初めに
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure(OCI)の「Select AI With RAG」をDifyと連携させることで、Difyの画面でOCI Object Storageにアップロードされたファイルを基に自然言語での回答を生成できます。この記事では、具体的な設定方法と手順を説明します。
手順1:プロファイルとベクターアイデックスの作成
1.1 プロファイルの作成
以下のSQLを実行し、RAGプロファイルを作成します。
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI.CREATE_PROFILE(
profile_name =>'RAG_PROFILE',
attributes =>'{
"provider": "oci",
"credential_name": "OCI_GENAI_CRED",
"vector_index_name": "MY_INDEX",
"embedding_model": "cohere.embed-multilingual-v3.0",
"model": "meta.llama-3.3-70b-instruct"
}');
end;
/
- credential_name:OCIのAPIキー名
- vector_index_name:ベクターアイデックスの名前
- embedding_model:Embeddingモデル
- model:回答生成用LLM(Llama 3.3 70B)
1.2 ベクターアイデックスの作成
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI.CREATE_VECTOR_INDEX(
index_name => 'MY_INDEX',
attributes => '{
"vector_db_provider": "oracle",
"location": "https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/your_object_storage_namespace/b/your-bucket-name/o/",
"object_storage_credential_name": "OCI_GENAI_CRED",
"profile_name": "RAG_PROFILE",
"vector_dimension": 1024,
"vector_distance_metric": "cosine",
"chunk_overlap": 128,
"chunk_size": 400,
"refresh_rate": 1
}');
END;
/
- location:Object StorageのバケットURL
- chunk_size:ファイル分割サイズ(400単語ずつ)
- refresh_rate:1分ごとにデータを更新
1.3 検証
SELECT
dbms_cloud_ai.generate(
prompt => 'サツキの妹はだれ?',
profile_name => 'RAG_PROFILE',
action => 'narrate'
)
FROM
dual;
手順2:Difyでチャットフロー構築
2.1 アプリの作成
Difyのダッシュボードで以下を設定:
2.2 HTTPリクエストの追加
カスタム作成したAPIエンドポイントを呼び出す設定を追加:
2.3 コードブロックの追加
回答から不要な情報を除去するためのコード:
import json
def main(json_body: str) -> dict:
json_data = json.loads(json_body)
result = json_data['result']
answer = result.split('Sources')[0] # 出典情報削除
return {
"result": answer,
}
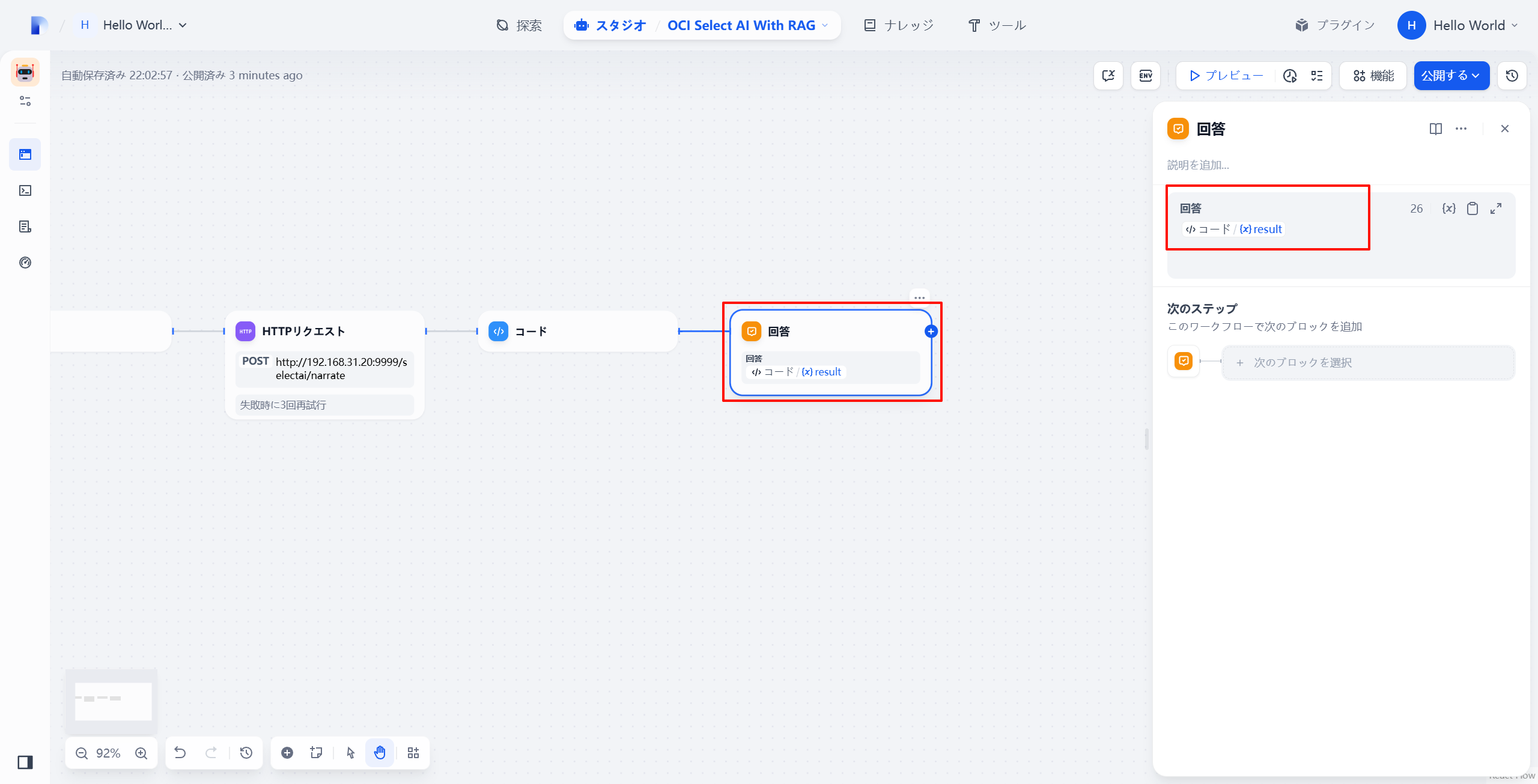
2.4 回答の追加
最終的な回答をユーザーに表示するコンポーネントを追加:
手順3:ファイルのアップロードとテスト
3.1 ナレッジの登録
- Difyの「ナレッジ」タブから「ナレッジを作成」をクリック。
- テキストファイルを選択します。このステップだけでファイルがOCI Object Storageにアップロードされましたので、「次へ」ボタンは押さない。
3.2 テスト実行
まとめ
この設定により、OCI Object Storageに保存されたドキュメントをRAG(Retrieve-and-Generate)方式で活用し、Dify経由で自然言語回答が可能になります。OCIとDifyの連携は、大規模なドキュメントベースのQ&Aシステム構築に最適です。是非お試しください!
参考資料:
その他
カスタムAPIのソースコード:
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
import oracledb
import os
import platform
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from functools import wraps
import logging
import time
from werkzeug.middleware.proxy_fix import ProxyFix
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Callable
# Initialize Flask application
app = Flask(__name__)
app.wsgi_app = ProxyFix(app.wsgi_app)
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
handlers=[logging.StreamHandler(), logging.FileHandler('app.log')]
)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# Load environment variables
load_dotenv()
# Initialize Oracle client (required for Linux systems)
if platform.system() == 'Linux':
try:
oracledb.init_oracle_client(lib_dir=os.getenv("ORACLE_CLIENT_LIB_DIR"))
logger.info("Oracle client initialized successfully")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to initialize Oracle client: {str(e)}")
raise
# Create database connection pool
pool = None
try:
pool = oracledb.create_pool(
dsn=os.getenv("ORACLE_23AI_CONNECTION_STRING"),
min=2,
max=10,
increment=1,
timeout=30,
getmode=oracledb.POOL_GETMODE_WAIT, # Wait for available connection
wait_timeout=10000, # Wait timeout in milliseconds
max_lifetime_session=3600, # Max lifetime of a connection in seconds
)
logger.info("Successfully created Oracle connection pool")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to create Oracle connection pool: {str(e)}")
raise
def validate_request_data(required_fields: List[str]) -> Callable:
"""Decorator to validate request data"""
def decorator(f):
@wraps(f)
def decorated_function(*args, **kwargs):
try:
data = request.get_json()
if not data:
return jsonify(error="Missing request body"), 400
missing_fields = [field for field in required_fields if field not in data or not data[field]]
if missing_fields:
return jsonify(error=f"Missing required fields: {', '.join(missing_fields)}"), 400
# Sanitize inputs
for field in data:
if isinstance(data[field], str):
data[field] = data[field].strip()
kwargs['data'] = data
return f(*args, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error validating request data: {str(e)}")
return jsonify(error="Invalid request format"), 400
return decorated_function
return decorator
def db_connection(f):
"""Decorator to handle database connection with retry logic"""
@wraps(f)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
conn = None
retries = 3
retry_delay = 0.5 # seconds
for attempt in range(retries):
try:
conn = pool.acquire()
kwargs['conn'] = conn
return f(*args, **kwargs)
except oracledb.DatabaseError as e:
error_obj, = e.args
# Only retry on connection errors, not on SQL errors
if error_obj.code in (-3113, -3114, -1034, -1012): # Connection-related error codes
logger.warning(f"Database connection error (attempt {attempt + 1}/{retries}): {str(e)}")
if attempt < retries - 1:
time.sleep(retry_delay)
retry_delay *= 2 # Exponential backoff
continue
logger.error(f"Database error: {str(e)}")
return jsonify(error="Database operation failed"), 500
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Unexpected error: {str(e)}")
return jsonify(error="Internal server error"), 500
finally:
if conn:
try:
pool.release(conn)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error releasing connection: {str(e)}")
return jsonify(error="Failed to connect to database after multiple attempts"), 503
return wrapper
def process_oracle_result(item: Any) -> Any:
"""Process Oracle result items to make them JSON serializable"""
if hasattr(item, 'read'): # Handle LOB objects
return item.read()
return item
def log_request_info(action: str, query: str) -> None:
"""Log request information with proper truncation"""
max_length = 100
truncated_query = query[:max_length] + '...' if len(query) > max_length else query
logger.info(f"Processing {action} request: {truncated_query}")
@app.route('/selectai/<action>', methods=['POST'])
@validate_request_data(['query'])
@db_connection
def ai_query(action: str, conn: oracledb.Connection, data: Dict[str, Any]) -> tuple:
"""Handle AI query requests"""
try:
query = data['query']
log_request_info(action, query)
with conn.cursor() as cursor:
if action == 'showsql':
cursor.execute("""
SELECT DBMS_CLOUD_AI.GENERATE(
prompt => :1,
profile_name => 'OCI_GENAI',
action => 'showsql'
) FROM dual
""", [query])
result = cursor.fetchone()
if result and result[0]:
generated_sql = process_oracle_result(result[0])
return jsonify(sql=generated_sql)
return jsonify(error="No SQL generated"), 404
elif action == 'runsql':
sql = query.replace('\\"', '"')
# Execute the query with proper error handling
try:
cursor.execute(sql)
# Process results
columns = [col[0] for col in cursor.description]
rows = [[process_oracle_result(item) for item in row] for row in cursor.fetchall()]
row_count = len(rows)
logger.info(f"Query returned {row_count} rows")
return jsonify(
columns=columns,
data=rows,
row_count=row_count
)
except oracledb.DatabaseError as e:
error_obj, = e.args
logger.error(f"SQL execution error: {error_obj.message}")
return jsonify(error=f"SQL execution error: {error_obj.message}"), 400
elif action == 'narrate':
cursor.execute("""
SELECT DBMS_CLOUD_AI.GENERATE(
prompt => :1,
profile_name => 'RAG_PROFILE',
action => 'narrate'
) FROM dual
""", [query])
result = cursor.fetchone()
if result and result[0]:
generated_result = process_oracle_result(result[0])
return jsonify(result=generated_result)
return jsonify(error="No SQL generated"), 404
else:
return jsonify(error=f"Invalid action: {action}"), 400
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error processing request: {str(e)}")
return jsonify(error=str(e)), 500
@app.route('/health', methods=['GET'])
def health_check() -> tuple:
"""Health check endpoint with detailed status information"""
start_time = time.time()
try:
status = {
'status': 'ok',
'database': False,
'pool_stats': {
'busy': pool.busy if pool else 0,
'opened': pool.opened if pool else 0,
'max': pool.max if pool else 0
},
'timestamp': int(start_time)
}
if pool:
try:
# Test database connection
conn = pool.acquire()
with conn.cursor() as cursor:
cursor.execute("SELECT 1 FROM dual")
cursor.fetchone()
pool.release(conn)
status['database'] = True
status['response_time_ms'] = int((time.time() - start_time) * 1000)
except Exception as e:
logger.warning(f"Database health check failed: {str(e)}")
status['status'] = 'degraded'
status['error'] = str(e)
else:
status['status'] = 'critical'
return jsonify(status), 200 if status['status'] == 'ok' else 503
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Health check failed: {str(e)}")
response_time = int((time.time() - start_time) * 1000)
return jsonify(
status='error',
error=str(e),
response_time_ms=response_time
), 500
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(
host=os.getenv('HOST', '0.0.0.0'),
port=int(os.getenv('PORT', 9999)),
debug=os.getenv('DEBUG', 'False').lower() == 'true'
)