概要
前回はドロネー三角形で分解するところまで実施しましたが、
今回は、分解した三角形をアフィン変換を利用して変形し、マスクを組み合わせることで切り取りも行ってみます。
手法の詳細については下記を参照して下さい。
結果
こんな感じになります。(左変換前、右変換後)
スマホの画面をmacのカメラで撮っているので画像が荒いですね。
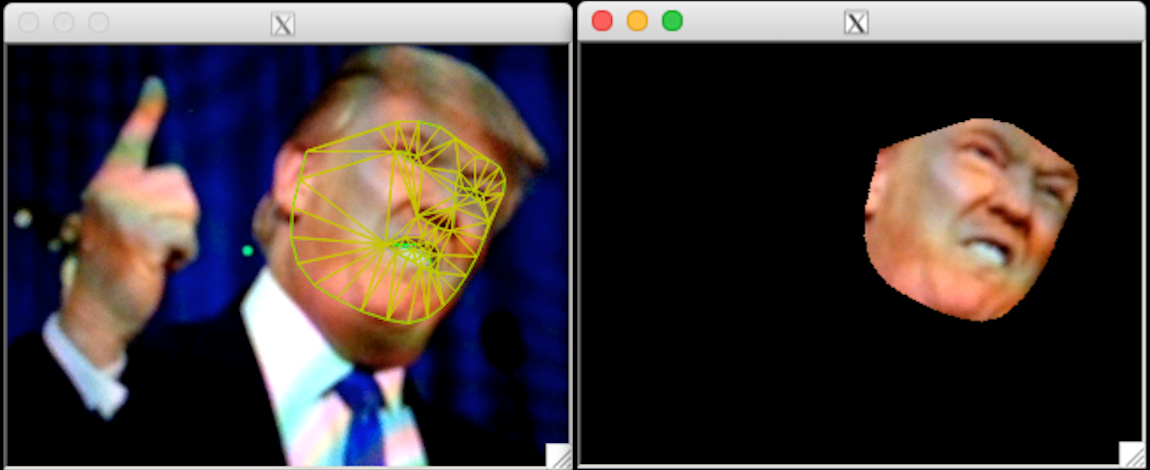
ちなみに、アフィン変換はしていますが、位置はそのままなので、顔部分を切り取ったような感じになっています。
ソースコード
前回のソースコード部分も多少変更しています。
# include <dlib/opencv.h>
# include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
# include <dlib/image_processing/frontal_face_detector.h>
# include <dlib/image_processing/render_face_detections.h>
# include <dlib/image_processing.h>
# include <dlib/gui_widgets.h>
# include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace dlib;
using namespace std;
const int WIDTH = 320;
const int HEIGHT = 240;
cv::Mat get_affined_image(std::vector<cv::Vec6f> triangles, cv::Rect rect, cv::Mat srcImg)
{
cv::Mat dstImg = cv::Mat::zeros(srcImg.rows, srcImg.cols, srcImg.type());
for(auto it = triangles.begin(); it != triangles.end(); it++)
{
cv::Vec6f &vec = *it;
// 画面外の点は無視する(ドロネー図を描くと必ず画面を内包する三角形が一個だけ出来てしまう)
dlib::vector<long, 2> p1((long)vec[0], (long)vec[1]);
if(!rect.contains(cv::Point(p1.x(),p1.y()))) {
continue;
}
dlib::vector<long, 2> p2((long)vec[2], (long)vec[3]);
if(!rect.contains(cv::Point(p2.x(),p2.y()))) {
continue;
}
dlib::vector<long, 2> p3((long)vec[4], (long)vec[5]);
if(!rect.contains(cv::Point(p3.x(),p3.y()))) {
continue;
}
// Input triangle
cv::vector <cv::Point2f> triIn;
triIn.push_back(cv::Point2f(vec[0],vec[1]));
triIn.push_back(cv::Point2f(vec[2],vec[3]));
triIn.push_back(cv::Point2f(vec[4],vec[5]));
// Output triangle
cv::vector <cv::Point2f> triOut;
triOut.push_back(cv::Point2f(vec[0],vec[1]));
triOut.push_back(cv::Point2f(vec[2],vec[3]));
triOut.push_back(cv::Point2f(vec[4],vec[5]));
// 余分な部分の計算をしないようにするため三角形を内包する矩形を求めておく
cv::Rect rectIn = boundingRect(triIn);
cv::Rect rectOut = boundingRect(triOut);
// 切り取られた三角形
cv::vector<cv::Point2f> tri1Cropped, tri2Cropped;
cv::vector<cv::Point> tri2CroppedInt;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
tri1Cropped.push_back(cv::Point2f(triIn[i].x - rectIn.x, triIn[i].y - rectIn.y));
tri2Cropped.push_back(cv::Point2f(triOut[i].x - rectOut.x, triOut[i].y - rectOut.y));
// fillConvexPoly needs a vector of Point and not Point2f
tri2CroppedInt.push_back(cv::Point((int)(triOut[i].x - rectOut.x), (int)(triOut[i].y - rectOut.y)));
}
// 元画像から最小矩形を切り取った部分をパッチにコピーする
cv::Mat img1Cropped;
srcImg(rectIn).copyTo(img1Cropped);
// 三角形のアフィン行列を求める
cv::Mat warpMat = getAffineTransform(tri1Cropped, tri2Cropped);
// 元画像からアフィン行列を実施する
cv::Mat img2Cropped = cv::Mat::zeros(rectOut.height, rectOut.width, img1Cropped.type());
warpAffine(img1Cropped, img2Cropped, warpMat, img2Cropped.size(), cv::INTER_LINEAR, cv::BORDER_REFLECT_101);
// マスクを生成
cv::Mat mask = cv::Mat::zeros(rectOut.height, rectOut.width, img1Cropped.type());
fillConvexPoly(mask, tri2CroppedInt, cv::Scalar(1.0, 1.0, 1.0), 16, 0);
// マスクをパッチに適用
multiply(img2Cropped, mask, img2Cropped);
// マスク部分ですでに値が入っている場合(境界線部分)は一旦0にする
multiply(dstImg(rectOut), cv::Scalar(1.0,1.0,1.0) - mask, dstImg(rectOut));
// 出力画像に追加する
dstImg(rectOut) = dstImg(rectOut) + img2Cropped;
}
return dstImg;
}
std::vector<image_window::overlay_line> render_triangles(std::vector<cv::Vec6f> triangles, cv::Rect rect)
{
std::vector<image_window::overlay_line> triangleLine;
for(auto it = triangles.begin(); it != triangles.end(); it++)
{
cv::Vec6f &vec = *it;
dlib::vector<long, 2> p1((long)vec[0], (long)vec[1]);
if(!rect.contains(cv::Point(p1.x(),p1.y()))) {
continue;
}
dlib::vector<long, 2> p2((long)vec[2], (long)vec[3]);
if(!rect.contains(cv::Point(p2.x(),p2.y()))) {
continue;
}
dlib::vector<long, 2> p3((long)vec[4], (long)vec[5]);
if(!rect.contains(cv::Point(p3.x(),p3.y()))) {
continue;
}
triangleLine.push_back(image_window::overlay_line(p1, p2, rgb_pixel(200,200,0)));
triangleLine.push_back(image_window::overlay_line(p2, p3, rgb_pixel(200,200,0)));
triangleLine.push_back(image_window::overlay_line(p3, p1, rgb_pixel(200,200,0)));
}
return triangleLine;
}
int main()
{
try
{
cv::VideoCapture cap(0);
cap.set(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH , WIDTH);
cap.set(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT , HEIGHT);
if (!cap.isOpened())
{
cerr << "Unable to connect to camera" << endl;
return 1;
}
image_window win1;
win1.set_size(WIDTH, HEIGHT+CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT);
image_window win2;
win2.set_size(WIDTH, HEIGHT+CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT);
// Load face detection and pose estimation models.
frontal_face_detector detector = get_frontal_face_detector();
shape_predictor pose_model;
deserialize("shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat") >> pose_model;
while(!win1.is_closed())
{
cv::Mat capImg;
cap >> capImg;
cv_image<bgr_pixel> cvCapImg(capImg);
// Detect faces
std::vector<rectangle> faces = detector(cvCapImg);
// Find the pose of each face.
std::vector<full_object_detection> shapes;
for (unsigned long i = 0; i < faces.size(); ++i) {
shapes.push_back(pose_model(cvCapImg, faces[i]));
}
// Display it all on the screen
win1.clear_overlay();
win1.set_image(cvCapImg);
win1.add_overlay(render_face_detections(shapes));
// Subdiv2D初期化
cv::Subdiv2D subdiv;
cv::Rect rect(0, 0, capImg.cols, capImg.rows);
subdiv.initDelaunay(rect);
// 顔を検出していない場合は何もしない
if(shapes.empty()) {
continue;
}
// 最初に検出した顔の点を追加
full_object_detection& d = shapes[0];
for (unsigned long j = 0; j < d.num_parts(); ++j) {
if(!rect.contains(cv::Point(d.part(j).x(),d.part(j).y()))) {
continue;
}
subdiv.insert(cv::Point2f(d.part(j).x(), d.part(j).y()));
}
// ドロネー三角形のリストを取得
std::vector<cv::Vec6f> triangles;
subdiv.getTriangleList(triangles);
// ドロネー三角形を表示
win1.add_overlay(render_triangles(triangles, rect));
// ドロネー三角形をアフィン変換した画像を表示
cv_image<bgr_pixel> cvCapImg2(get_affined_image(triangles, rect, capImg));
win2.clear_overlay();
win2.set_image(cvCapImg2);
}
}
catch(serialization_error& e)
{
cout << "You need dlib's default face landmarking model file to run this example." << endl;
cout << "You can get it from the following URL: " << endl;
cout << " http://dlib.net/files/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat.bz2" << endl;
cout << endl << e.what() << endl;
}
catch(exception& e)
{
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
}