Introduction
For people who works as a Web Developer might be familiar with the concept of DOM or more specifically Original DOM, huh 😃
Have you ever wondered huge sites like Facebook, Twitter, GMail, etc with million lines of code, how they could manage DOM Tree ?
And of course, with DOM only, it is difficult for web developers to handle such million stuffs. From there, it came out the concept Virtual DOM and Shadow DOM.
So in this article, let's learn more about the Original DOM, Shadow DOM and Virtual DOM to get a full view of them.
Let's get started ^^
Original DOM
Overview
DOM stands for Document Object Model.
The DOM includes:
- Object-based representation of the HTML document
Elements in DOM Structure are defined as objects, methods, and properties that can be accessed easily.
They are treated as nodes and are represented as DOM Tree.
<html> -> document node
<head> -> element node - head
<title>
HTML DOM -> text node
</title> -> element node - title
</head>
<body> -> element node - body
</body>
</html>
- DOM APIs
The HTML DOM provides APIs for browsing and editing nodes.
Specific examples of APIs can be mentioned as getElementById () used to access an element by id or removeChild () used to remove a child element based on its parent.
Shadow DOM
Overview
Mozilla has summarized 3 basic characteristics of the Shadow DOM:
Shadow DOM can be thought of as:
- Isolated DOM
- A “lite” version of the DOM
- NOT of a full standalone document
The reason for saying so is that the stylesheet or javascript from outside can't affect the Shadow DOM and vice versa.
For example, we have the <Video> tag as a custom element.
The structure of a DOM shadow
With Shadow DOM, we will learn a new concept called Shadow Root. Shadow Root's content will not be rendered by the browser but the Shadow Host. The Shadow Host is treated as a normal element, but the content inside it (including the stylesheet) will be packaged and independent with the outside world:
Create a DOM shadow
<style> p { color: green } </style>
<p id="sd-root">I am Shadow Root</p>
<script>
const host = document.querySelector('#sd-root');
const root = host.createShadowRoot();
root.innerHTML = `
<style> p { color: gray }</style>
<p>Hello <strong>Shadow DOM</strong></p>
`;
</script>
Guess what the result will be 🤔🤔. . .

Here when the browser is finished rendering we will get:

instead of
When inspecting the element, we will see like this:
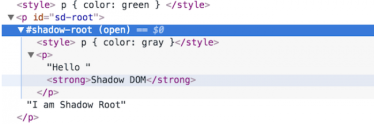
Thus, we will have a few comments as follows:
- Though
Shadow DOM's inner styles are conflicted with the outside's one, it's still okay because of the characteristics ofShadow DOM(scoped style sheet) - When we access
.innerHTML ()of element#sd-root, we ONLY get the initialization text: "I am Shadow Root" and also can not affect anything insideShadow Root.
Okay, now we've known better about
DOM
- The bright part (or often called the Light DOM) is what we can interact with.
- The dark part of it, the shadow (Shadow DOM) only reflects on how it will be rendered when the Light DOM changes.
And of course, we can never touch the shadow of an object 😄😄
Oohh, DOM is so good, so why do we need Virtual DOM ? 🙄🙄
Let's find out more together 😛😛
Virtual DOM
Overview
Although this concept has existed for a long time, it only became popular when it's used in popular libraries like ReactJS, VueJS ...
As its name implies, Virtual DOM. Virtual, means unreal.
Virtual-DOM is an Object that contains the information needed to create a DOM (Document Object Model).
Virtual DOM is capable of calculating and updating node without using DOM APIs. After updating the Virtual DOM, changes will be made to Original DOM.
As some of the features I mentioned above, Virtual DOM are seen as an effective way to solve the updating problem with DOM, it's no need to re-render the whole DOM Tree.
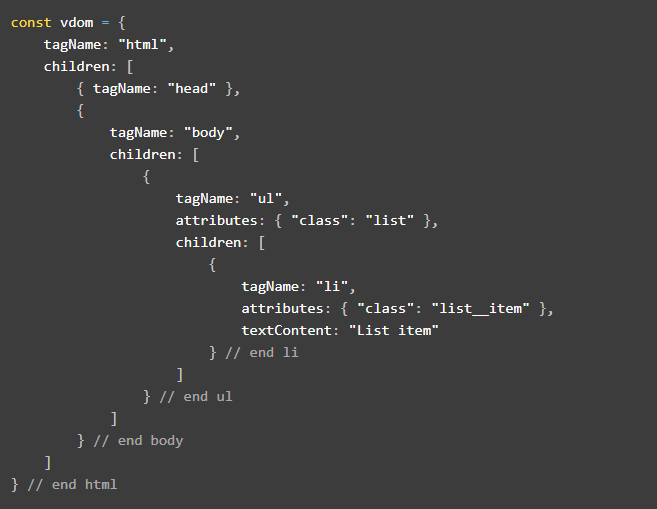
Here is a specification DOM Tree:

and is converted to Virtual DOM:
In fact, instead of having to work with all objects, we often work with the smaller object corresponding to Virtual DOM's components.
Mechanism
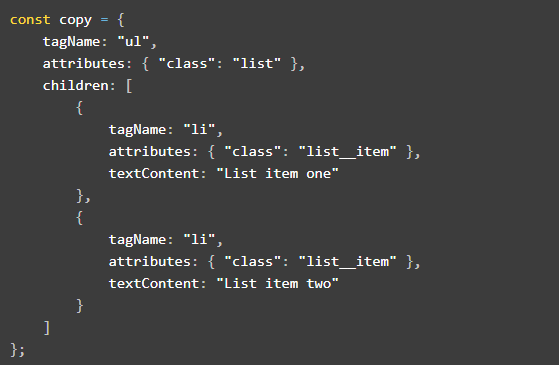
Initially, an object that serves as a virtual DOM's snapshot will be created:
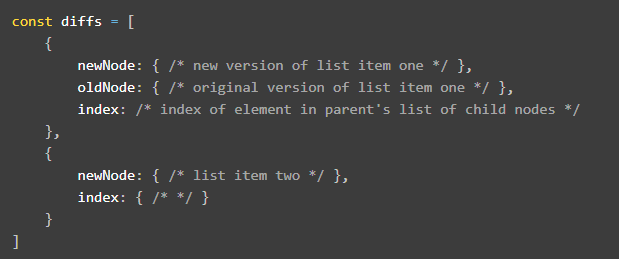
This copy version is used to create a diff comparison with the virtual DOM original version , basically it will look like this:
From there, Engine will know which elements have to be updated in original DOM, it only executes update when there is a change.
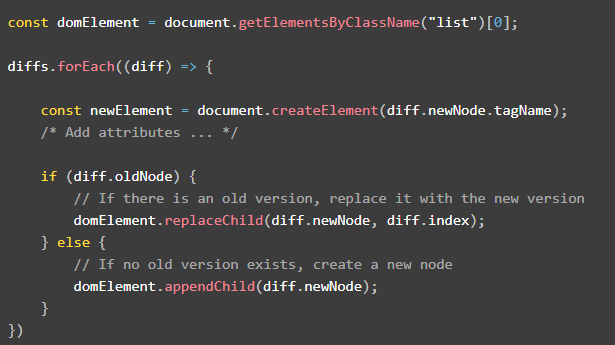
To do this, just loop through the diff whether when adding a new node or when updating existed one:
Then, update list, rewrite the entire template, run the function render(), display the changes view.
Although it is said to be entire template, only the parts that have actually changed will be updated. The changes made to this object are then collated and modified against original DOM.
Why use Virtual DOM?
1. Speed
Previously, I thought the reason that Virtual DOM is faster than Original DOM is that setting the object's attributes is faster than updating the DOM , but it's not you guys 😂😂
The fact is that updating the DOM not take much time compared to updating attributes of object.
What really affects speed performance here is that when the DOM changes, the browser has to recalculate CSS, build layout, paint template ...
Because the structure of DOM is tree structure, so when you want to change element and its tags and sub tags, the browser has to rerun process Reflow/Layout. The more items you have, the slower your web will be 😦
Hmmm ...
To understand this issue more deeply, let's explore one more concept that is about mechanism binding.
2. Data-binding
The concept data-binding can be understood simply as:
Data-binding: Data in Model changes <=> View changes.
Data-binding in the real DOM
In some famous frameworks using mechanism data-binding such as BackboneJS, AngularJS, when Object Model's datas change, it will:
- Confirm the
event+ relatedView Object - Impact on the DOM's elements and reflect that datas change.
Data-binding in the virtual DOM
In the frameworks using
Virtual-DOM,Virtual-DOMacts as bothModelandView
Thus, when Virtual-DOM changing, all the above changes on Model will led to changes on View and vice versa.
Although it does not impact directly to the DOM elements, it's still able to implement mechanisms data-binding. This makes the application speed significantly increased.
Conclusion
So we've got the idea what Original DOM, Shadow DOM, Virtual DOM are. Hopefully this article can help you understand more about DOM and related issues.
Wishing you a productive week !
Thanks for reading ❤