データフォーマット(data format)の分類
| フォーマット | 対象 |
|---|---|
ファイルフォーマット(file format) |
ファイル |
メッセージフォーマット(message format; 電文フォーマット) |
ネットワーク経由で伝送されるメッセージ
|
汎用フォーマット
標準化された主な汎用フォーマットは、以下の通り。
| 形式 | データ構造 | ライブラリ |
|---|---|---|
CSV(Comma-Separated Values)
|
値のみ (=デリミタで順序づけ) |
・opencsv・ Apache Commons CSV
|
プロパティファイル |
キーと値 (=ペアデリミタで紐付け) |
・java.util.Properties・ java.util.ResourceBundle
|
XML(eXtensible Markup Language)
|
マップのネスト
|
・JAXP
|
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)
|
リストとマップのネスト
|
・Jackson・ gson
|
Microsoft Office |
Microsoft Officeアプリケーション専用 |
・Apache POI
|
アーカイブファイル |
圧縮済みファイル |
・java.util.zip (.zip)・ Apache Commons Compress (.tar) |
音声(サンプリング形式/シンセサイザ形式) |
音声ファイル |
・javax.sound.sampled・ javax.sound.midi (.mid) |
画像 |
画像ファイル |
・Apache Commons Imaging・ javax.imageio
|
音声形式の分類
音声形式には、以下の2形式が存在する。
| 形式 | 格納データ | メリット | デメリット |
|---|---|---|---|
サンプリング形式 |
全ての音情報 | あらゆる音声に対応 |
ファイルサイズが大きい
|
シンセサイザ形式 |
楽譜情報 |
ファイルサイズが小さい
|
対応楽器が限定的 |
CSVファイルの操作(CSV解析)
CSVファイルは、opencsvやApache Commons CSVライブラリを利用して操作することができる。
Apache Commons CSVの場合、CSV解析で利用するクラスは以下の通り。
| クラス | 内容 |
|---|---|
CSVFormat |
CSV形式とCSV解析メソッドを定義するクラス |
CSVParser |
CSVファイルのテーブルデータを保持するクラス(イテレータ) |
CSVRecord |
CSVファイルのレコードデータを保持するクラス |
CSVPrinter |
CSVファイルへの書き込みメソッドを定義するクラス |
定義(Apache Commons CSV)
// 「CSV解析」を行うCSVParserオブジェクトの生成、
// -> 「解析結果」はCSVRecordオブジェクトが保持
CSVParser CSVFormat.parse(Reader in)
// パラメータ
// in: 「文字ストリーム」を読み込むReaderオブジェクト
サンプルコード
参考1: Apache Commons CSV
参考2: Introduction to Apache Commons CSV
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.commons.csv.*;
public class CSVWR {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// CSVに格納するデータ群
RecordData rd1 = new RecordData("Record1", "ABC", "あいう", 123);
RecordData rd2 = new RecordData("Record2", "DEF", "えおか", 456);
RecordData rd3 = new RecordData("Record3", "GHI", "きくけ", 789);
RecordData rd4 = new RecordData("Record4", "JKL", "こさし", 1011);
RecordData rd5 = new RecordData("Record5", "MNO", "すせそ", 1112);
// レコードデータ(List<RecordData>型)
// -> 各要素は"1つ"のクラスオブジェクトデータとなり、各レコードはダブルクオテーション("")で囲まれる
// <- データ内にカンマ(,)が含まれる場合、そのデータはダブルクオテーションで囲まれる
// => レコードとして出力する際は、クラスオブジェクトの各フィールドを取り出す必要がある
List<RecordData> listRD = new ArrayList<>();
listRD.add(rd1);
listRD.add(rd2);
listRD.add(rd3);
listRD.add(rd4);
listRD.add(rd5);
// -- CSV形式データをCSVファイルに出力 --
try (
/*
データの流れ:
JVM (-> CSVFormat) -> CSVPrinter -> BufferedWriter
-> FileWriter -> CSVファイル
*/
// 「テキストファイル」に文字列を書き込むFileWriterオブジェクトの生成
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("src/test.csv", true);
// バッファリングしながら「文字列」を書き込むBufferedOutputStreamオブジェクトの生成
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
// CSVFormatオブジェクトの定義・CSVPrinterオブジェクトの取得(=CSVファイルの作成)
// -> CSVPrinterオブジェクトの生成時にCSVファイルが作成される
CSVPrinter p = new CSVPrinter(bw, CSVFormat
// CSV形式の指定
.DEFAULT
// カラム名(=ヘッダ)の書き込み
.withHeader("Record", "data 1", "data 2", "data 3")
);
) {
// レコードデータ(List<String>型)の書き込み
// -> RecordData型だと"1つ"のオブジェクトとして扱われるため、各フィールドの値を個別に取り出して指定
for (RecordData data : listRD) {
p.printRecord(
data.getRec(),
data.getStr1(),
data.getStr2(),
Integer.toString(data.getI())
);
}
// 強制書き込み
p.flush();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Some exception(Output) occurred.");
}
// -- 書き込みの終了待機 --
// -> 待機しない場合は書き込みが間に合わずIOExceptionが送出
try {
Thread.sleep(700);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Exception occurred in sleep().");
}
// -- CSVファイルの読み込み --
try (
/*
データの流れ:
CSVファイル(クラスパス基準) -> InputStream -> InputStreamReader -> FileReader
-> BufferedReader -> CSVParser -> CSVRecord -> JVM
*/
// CSVファイルを「バイトストリーム」経由で読み込むInputStreamオブジェクト(クラスパス経由)
// -> InputStreamは「バイトストリーム」を表すため、バイトストリーム -> 文字ストリーム への変換が必要
// <- バイトストリームを利用することで、「あらゆる文字コードに対応」かつ「読み込みが最速」となる
InputStream is = Main.class.getResourceAsStream("src/test.csv");
// バイトストリーム -> 文字ストリーム への変換を行うInputStreamReaderオブジェクトの生成
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
// BufferedReaderオブジェクトの生成
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
) {
if (Files.exists(Paths.get("src/test.csv"))) {
// CSVファイルの「テーブルデータ」を保持するCSVParserオブジェクトの取得
// -> CSVFormatのメソッドを利用してCSV解析を行う
// <- CSVParserはIterable<CSVRecord>の実装クラス
CSVParser csvp = CSVFormat
// CSV形式の指定
.DEFAULT
// カラムの指定
.withHeader("Record", "data A", "data B", "data C")
// 1行目をカラム名(=ヘッダ)としてスキップ
.withFirstRecordAsHeader()
// 値のトリム(=前後の空白を除外)
.withIgnoreSurroundingSpaces()
// 空白行のスキップ
.withIgnoreEmptyLines()
// CSV解析の実行、CSVParserオブジェクトの取得
.parse(br);
// CSVRecordを取得・コンソールへの出力
for (CSVRecord csvr : csvp) {
// CSVRecordオブジェクトが保持する値の取得
// -> get()メソッドはインデックス・カラム名を指定した値の取得が可能
String rec = csvr.get(0);
String str1 = csvr.get(1);
String str2 = csvr.get(2);
int i = Integer.parseInt(csvr.get(3));
System.out.println(rec + ": " + "(" + str1 + ", " + str2 + ", " + i + ")");
}
}
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("NumberFormatException occurred.");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Some exception(Input) occurred.");
}
}
}
class RecordData {
// フィールド
private String rec;
private String str1;
private String str2;
private int i;
// コンストラクタ
RecordData(String rec, String str1, String str2, int i) {
this.rec = rec;
this.str1 = str1;
this.str2 = str2;
this.i = i;
}
// ゲッタ(=アクセサ)
public String getRec() {
return this.rec;
}
public String getStr1() {
return this.str1;
}
public String getStr2() {
return this.str2;
}
public int getI() {
return this.i;
}
}
Record,data 1,data 2,data 3
Record1,ABC,あいう,123
Record2,DEF,えおか,456
Record3,GHI,きくけ,789
Record4,JKL,こさし,1011
Record5,MNO,すせそ,1112
// 最終行は空白行(直前の行で「改行コード」が挿入されるため)
Record1: (ABC, あいう, 123)
Record2: (DEF, えおか, 456)
Record3: (GHI, きくけ, 789)
Record4: (JKL, こさし, 1011)
Record5: (MNO, すせそ, 1112)
プロパティファイルの操作
参考: ResourceBundleのgetKeys()メソッド
Propertiesクラスを利用することで、プロパティの読み書きを行うことができる。
また、ResourceBundleクラスを利用することで、クラスパスやロケールに基づくプロパティファイルの読み込みが可能となる。
サンプルコード
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.*;
class PropertyFileWR {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 「キー」と「値」をもつプロパティデータ
Properties p = new Properties();
// プロパティデータのセット
p.setProperty("key1", "value1");
p.setProperty("key2", "value2");
p.setProperty("key3", "value3");
// プロパティファイルへの書き込み
try (
// プロパティファイル(=.properties)に「テキストデータ」を書き込むFileWriterオブジェクト
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("src/p.properties");
) {
// プロパティファイルの出力・コメントの指定
p.store(fw, "Test Properties");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Some exceptions occurred in output.");
}
// プロパティファイルの読み込み
try {
// 「クラスパス」を起点としたファイルの読み込み
// -> プロパティファイルの「読み込み」時のみ、クラスパスを起点とするResourceBundleクラスが利用可能
ResourceBundle rb = ResourceBundle.getBundle("src.p");
// プロパティの「キー」のリスト
Enumeration<String> keyList = rb.getKeys();
// プロパティの「値」の読み込み
List<String> valList = new ArrayList<>();
valList.add(rb.getString("key1"));
valList.add(rb.getString("key2"));
valList.add(rb.getString("key3"));
// 取得したプロパティをコンソールに出力
while (keyList.hasMoreElements()) {
for (int i = 0; i < valList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(keyList.nextElement() + ": " + valList.get(i));
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Some exceptions occurred in input.");
}
}
}
# Test Properties
# Wed Jul 07 16:12:02 JST 2021
key1=value1
key2=value2
key3=value3
// 最終行は空白行(直前の行で「改行コード」が挿入されるため)
key1: value1
key2: value2
key3: value3
XMLファイルの操作(XML解析)
参考1: XMLの読み込み
参考2: XPath
HTML同様にタグで値を囲むXMLファイルは、Javaで標準提供されたJAXPを利用し、操作することができる。
なお、JAXPはjavax.xml・org.w3c.domパッケージを包含しており、DOM形式でXMLデータを管理する。
ここで、XMLデータを管理するAPIは、以下の4種類存在する。
| API | 内容 |
|---|---|
DOM(Document Object Model) |
・タグをノード、ノードをノードツリー(DOMツリー)として管理・ XMLデータをメモリに全て展開し探索を行う |
SAX(Simple API for XML Processing) |
・タグをイベントとして管理・ XMLデータをメモリに順番に展開し探索を行う・ 読み込み専用
|
StAX(Streaming API for XML) |
・タグをイベントとして管理・ XMLデータをメモリに順番に展開し探索を行う・ 読み書き可能
|
XPath(XML Path Language) |
・タグおよび属性をノード、ノードをノードツリーとして管理 |
サンプルコード(DOM)
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.xml.parsers.*;
import javax.xml.transform.*;
import javax.xml.transform.dom.DOMSource;
import javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamResult;
import org.w3c.dom.*;
public class XMLWR {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// -- XML形式データをXMLファイルに出力 --
/*
try節で初期化するインスタンスをnullで初期化
-> try節で宣言された変数はtry節外から"見えない"
*/
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = null;
DocumentBuilder db = null;
// XML文書(=Document)の定義
try {
// DocumentBuilderの「ファクトリ」の生成
dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// Documentを生成するDocumentBuilderオブジェクトの生成
db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("DocumentBuilder cannot be made.");
}
// Documentオブジェクトの生成
Document d = db.newDocument();
// XMLの構成要素(=タグ)の作成
Element parent = d.createElement("parent");
Element child1 = d.createElement("child1");
Element child2 = d.createElement("child2");
Element grandchild1_1 = d.createElement("grandchild1_1");
Element grandchild2_1 = d.createElement("grandchild2_1");
Element grandchild1_2 = d.createElement("grandchild1_2");
// タグに「属性」と「属性値」を追加
parent.setAttribute("id", "100");
child1.setAttribute("id", "110");
child2.setAttribute("id", "120");
grandchild1_1.setAttribute("id", "111");
grandchild2_1.setAttribute("id", "112");
grandchild1_2.setAttribute("id", "121");
// タグ内の「文字列情報」を追加
// -> XMLは「最下位タグ」のみ文字列情報を保持
grandchild1_1.appendChild(d.createTextNode("1st Child of child1"));
grandchild2_1.appendChild(d.createTextNode("2nd Child of child1"));
grandchild1_2.appendChild(d.createTextNode("Child of child2"));
// Documentに親タグ(parentタグ)をネスト
// <- ElementインタフェースはNodeインタフェースを継承
d.appendChild(parent);
// 親タグ(parentタグ)に子タグ(childタグ)をネスト
parent.appendChild(child1);
parent.appendChild(child2);
// 子タグ(childタグ)に孫タグ(grandchildタグ)をネスト
child1.appendChild(grandchild1_1);
child1.appendChild(grandchild2_1);
child2.appendChild(grandchild1_2);
/*
try節で初期化するインスタンスをnullで初期化
-> try節で宣言された変数はtry節外から"見えない"
*/
Transformer t = null;
// Transformerオブジェクトの生成
try {
// Transformerの「ファクトリ」の生成
TransformerFactory tf = TransformerFactory.newInstance();
// 「Document -> XMLファイル への変換」を行うTransformerオブジェクトの生成
t = tf.newTransformer();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Transformer cannot be made.");
}
// -- 出力方式の設定開始 --
// 「インデント」の有効化
t.setOutputProperty("indent", "yes");
// 「文字コード」の指定
t.setOutputProperty("encoding", "UTF-8");
// -- 出力方式の設定終了 --
// 「Document -> DOMSource -> XMLファイル(=StreamResult)」への変換
try {
// Document -> DOMSource への変換
DOMSource doms = new DOMSource(d);
// 出力先ファイルパス(=ファイル名)の指定
File f = new File("src/test.xml");
// 「マークアップ形式ファイルの出力先情報」を保持するStreamResultオブジェクトの生成
StreamResult sr = new StreamResult(f);
// DOMSource -> XMLファイル(=StreamResult) への変換(=XMLファイルの出力)
t.transform(doms, sr);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Conversion from Document to XML failed");
}
// -- 書き込みの終了待機 --
// -> 待機しない場合は書き込みが間に合わずIOExceptionが送出
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Exception occurred in sleep().");
}
// -- XML文書の読み込み(XML解析) --
try {
// XMLファイルを「バイトストリーム」経由で読み込むInputStreamオブジェクト
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("src/test.xml");
// 「XML解析結果」を保持するDocumentオブジェクトの取得(XML解析)
//Document dp = db.parse(is);
Document dp = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance().newDocumentBuilder().parse(is);
// 最上位タグ(親タグ)の取得
Element ep = dp.getDocumentElement();
// 子タグの取得
Element ec1 = findChildByTag(ep, "child1");
Element ec2 = findChildByTag(ep, "child2");
// 孫タグの取得
List<Element> grandchildList = new ArrayList<>();
grandchildList.add(findChildByTag(ec1, "grandchild1_1"));
grandchildList.add(findChildByTag(ec1, "grandchild2_1"));
grandchildList.add(findChildByTag(ec2, "grandchild1_2"));
// タグ内の「文字列情報」を取得
List<String> textList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Element grandchild : grandchildList) {
textList.add(grandchild.getTextContent());
}
// XML解析結果の出力
for (int i = 0; i < grandchildList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(grandchildList.get(i).getTagName() + ": " + textList.get(i));
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Input-related Exception occurred.");
}
}
// 子タグ(=Elementオブジェクト)を返却する静的メソッド
static Element findChildByTag(Element parent, String childTagName) throws Exception {
// 子タグを全て取得
NodeList children = parent.getChildNodes();
// 子タグの線形探索
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
// 子タグの各要素がElementオブジェクトであることを保証
if (children.item(i) instanceof Element) {
// 子タグの取得
// -> NodeList.item()の返却型はNode型であるため、
// Node -> Element へのダウンキャストが必要
Element child = (Element) children.item(i);
// 引数のタグ名と一致している場合は子タグを返却
if (child.getTagName().equals(childTagName)) {
return child;
}
}
}
//見つからない場合はnullを返却
System.out.println("Cannot find designated child tag.");
return null;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
<parent id="100">
<child1 id="110">
<grandchild1_1 id="111">1st Child of child1</grandchild1_1>
<grandchild2_1 id="112">2nd Child of child1</grandchild2_1>
</child1>
<child2 id="120">
<grandchild1_2 id="121">Child of child2</grandchild1_2>
</child2>
</parent>
grandchild1_1: 1st Child of child1
grandchild2_1: 2nd Child of child1
grandchild1_2: Child of child2
JSONファイルの操作(JSON解析)
JSONファイルは、Jacksonやgsonライブラリを利用して操作することができる。
Jacksonを利用する場合、アナテイションによるJSON形式の指定を可能にするjackson.annotation、
JSONデータ ⇄ Javaオブジェクトの変換を行うjackson.databind、
JSON解析によるJSONデータの整形を行うjackson.coreライブラリを利用する。
その中でも特に利用するクラスは、以下の通り。
| クラス | ライブラリ | 内容 |
|---|---|---|
| - | jackson.annotation |
JSON形式を指定するアナテイション |
ObjectMapper |
jackson.databind |
JSONデータの読み書きを行うメソッドを定義 |
ObjectWriter |
jackson.databind |
JSONデータの書き込み・JSONファイルへの出力を行う |
JsonNode |
jackson.databind |
JSONデータのタグを表現 |
DefaultPrettyPrinter |
jackson.core |
JSONデータの整形を行う |
サンプルコード(Jackson)
参考1: Jackson
参考2: jackson-databind
参考3: jackson-core
参考4: jackson-annotations
import java.io.File;
import java.util.List;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.*;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.util.DefaultPrettyPrinter;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.*;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.exc.InvalidDefinitionException;
public class JSONWR {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// JSONデータ
JSONGrandchild g1c1 = new JSONGrandchild("1st Child of Child1", 111);
JSONGrandchild g2c1 = new JSONGrandchild("2nd Child of Child1", 112);
JSONGrandchild gc2 = new JSONGrandchild("Child of Child2", 121);
JSONChild c1 = new JSONChild("1st Child of Parent", 110, List.of(g1c1, g2c1));
JSONChild c2 = new JSONChild("2nd Child of Parent", 120, List.of(gc2));
JSONChild c3 = new JSONChild("3rd Child of Parent", 130, List.of());
JSONParent p = new JSONParent("Parent", 100, List.of(c1, c2, c3));
JSONData data = new JSONData(p);
// JSONデータにアクセスするObjectMapperオブジェクトの生成
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
// -- JSONデータ -> JSON文字列 に変換する場合 --
String json = "";
try {
// JSONデータ -> JSON文字列への変換
json = mapper
// JSONデータの整形
.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter()
// JSONデータ -> JSON文字列(String型) への変換
.writeValueAsString(data);
System.out.println(json);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Conversion from JSONData to String has failed.");
}
// -- JSONデータをJSONファイルに出力する場合 --
// JSONデータの「整形」を行うDefaultPrettyPrinterオブジェクトの取得
DefaultPrettyPrinter printer = new DefaultPrettyPrinter();
// JSONデータの「書き込み」を行うObjectWriterオブジェクトの取得
ObjectWriter writer = mapper.writer(printer);
// JSONファイルへの出力
try {
// JSONデータの書き込み、JSONファイルへの出力
writer.writeValue(new File("src/test.json"), data);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Output to JSON File has failed.");
}
JSONData resData = null;
// -- JSONファイルの読み込み --
try {
// JSONデータオブジェクトの取得
resData = mapper.readValue(new File("src/test.json"), JSONData.class);
}
catch (InvalidDefinitionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Input from JSON File has failed.");
}
// 「データバインディング」によるJSONデータの取得
JSONParent resP = resData.getParent();
JSONChild resC1 = resP.getChildren().get(0);
JSONChild resC2 = resP.getChildren().get(1);
JSONChild resC3 = resP.getChildren().get(2);
JSONGrandchild resG1C1 = resC1.getGrandchildren().get(0);
JSONGrandchild resG2C1 = resC1.getGrandchildren().get(1);
JSONGrandchild resGC2 = resC2.getGrandchildren().get(0);
System.out.println("parent: " + resP);
System.out.println("child1: " + resC1);
System.out.println("child2: " + resC2);
System.out.println("child3: " + resC3);
System.out.println("child1 of child1: " + resG1C1);
System.out.println("child2 of child1: " + resG2C1);
System.out.println("child of child2: " + resGC2);
}
}
// -- JSONデータ構造を定義するクラス --
// -> JSONファイルの「読み込み」時の「データバインディング」でも利用
// 「データ順序」は@JsonPropertyOrder()アナテイションで記述
@JsonPropertyOrder({
"parent"
})
// JSONデータを保持するクラス
class JSONData {
// 「キー」は@JsonProperty()アナテイションで記述
@JsonProperty("parent")
private JSONParent parent;
// コンストラクタ
// -> JSONファイルの読み込み時に「Class<E>」として参照するため、
// 各クラスにデフォルトコンストラクタを用意しておく必要がある
public JSONData() {}
public JSONData(JSONParent p) {
this.parent = p;
}
// ゲッタ(=アクセサ)
public JSONParent getParent() {
return this.parent;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.parent.toString();
}
}
@JsonPropertyOrder({
"relationship",
"id",
"child"
})
class JSONParent {
@JsonProperty("relationship")
private String ps;
@JsonProperty("id")
private int pi;
@JsonProperty("child")
private List<JSONChild> children;
// コンストラクタ
public JSONParent() {}
public JSONParent(String ps, int pi, List<JSONChild> cs) {
this.ps = ps;
this.pi = pi;
this.children = cs;
}
// ゲッタ(=アクセサ)
public String getPs() {
return this.ps;
}
public int getPi() {
return this.pi;
}
public List<JSONChild> getChildren() {
return this.children;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return JSONParent.class.getSimpleName() + "(" + this.getPs() + ", " + this.getPi() + ", " + this.getChildren() + ")";
}
}
@JsonPropertyOrder({
"relationship",
"id",
"child"
})
class JSONChild {
@JsonProperty("relationship")
private String cs;
@JsonProperty("id")
private int ci;
@JsonProperty("child")
private List<JSONGrandchild> grandchildren;
// コンストラクタ
public JSONChild() {}
public JSONChild(String cs, int ci, List<JSONGrandchild> gs) {
this.cs = cs;
this.ci = ci;
this.grandchildren = gs;
}
// ゲッタ(=アクセサ)
public String getCs() {
return this.cs;
}
public int getCi() {
return this.ci;
}
public List<JSONGrandchild> getGrandchildren() {
return this.grandchildren;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return JSONChild.class.getSimpleName() + "(" + this.getCs() + ", " + this.getCi() + ", " + this.getGrandchildren() + ")";
}
}
@JsonPropertyOrder({
"relationship",
"id"
})
class JSONGrandchild {
@JsonProperty("relationship")
private String gs;
@JsonProperty("id")
private int gi;
// コンストラクタ
public JSONGrandchild() {}
public JSONGrandchild(String gs, int gi) {
this.gs = gs;
this.gi = gi;
}
// ゲッタ(=アクセサ)
public String getGs() {
return this.gs;
}
public int getGi() {
return this.gi;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return JSONGrandchild.class.getSimpleName() + "(" + this.getGs() + ", " + this.getGi() + ")";
}
}
{
"parent" : {
"relationship" : "Parent",
"id" : 100,
"child" : [ {
"relationship" : "1st Child of Parent",
"id" : 110,
"child" : [ {
"relationship" : "1st Child of Child1",
"id" : 111
}, {
"relationship" : "2nd Child of Child1",
"id" : 112
} ]
}, {
"relationship" : "2nd Child of Parent",
"id" : 120,
"child" : [ {
"relationship" : "Child of Child2",
"id" : 121
} ]
}, {
"relationship" : "3rd Child of Parent",
"id" : 130,
"child" : [ ]
} ]
}
}
{
"parent" : {
"relationship" : "Parent",
"id" : 100,
"child" : [ {
"relationship" : "1st Child of Parent",
"id" : 110,
"child" : [ {
"relationship" : "1st Child of Child1",
"id" : 111
}, {
"relationship" : "2nd Child of Child1",
"id" : 112
} ]
}, {
"relationship" : "2nd Child of Parent",
"id" : 120,
"child" : [ {
"relationship" : "Child of Child2",
"id" : 121
} ]
}, {
"relationship" : "3rd Child of Parent",
"id" : 130,
"child" : [ ]
} ]
}
}
parent: JSONParent(Parent, 100, [JSONChild(1st Child of Parent, 110, [JSONGrandchild(1st Child of Child1, 111), JSONGrandchild(2nd Child of Child1, 112)]), JSONChild(2nd Child of Parent, 120, [JSONGrandchild(Child of Child2, 121)]), JSONChild(3rd Child of Parent, 130, [])])
child1: JSONChild(1st Child of Parent, 110, [JSONGrandchild(1st Child of Child1, 111), JSONGrandchild(2nd Child of Child1, 112)])
child2: JSONChild(2nd Child of Parent, 120, [JSONGrandchild(Child of Child2, 121)])
child3: JSONChild(3rd Child of Parent, 130, [])
child1 of child1: JSONGrandchild(1st Child of Child1, 111)
child2 of child1: JSONGrandchild(2nd Child of Child1, 112)
child of child2: JSONGrandchild(Child of Child2, 121)
直列化(serialization)
参考: 発展学習6日目(ファイルの分類)
インスタンス ⇄ バイト列 の変換(=直列化)を行う直列化クラスは、Serializableインタフェースの実装クラスである必要がある。
直列化クラスは、ObjectInputStream・ObjectOutputStreamを通じてシリアライズ処理を行ったあと、
バイナリファイルの読み書きを行うFileInputStream・FileOutputStreamを用いて直列化データの読み書きが可能となる。
また、直列化クラスのバージョンを管理するシリアルバージョンUIDによって、フィールドの変更を検知することができる。
サンプルコード
import java.io.*;
public class SerializationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 直列化を行う直列化クラスオブジェクト
SerializedData dataBefore = new SerializedData("ABC", 123, new SerializedClass("あいう", 456));
// インスタンス -> バイト列 のシリアライズ処理・ファイル出力
try (
// 「バイナリファイル」に書き込むFileOutputStreamフィルタの生成
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src/serializedData.dat");
// インスタンス -> バイト列 の変換(=シリアライズ処理)を行うObjectOutputStreamフィルタの生成
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
) {
// シリアライズ処理
oos.writeObject(dataBefore);
// 強制書き込み
oos.flush();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Serialization has failed.");
}
// バイナリファイルの読み込み・バイト列 -> インスタンス のデシリアライズ処理
try (
// 「バイナリファイル」を読み込むFileInputStreamフィルタの生成
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src/serializedData.dat");
// バイト列 -> インスタンス の変換(=デシリアライズ処理)を行うObjectInputStreamフィルタの生成
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
) {
SerializedData dataAfter = (SerializedData) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(dataAfter);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Deserialization has failed.");
}
}
}
// 直列化クラス
// -> インスタンス ⇄ バイト列 の直列化を行うクラスはSerializableインタフェースの実装クラス
class SerializedData implements Serializable {
// 直列化クラスの「バージョン」を表現するシリアルバージョンUID
private static final long serialVersionUID = 123456789L;
private String str;
private int i;
private SerializedClass sc;
// コンストラクタ
public SerializedData(String str, int i, SerializedClass sc) {
this.str = str;
this.i = i;
this.sc = sc;
}
// ゲッタ(=アクセサ)
public String getStr() {
return this.str;
}
public int getI() {
return this.i;
}
public SerializedClass getSc() {
return this.sc;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SerializedData(" + this.getStr() + ", " + this.getI() + ", " + this.getSc() + ")";
}
}
// 直列化クラスのフィールドクラスも同様にSerializableインタフェースの実装クラスでなければならない
class SerializedClass implements Serializable {
private String str;
private int i;
// コンストラクタ
public SerializedClass(String str, int i) {
this.str = str;
this.i = i;
}
// ゲッタ(=アクセサ)
public String getStr() {
return this.str;
}
public int getI() {
return this.i;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SerializedClass(" + this.getStr() + ", " + this.getI() + ")";
}
}
% xxd serializedData.dat
00000000: aced 0005 7372 000e 5365 7269 616c 697a ....sr..Serializ
00000010: 6564 4461 7461 0000 0000 075b cd15 0200 edData.....[....
00000020: 0349 0001 694c 0002 7363 7400 114c 5365 .I..iL..sct..LSe
00000030: 7269 616c 697a 6564 436c 6173 733b 4c00 rializedClass;L.
00000040: 0373 7472 7400 124c 6a61 7661 2f6c 616e .strt..Ljava/lan
00000050: 672f 5374 7269 6e67 3b78 7000 0000 7b73 g/String;xp...{s
00000060: 7200 0f53 6572 6961 6c69 7a65 6443 6c61 r..SerializedCla
00000070: 7373 6dfd 9432 5981 aba2 0200 0249 0001 ssm..2Y......I..
00000080: 694c 0003 7374 7271 007e 0002 7870 0000 iL..strq.~..xp..
00000090: 01c8 7400 09e3 8182 e381 84e3 8186 7400 ..t...........t.
000000a0: 0341 4243 .ABC
SerializedData(ABC, 123, SerializedClass(あいう, 456))
Microsoft Officeファイルの操作
参考: Apache POI
Microsoft Office形式ファイルは、Apache POIライブラリを通じて操作することができる。
Excelファイルを操作する場合、以下のjarファイルを依存関係ライブラリを含めてクラスパスに追加する必要がある。
| ライブラリ | 内容 | 依存関係ライブラリ |
|---|---|---|
poi |
Coreライブラリ |
・commons-codec・ commons-collections・ commons-math
|
poi-ooxml |
Excel用ライブラリ |
・commons-compress・ SparseBitSet・ curvesapi
|
poi-ooxml-lite |
Excel用ライブラリ |
・xmlbeans
|
サンプルコード
参考1: Apache POIによるExcel操作
参考2: Apache POIの依存関係
参考3: Apache POIでのセル操作
import java.io.*;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.*;
public class Office {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// -- Excelファイルの書き出し --
// 「Excelブック」を表すWorkbookオブジェクトの生成
// -> XSSFWorkbookはWorkbookインタフェースの実装クラスであり、
// Excel2007以降のExcelフォーマット形式に対応
Workbook book = new XSSFWorkbook();
// 「Excelシート」を表すSheetオブジェクトの生成
Sheet sheet = book.createSheet("test");
// 「行」を表すRowオブジェクトの生成
Row row1 = sheet.createRow(0);
// 「セル」を表すCellオブジェクトの生成
Cell cellA1 = row1.createCell(0);
Cell cellB1 = row1.createCell(1);
Cell cellC1 = row1.createCell(2);
// セルに「値」をセット
cellA1.setCellValue(123);
cellB1.setCellValue(456);
// セルに「関数」をセット
// -> 冒頭の「=(イコール)」は不要
cellC1.setCellFormula("A1+B1");
// 「フォントスタイル」を表すFontオブジェクトの生成
// -> スタイル毎にオブジェクトを作成する必要がある
Font f = book.createFont();
// 「太字」にする
f.setBold(true);
// 「文字色」の指定
// -> 「色」は列挙型IndexedColorsの定数を利用
f.setColor(IndexedColors.GREEN.getIndex());
// 「セルスタイル」を表すCellStyleオブジェクトの生成
// -> スタイル毎にオブジェクトを作成する必要がある
CellStyle cs_B1 = book.createCellStyle();
CellStyle cs_C1 = book.createCellStyle();
// 「枠線」の指定
// -> 枠線は上下左右個別に設定する必要がある
// <- 「枠線の種類」は列挙型BorderStyleの定数を利用
cs_C1.setBorderTop(BorderStyle.MEDIUM);
cs_C1.setBorderBottom(BorderStyle.HAIR);
cs_C1.setBorderLeft(BorderStyle.DASHED);
cs_C1.setBorderRight(BorderStyle.DOTTED);
// 「背景色」の指定
cs_C1.setFillForegroundColor(IndexedColors.YELLOW.getIndex());
// 「塗りつぶしパターン」の指定
// -> 「パターン」は列挙型FillPatternTypeの定数を利用
cs_C1.setFillPattern(FillPatternType.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
// セルスタイルに「フォントスタイル」をセット
cs_B1.setFont(f);
// セルに「セルスタイル」をセット
cellB1.setCellStyle(cs_B1);
cellC1.setCellStyle(cs_C1);
// Excelファイルへの出力
try (
// 「バイナリファイル」への書き込み・出力を行うFileOutputStreamオブジェクトの生成
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("src/test.xlsx")
) {
book.write(os);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Output to Excel File has failed.");
}
finally {
try {
// Workbookオブジェクトの解放処理
book.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Closing Workbook has failed.");
}
}
// -- Excelファイルの読み込み --
try (
// 「バイナリファイル」を読み込むFileInputStreamオブジェクトの生成
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src/test.xlsx");
// 「Excelブック」の情報を格納するWorkbookオブジェクトの生成
// -> Workbookの「ファクトリ」であるWorkbookFactoryを利用
Workbook bookR = WorkbookFactory.create(fis);
) {
// 「Excelシート」を指定して読み込む
Sheet sheetR = bookR.getSheet("test");
// 「行」を指定して読み込む
Row row1R = sheetR.getRow(0);
// 「セル」を指定して読み込む
Cell B1 = row1R.getCell(1);
Cell C1 = row1R.getCell(2);
// FormulaEvaluatorオブジェクトを生成するCreationHelperオブジェクトの取得
CreationHelper helper = bookR.getCreationHelper();
// セルに記述された「関数を実行」するFormulaEvaluatorオブジェクトの生成
FormulaEvaluator evaluator = helper.createFormulaEvaluator();
// セルに記述された関数の実行・実行結果を格納するCellValueオブジェクトの取得
CellValue resBefore = evaluator.evaluate(C1);
// 実行結果の型に応じて値を取得
// -> 型に応じた取得メソッドを使用しないとnullが返却される
String resAfter = "";
switch (resBefore.getCellType()) {
case STRING: resAfter = resBefore.getStringValue(); break;
case NUMERIC: resAfter = Double.toString(resBefore.getNumberValue()); break;
case BOOLEAN: resAfter = Boolean.toString(resBefore.getBooleanValue()); break;
default: break;
}
// 「取得した値」の出力
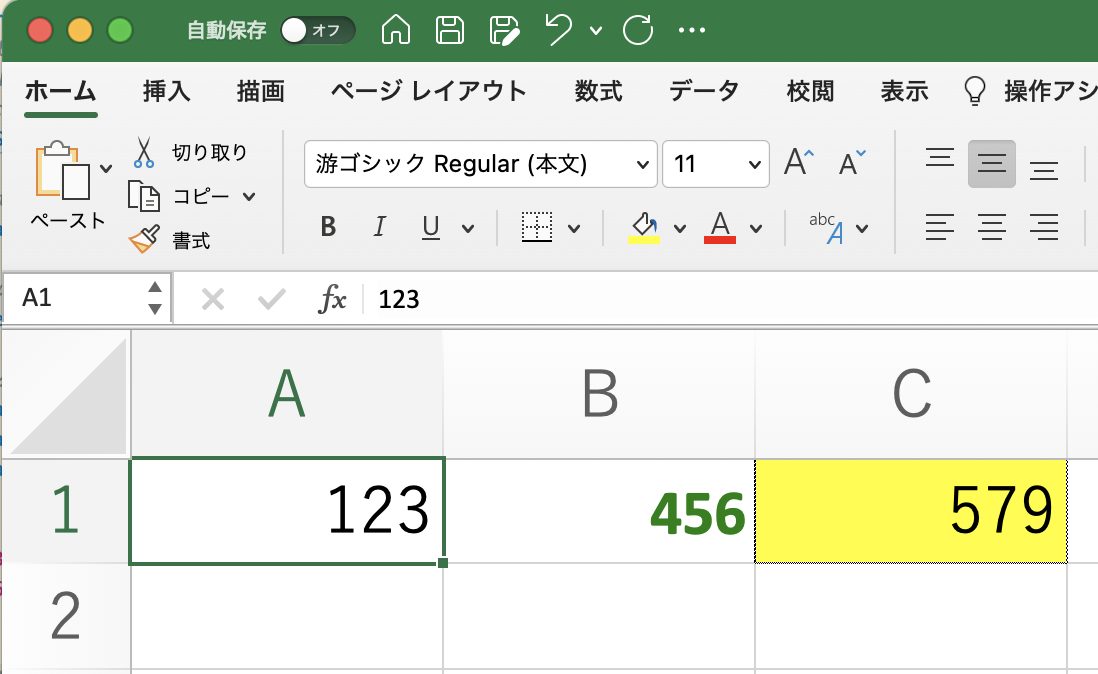
System.out.println(B1);
System.out.println("Before: " + C1);
System.out.println("After: " + resAfter);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Some exceptions has occurred in input from Excel File.");
}
}
}
456.0
Before: A1+B1
After: 579.0
アーカイブ形式ファイルの操作
複数のファイルを圧縮したアーカイブファイルは、java.util.zipパッケージを利用して操作することができる。
サンプルコード
import java.util.*;
import java.util.zip.*;
public class Archive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// 「圧縮ファイル」を読み込むZipFileオブジェクトの生成
ZipFile file = new ZipFile("src/archivedData.zip");
) {
// 圧縮ファイルの「中身(=ZipEntry)」を格納するArrayListオブジェクトの取得
ArrayList<? extends ZipEntry> list = Collections.list(file.entries());
// 要素毎にファイル情報を取得
for (ZipEntry e : list) {
// ファイル名
String name = e.getName();
// 圧縮後サイズ
long compressedSize = e.getCompressedSize();
// 圧縮前サイズ
long size = e.getSize();
System.out.println("file name: " + name);
System.out.println("compressed size: " + compressedSize + "[Byte]");
System.out.println("size: " + size + "[Byte]");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Opening archived file has failed.");
}
}
}
音声ファイル(サンプリング形式/シンセサイザ形式)の操作
音声ファイルは、Java標準APIであるJava Sound APIを利用して再生することができる。
シンセサイザ形式ファイル(=MIDIファイル)では、音声データはSequenceクラス、プレーヤーはSequencerクラスが管理し、
サンプリング形式ファイルでは、音声データは管理せず、プレーヤーはClipクラスが担っている。
サンプルコード
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.sound.midi.*;
import javax.sound.sampled.*;
public class SoundPlay {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 「MIDIファイルの停止」「wavファイルの再生・停止」で利用するScannerオブジェクト
Scanner stdIn = new Scanner(System.in);
// -- 「MIDIファイル」の再生 --
try (
// 「MIDIファイル」を再生するSequencerオブジェクト(=シーケンサ; シンセサイザ)の取得
// -> MIDIファイルへのアクセサ(=システムリソース)を生成するMidiSystemクラスの静的メソッドを利用
Sequencer sequencer = MidiSystem.getSequencer();
) {
// シーケンサの再生準備
sequencer.open();
// 「シンセサイザ形式の音声データ」を保持するSequenceオブジェクトの生成
Sequence seq = MidiSystem.getSequence(new File("src/paleBlue.MID"));
// シーケンサに音声情報をセット
sequencer.setSequence(seq);
// 「ループ」の指定
// -> ループしない場合は引数に"-1"を指定
sequencer.setLoopCount(-1);
// MIDIファイルの再生
sequencer.start();
// MIDIファイルの停止を促す
System.out.println("Push Enter to stop MIDI Sound.");
stdIn.nextLine();
// MIDIファイルの停止
sequencer.stop();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Playing MIDI file has failed.");
// MIDIファイルの再生・停止中に例外が送出された場合はScannerをここでクローズ
stdIn.close();
}
// -- 「サンプリング形式ファイル」の再生 --
try (
// 「サンプリング形式ファイル」の読み込みを行うAudioInputStreamフィルタの生成
// -> サンプリング形式ファイルへのアクセサ(=システムリソース)を生成するAudioSystemクラスの静的メソッドを利用
// <= "mp3"ファイルは標準ライブラリでは再生不可
AudioInputStream ais = AudioSystem.getAudioInputStream(new File("src/bark.wav"));
) {
// 「サンプリング形式の音声データ」を再生するClipオブジェクト(=プレーヤー)
Clip clip = AudioSystem.getClip();
// プレーヤーの再生準備
clip.open(ais);
String str = "";
do {
// 「音声ファイル」の再生を促す
System.out.println("Push Enter to play sound.");
stdIn.nextLine();
// 「音声ファイル」の再生
clip.start();
// 「シーク」を最初に戻す
clip.setFramePosition(0);
// 「音声ファイル」の再生を促す
System.out.println("Push \"1\" to stop sound.");
str = stdIn.nextLine();
} while (!(str.equals("1")));
// 「音声ファイル」の停止
clip.stop();
}
catch (UnsupportedAudioFileException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("File format is not adapted.");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Playing sound file has failed.");
}
finally {
// Scannerオブジェクトのクローズ処理
stdIn.close();
}
}
}
Push Enter to stop MIDI Sound.
Push Enter to play sound.
Push "1" to stop sound.
// 「1」が入力されなかったため再度再生処理に戻る(ループ処理)
Push Enter to play sound.
Push "1" to stop sound.
1 // ここで再生が終了
画像ファイルの操作
画像ファイルは、Apache Commons Imagingライブラリや、Java標準APIであるImageIOクラスの静的メソッドを利用して操作することができる。
ただし、半透明情報をもつPNGともたないJPEG間の変換時は、半透明情報の除去処理を記述する必要がある。
サンプルコード
import java.awt.image.*;
import java.io.*;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
public class Picture {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// 「バイナリファイルの出力先情報」を保持するFileOutputStreamオブジェクトの生成
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src/dog.png")
) {
// 「画像データ」を保持するBufferedImageオブジェクト
// -> ImageIOの静的メソッドを利用して「画像ファイル」を読み込む
BufferedImage image = ImageIO.read(new File("src/dog.jpg"));
// 画像データの「サイズ情報」の取得
int h = image.getHeight();
int w = image.getWidth();
System.out.println("image size: " + w + "x" + h);
// 「画像データ」の変換
// -> ImageIOの静的メソッドを利用して「画像データ」を出力
// <- 「変換元画像データ」「画像フォーマット形式」「出力先情報」を引数にとる
ImageIO.write(image, "png", fos);
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Some exception has occurred.");
}
}
}
image size: 1280x853
用語集
| 用語 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| データフォーマット(data format) | データの形式や順序(=データ構造)を定めたルール。 |
| デリミタ(delimiter) |
要素を区切る記号または文字。 |
| 直列化(serialization) |
インスタンス ⇄ バイト列 の変換。 |
| イテレータ(iterator) |
コレクション要素へのアクセス用インタフェース。 |