Outline
フルスクリーンショットで画像を比較する機能は、T-DASHの標準動作でサポートされている
ただ、特定の要素の画像を比較したい場合、工夫がいる。
Yahoo Top Pageを例とする
https://www.yahoo.co.jp/
以下図のように、赤枠の部分を期待画像と比較したい場合である
技術的情報
pythonで3つの機能を用いる
・selenium libraryを用いてフルスクリーンショットを取る
・selenium libraryを用いてxpathの要素のlocation情報を取得する
・Image libraryを用いて画像を切り抜く
これにより、現在のページのxpathの画像ファイルを作成することができる。
あとは、2つの画像比較を行い、一致度を計算し、指定数値以上であるかを検証すればよい
T-DASH 実装
カスタム動作
robotframework library
以下設定ファイルを Image.yaml で保存する
ACT-CAT-CUSTOM-53c469f0-2a3e-4504-9e31-aa8d3da6ff99:
action_category_name: Image
icon: ''
color: '#57fe30'
custom_data:
file_name: Image
pip_list: []
library_list:
- lib_image.py
actions:
ACT-CUSTOM-bc9e7d9e-7db8-4549-bbe4-c6265f25bf92:
action_name: 数字が大きいことを検証
action_type: expectation
action_format: 「設定値1」の値が期待値「設定値2」より高いことを検証
action_note: ''
action_args:
- value1
- value2
action_def:
- - Log
- ${value1}
- - Log
- ${value2}
- - Should Be True
- ${value1} > ${value2}
ACT-CUSTOM-344faacc-ce34-4438-8a7c-e1eb7d8ac943:
action_name: xpathの要素をPNG画像にする
action_type: operation
action_format: 画面「画面名」要素「要素名」を「設定値」にPNG画像する
action_note: ''
action_args:
- screen
- element
- value
action_def:
- - save_xpath_element_screenshot
- ${location}
- ${value}
- - Log
- ' <img src="${value}">'
- html=true
ACT-CUSTOM-e73dd0bb-100b-4a53-ae65-a7c52779a9e5:
action_name: 2つの画像を比較する
action_type: operation
action_format: 画像1「設定値1」と画像2「設定値2」を比較する
action_note: ''
action_args:
- value1
- value2
action_def:
- - ${vars}=
- Get Variables
- - Log
- ${vars['\${OUTPUT_DIR}']}
- - Set Test Variable
- ${image}
- \\diff_image.png
- - Set Test Variable
- ${diff_image}
- ${vars['\${OUTPUT_DIR}']}${image}
- - save_diff_image
- ${value1}
- ${value2}
- ${diff_image}
- - 'Log '
- <img src="${diff_image}">
- html=true
- - ${diff_ratio} =
- calculate_matching
- ${value1}
- ${value2}
- - Log
- ${diff_ratio}
- - Set Suite Variable
- ${share_diff_ratio}
- ${diff_ratio}
次に、Image.yamlをT-DASHの動作定義 -> カスタム動作 -> カスタム動作をインポート にてインポートし、実際にインポートされた設定内容を開く
「xpathの要素をPNG画像にする」の設定を開く
ここで、「ライブラリを追加する」を開く
⇒pythonのライブラリ追加に続く。
python ライブラリ
以下スクリプトを lib_image.pyのファイル名として保存する
import cv2
import numpy as np
import base64
from robot.libraries.BuiltIn import BuiltIn
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from PIL import Image
import io
def save_xpath_element_screenshot(xpath, output_path):
"""
save xpath element by png format
Args:
xpath (str): スクリーンショットを撮りたい要素のXPath。
output_path (str): スクリーンショットの保存パス。
"""
driver = None
driver = BuiltIn().get_library_instance('SeleniumLibrary').driver
element = driver.find_element(By.XPATH, xpath)
# get element size & location
location = element.location
size = element.size
cdp_browser = ['chrome', 'MicrosoftEdge', 'chrome-headless-shell', 'edge-headless-shell']
browser_name = driver.capabilities['browserName']
image = None
if browser_name in cdp_browser:
width = driver.execute_script("return document.body.scrollWidth;")
height = driver.execute_script("return document.body.scrollHeight;")
# 高さが0の場合は、htmlの高さを取得
if height == 0:
height = driver.execute_script("return document.documentElement.scrollHeight;")
if height == 0:
height = 10000
print(f"full screen size is {width} x {height}")
viewport = {
"x": 0,
"y": 0,
"width": width,
"height": height,
"scale": 1
}
# Chrome Devtools Protocolコマンドを実行し、取得できるBase64形式の画像データをデコードしてファイルに保存
image_base64 = driver.execute_cdp_cmd(
"Page.captureScreenshot", {"clip": viewport, "captureBeyondViewport": True})
img_bytes = base64.b64decode(image_base64["data"])
else:
image_base64 = driver.get_full_page_screenshot_as_base64()
img_bytes = base64.b64decode(image_base64)
img = Image.open(io.BytesIO(img_bytes ))
left = location['x']
top = location['y']
right = location['x'] + size['width']
bottom = location['y'] + size['height']
# cut element
element_image = img.crop((left, top, right, bottom))
element_image.save(output_path)
print(f"save XPath element in {output_path}")
def calculate_matching (file1,file2):
img1 = cv2.imread(file1)
img2 = cv2.imread(file2)
if img1.shape[0] > img2.shape[0]:
print( "crop image1 " )
cropped_img = img1[0:img2.shape[0], 0:img1.shape[1]]
img1 = cropped_img
elif img1.shape[0] < img2.shape[0]:
print( "crop image2 " )
cropped_img = img2[0:img1.shape[0], 0:img2.shape[1]]
img2 = cropped_img
height = img1.shape[0]
width = img1.shape[1]
print( "image size = " + str(height) + ' ' + str(width) )
img_size = (int(width), int(height))
rate = np.count_nonzero(img1 == img2) / img1.size
return rate
def save_diff_image (file1,file2,file3):
img1 = cv2.imread(file1)
img2 = cv2.imread(file2)
print( "image1 size = " + str (img1.shape[0]) + ' ' + str (img1.shape[1]) )
print( "image2 size = " + str (img2.shape[0]) + ' ' + str (img2.shape[1]) )
if img1.shape[0] > img2.shape[0]:
if img1.shape[1] > img2.shape[1]:
print( "crop image1 {img2.shape[0]} x {img2.shape[1]}" )
cropped_img = img1[0:img2.shape[0], 0:img2.shape[1]]
img1 = cropped_img
else:
print( "crop image1&2 {img2.shape[0]} x {img1.shape[1]}" )
cropped_img = img1[0:img2.shape[0], 0:img1.shape[1]]
img1 = cropped_img
cropped_img = img2[0:img2.shape[0], 0:img1.shape[1]]
img2 = cropped_img
elif img1.shape[0] < img2.shape[0]:
if img1.shape[1] > img2.shape[1]:
print( "crop image1&2 {img1.shape[0]} x {img2.shape[1]}" )
cropped_img = img1[0:img1.shape[0], 0:img2.shape[1]]
img1 = cropped_img
cropped_img = img2[0:img1.shape[0], 0:img2.shape[1]]
img2 = cropped_img
else:
print( "crop image2 {img1.shape[0]} x {img1.shape[1]}" )
cropped_img = img2[0:img1.shape[0], 0:img1.shape[1]]
img2 = cropped_img
im_diff = img1.astype(int) - img2.astype(int)
im_diff_abs = np.abs(im_diff)
im_diff_abs_norm = im_diff_abs / im_diff_abs.max() * 255
cv2.imwrite(file3, im_diff_abs_norm)
①作成したpython scriptを自作ライブラリのフォルダに格納する
フォルダは、「ファイルを開く」を選択すると、格納先がエクスプローラーで指定される。
②自作ライブラリから、今回追加した「lib_image.py」を選び、⊕をクリックする。
すると、Libraryにリストされる
テストケース
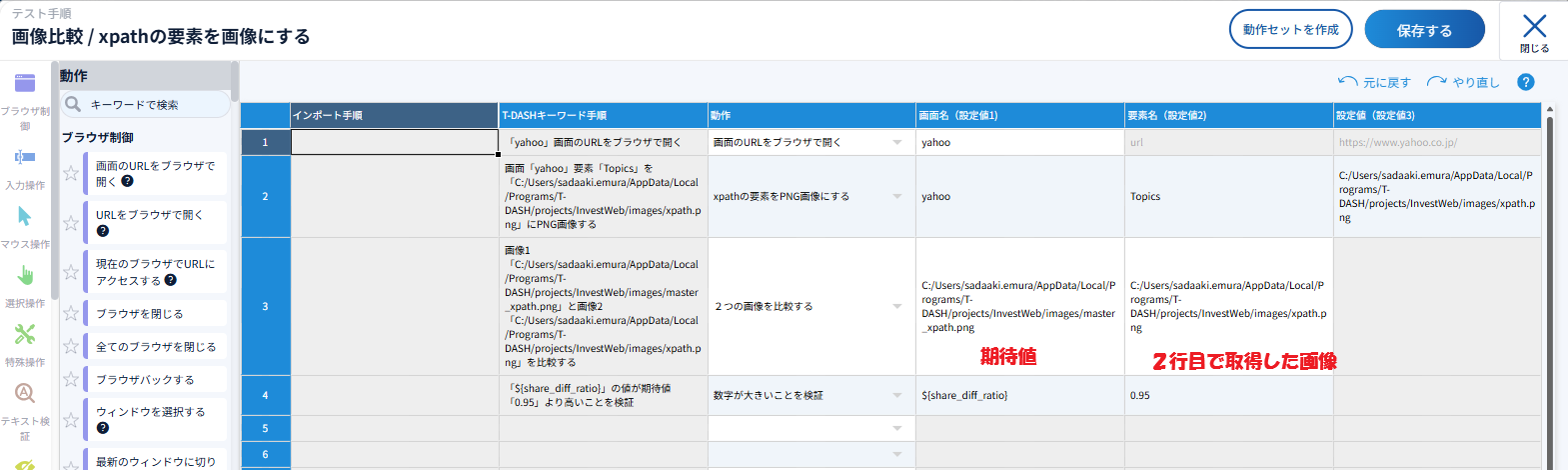
2行目で、画像を取得したいxpath(画面定義)を指定し、保存先を指定する
3行目で、期待値画像と2行目で作成された画像を比較する 差分が変数${share_diff_ratio}に格納される
4行目で、期待値0.95と比較を行う
実行結果
期待値(左)と実際値(真ん中)が異なる(エラー)の例を示す。
差分画像(右)が黒であると、差分がないことを示す。