はじめに
まとまった記事がなかったので書く。
ターゲット層は主にJavaやPythonなど、既に他のプログラミング言語を触ったことのある人。
そもそもVue.jsで何ができる?
- 機能(コンポーネント)ごとに分けて開発することができる
- 単一責任の原則
- たとえば、ブラウザ上に表示される機能だけでも、画面、入力フォーム、表示部分など
- Vue.jsに限った話ではないけれど...Typescript含め、Javascriptはクライアントサイドで動くHTMLの補助スクリプト的な側面が強かった
- なので機能ごとに分けて開発する、みたいな概念は他の言語だと当たり前だけど粗雑だった
- が、ここ最近になって急速に発展した
- 要はJavascriptもそろそろ他のプログラミング言語と同じ機能がほしいよね、というお話
- したがって他のプログラミング言語を触っていればあまり学習コストはかからない(と思う)
- リアルタイムにデータを反映させることも得意
- たとえばYouTubeライブの視聴者数とか。
- これまでだとページ更新するとか、ボタン押してイベント発火させるとか、そういうのが必要だった
- たとえばYouTubeライブの視聴者数とか。
See the Pen Simple Vue Example by Joseph Gengarella (@Wyrlor) on CodePen.
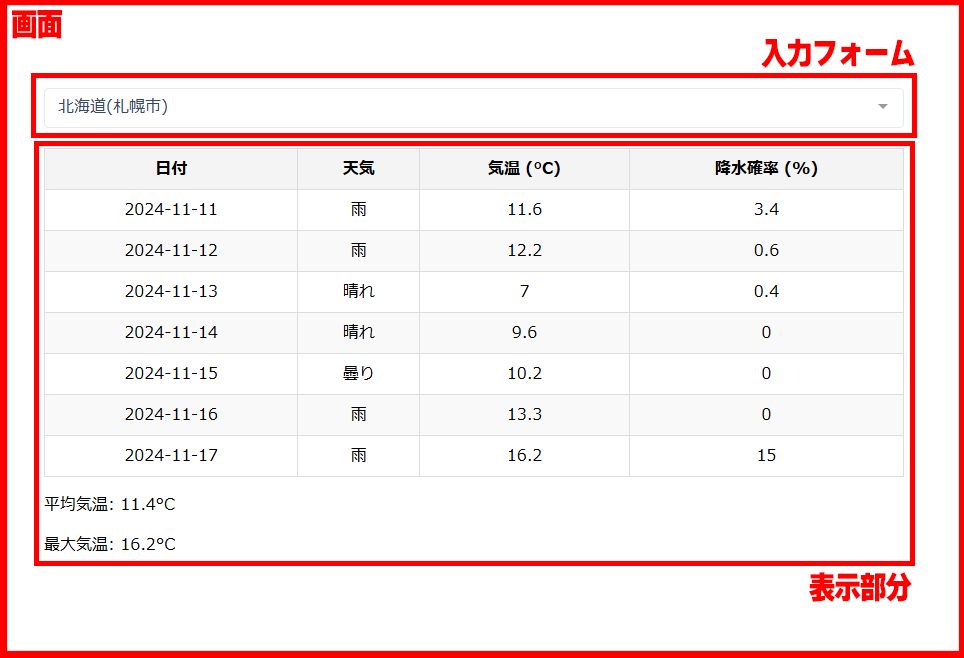
天気アプリ
作成した天気アプリになぞって入門解説する。環境構築等は他記事へ。
処理内容としては
-
選択を検知したら、各地域に応じて天気情報を取得するAPIを叩く
https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast/?latitude=${latitude}&longitude=${longitude}&daily=weathercode,temperature_2m_max,precipitation_sum&timezone=Asia/Tokyo
というきわめてシンプルなWebアプリ。
ディレクトリ構成
Vue.jsの基本構成
App.vue
<template>
<!-- ここにHTML -->
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
// ここにTypescript(Javascript)
</script>
<style>
/* ここにCSS */
</style>
コンポーネントの表示
親子関係
- 親コンポーネント、子コンポーネントという概念が存在する
- 画面が親で、画面(App)に機能(Form, Display)が乗っているイメージ
App.vue
<template> <div> <Form /> <Display /> </div> </template> <script setup lang="ts"> import { ref } from "vue"; import Form from "./components/Form.vue"; import Display from "./components/Display.vue"; ...- コンポーネントの
*.vueファイルをimportして、template内で<Form />のように書く - なお、
.tsからimportしたいデータはexportするweather.ts// importするものはexportする export interface Weather { date: string; weatherCode: number; temperature: number; rainProb: number; sunset?: string; sunrise?: string; }
- コンポーネントの
リアクティブ
- コード内部の値が変わると、画面にも即時反映させる機能
- つまり、リアルタイムで値が変わる
- Vue.jsの核の部分
-
ref- 文字列や数値などのプリミティブな値に使用する(とされている)
- 実用上はオブジェクト型でも使われている
-
ref<型>(データ)App.vueconst weatherData = ref<WeatherData>(new WeatherData([])); - 値の設定、取得は
.valueでアクセスするApp.vueweatherData.value = new WeatherData(data) console.log("Fetched weather data:", weatherData.value);
-
reactive- オブジェクトや配列などのデータ型に使用する
-
refと違ってそのままアクセス可能 - リアクティブでない変数と区別ができないので、あまり使われないらしい
-
reactive(オブジェクトなど)const state = reactive({ message: 'Hell World!' }); console.log(state.message);
ディレクティブ
- HTMLに対して独自の属性を追加することで、動的な変化を与える役割を果たす
- マスタッシュ構文
-
{{ }}で値を埋め込むことができるDisplay.vue<td>{{ day.date }}</td> <td>{{ getWeatherDescription(day.weatherCode) }}</td> <td>{{ day.temperature }}</td> <td>{{ day.rainProb }}</td>
-
-
v-if- 中身が
trueのときに要素を表示Display.vue<div v-if="weatherValue.getRawWeatherData.length"> <p>平均気温: {{ props.weatherValue.getAverageTemperature() }}°C</p> <p>最大気温: {{ props.weatherValue.getMaxAverageTemperature() }}°C</p> </div>
- 中身が
-
v-model- input要素やselect要素など、ユーザーが入力した値を同期的に保持する
- 内容をリアルタイムで更新
Form.vue
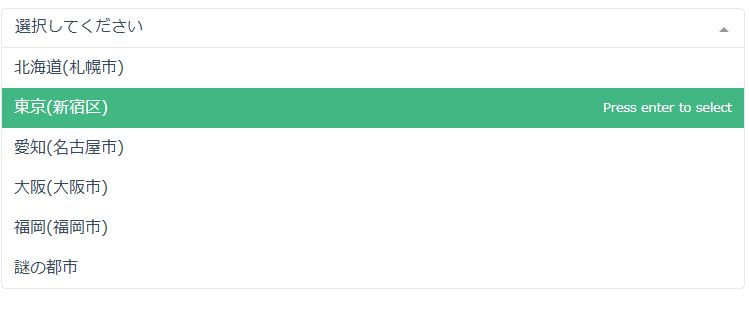
<template> <div> <VueMultiselect placeholder="選択してください" v-model="selectedPrefecture" v-bind:options="prefectures" label="name" /> </div> </template> <script setup lang="ts"> import { ref, defineEmits } from "vue"; import VueMultiselect from "vue-multiselect"; const prefectures = [ { name: "北海道(札幌市)", latitude: 43.0643, longitude: 141.3468 }, { name: "東京(新宿区)", latitude: 35.6895, longitude: 139.6917 }, ... ] const selectedPrefecture = ref<typeof prefectures[0] | null>(null);
-
v-bind- HTML要素の属性値とVue側の値を対応(バインド)させる
- 以下だとコンボボックスの
options項目をprefecturesのnameと対応させているForm.vue<template> <div> <VueMultiselect placeholder="選択してください" v-bind:options="prefectures" label="name" /> </div> </template> ... const prefectures = [ { name: "北海道(札幌市)", latitude: 43.0643, longitude: 141.3468 }, { name: "東京(新宿区)", latitude: 35.6895, longitude: 139.6917 }, { name: "愛知(名古屋市)", latitude: 35.1802, longitude: 136.9065 }, { name: "大阪(大阪市)", latitude: 34.6863, longitude: 135.5200 }, { name: "福岡(福岡市)", latitude: 33.6063, longitude: 130.4179 }, { name: "謎の都市", latitude: 1000, longitude: 1000 }, ]; ... -
v-bind:は:に省略可能- ちなみに以下は
forで繰り返される部分に識別子をバインドしている(でないと区別できない) - このように
v-bindは他のディレクティブと併用することが多い
Form.vue<tr v-for="day in weatherValue.getRawWeatherData" :key="day.date"> <td>{{ day.date }}</td> <td>{{ getWeatherDescription(day.weatherCode) }}</td> <td>{{ day.temperature }}</td> <td>{{ day.rainProb }}</td> </tr> - ちなみに以下は
-
v-on- 要素にイベントリスナーを設定する(select, changeなど)
- コンボボックスで選択されると
onSelectが走る
Form.vue<VueMultiselect placeholder="選択してください" v-on:select="onSelect" v-model="selectedPrefecture" v-bind:options="prefectures" label="name" /> ... function onSelect() { if (selectedPrefecture.value) { const { latitude, longitude } = selectedPrefecture.value; emit("selectLocation", latitude, longitude); } }-
v-on:は@に省略可能-
selectLocationの変更を検知するとfetchWeatherが走る
-
App.vue<Form @selectLocation="fetchWeather" />
- マスタッシュ構文
Emit
- 子コンポーネントから親コンポーネントにデータを渡す
- たとえばフォーム情報を受け取って対応するデータを表示することを考える
- 子同士間のデータ移動はできない
-
Form.vueとDisplay.vue
-
- つまり、親に一旦渡してから別の子に渡す
-
Form.vue⇔App.vue⇔Display.vue
-
Form.vue// 地域が選択されたらAPI用にlatitudeとlogitudeを親Appに渡す function onSelect() { if (selectedPrefecture.value) { const { latitude, longitude } = selectedPrefecture.value; // Emitの設定 // emit("イベント名", 引数...) emit("selectLocation", latitude, longitude); } } // Emitの定義 // const emit = defineEmits<{(e: "イベント名", 引数): 型,...}(); const emit = defineEmits<{ (e: "selectLocation", latitude: number, longitude: number): void; }>();App.vue<!-- @イベント名="実行関数" Emitsのイベント名を指定する --> <Form @selectLocation="fetchWeather" />- 上記の場合はフォーム内のコンボボックスで、他の項目が選択された場合に新たな処理をしたいので、
v-onで渡している- たとえば
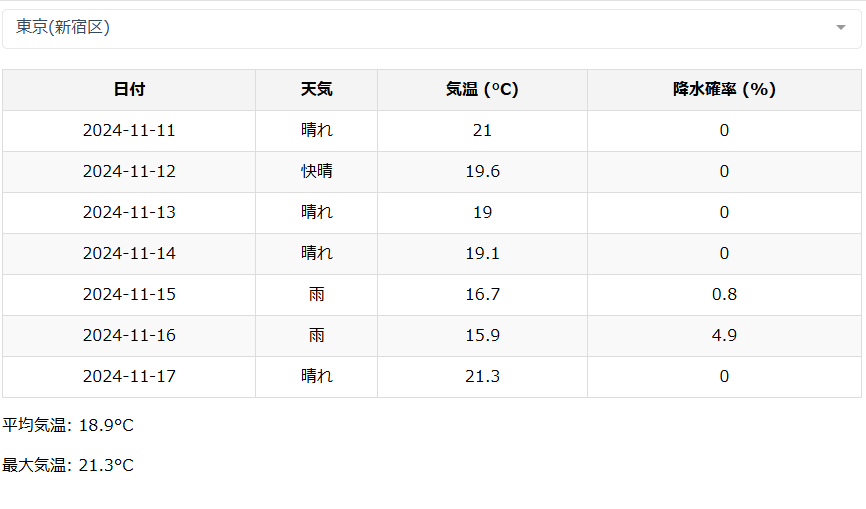
大阪(大阪市)を選択するとApp.vueを経由して天気情報が表示される
- たとえば
- 子コンポーネントに
defineEmitsでEmitを定義し、emit()で設定する - 親コンポーネントは
@イベント名="実行関数"で受け取る - 複数のデータを渡したい場合はオブジェクトの形で渡す
defineEmits<{(e: "Event1", value1: type1): void, (e: "Event2"): void, ...}()
Props
- 親コンポーネントから子コンポーネントにデータを渡す
-
Emitで説明したApp.vue⇔Display.vueの部分
App.vue<!-- :共有変数="実際のオブジェクト" Propsで渡すデータを指定する --> <Display :weatherValue="weatherData" />Display.vue// const props = defineProps<{ 親コンポーネントから受け取るオブジェクト }>(); const props = defineProps<{ weatherValue: WeatherData }>();- 基本的には
v-bindで渡し、子コンポーネントはv-bindのキー名で受け取る - 本来は
props.でアクセスするが、省略できるDisplay.vue<!-- props.がなくてもアクセスできる --> <tbody v-if="weatherValue.getRawWeatherData.length"> <tr v-for="day in weatherValue.getRawWeatherData" :key="day.date"> ... <!-- props.でアクセスしてもよい --> <p>平均気温: {{ props.weatherValue.getAverageTemperature() }}°C</p> <p>最大気温: {{ props.weatherValue.getMaxAverageTemperature() }}°C</p> - 複数のデータを渡したい場合はオブジェクトの形で渡す
defineProps<{ value1: type1, value2: type2, ... }>()
-

TypeScript
宣言構文
-
var- 再代入:可能、再定義:可能
- ES6以前に使われていたもので、当時はこれしか使えなかった
- 再代入も再定義もできるアブナイ爆弾なので、今はほとんど使われない
var x = 10; x = 20; var x = 5; -
let- 再代入:可能、再定義:不可能
- 再代入する必要があるものはこれを使う
weather.tsgetAverageTemperature(): number | string { let total = 0; for (const day of this.data) { total += day.temperature; } // let total = 10; ←これはできない(この位置で) return (total / this.data.length).toFixed(1); } -
const- 再代入:不可能、再定義:不可能
- たぶん一番使われている。定数的な扱い
weatherService.tsconst API_URL = "https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast"; // API_URL = "https://example.com" ←これはできない // const API_URL = "test" ←これもできない
型注釈
- 変数の型を定義できる
weather.ts
export interface Weather { date: string; weatherCode: number; temperature: number; rainProb: number; sunset?: string; sunrise?: string; } - このためにTypescriptができたといっても過言ではない
- とはいえJavascriptが他のプログラミング言語に追いついただけなので、あまり真新しさはない
型推論
- 型注釈を(安全に)省略できる
weather.ts
let total = 0; for (const day of this.data) { total += day.temperature; } - 関数の引数は型推論できない
App.vue
async function fetchWeather(latitude: number, longitude: number) { ...
プリミティブ型(基本データ型)
- 他のプログラミング言語とほぼ一緒
-
number:数値型 -
string:文字型 -
booolean:真偽値型 nullundefined
-
など
複合型
- これもユニオン型以外ほぼ一緒
- 配列
-
[]で囲む
let numbers: number[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; -
- オブジェクト
-
{}で囲む
Form.vue{ name: "北海道(札幌市)", latitude: 43.0643, longitude: 141.3468 }, -
- ユニオン型
- 変数の型を複数許容するデータ型。
|でつなげる。 - たとえば以下のようにしておけば、
toFixed()で返却されるのはstringだがこれを削除してもエラーにならない(numberも受け付ける)
weather.tsgetAverageTemperature(): number | string { ... return (total / this.data.length).toFixed(1); } - 変数の型を複数許容するデータ型。
- 配列
基本構文
-
forだけちょっと真新しいかも-
ifDisplay.vueconst getWeatherDescription = (code: number): string => { if (code >= 0 && code <= 1) return "快晴"; else if (code <= 3) return "晴れ"; else if (code <= 45) return "曇り"; else if (code <= 80) return "雨"; else if (code <= 95) return "雷雨"; else return "雪"; } -
switchswitch (value) { case 0: case 1: return "快晴"; break; case 2: case 3: return "晴れ"; break; default: return "晴れていない"; break; } -
whilelet count = 10; while (count > 0) { count--; } -
try-catchApp.vuetry { const data = await fetchWeatherData(latitude, longitude); weatherData.value = new WeatherData(data); console.log("Fetched weather data:", weatherData.value); } catch (err) { console.error("Weather data fetch failed:", err); weatherData.value = new WeatherData([]); } -
forfor (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) { console.log(i); } -
for...in- リストの先頭から末尾まで走査し、各要素のインデックスが返される
weather.tsfor (const day in this.data) { // dayはthis.dataにおける各要素のインデックス maxTemp = Math.max(maxTemp, this.data[day].temperature); } -
for...of- リストの先頭から末尾まで走査し、各要素の値が返される
weather.tsfor (const day of this.data) { // dayはthis.dataにおける各要素の値 total += day.temperature; }
-
関数
- 普通の関数
function onSelect() { if (selectedPrefecture.value) { const { latitude, longitude } = selectedPrefecture.value; emit("selectLocation", latitude, longitude); } } - アロー関数
-
(引数) => {処理}の形で関数を超簡略化
Display.vueconst getWeatherDescription = (code: number): string => { if (code >= 0 && code <= 1) return "快晴"; ... else return "雪"; } /* 以下と同じ const getWeatherDescription = (function(code: number): string { if (code >= 0 && code <= 1) return "快晴"; ... else return "雪"; }) */ -
インタフェース
- 他のプログラミング言語とほぼ一緒
- ちなみに変数名に続いて ? をつけると、あってもなくてもいいプロパティになる(オプショナルプロパティ)
weather.ts
export interface Weather { date: string; weatherCode: number; temperature: number; rainProb: number; sunset?: string; sunrise?: string; }
クラス
- これもほぼ一緒だが、
setter/getter用のキーワードが用意されている -
setterは戻り値がないので型定義不要weather.tsexport class WeatherData { public data: Weather[]; constructor(data: Weather[]) { this.data = data; } set setWeatherData(data: Weather[]) { this.data = data; } get getRawWeatherData(): Weather[] { return this.data; } ... }
非同期処理
-
asyncで非同期関数を定義し、awaitで非同期処理が完了するのを待つweatherService.tsexport async function fetchWeatherData(latitude: number, longitude: number): Promise<Weather[]> { const response = await fetch( `${API_URL}?latitude=${latitude}&longitude=${longitude}&daily=weathercode,temperature_2m_max,precipitation_sum&timezone=Asia/Tokyo` ); const responseCode: boolean = response.ok if(responseCode) { const data = await response.json(); ... } - 非同期処理には他の書き方も存在するが、今のところ上記の書き方が最先端で簡潔
今回話さなかったこと
- Vue 3 には別の書き方もある(Options API)
- Vue3デビューcomposition APIとoptions APIについて簡単に比較してみた
- 今回解説したのはComposition API
- Composition APIのほうが新しくてスッキリ書ける
- Vue Router
- ページ遷移処理を簡単にする
- ページリンクとかをまとめて書ける
- はじめに - Vue Router