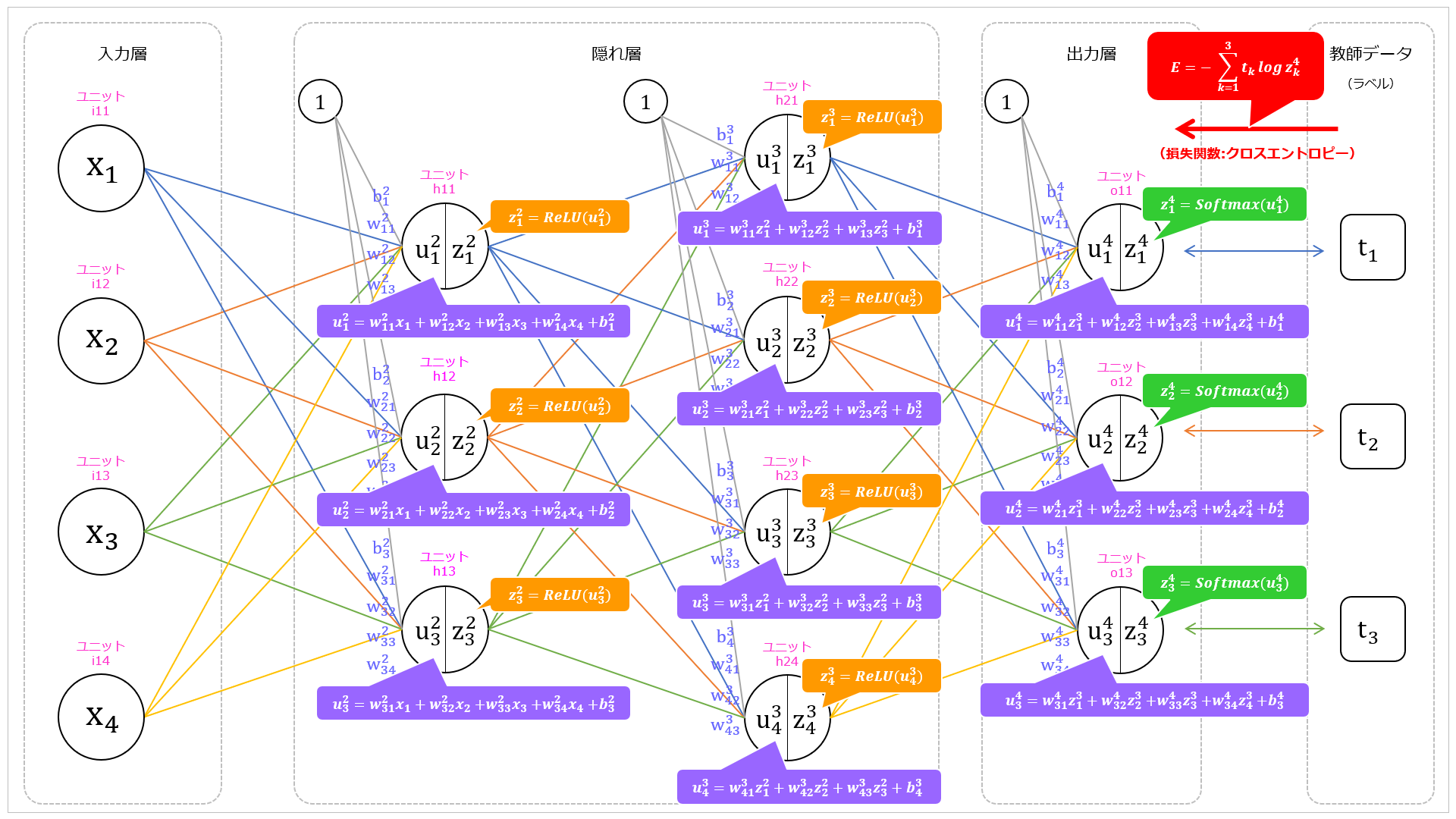
損失関数
前回で最終出力の $z_1^4, z_2^4, z_3^4$ がわかりました。
これらの値がそれぞれ $t_1, t_2, t_3$ と同じ(か、ひじょうに近い値)であれば期待した出力といえます。
しかし、重みやバイアスの初期値は適当な(いいかげんな・ランダムな)値になっているため、初めから期待した出力になるわけではありません。
そこで、損失関数を使い、現時点の出力が期待する出力とどれだけ乖離しているか(誤差)を調べ、
出力が期待する値になるように、重みやバイアスといったパラメータを調整していきます。
今回、出力層の活性化関数には $Softmax$ 関数を適用しているので、
損失関数にはクロスエントロピー誤差(交差エントロピー誤差)を採用します。
クロスエントロピー誤差
このニューラルネットワークでのクロスエントロピー誤差($E$)は以下の式で表されます。
E = - \sum_{k=1}^3 t_k \log z_k^4
$\sum$ を展開するとこのようになります。
E = - \sum_{k=1}^3 t_k \log z_k^4 = - (t_1 \log z_1^4 + t_2 \log z_2^4 + t_3 \log z_3^4)
教師データ
今回、教師データは one-hot表現 としています。
これは、正解のラベルが 1 でそれ以外は 0 となっているデータです。
例えば、$t_2$ が正解ラベルの場合、次のようになります。
\begin{bmatrix}
t_1 \\
t_2 \\
t_3
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
0 \\
1 \\
0
\end{bmatrix}
誤差の計算
具体的に誤差の計算をしてみます。
いま、期待する出力として、以下の出力を得たいとします。
\begin{bmatrix}
t_1 \\
t_2 \\
t_3
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
もも \\
りんご \\
ぶどう
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
0 \\
1 \\
0
\end{bmatrix}
つまり、りんごの出力(このニューラルネットワークでは $z_2^4$)が最大になるようにしたいとします。
ところが、ニューラルネットワークの最終出力が次のような場合、損失関数の値はどのようになるでしょうか。
(出力層ではソフトマックス関数を適用しているので、出力の総和が 1 になっています。)
\begin{bmatrix}
もも \\
りんご \\
ぶどう
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
z_1^4 \\
z_2^4 \\
z_3^4
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
0.5 \\
0.2 \\
0.3
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{align}
E &= - (t_1 \log z_1^4 + t_2 \log z_2^4 + t_3 \log z_3^4) \\
&= - (0 \times \log 0.5 + 1 \times \log 0.2 + 0 \times \log 0.3) \\
&= - (0 \times (-0.30) + 1 \times (-0.70) + 0 \times (-0.52)) \\
&= - (-0.70) \\
&= 0.70
\end{align}
では、最終出力が次のようだった場合はどうなるでしょうか。
今回は、りんごの出力が最大になっています。
\begin{bmatrix}
もも \\
りんご \\
ぶどう
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
z_1^4 \\
z_2^4 \\
z_3^4
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
0.3 \\
0.5 \\
0.2
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{align}
E &= - (t_1 \log z_1^4 + t_2 \log z_2^4 + t_3 \log z_3^4) \\
&= - (0 \times \log 0.3 + 1 \times \log 0.5 + 0 \times \log 0.2) \\
&= - (0 \times (-0.52) + 1 \times (-0.30) + 0 \times (-0.70)) \\
&= - (-0.30) \\
&= 0.30
\end{align}
先ほどと比べて損失関数の値が小さくなっています。
さらに次のような場合はどうでしょうか。
今度はさらにりんごの出力値が大きくなっています。
\begin{bmatrix}
もも \\
りんご \\
ぶどう
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
z_1^4 \\
z_2^4 \\
z_3^4
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
0.05 \\
0.90 \\
0.05
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{align}
E &= - (t_1 \log z_1^4 + t_2 \log z_2^4 + t_3 \log z_3^4) \\
&= - (0 \times \log 0.05 + 1 \times \log 0.90 + 0 \times \log 0.05) \\
&= - (0 \times (-1.30) + 1 \times (-0.05) + 0 \times (-1.30)) \\
&= - (-0.05) \\
&= 0.05
\end{align}
先ほどと比べてさらに損失関数の値が小さくなっています。
まとめ
このように、正しい(期待する)出力に近ければ近いほど損失関数の値は小さくなっていきます。
なので、損失関数の値が小さくなるような出力となるように、重みやバイアスなどのパラメータを調整すれば、
正しい判断のできるニューラルネットワークになります。
また、ソフトマックス関数が出力を確率として求めていることを考えると、
2つめの例では 50% (0.5) の確率でりんごだと思っていて、
3つめの例では 90% (0.9) の確率でりんごだと思っていると考えることができます。
損失関数の値は、ニューラルネットワークがどの程度(自信をもって)正しく判断しているかの目安になります。