目標
echoを触れる環境を用意できたので、公式ドキュメントを読みながらミドルウェア機能を見て理解していく
作業前の構成などは
https://github.com/dsrice/go_echo/tree/part2
を参照してください。
基本認証(Basic Auth)
公式ドキュメントに従ってserver.goに実装を追加
package infra
import (
"app/controllers"
"crypto/subtle"
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4"
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4/middleware"
)
type Server struct {
Echo *echo.Echo
}
func NewServer() *Server {
return &Server{
Echo: echo.New(),
}
}
func (server *Server) Start() {
server.Echo.Use(middleware.BasicAuth(func(username, password string, c echo.Context) (bool, error) {
if subtle.ConstantTimeCompare([]byte(username), []byte("joe")) == 1 &&
subtle.ConstantTimeCompare([]byte(password), []byte("secret")) == 1 {
return true, nil
}
return false, nil
}))
server.Echo.GET("/", controllers.NewHelloController().GetMessage)
server.Echo.Start(":1323")
}
設定ができたらサーバーを起動(*1)
その後、http://localhost:1323 にブラウザからアクセスするとBasic認証が要求されるようになります
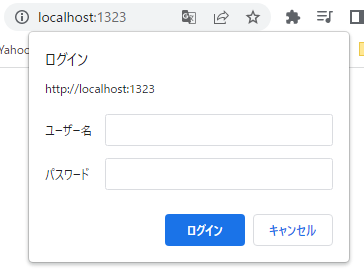
今回はユーザー名はjoe、パスワードはsecretで固定になっている。
この組み合わせ以外を送信すると401エラーになる。
今のままだと、すべてのURLでBasic認証が要求されてしまうので詳細設定を試みる。
カスタム設定のさいはこちらを使う
server.Echo.Use(middleware.BasicAuthWithConfig(middleware.BasicAuthConfig{}))
公式ドキュメントより、設定内容は、
BasicAuthConfig struct {
// Skipper defines a function to skip middleware.
Skipper Skipper
// Validator is a function to validate BasicAuth credentials.
// Required.
Validator BasicAuthValidator
// Realm is a string to define realm attribute of BasicAuth.
// Default value "Restricted".
Realm string
}
Skipperは、Basic認証をする、しないかのハンドリング処理、booleanを戻り値とした処理でtrueが返ってくるとBasic認証しなくなる。
Validatorが、Basic認証の実処理
Realmが、Basic Realmの指定で、ブラウザはWWW-AuthenticateにBasic realm=”値”というヘッダがセットされた401レスポンスを受け取ったら、IDとPASSWORDを入力するダイアログを表示するようになる。
試しに、以下の内容にすると、http://localhost:1323 にアクセスしてもBasic認証しなくなる
package infra
import (
"app/controllers"
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4"
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4/middleware"
)
type Server struct {
Echo *echo.Echo
}
func NewServer() *Server {
return &Server{
Echo: echo.New(),
}
}
func (server *Server) Start() {
server.Echo.Use(middleware.BasicAuthWithConfig(middleware.BasicAuthConfig{
Skipper: func(c echo.Context) bool {
if c.Request().RequestURI == "/" {
return true
}
return false
},
Validator: func(username string, password string, context echo.Context) (bool, error) {
if username == "joe" && password == "test" {
return true, nil
}
return false, nil
},
Realm: "Restricted",
}))
server.Echo.GET("/", controllers.NewHelloController().GetMessage)
server.Echo.Start(":1323")
}
今回APIの利用のみを考えているので、Basic認証は利用しない。
ボディダンプ
リクエストおよびレスポンスのペイロードをキャプチャして、登録したハンドラーを呼び出します。
要は、リクエストおよびレスポンスボディの内容をログなどに出力することが可能になる。
公式ドキュメントに書かれているが、ファイルアップロード、ダウンロードといったペイロードが大きくなる処理では利用しないように呼びかけられている。
試しに使用してみると
package infra
import (
"app/controllers"
"fmt"
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4"
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4/middleware"
)
type Server struct {
Echo *echo.Echo
}
func NewServer() *Server {
return &Server{
Echo: echo.New(),
}
}
func (server *Server) Start() {
server.Echo.Use(middleware.BodyDump(func(c echo.Context, reqBody, resBody []byte) {
fmt.Printf("Request: %v\n", string(reqBody))
fmt.Printf("Response: %v\n", string(resBody))
}))
server.Echo.GET("/", controllers.NewHelloController().GetMessage)
server.Echo.Start(":1323")
}
実装後サーバーを起動、http://localhost:1323 にアクセスするとコンソールには、
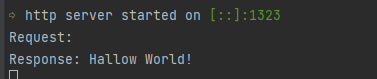
といった形に出力される。
このままでは、公式ドキュメントに書かれている注意事項を守れないので設定をちゃんとする。
ボディダンプのカスタム設定は、
server.Echo.Use(middleware.BodyDumpWithConfig(middleware.BodyDumpConfig{}))
を使う。
公式ドキュメントにより、設定内容は以下のようになっている。
BodyDumpConfig struct {
// Skipper defines a function to skip middleware.
Skipper Skipper
// Handler receives request and response payload.
// Required.
Handler BodyDumpHandler
}
Skipperは、処理をするしないの切り分ける関数を設定する。
戻り値はbooleanでtrueのときにハンドラーの処理を実施しないようになる。
Skipperを設定することでファイルダウンロードのようなペイロードを大きいときに処理をしないといったことが可能になる。
Handlerは、先ほど設定したボディダンプの実処理になる。
試しに以下の内容に直すと、http://localhost:1323 にアクセスしてもコンソール上に出力されなくなる。
package infra
import (
"app/controllers"
"fmt"
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4"
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4/middleware"
)
type Server struct {
Echo *echo.Echo
}
func NewServer() *Server {
return &Server{
Echo: echo.New(),
}
}
func (server *Server) Start() {
server.Echo.Use(middleware.BodyDumpWithConfig(middleware.BodyDumpConfig{
Skipper: func(c echo.Context) bool {
if c.Request().RequestURI == "/" {
return true
}
return false
},
Handler: func(context echo.Context, reqBody, resBody []byte) {
fmt.Printf("Request: %v\n", string(reqBody))
fmt.Printf("Response: %v\n", string(resBody))
},
}))
server.Echo.GET("/", controllers.NewHelloController().GetMessage)
server.Echo.Start(":1323")
}
ボディリミット
リクエストボディのサイズ制限機能
公式ドキュメントには、Content-Lengthと実際に読みったコンテンツサイズの両方をみるとのことなのでセキュリティ面も考慮されている。
検証する環境を用意しないので試し実装はしない。
こちらもカスタム設定できるようになっていて
設定内容は、公式ドキュメントより
BodyLimitConfig struct {
// Skipper defines a function to skip middleware.
Skipper Skipper
// Maximum allowed size for a request body, it can be specified
// as `4x` or `4xB`, where x is one of the multiple from K, M, G, T or P.
Limit string `json:"limit"`
}
Skipperはサイズ確認の実施有無のハンドリングを行う関数を設定する。
関数は戻り値をbooleanとしてtrueのときにサイズ確認がしなくなる。
Limitは、最大サイズの指定で実数字でなく、4MBとすると4メガ制限になる。
Casbin認証
今回はスキップ
理由は、Casbin認証を私が理解していないためちゃんと調べてまとめることにする
単純にスキップしないのは、公式ドキュメントの内容を読んで気になったから
CORS
CORS仕様の実装が行える機能
近年対応は当たり前なので機能としてあるのは非常にありがたい気がする。
試す環境を用意しないので、設定内容の説明のみとする。
公式ドキュメントより
CORSConfig struct {
// Skipper defines a function to skip middleware.
Skipper Skipper
// AllowOrigin defines a list of origins that may access the resource.
// Optional. Default value []string{"*"}.
AllowOrigins []string `yaml:"allow_origins"`
// AllowOriginFunc is a custom function to validate the origin. It takes the
// origin as an argument and returns true if allowed or false otherwise. If
// an error is returned, it is returned by the handler. If this option is
// set, AllowOrigins is ignored.
// Optional.
AllowOriginFunc func(origin string) (bool, error) `yaml:"allow_origin_func"`
// AllowMethods defines a list methods allowed when accessing the resource.
// This is used in response to a preflight request.
// Optional. Default value DefaultCORSConfig.AllowMethods.
AllowMethods []string `yaml:"allow_methods"`
// AllowHeaders defines a list of request headers that can be used when
// making the actual request. This is in response to a preflight request.
// Optional. Default value []string{}.
AllowHeaders []string `yaml:"allow_headers"`
// AllowCredentials indicates whether or not the response to the request
// can be exposed when the credentials flag is true. When used as part of
// a response to a preflight request, this indicates whether or not the
// actual request can be made using credentials.
// Optional. Default value false.
AllowCredentials bool `yaml:"allow_credentials"`
// ExposeHeaders defines a whitelist headers that clients are allowed to
// access.
// Optional. Default value []string{}.
ExposeHeaders []string `yaml:"expose_headers"`
// MaxAge indicates how long (in seconds) the results of a preflight request
// can be cached.
// Optional. Default value 0.
MaxAge int `yaml:"max_age"`
}
Skipperは、CORSの実施有無のハンドリングする関数を設定する。関数の戻り値はbooleanで、trueが戻るとCORSが実施されなくなる。
AllowOriginsとAllowOriginFuncは、許可元設定関連明確なら、AllowOriginsに文字列配列で設定するだけでよい、
環境などに依存するケースは、AllowOriginFuncを使ってハンドリング関数を設定する。
AllowOriginsとAllowOriginFuncの両方設定がある場合、AllowOriginFuncが優先される。
AllowMethodsは許可メソッド設定。文字列配列で指定するが、net/hpptにhttp.MethodGetなどメソッド文字列の定数があるのでこちらを使って設定したほうが、丁寧な気がする。
AllowHeadersは許可ヘッダー設定。プリフライトリクエストのレスポンスで帰ってくるのはここの内容。
AllowCredentialsはクレデンシャル設定。資格情報を活用する場合は、trueにする必要がある。
ExposeHeadersは許可ヘッダー設定。リクエストヘッダーに該当ヘッダーにない場合はアクセスできなくなる。
MaxAgeはプリフライトリクエストのキャッシュ時間。-1を設定にするとキャッシュにいれず毎回プリフライトリクエスト実施するようになる。
FireFoxは24時間、Chromiumで2時間がデフォルト設定になっている。0を設定するとクライアント側が自動で判定する。
CSRF
CSRF対策の設定
どちらかという画面がある場合に利用されるのがメインになっている。
APIに関しては、利用者の認証処理を正しく用意されていれば利用しなくてもよさそう
カスタム設定が可能で、内容は、
CSRFConfig struct {
// Skipper defines a function to skip middleware.
Skipper Skipper
// TokenLength is the length of the generated token.
TokenLength uint8 `json:"token_length"`
// Optional. Default value 32.
// TokenLookup is a string in the form of "<source>:<key>" that is used
// to extract token from the request.
// Optional. Default value "header:X-CSRF-Token".
// Possible values:
// - "header:<name>"
// - "form:<name>"
// - "query:<name>"
// - "cookie:<name>"
TokenLookup string `json:"token_lookup"`
// Context key to store generated CSRF token into context.
// Optional. Default value "csrf".
ContextKey string `json:"context_key"`
// Name of the CSRF cookie. This cookie will store CSRF token.
// Optional. Default value "_csrf".
CookieName string `json:"cookie_name"`
// Domain of the CSRF cookie.
// Optional. Default value none.
CookieDomain string `json:"cookie_domain"`
// Path of the CSRF cookie.
// Optional. Default value none.
CookiePath string `json:"cookie_path"`
// Max age (in seconds) of the CSRF cookie.
// Optional. Default value 86400 (24hr).
CookieMaxAge int `json:"cookie_max_age"`
// Indicates if CSRF cookie is secure.
// Optional. Default value false.
CookieSecure bool `json:"cookie_secure"`
// Indicates if CSRF cookie is HTTP only.
// Optional. Default value false.
CookieHTTPOnly bool `json:"cookie_http_only"`
}
SkipperはCSRF実施有無をハンドリングする関数を設定する。関数の戻り値はbooleanを使い、trueのときにCSRFを実施しない
TokenLengthは、CSRFの際のトークンサイズ指定になる。
TokenLookupは、リクエスト時のトークン設定個所
ContextKeyは、トークン作成時のContextのキー情報
CookieNameは、トークン設定がCookieの際の名称
CookieDomainは、トークン設定がCookieの時のドメイン情報
CookiePathは、トークン設定がCookieの時のパス情報
CookieMaxAgeは、トークン設定がCookieの時の生存時間
CookieSecureは、トークン設定がCookieのときのセキュア属性設定
CookieHTTPOnlyは、トークン設定がCookieのときのHTTP設定
Decompress
HeaderのContent-Encoding 「gzip」のときにメモリ上に自動解凍を行うようにする設定になる。
解凍はメモリ内で行われ、リクエストの存続期間中保持されます。
と書かれているが、扱う際はいずこに?
結論は、
Bodyにgzip.Readerで入っています。
本来gzipファイルを扱うには、
// gzipファイルのオープン.
f, _ := os.Open("C:\\programs\\file.gz")
// gzipのdescompressをし、リーダー作成.
reader, _ := gzip.NewReader(f)
result := make([]byte, 100)
// データリードをして、resultに内容が入る.
count, _ := reader.Read(result)
といった実装が必要で、実際にはContext-Encodingを確認して使い分ける必要がある。
活用する方針がないわけではないが、今回は利用しない
設定方法は
e.Use(middleware.Decompress())
カスタム設定では、ほかのものと同じようにSkipperを設定することができる
Gzip
Responseの応答をgzip圧縮できるようになる。
設定方法は、
e.Use(middleware.Gzip())
カスタム設定では、
SkipperとLevelを設定することができる。
Levelはgzipの圧縮レベルになる。
gzipで変えるのでクライアント側の対応が必要だが、
レスポンスデータが大容量になるのなら効果がある設定
今回はそれほど大きくなる予定はないのでこちらも保留
Jaeger
こちらはJaeger自体の話を含めて別記事にします
JWT
JWT認証設定のミドルウェアになります。
仕様上の注意としてgoモジュールの取得が必要になる。
go get github.com/labstack/echo-jwt/v4
簡単に利用する際は秘密鍵のみを設定すれば使えるのだが、
利用する際はカスタム設定を使うほうが一般的な気がする。
type Config struct {
// Skipper defines a function to skip middleware.
Skipper middleware.Skipper
// BeforeFunc defines a function which is executed just before the middleware.
BeforeFunc middleware.BeforeFunc
// SuccessHandler defines a function which is executed for a valid token.
SuccessHandler func(c echo.Context)
// ErrorHandler defines a function which is executed when all lookups have been done and none of them passed Validator
// function. ErrorHandler is executed with last missing (ErrExtractionValueMissing) or an invalid key.
// It may be used to define a custom JWT error.
//
// Note: when error handler swallows the error (returns nil) middleware continues handler chain execution towards handler.
// This is useful in cases when portion of your site/api is publicly accessible and has extra features for authorized users
// In that case you can use ErrorHandler to set default public JWT token value to request and continue with handler chain.
ErrorHandler func(c echo.Context, err error) error
// ContinueOnIgnoredError allows the next middleware/handler to be called when ErrorHandler decides to
// ignore the error (by returning `nil`).
// This is useful when parts of your site/api allow public access and some authorized routes provide extra functionality.
// In that case you can use ErrorHandler to set a default public JWT token value in the request context
// and continue. Some logic down the remaining execution chain needs to check that (public) token value then.
ContinueOnIgnoredError bool
// Context key to store user information from the token into context.
// Optional. Default value "user".
ContextKey string
// Signing key to validate token.
// This is one of the three options to provide a token validation key.
// The order of precedence is a user-defined KeyFunc, SigningKeys and SigningKey.
// Required if neither user-defined KeyFunc nor SigningKeys is provided.
SigningKey interface{}
// Map of signing keys to validate token with kid field usage.
// This is one of the three options to provide a token validation key.
// The order of precedence is a user-defined KeyFunc, SigningKeys and SigningKey.
// Required if neither user-defined KeyFunc nor SigningKey is provided.
SigningKeys map[string]interface{}
// Signing method used to check the token's signing algorithm.
// Optional. Default value HS256.
SigningMethod string
// KeyFunc defines a user-defined function that supplies the public key for a token validation.
// The function shall take care of verifying the signing algorithm and selecting the proper key.
// A user-defined KeyFunc can be useful if tokens are issued by an external party.
// Used by default ParseTokenFunc implementation.
//
// When a user-defined KeyFunc is provided, SigningKey, SigningKeys, and SigningMethod are ignored.
// This is one of the three options to provide a token validation key.
// The order of precedence is a user-defined KeyFunc, SigningKeys and SigningKey.
// Required if neither SigningKeys nor SigningKey is provided.
// Not used if custom ParseTokenFunc is set.
// Default to an internal implementation verifying the signing algorithm and selecting the proper key.
KeyFunc jwt.Keyfunc
// TokenLookup is a string in the form of "<source>:<name>" or "<source>:<name>,<source>:<name>" that is used
// to extract token from the request.
// Optional. Default value "header:Authorization".
// Possible values:
// - "header:<name>" or "header:<name>:<cut-prefix>"
// `<cut-prefix>` is argument value to cut/trim prefix of the extracted value. This is useful if header
// value has static prefix like `Authorization: <auth-scheme> <authorisation-parameters>` where part that we
// want to cut is `<auth-scheme> ` note the space at the end.
// In case of JWT tokens `Authorization: Bearer <token>` prefix we cut is `Bearer `.
// If prefix is left empty the whole value is returned.
// - "query:<name>"
// - "param:<name>"
// - "cookie:<name>"
// - "form:<name>"
// Multiple sources example:
// - "header:Authorization:Bearer ,cookie:myowncookie"
TokenLookup string
// TokenLookupFuncs defines a list of user-defined functions that extract JWT token from the given context.
// This is one of the two options to provide a token extractor.
// The order of precedence is user-defined TokenLookupFuncs, and TokenLookup.
// You can also provide both if you want.
TokenLookupFuncs []middleware.ValuesExtractor
// ParseTokenFunc defines a user-defined function that parses token from given auth. Returns an error when token
// parsing fails or parsed token is invalid.
// Defaults to implementation using `github.com/golang-jwt/jwt` as JWT implementation library
ParseTokenFunc func(c echo.Context, auth string) (interface{}, error)
// Claims are extendable claims data defining token content. Used by default ParseTokenFunc implementation.
// Not used if custom ParseTokenFunc is set.
// Optional. Defaults to function returning jwt.MapClaims
NewClaimsFunc func(c echo.Context) jwt.Claims
}
Skipperは恒例となっているスキップ設定。JWT認証が不要なケースがあるときに設定する。
BeforeFuncはJWT認証前に実施する処理を設定できる。
SuccessHandlerはJWT認証成功時の処理を設定できる
ErrorHandlerはJWT認証失敗時の処理を設定できる
ContinueOnIgnoredErrorはエラー時の処理結果を無視するかの設定。認証成功時のみ特定のメニューだすなど
認証前にも使える機能があったりするときに活用できる。
ContextKeyはJWTを複合して得られた情報をContext内に格納する際のキー情報
SigningKeyは秘密鍵
SigningKeysは複数の秘密鍵を設定。使い分けはKeyFuncで実施する。
SigningMethodは暗号アルゴリズムの種類
KeyFuncは、JWTの判定処理。複数の秘密鍵を使い分ける際は、使い分けに関する処理も追記する。
TokenLookupは、リクエスト時のJWT情報の設定個所。複数設定もできる。
TokenLookupFuncs、複数の種類のJWT情報の設定確認。宣言のみでなく、詳細を記述できる。
ParseTokenFuncは、基本的な処理はgithub.com/golang-jwt/jwtに依存しているのだが、
このモジュールに依存しない形式でJWT認証の関連設定を行う場合に利用する。
NewClaimsFuncは、JWTの構成情報
APIの認証にJWTを利用予定なので使う際に細かく見ていくことにするが、
大枠の利用はカスタム設定がメインかと
Key Auth
キー認証設定になり、
リクエストに指定したルールのキーがない場合は、400エラー
キーがあっても無効な場合は401エラーを返す。
JWT認証との最大の違いは、Contextに入れる処理などは用意されていない。
サービス利用キーみたいな、ユーザー認証とは別観点の認証を設けたいときに利用するのは
活用できそうな機能
Logger
ロガー関連のミドルウェアだが、2種類の異なるミドルウェアが存在している。
- Logger 文字列テンプレートベースのロガーで、扱いが簡単な一方で、制約が多い
- RequestLogger 関数ベースのロガーで、カスタマイズをすることができる。これによりサードパーティのロガーライブラリの利用に適している。
詳細は公式ドキュメントと同じなので割愛するが、
RequestLoggerでカスタマイズする際は、RequestLoggerValueでHttpリクエストの情報を取得することができるようになっている。
詳細は、Gitを見に行く必要がある。(https://github.com/labstack/echo/blob/master/middleware/request_logger.go)
Method Override
POSTのみに使用することができるオーバーライド設定のミドルウェア
ファイヤーウォールなどの関係でPUTやDELETEを許可されないケースがある場合、
POST要求を通じてPUTやDELETE要求を送る必要がある場合に使用します。
Prometheus
こちらはPrometheus自体の話を含めて別記事にします
Proxy
HTTP/WebSocketのリバースプロキシを提供します。
普通のリバースプロキシの設定というよりアプリケーションよりな設定をするときに使用することが多そう。
V1からV2に強制変換などがあるが、ちゃんとしてWrebサーバーがあればあまり使わなさそうな機能だった
カスタム設定では、
// ProxyConfig defines the config for Proxy middleware.
ProxyConfig struct {
// Skipper defines a function to skip middleware.
Skipper Skipper
// Balancer defines a load balancing technique.
// Required.
Balancer ProxyBalancer
// Rewrite defines URL path rewrite rules. The values captured in asterisk can be
// retrieved by index e.g. $1, $2 and so on.
Rewrite map[string]string
// RegexRewrite defines rewrite rules using regexp.Rexexp with captures
// Every capture group in the values can be retrieved by index e.g. $1, $2 and so on.
RegexRewrite map[*regexp.Regexp]string
// Context key to store selected ProxyTarget into context.
// Optional. Default value "target".
ContextKey string
// To customize the transport to remote.
// Examples: If custom TLS certificates are required.
Transport http.RoundTripper
// ModifyResponse defines function to modify response from ProxyTarget.
ModifyResponse func(*http.Response) error
Skipperはほかの機能と同様にtrueのときにプロキシ機能を利用しない
Balancerは用意されているProxyBlancer(Interface)に注入したルールを設定する。
Rewriteは書き換えルールの設定
RegexRewriteは書き換えルールを正規表現を使って設定
ContextKeyは使用したProxyTargetの情報をContext内にいれるときのkey値
Transportは通信におけるカスタム設定。リトライ処理や通信宣言も設けられる。
ModifyResponseはProxyTargetからのレスポンスの共通変更処理
Rate Limiter
一定期間内に特定のIP、IDからサーバーへのリクエスト量を制限するもの
デフォルトではリクエストの追跡をメモリ内で行っているが、大量のリクエストなど状況では最適ではないとのこと
APIを公開したときの利用者への制限を課す時には有効なミドルウェアだと思う。
Recover
panicから回復し、スタックトレースを出力
HTTPErrorHandlerに処理をします。
Go言語では基本panicは使わない実装をすべきですが、モジュールによってはpanicが使われいるときがあり、意図しない異常終了をしてしまう可能性があるので設定しておいたほうが安全かもしれない。
デフォルト設定で簡単に利用できるが、異常終了したことを検知できないのでカスタム設定で使うほうがいいかもしれない
// LogErrorFunc defines a function for custom logging in the middleware.
LogErrorFunc func(c echo.Context, err error, stack []byte) error
RecoverConfig struct {
// Skipper defines a function to skip middleware.
Skipper Skipper
// Size of the stack to be printed.
// Optional. Default value 4KB.
StackSize int `yaml:"stack_size"`
// DisableStackAll disables formatting stack traces of all other goroutines
// into buffer after the trace for the current goroutine.
// Optional. Default value false.
DisableStackAll bool `yaml:"disable_stack_all"`
// DisablePrintStack disables printing stack trace.
// Optional. Default value as false.
DisablePrintStack bool `yaml:"disable_print_stack"`
// LogLevel is log level to printing stack trace.
// Optional. Default value 0 (Print).
LogLevel log.Lvl
// LogErrorFunc defines a function for custom logging in the middleware.
// If it's set you don't need to provide LogLevel for config.
LogErrorFunc LogErrorFunc
}
Skipperはほかの機能と同様にtrueのときにRecover機能を利用しない
StackSizeはスタックサイズの設定。デフォルト値は4KB
DisableStackAllはtrueにすることですべてのスタックトレースを無効にする設定
DisablePrintStackはスタックトレースのprint設定
LogLevelはログの出力レベル設定
LogErrorFuncはエラーログの出力処理
Redirect
リダイレクトには複数種類用意されている。
- HTTPSリダイレクト
- HTTP要求はHTTPSにリダイレクトする
- HTTPS WWW リダイレクト
- HTTP要求をHTTPS WWWにリダイレクトする
- HTTPS NonWWW リダイレクト
- HTTP要求をHTTPS non WWWにリダイレクトする
- WWWリダイレクト
- WWW以外のリクエストをWWWにリダイレクトする
- NonWWWリダイレクト
- WWWをnon WWWにリダイレクトする。
カスタム設定も可能になっている。
- WWWをnon WWWにリダイレクトする。
Request ID
リクエストIDはリクエストに一意になるIDを付与します。
宣言のみで使えるようにしても問題ないし、カスタム設定を使ってリクエスト側からID指定することも可能
運用ルール次第なところもあるが、活用してトレースに役立てたい機能
ControllerでリクエストIDを取得したい場合は、Contextにあるのでそこから取得すればよい。
デフォルト設定だと
c.Response().Header().Get(echo.HeaderXRequestID)
で取得できる。
Rewrite
指定したルールに基づいてURLパスを書き換えるミドルウェア
ユーザーにはわかりやすいURLを表示、内部処理では必要な形式に戻すといったときに活用できるもの
Secure
XSS攻撃、コンテンツタイプスニッフィング、クリックジャッキングなどインジェクション攻撃に対する保護を提供するミドルウェア
公開するなら設定は必須と思える。
デフォルト設定で提供しもいいし、カスタム設定で細かいところに拘ってもいいと思う。
Session
HTTPセッション管理のミドルウェア
基本はCookieとファイルシステムベースのセッションストアが提供される。
gorilla/sessionsを使っているのがネック(https://github.com/gorilla/sessions)
なぜかという実はこのレポジトリは積極的にメンテナンスされずすでにアーカイブモードになっている。
セッションに重要な情報をいれないことが主流でもあるので使うことにあまり問題でないのかもしれない。
カスタム設定で設定できるsession.Storeはgorilla/sessionに提供されているinterfaceなので
自作してものを提供できるが、管理部分はgorilla側が握っているのであまりカスタムしないかもしれない
type Store interface {
// Get should return a cached session.
Get(r *http.Request, name string) (*Session, error)
// New should create and return a new session.
//
// Note that New should never return a nil session, even in the case of
// an error if using the Registry infrastructure to cache the session.
New(r *http.Request, name string) (*Session, error)
// Save should persist session to the underlying store implementation.
Save(r *http.Request, w http.ResponseWriter, s *Session) error
}
そういった意味では、Cookieを使うのはIDでサーバーサイドでセッション情報管理していく時代なのかなと感じる状況だった。
Static
静的ファイルを提供するミドルウェア
設定はルートディレクトリを設定し、その配下を提供することができる。
カスタム設定では、ブラウジングの見つめるなどの設定もできる。
Timeout
長時間実行対策に利用するタイムアウトの設定をするミドルウェア
カスタム設定では、タイムアウト時のエラーハンドリングができるの活用する価値がありそうな気がする。
Trailing Slash
リクエストURIに末尾のスラッシュ輸むを設定できるミドルウェア
URLの統一ができることはメリットな気がする。
*1について
設定後に起動したときに正常に記載してもエラーになることがある模様
ミドルウェア系の機能を使うのときに追加モジュールが必要のためだった。
私は
go get github.com/labstack/echo/v4/middleware@v4.10.2
のみで解決しています。
コンソール上には足りていないモジュールのインストールコマンドが表示されると思うので
その指示に従って解決すればいいと思います。