000 * k;
if (total == y) {
console.log("%d %d %d", i, j, k);
break findloop;
} else if (i == n) {
console.log("-1 -1 -1");
}
}
}
};
main(require("fs").readFileSync("/dev/stdin", "utf8"));
2重ループからのbreak
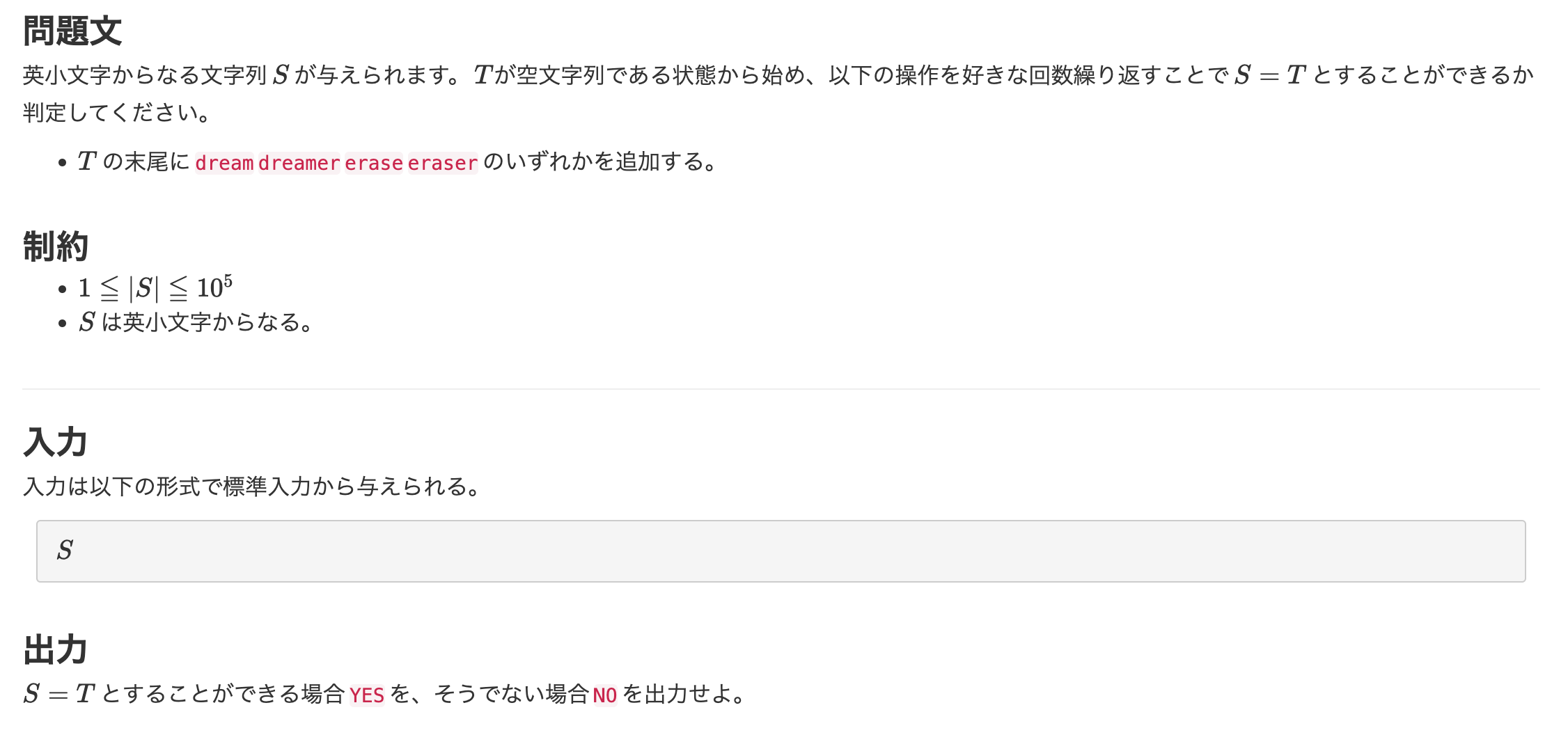
【9問目】ABC049C - 白昼夢
これは難しすぎて流石に解説見ました。
考え方
直感的に思いついたのは、「Sの先頭から見ていって、dream, dreamer, erase, eraserのどれかと一致したらその部分を削除してまた繰り返す…」 みたいなことすればいけそうじゃね…???
でもすぐにこんな壁にぶちあたった。
「先頭5文字を見てdreamだったとしても、それが、dreamなのかdreamerなのかわかんねえな…」
「なら、7文字目まで見ればdreamかdreamerかは判定できそうやな。いや待て、それがdreamerなのか、dream+er(eraseの先頭のer)なのか区別できないやんけ」
「ふむふむ。(解説に手を伸ばす)」
なんと、Sを後ろから見ていく らしい。そうすれば5or7文字見た時点で必ず指定した単語に一致するか判定できるとのこと。
今回は、後ろから見る代わりに、4つの単語と文字列Sを反転させて前から見ていくことにした。
const main = (input) => {
s = input.trim();
s = s.split("").reverse();
words = ["dream", "dreamer", "erase", "eraser"];
words = words.map((word) => word.split("").reverse().join(""));
tmp_word = "";
for (i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
tmp_word += s[i];
if (words.includes(tmp_word)) {
tmp_word = "";
continue;
} else if (tmp_word.length >= 7) {
break;
}
}
if (tmp_word == "") {
ans = "YES";
}else{
ans = "NO";
}
console.log(ans);
};
main(require("fs").readFileSync("/dev/stdin", "utf8"));
文字列の反転
s.split("").reverse().join("")で文字列を反転して、後ろから読んだ状態にできた。
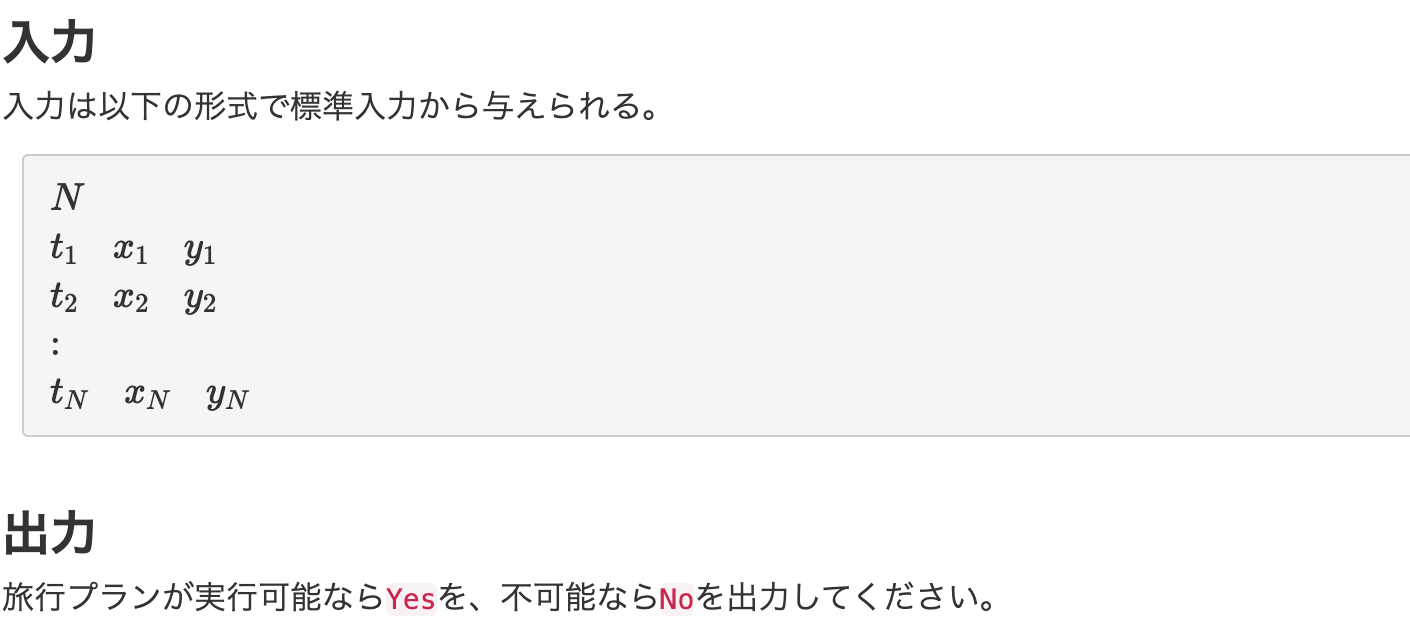
【10問目】ABC086C - Traveling
考え方
整理すると、「単位時間あたりに1回だけ、二次元平面上の隣あった格子点に移動できるAtCoDeer君が、入力で与えられるチェックポイントを時間通りに通過できるかを判定」 する問題。
旅行プランが実行可能かどうかを出力すれば良いので、どのような条件の時に実行可能か実行不可能かを考えれば良い。わざわざ「原点スタートで左右上下の4通りの移動が考えられるからどれかに移動する繰り返し処理を…」みたいなことはしなくてよさそう。
入力に対して上から2地点ずつ処理していく。現在地をcurrent、次の目的地をnextとする。次の目的地に到達可能な場合は次の2つの条件が考えられる。
-
nextにいる時刻-currentにいる時刻>currentとnextの距離 -
nextにいる時刻-currentにいる時刻とcurrentとnextの距離の偶奇が一致
まず1について。単位時間で1の距離しか移動できないので、使える時間よりも距離の方が大きかったらそもそも遠すぎて到達できない、ということ。
2について。時間内に到達はできるが、目標の時刻ではないため、時間が余ってしまった場合を考える。余った時間が2の倍数なら、「右に1移動してから左に1移動する」 という処理を目標の時刻まで繰り返せば良い。もし余った時間が2の倍数でない場合は、ピッタリに到達することは不可能となる。
const main = (input) => {
input = input.trim().split("\n");
output = "Yes";
n = input[0];
// 現在地 (最初は原点)
current = {
t: 0,
x: 0,
y: 0,
};
// 入力を上から順に判定
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
next_info = input[i].split(" ");
// 次の目的地
next = {
t: parseInt(next_info[0]),
x: parseInt(next_info[1]),
y: parseInt(next_info[2]),
};
dif_t = next.t - current.t; // 現在時刻から次の目的地到達までの時間
dist = Math.abs(next.x - current.x) + Math.abs(next.y - current.y); // 現在地から次の目的地までのマンハッタン距離
if (dif_t < dist || (dist - dif_t) % 2 != 0) { // 条件1 or 条件2 のどちらかを満たせない場合
output = "No";
break;
} else {
current = next;
}
}
console.log(output);
};
main(require("fs").readFileSync("/dev/stdin", "utf8"));
マンハッタン距離
定義はこちらの記事がわかりやすかった。直線距離ではなく、二次元平面上の格子点上を辿った時の最短距離のことらしい。碁盤の目状の街を考えるとわかりやすい。
Math.abs()
これを使うと引数で指定した式の絶対値を返してくれる。