はじめに
ざっくり言うと
- AWS攻撃ツールPacuによるアクセスをAWSのセキュリティ機能Amazon GuardDutyで検知できるか試した
対象とする人
- AWSのアカウントの運用・管理を任されている
- クラウドセキュリティに興味がある人
やること
- Pacuの概要と機能紹介
- Google ColabでPacuを動かす
- GuardDutyでPacuを検知できたか確認する
Pacu
概要
Pacu is an open source AWS exploitation framework, designed for offensive security testing against cloud environments. Created and maintained by Rhino Security Labs, Pacu allows penetration testers to exploit configuration flaws within an AWS account, using modules to easily expand its functionality. Current modules enable a range of attacks, including user privilege escalation, backdooring of IAM users, attacking vulnerable Lambda functions, and much more.
GitHub - RhinoSecurityLabs/pacu
PacuはオープンソースのAWSエクスプロイトフレームワークである。Pacuという名前は南米アマゾン川に生息するピラニアの仲間「Pacu」に因んでいる。開発元は米国シアトルのRhinoSecurityLabs。
Pacuを利用すれば 不正な権限昇格 や 脆弱なLambda関数への攻撃 などを行うことが可能であり、自分で自分のAWS環境を突いてセキュリティ上の抜け穴がないかどうかチェックすることができる。
大まかな機能を下記にまとめる。
| 機能 | 概要 |
|---|---|
| confirm_permissions | 現在のアカウントの権限周りの設定を調査する |
| privesc_scan | 権限の不正昇格 |
| cloudtrail_csv_injection | CloudTrailの出力csvファイルに不正な文字列を混入させる |
| disrupt_monitoring | CloudTrailやCloudWatchなどのログ、モニタリングを撹乱する |
| backdoor_users_[keys/passwords] | IAMアカウントに対してバックドアを仕掛ける |
| sysman_ec2_rce | SSM1を不正利用しEC2で不正なコードを実行させる |
| backdoor_ec2_sec_groups | セキュリティグループにバックドアを仕掛ける |
このようなエクスプロイトツールは攻撃者のハッキングツールとなってしまうことがよくあるが、利用する際にユーザ自身のアクセスキーを登録する必要があるためPacuが悪用される可能性はあまりないと思われる。
ただし、どこかでアクセスキーを不正に入手した攻撃者がPacuでアクセスしてくる可能性は存分に考えられるため、こういったツールによるアクセスを想定しておくのはセキュリティ向上のために非常に重要である。
インストールと設定
公式サイトからそのまま引用
git clone https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/pacu
cd pacu
bash install.sh
python3 pacu.py
LinuxとMacOSXをサポートと記載があったが、Windows用のinstall手順も紹介されている。
AWSのSDKが動作すれば環境はあまり関係なさそうだ。
サーバを立てるのもメンドくさいのでGoogle Colabからやってみた。
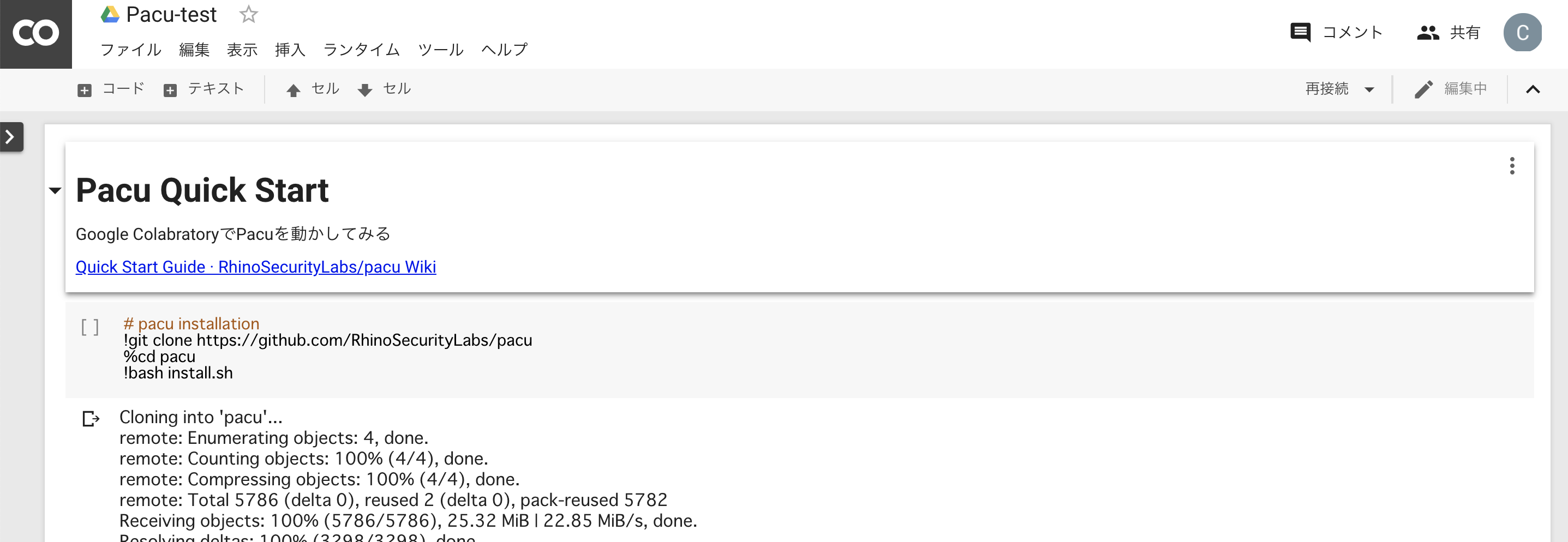
普通にできた。各コマンドの先頭に"!"をつければそのまま実行可能。ただし、cdコマンドだけは"%"を付けるのに注意。
【秒速で無料GPUを使う】深層学習実践Tips on Colaboratory - Qiita
Pacuを実行してみよう。
ピラニアっぽいロゴが表示された。
初めて使う場合はセッション名をつけるかどうか聞かれるので適当に名前を付けておく。設定したアクセスキーやリージョンなどはセッションごとに保存されるため、次回以降はセッションを指定すれば設定が読み込まれる。
Pacuで実行できるコマンドの一覧はこちら。
Pacu command info:
list/ls List all modules
search [cat[egory]] <search term> Search the list of available modules by name or category
help Display this page of information
help <module name> Display information about a module
whoami Display information regarding to the active access keys
data Display all data that is stored in this session. Only fields
with values will be displayed
data <service>|proxy Display all data for a specified service or for PacuProxy
in this session
services Display a list of services that have collected data in the
current session to use with the "data" command
regions Display a list of all valid AWS regions
update_regions Run a script to update the regions database to the newest
version
set_regions <region> [<region>...] Set the default regions for this session. These space-separated
regions will be used for modules where regions are required,
but not supplied by the user. The default set of regions is
every supported region for the service. Supply "all" to this
command to reset the region set to the default of all
supported regions
run/exec <module name> Execute a module
set_keys Add a set of AWS keys to the session and set them as the
default
swap_keys Change the currently active AWS key to another key that has
previously been set for this session
exit/quit Exit Pacu
Other command info:
aws <command> Run an AWS CLI command directly. Note: If Pacu detects "aws"
as the first word of the command, the whole command will
instead be run in a shell so that you can use the AWS CLI
from within Pacu. Due to the command running in a shell,
this enables you to pipe output where needed. An example
would be to run an AWS CLI command and pipe it into "jq"
to parse the data returned. Warning: The AWS CLI's
authentication is not related to Pacu. Be careful to
ensure that you are using the keys you want when using
the AWS CLI. It is suggested to use AWS CLI profiles
to solve this problem
[ADVANCED] PacuProxy command info:
proxy [help] Control PacuProxy/display help
start <ip> [port] Start the PacuProxy listener - port 80 by default.
The listener will attempt to start on the IP
supplied, but some hosts don't allow this. In
this case, PacuProxy will listen on 0.0.0.0 and
use the supplied IP to stage agents and it should
work the same
stop Stop the PacuProxy listener
kill <agent_id> Kill an agent (stop it from running on the host)
list/ls List info on remote agent(s)
use none|<agent_id> Use a remote agent, identified by unique integers
(use "proxy list" to see them). Choose "none" to
no longer use any proxy (route from the local
host instead)
shell <agent_id> <command> Run a shell command on the remote agent
fetch_ec2_keys <agent_id> Try to read the meta-data of the target agent to
request a set of temporary credentials for the
attached instance profile (if there is one),
then save them to the Pacu database and set
them as the active key pair
stager sh|ps Generate a PacuProxy stager. The "sh" format is
for *sh shells in Unix (like bash), and the "ps"
format is for PowerShell on Windows
set_keysコマンドでアクセスキーを登録しておく。
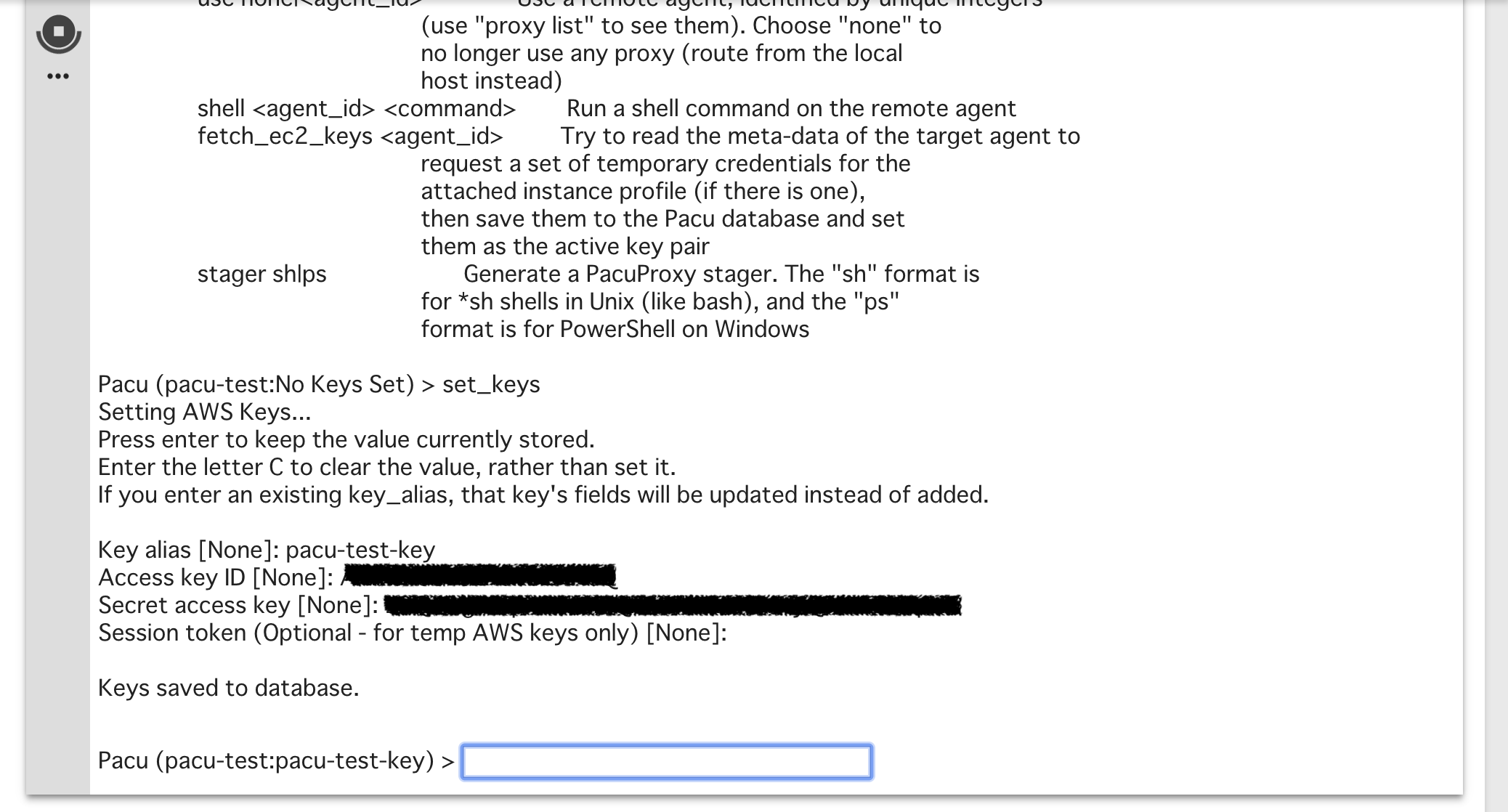
初期設定はここまで。
攻撃用モジュール一覧
攻撃用の機能はモジュールと呼ばれる。ソースコードを確認するとPythonSDKを使った2スクリプトのようだ。詳細はModule Detailsにまとめられている。
Pacuのプロンプトにlsと入力すれば実行可能なモジュールを一覧表示することができる。
Pacu (pacu-test:pacu-test-key) > ls
[Category: RECON_UNAUTH]
s3__bucket_finder
iam__enum_assume_role
iam__enum_users
[Category: ENUM]
ec2__download_userdata
codebuild__enum
lambda__enum
iam__enum_users_roles_policies_groups
lightsail__enum
aws__enum_account
iam__enum_permissions
aws__enum_spend
iam__get_credential_report
ec2__enum
iam__detect_honeytokens
iam__bruteforce_permissions
inspector__get_reports
ebs__enum_volumes_snapshots
ec2__check_termination_protection
glue__enum
[Category: ESCALATE]
iam__privesc_scan
[Category: LATERAL_MOVE]
cloudtrail__csv_injection
vpc__enum_lateral_movement
[Category: EXPLOIT]
ebs__explore_snapshots
lightsail__generate_temp_access
ec2__startup_shell_script
systemsmanager__rce_ec2
lightsail__download_ssh_keys
api_gateway__create_api_keys
lightsail__generate_ssh_keys
[Category: PERSIST]
lambda__backdoor_new_roles
iam__backdoor_users_keys
lambda__backdoor_new_users
ec2__backdoor_ec2_sec_groups
iam__backdoor_assume_role
iam__backdoor_users_password
lambda__backdoor_new_sec_groups
[Category: EXFIL]
s3__download_bucket
rds__explore_snapshots
[Category: EVADE]
waf__enum
elb__enum_logging
guardduty__whitelist_ip
detection__disruption
cloudwatch__download_logs
detection__enum_services
cloudtrail__download_event_history
この中から実行したいモノを選んでrunコマンドで実行する。
モジュールの実行
試しに南米リージョン(sa-east-1)のLambda関数を調べてみる。sa-east-1は普段使わないがテスト用にLambda関数を1つ作成しておいた。
run lambda__enum --regions sa-east-1
のように入力する。
pacu-test-dayoというLambda関数が見つかった。もしこれがセキュリティグループを変更する関数だったとしたら悪用されてしまう可能性もある。
全リージョンのLambda関数を数え上げることも可能なので、うっかり作成して忘れ去られていたLambda関数を見つけるといった使い方もあるだろう。
このようにPacuによって自分で自分のAWS環境を調査したり、突いてみたりすることができる。
AWS GuardDuty
一方、AWSには素晴らしいセキュリティツールがある。
概要
Amazon GuardDuty は、AWS アカウントとワークロードを保護するために悪意のある操作や不正な動作を継続的にモニタリングする脅威検出サービスです。アカウント侵害の可能性を示す異常な API コールや不正なデプロイなどのアクティビティをモニタリングします。インスタンスへの侵入の可能性や攻撃者による偵察も検出します。Amazon GuardDuty(インテリジェントな脅威検出) | AWS
要するにAWSの定めたルールや機械学習に基づいたスゴイ攻撃検知ツールである。
最近は「セキュリティ・オートメーション」という概念3が注目を集めているが、GuardDutyはそのトリガーとなる重要な機能である。re:Invent2018で発表されたSecurity Hubとも密接に関わってくるはずなので、是非とも使いこなせるようになりたいらなければならない。
AWS によるセキュリティ・オートメーションの実践|AWS Summit Tokyo 2018 - YouTube
スライドはここ
検知できる脅威一覧
GuardDutyによって検知できる脅威は下記の通りである。
| 結果タイプ | 概要 |
|---|---|
| Backdoor | C2サーバと通信をしている可能性がある |
| Behavior | リソースの振る舞いが異なる |
| CryptoCurrency | 暗号通貨関連で不審な振る舞いをしている |
| PenTest | Kali Linuxからアクセスがあった |
| Persistence | 今までなかったネットワークや権限などの設定変更があった |
| Recon | ポートスキャンやSGの設定を調査するような振る舞いをしている/されている |
| ResourceConsumption | APIによるEC2インスタンスの起動4 |
| Stealth | セキュリティポリシーの弱化やログ・モニタリングの撹乱 |
| Trojan | マルウェアによる通信の可能性がある |
| UnauthorizedAccess | 不正アクセス全般(ブルートフォースやTorからのアクセス) |
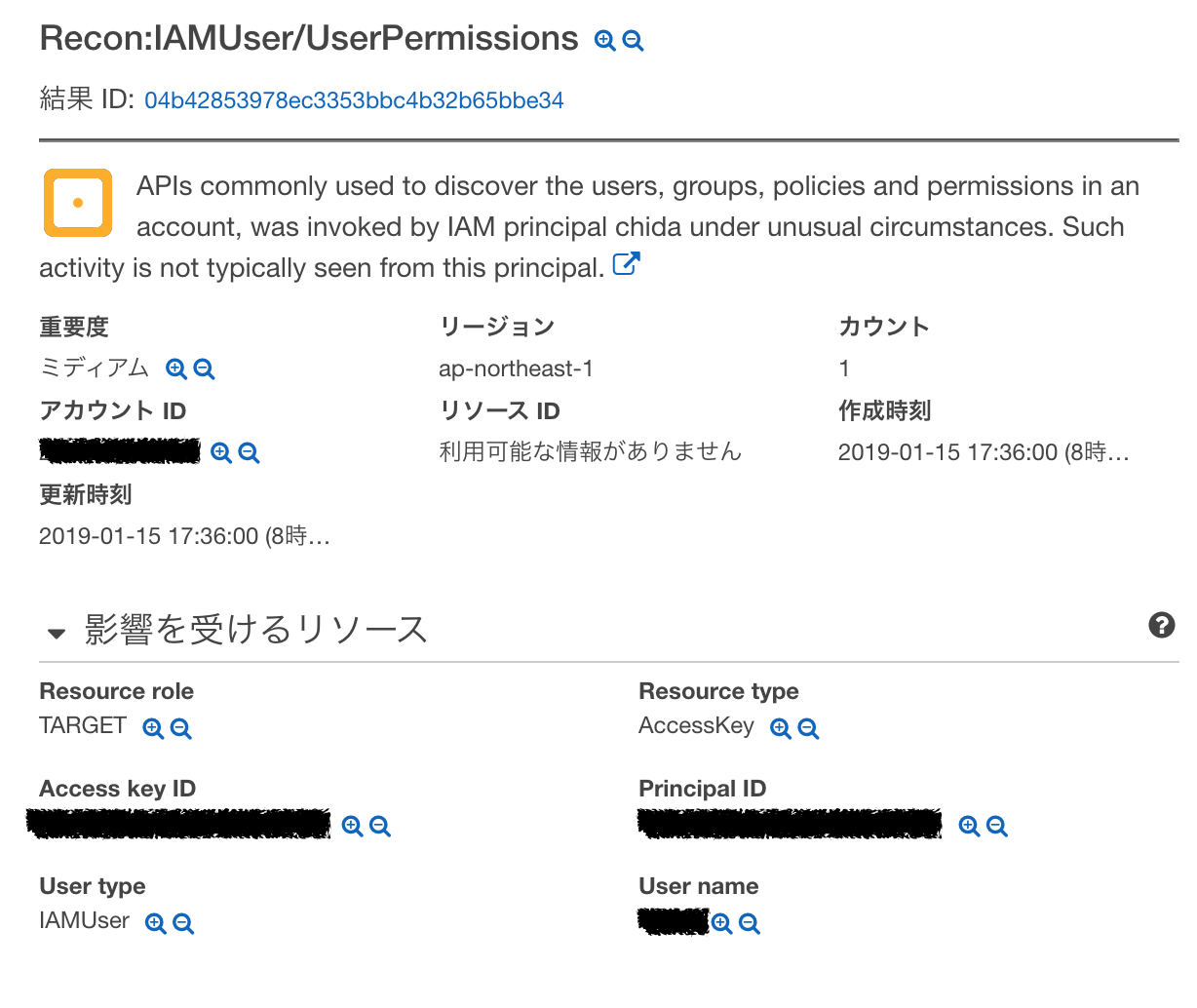
なるほど。これなら先ほどのPacuによるアクセスを検知できるのではなかろうか。
Pacu VS GuardDuty
実験結果
AWSのセキュリティ機能「GuardDuty」はPacuによるアクセスを検知できるのか実験してみた。
少しガチな感じのIAM系のモジュールをいくつか実行した。詳細はほとんど見せられないため省略。
GuardDutyはリージョン単位のサービスなので自分が普段使っている東京リージョンで確認する。
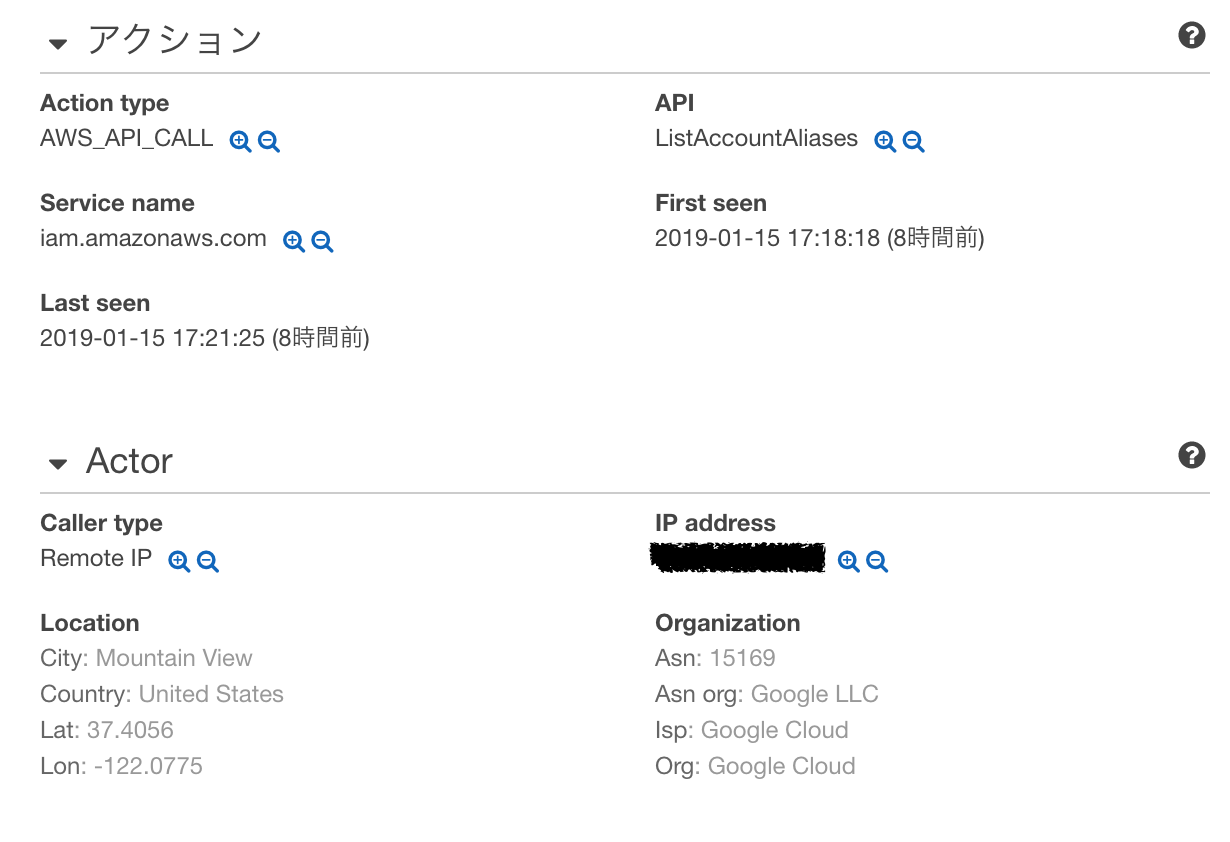
おお。しっかりバレているではないか。(Mountaion Viewから突然APIが叩かれているのであからさまに怪しいが)
余談☕️ツンデレGuardDuty
これでは面白くないのでアクセス元のIPアドレスを色々変えて調べてみた。
自宅のPC…
AWSのEC2インスタンス…
GCPの国内リージョンのインスタンス…
色々やってみたがGuardDutyが反応することは…なかった。
GuardDutyはIAMアカウントの振る舞いを見ているのだろう。
察するに
「このIAMユーザは常日頃から怪しい行動をする」
↓
「これがこの人にとって普通なんだ。検知しなくていいよね。」
↓
「またいつものやつか。もう知らない。」
というように判断されているのではなかろうか。
僕のIAMアカウントはAWS認定不審ユーザリストに仲間入りしてしまったのかもしれない。
おわりに
GuardDutyはPacuの怪しげなアクセスをしっかり検知してくれた。
調子に乗ってGuardDutyをつついて遊んでいると、僕のように見向きもされなくなってしまうのでご注意を…