世の中SDx時代ですが、一方でBGPもまだまだ現役で活躍しています。ここではBGPのスケール手法を2つ紹介します。
BGP Route ReflectorとBGP Route Server
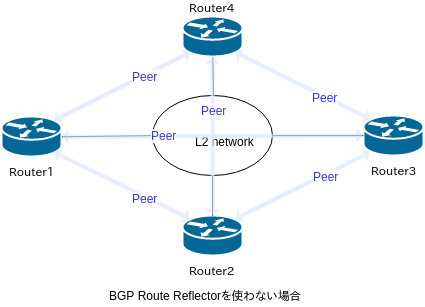
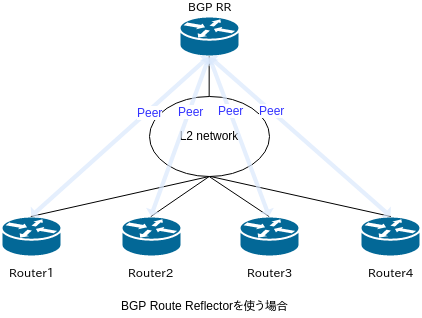
BGP Route Reflector(以降、RR)は、ネットワークエンジニアにとっては馴染みのある技術で、iBGPのスケーラビリティを担保するために必須のものです。RRを使わない場合、iBGPではフルメッシュでピアを確保する必要があり、仮にn台のBGPスピーカでピアリングしようとするとn(n-1)/2個のピア設定が必要となります。BGPスピーカが4,5台までであればRRがなくてもいいのですが、それ以上になると設定・管理が厳しくなってきます。RRを使うことでピア数はn個ににまで抑えられます(実際はRRを二重化することが多いので、その場合ピア数は2n個)。
BGP Route ReflectorはiBGPで用いられますが、これのeBGP版がBGP Route Server(以降、RS)です。こちらはRRに比べると馴染みがないかもしれません。主にIX(Internet eXchange)での利用を想定した技術です。eBGPは、組織間でのPoint to Point接続で使うことが多いので、eBGPでフルメッシュ接続したいというニーズがあまりないのですが、IXでは同一ネットワーク上で多数のeBGPピアを設定するケースがあります(私はIXの関係者ではないので正確なことはわかりませんが)。RSの場合はピア数の削減による運用負荷の軽減という目的が主だと思いますが、RSと同様スケールアウトしやすいという特徴があります。
以下、RRとRSの比較表です。
| 項目 | BGP RR | BGP RS |
|---|---|---|
| iBGP/eBGP | iBGP | eBGP |
| コントロールプレーン | ハブ&スポーク | ハブ&スポーク |
| データプレーン | フルメッシュ | フルメッシュ |
| 利用できる経路制御用アトリビュート | LocalPreference | LocalPreference, AS-Path, MED |
| dynamic peering(ピア接続の自動化) | 可(RRによる) | 不可(AS数が少なければ可) |
RRもRSもコントロールプレーン(制御)はハブ&スポークで設定量・運用負荷の削減し、データプレーン(経路)はフルメッシュとしてネットワークを効率利用してるという点は同じです。ただし、RSはeBGPなので、利用できるBGPアトリビュートが多く、RRよりも経路制御を柔軟に行うことができます。一方、RSを用いる場合、ピアごとに異なるAS番号を指定する必要があるため、dynamic peeringの利用が(ほぼほぼのケースで)できません。
スケーラビリティに関しては、RR, RSの性能次第ですが、1,000ピアくらいであればおそらく問題ないでしょう。
BGP Route ReflectorとBGP Route Serverの設定
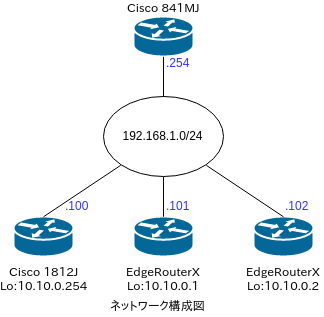
BGP Route Reflectorは大体どこのベンダでもサポートしています。BGP Route Serverは、CiscoのISRシリーズ、ASRシリーズが対応しています。ソフトウェアとしては、QuaggaやGoBGPが対応しています。今回はCisco 841MJをハブ側(RR, RS)として、Cisco 1812J、EdgeRouterX 2台をスポーク側にします。
Route Reflectorによる接続
すべてのルータをAS65000に所属させ、Cisco 841MJをRRとします
コンフィグ
[Cisco 841MJ]
router bgp 65000
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 192.168.1.100 remote-as 65000
neighbor 192.168.1.101 remote-as 65000
neighbor 192.168.1.102 remote-as 65000
!
address-family ipv4
neighbor 192.168.1.100 activate
neighbor 192.168.1.100 route-reflector-client
neighbor 192.168.1.101 activate
neighbor 192.168.1.101 route-reflector-client
neighbor 192.168.1.102 activate
neighbor 192.168.1.102 route-reflector-client
exit-address-family
[Cisco 1812J]
conf t
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.10.0.254 255.255.255.255
interface FastEthernet0
ip address 192.168.1.100 255.255.255.0
router bgp 65000
bgp router-id 10.10.0.254
neighbor 192.168.1.254 remote-as 65000
address-family ipv4
neighbor 192.168.1.254 activate
no auto-summary
no synchronization
network 10.10.0.254 mask 255.255.255.255
end
[EdgeRouterX #1]
configure
set interfaces ethernet eth0 address 192.168.1.101/24
set interfaces ethernet eth0 duplex auto
set interfaces ethernet eth0 speed auto
set interfaces loopback lo address 10.10.0.1/32
set protocols bgp 65000 neighbor 192.168.1.254 remote-as 65000
set protocols bgp 65000 neighbor 192.168.1.254 soft-reconfiguration inbound
set protocols bgp 65000 network 10.10.0.1/32
set protocols bgp 65000 parameters router-id 10.10.0.1
end
[EdgeRouterX #2]
configure
set interfaces ethernet eth0 address 192.168.1.102/24
set interfaces ethernet eth0 duplex auto
set interfaces ethernet eth0 speed auto
set interfaces loopback lo address 10.10.0.2/32
set protocols bgp 65000 neighbor 192.168.1.254 remote-as 65000
set protocols bgp 65000 neighbor 192.168.1.254 soft-reconfiguration inbound
set protocols bgp 65000 network 10.10.0.2/32
set protocols bgp 65000 parameters router-id 10.10.0.2
end
設定確認
Cisco 1812Jからルーティングの状態を確認していきます。
Router#sh ip bgp summary
BGP router identifier 10.10.0.254, local AS number 65000
BGP table version is 4, main routing table version 4
3 network entries using 396 bytes of memory
3 path entries using 156 bytes of memory
3/2 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 504 bytes of memory
2 BGP rrinfo entries using 48 bytes of memory
0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
Bitfield cache entries: current 1 (at peak 1) using 32 bytes of memory
BGP using 1136 total bytes of memory
BGP activity 3/0 prefixes, 3/0 paths, scan interval 60 secs
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
192.168.1.254 4 65000 11 9 4 0 0 00:06:11 2
ピア先はRRのみです。自身のAS番号とピアのAS番号が同じなのでiBGP接続ということがわかります。
Router#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 4, local router ID is 10.10.0.254
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i10.10.0.1/32 192.168.1.101 1 100 0 i
*>i10.10.0.2/32 192.168.1.102 1 100 0 i
*> 10.10.0.254/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
経路情報に関しては、直接ピアリングしていない192.168.1.101, 192.168.1.102からも受け取っています。
Router#ping 10.10.0.1 so 10.10.0.254
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.0.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 10.10.0.254
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
10.10.0.254 -> 10.10.0.1へのpingが成功していることがわかります。
Router#ping 10.10.0.2 so 10.10.0.254
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.0.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 10.10.0.254
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
10.10.0.254 -> 10.10.0.2へのpingが成功していることがわかります。
Route Serverによる接続
Cisco 841MJをRSとし、AS65000に所属させます。Cisco 1812J, EdgeRouterX #1, EdgeRouterX #2は、それぞれAS65100, AS65101, AS65102に所属させます。
コンフィグ
[Cisco 841MJ]
conf t
router bgp 65000
neighbor 192.168.1.100 remote-as 65100
neighbor 192.168.1.101 remote-as 65101
neighbor 192.168.1.102 remote-as 65102
address-family ipv4 unicast
neighbor 192.168.1.100 activate
neighbor 192.168.1.100 route-server-client
neighbor 192.168.1.101 activate
neighbor 192.168.1.101 route-server-client
neighbor 192.168.1.102 activate
neighbor 192.168.1.102 route-server-client
end
[Cisco 1812J]
conf t
interface Loopback0
ip address 10.10.0.254 255.255.255.255
interface FastEthernet0
ip address 192.168.1.100 255.255.255.0
exit
router bgp 65100
bgp router-id 10.10.0.254
no bgp enforce-first-as
neighbor 192.168.1.254 remote-as 65000
address-family ipv4
neighbor 192.168.1.254 activate
no auto-summary
no synchronization
network 10.10.0.254 mask 255.255.255.255
end
[EdgeRouterX #1]
configure
set interfaces ethernet eth0 address 192.168.1.101/24
set interfaces ethernet eth0 duplex auto
set interfaces ethernet eth0 speed auto
set interfaces loopback lo address 10.10.0.1/32
set protocols bgp 65101 neighbor 192.168.1.254 remote-as 65000
set protocols bgp 65101 neighbor 192.168.1.254 soft-reconfiguration inbound
set protocols bgp 65101 network 10.10.0.1/32
set protocols bgp 65101 parameters router-id 10.10.0.1
end
[EdgeRouterX #2]
configure
set interfaces ethernet eth0 address 192.168.1.102/24
set interfaces ethernet eth0 duplex auto
set interfaces ethernet eth0 speed auto
set interfaces loopback lo address 10.10.0.2/32
set protocols bgp 65102 neighbor 192.168.1.254 remote-as 65000
set protocols bgp 65102 neighbor 192.168.1.254 soft-reconfiguration inbound
set protocols bgp 65102 network 10.10.0.2/32
set protocols bgp 65102 parameters router-id 10.10.0.2
end
設定確認
こちらもCisco 1812Jからルーティングの状態を確認していきます。
Router#sh ip bgp summ
BGP router identifier 10.10.0.254, local AS number 65100
BGP table version is 4, main routing table version 4
3 network entries using 396 bytes of memory
3 path entries using 156 bytes of memory
4/3 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 672 bytes of memory
2 BGP AS-PATH entries using 48 bytes of memory
0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
Bitfield cache entries: current 1 (at peak 1) using 32 bytes of memory
BGP using 1304 total bytes of memory
BGP activity 6/3 prefixes, 6/3 paths, scan interval 60 secs
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
192.168.1.254 4 65000 42 30 4 0 0 00:06:08 2
ピア先はAS65000(RS)のみです。
Router#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 4, local router ID is 10.10.0.254
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.10.0.1/32 192.168.1.101 1 0 65101 i
*> 10.10.0.2/32 192.168.1.102 1 0 65102 i
*> 10.10.0.254/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
BGPテーブルを見ると、AS65000を中継して経路情報を受け取っているにもかかわらず、AS65101, AS65102から直接経路情報を受け取っているように見えます。もちろんNext Hopも192.168.1.254(AS65000)を中継しません。
Router#ping 10.10.0.1 so 10.10.0.254
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.0.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 10.10.0.254
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
10.10.0.254 -> 10.10.0.1へのpingが成功していることがわかります。
Router#ping 10.10.0.2 so 10.10.0.254
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.0.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 10.10.0.254
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
10.10.0.254 -> 10.10.0.2へのpingが成功していることがわかります。
この検証ではRRとRSの差はあまり感じないですが、経路制御を柔軟に行う必要があれば複数のアトリビュートを活用できるRSを、そうでなければdynamic peeringを利用できるRRのほうが運用しやすいと思います。
適用例
RRはデータセンターネットワークやキャリアネットワークの中でよく登場します。RSはIXの中で使われます。意外なところとしては、広域イーサ上での適用も可能です。広域イーサ上でフルメッシュ構成を検討する場合、従来はOSPFで実装することが多かったと思います。OSPFでは、フルメッシュ接続できるのはルータ50〜100台程度までで、それ以上になるとネットワークの分割が必須となります。その点はスケールしやすいRRやRSのほうが有利です。また、RSではeBGPの豊富なアトリビュートをフル活用することで、OSPFをはるかに上回る柔軟な経路制御を行うこともできます。
いまからネットワーク構築するならSDx系の導入を検討すると思いますが、「枯れた技術を使いたい」、「ベンダロックインを避けたい」、「今ある機器を有効活用したい」というケースでは、RRやRSの導入でSDx系の技術が成熟するまで様子を見るというのも1つの手です。