普段強化学習,逆強化学習を研究しているのですが,最近おもしろいことを知って実装してみたので,アドベントカレンダーのネタにさせていただきます.
予備知識
前提となるマルコフ決定過程と価値反復法について概説します.
マルコフ決定過程
マルコフ決定過程(MDP)とは,マルコフ過程(次状態は現状態にのみ影響されるマルコフ性をもつ過程)に意思決定である行動を加えた過程です.詳しい説明はネット上に多くあると思うので割愛します.
価値反復法
価値反復法(Value Iteration)とは,動的計画法と呼ばれるアルゴリズムの一種です.
ある状態$s$の価値を次の手順で求めます.
- $V$, $Q$ を初期化
- $s$, $a$ について収束するまで繰り返し:
- $Q(s,a)=R(s)+\gamma \sum_{s^{\prime}} P(s^{\prime}|s,a)V(s^{\prime})$を計算
- $V(s)=\max_a Q(s,a)$
einsumによる実装
numpy.einsumは,アインシュタインの縮約記法による行列計算の実装を手軽に行なえます.
今回の場合,上の式の右辺の$\sum_{s^{\prime}} P(s^{\prime}|s,a)V(s^{\prime})$の項は次のように書けます.
np.einsum("ijk,k->ij", P, V)
コード
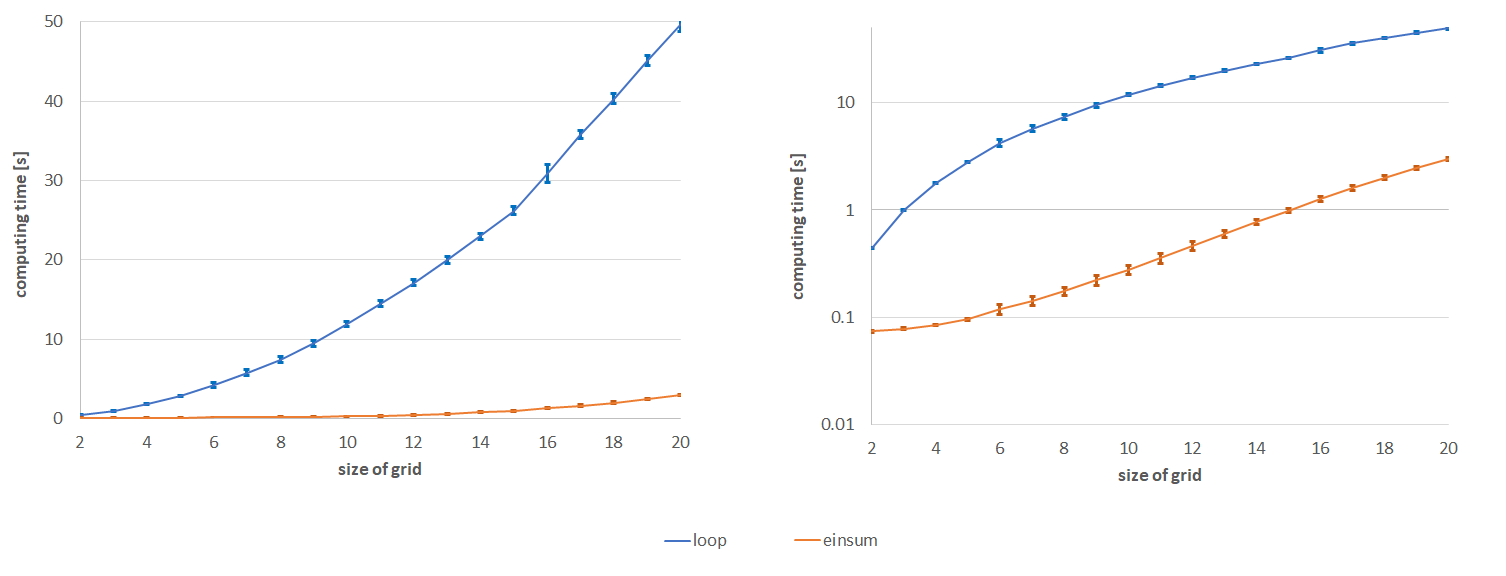
Gridworld(格子世界)という強化学習の基本中の基本の問題で実験しました.
einsumによる実装と,よくあるループによる実装の計算時間が,Gridの一辺の長さを増やしていった際にどう変化するのか比較しました.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
from makeP import makeProb
import time
for statenum in range(2, 101):
list_einsum = []
list_loop = []
for ite in range(100):
print(".", end="", flush=True)
x_size = statenum
y_size = statenum
n_states = int(x_size * y_size)
P = makeProb(x_size, y_size)
R = np.ones(n_states)*-0.01
R[int(n_states-1)] = 1
Q = np.zeros((n_states, 4))
V = np.zeros(n_states)
delta = np.inf
eps = 0.0
gamma = 0.95
t1 = time.time()
for _ in range(10000):
Q = R[:, None] + gamma * np.einsum("ijk,k->ij", P, V)
V = np.max(Q, axis=1)
t2 = time.time()
list_einsum.append(t2-t1)
Q = np.zeros((n_states, 4))
V = np.zeros(n_states)
t1 = time.time()
for _ in range(10000):
for s in range(n_states):
for a in range(4):
Q[s][a] = R[s, None] + gamma * np.dot(P[s,a,:], V)
V[s] = np.max(Q[s, :])
t2 = time.time()
list_loop.append(t2-t1)
print("")
ar_einsum = np.array(list_einsum)
ar_loop = np.array(list_loop)
print("EINSUM: ", "size: ", statenum, "mean: ", np.mean(ar_einsum), "median: ", np.median(ar_einsum), "stdev: ", np.std(ar_einsum))
print("LOOP : ", "size: ", statenum, "mean: ", np.mean(ar_loop), "median: ", np.median(ar_loop), "stdev: ", np.std(ar_loop))
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
def makeProb(x_size, y_size, n_action=4):
# make transition prob
n_states = x_size*y_size
# S, A, S'
P = np.zeros(( n_states, n_action, n_states ))
for s in range(n_states):
#left is wall
if s%x_size == 0:
if s == 0:
P[0][1][x_size] = 1
P[0][3][1] = 1
elif s > (x_size*(y_size-1)-1):
P[s][0][s-x_size] = 1
P[s][3][s+1] = 1
else:
P[s][0][s-x_size] = 1
P[s][1][s+x_size] = 1
P[s][3][s+1] = 1
#right is wall
elif (s+1)%x_size == 0:
if s == (x_size*y_size-1):
P[s][0][s-x_size] = 1
P[s][2][s-1] = 1
elif s < x_size:
P[s][1][s+x_size] = 1
P[s][2][s-1]=1
else:
P[s][0][s-x_size] = 1
P[s][1][s+x_size] = 1
P[s][2][s-1] = 1
#upper is wall
elif s < x_size and s%x_size!=0 and (s+1)%x_size !=0 :
P[s][1][s+x_size] = 1
P[s][2][s-1] = 1
P[s][3][s+1] = 1
#lower is wall
elif s > (x_size*(y_size-1)-1) and s%x_size!=0 and (s+1)%x_size !=0:
P[s][0][s-x_size] = 1
P[s][2][s-1] = 1
P[s][3][s+1] = 1
else:
P[s][0][s-x_size] = 1
P[s][1][s+x_size] = 1
P[s][2][s-1] = 1
P[s][3][s+1] = 1
return P
結果
einsumの圧勝.
何が嬉しいのかというと,例えば逆強化学習のInner-loop(内部にある強化学習のループ)が速く解けるようになったり.