URLからデータを取得する流れ
(1) ソケットを作成(socket)
↓
(2) ドメイン名をDNSでIPに変換(gethostbyname など)
↓
(3) IPアドレスとポート80にソケットでTCP接続(connect)
↓
(4) HTTPリクエスト(テキスト)をソケットから送信(write/send)
↓
(5) HTTPレスポンスをソケットから受信(read/recv)
↓
(6) ソケットを閉じて通信終了(close)
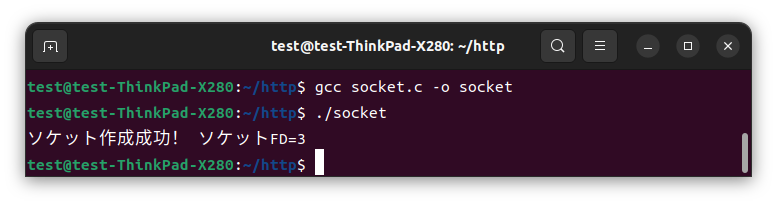
1.ソケットを生成
Linuxではソケットもファイルと同じくファイルディスクリプタ(FD)で管理される。
ここでソケットFDを生成しておくとwrite()やclose()で扱えるようになる。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, // IPv4
SOCK_STREAM, // 信頼性のある通信
0); // プロトコル自動選択(SOCK_STREAMならTCPが選ばれる)
if(sockfd < 0){
puts("ソケット作成失敗!");
return 1;
}
printf("ソケット作成成功! ソケットFD=%d\n",sockfd);
// ソケットを閉じる
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
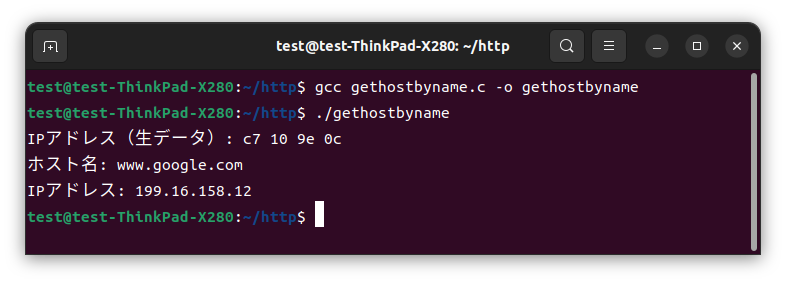
2.ドメイン→IPアドレスへ変換
ドメイン名をIPアドレスに変換する。
gethostbyname()も自作できなくはないが、複雑な上にかなり話が逸れるので今回は標準関数を仕様して、次回自力で実装する。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
const char *host = "www.google.com";
//ホスト名→IPアドレスへ変換
struct hostent *server = gethostbyname(host);
if(server == NULL) {
puts("解析失敗");
return 1;
}
//gethostbyname()が返したIPアドレス
struct in_addr *addr = (struct in_addr *)server->h_addr_list[0];
//16進数で表示
unsigned char *bytes = (unsigned char *)&(addr->s_addr);
printf("IPアドレス(生データ): ");
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(addr->s_addr); i++) {
printf("%02x ", bytes[i]);
}
printf("\n");
//10進数で表示
char *ip = inet_ntoa(*addr);
printf("ホスト名: %s\n", host);
printf("IPアドレス: %s\n", ip);
return 0;
}
hostent構造体の定義
Grepで検索する
test@test-ThinkPad-X280:~/http$ grep -A10 'struct hostent' /usr/include/netdb.h
struct hostent
{
char *h_name; /* Official name of host. */
char **h_aliases; /* Alias list. */
int h_addrtype; /* Host address type. */
int h_length; /* Length of address. */
char **h_addr_list; /* List of addresses from name server. */
#ifdef __USE_MISC
# define h_addr h_addr_list[0] /* Address, for backward compatibility.*/
#endif
};
in_addr構造体の定義
※server->h_addr_list[0]の中身を表示する為に使っただけで、最終的にhtmlを取得するソースの中では使用していない。(記事の一番した参照)
Grepで検索する
test@test-ThinkPad-X280:~$ grep -A3 'struct in_addr' /usr/include/netinet/in.h
struct in_addr
{
in_addr_t s_addr;
};
test@test-ThinkPad-X280:~$ grep typedef /usr/include/netinet/in.h | grep in_addr_t
typedef uint32_t in_addr_t;
test@test-ThinkPad-X280:~$ echo '#include <stdint.h>' | gcc -E -dD -xc - | grep int32_t
typedef signed int __int32_t;
typedef unsigned int __uint32_t;
typedef __int32_t __int_least32_t;
typedef __uint32_t __uint_least32_t;
typedef __int32_t int32_t;
typedef __uint32_t uint32_t;
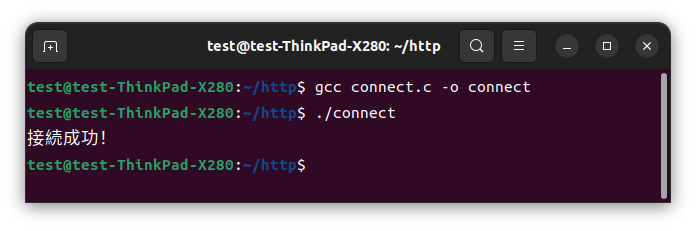
3.サーバへ接続
ソケットを作成し、接続先のIPアドレスも取得できたら、いよいよ「TCP接続」を行います。
connect()を用いてソケットから指定されたIPアドレスとポート番号に接続を試みます。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int main() {
const char *host = "example.com";
const int port = 80;
// ソケット生成 (上で説明済み)
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (sockfd < 0) {
puts("socket");
return 1;
}
// ドメイン→IP変換
struct hostent *server = gethostbyname(host);
if(server == NULL) {
puts("解析失敗");
return 1;
}
struct sockaddr_in server_addr;
memset(&server_addr, 0, sizeof(server_addr));// 構造体の全てのバイトを0で初期化
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;//IPv4使用
server_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
memcpy(&server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr,
server->h_addr, // ドメインから取得したIPアドレス
server->h_length // IPアドレスの長さ
);
// サーバーへ接続する
if (connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr)) < 0) {
puts("connect");
close(sockfd);
return 1;
}
printf("接続成功!\n");
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}
memset() とは?
void *memset(void *s, int c, size_t n);
s: 初期化したいメモリ領域の先頭ポインタ
c: 埋める値(0〜255、1バイト)
n: 何バイト分埋めるか
4.HTTPリクエストの文字列を生成
以下の文字列を生成する。
Hostは接続先によって変更。
GET / HTTP/1.1\r\n
Host: www.google.com\r\n
Connection: close\r\n
\r\n
5. HTTPリクエストを送信する
TCP接続済みのソケットFDに対して、HTTPリクエスト文字列(request)を送信します。
write() はファイルに書き込むのと同様に使えます。
(Linuxでは全てをファイルとして扱う)
if (write(sockfd, request, strlen(request)) < 0) {
puts("write");
close(sockfd);
return 1;
}
6. HTTPレスポンスを受信して表示する
read()から取得する。
一回で全て取得出来るとは限らないのでwhileでループにして取得していく。
実際にはTCPソケットが内部的に持っている受信バッファから少しずつ取得している。
あまり細かいことはLinuxカーネル内部の実装を読まないと分からない。
char buffer[2048];
int bytes;
while ((bytes = read(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)-1)) > 0) {
buffer[bytes] = '\0';
printf("%s", buffer);
}
example.comからデータを取得する。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int main() {
const char *host = "example.com";
const int port = 80;
// ソケットを生成
int sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (sockfd < 0) {
perror("socket");
return 1;
}
// ドメイン→IPアドレスへ変換
struct hostent *server = gethostbyname(host);
if (server == NULL) {
puts("ip取得!");
return 2;
}
struct sockaddr_in server_addr;
memset(&server_addr, 0, sizeof(server_addr));
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
memcpy(&server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr, server->h_addr, server->h_length);
// サーバーへ接続する
if (connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr)) < 0) {
puts("connect");
close(sockfd);
return 3;
}
// HTTPリクエストの文字列を生成
char request[1024];
snprintf(request, sizeof(request),
"GET / HTTP/1.1\r\n"
"Host: %s\r\n"
"Connection: close\r\n"
"\r\n", host);
if (write(sockfd, request, strlen(request)) < 0) {
puts("write");
close(sockfd);
return 4;
}
// HTTPレスポンスを受信して表示する
char buffer[2048];
int bytes;
while ((bytes = read(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer)-1)) > 0) {
buffer[bytes] = '\0';
printf("%s", buffer);
}
// socketを閉じる
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}