OpenGL Insightsの15章ボケレンダリングによる被写界深度(Chapter 15. Depth of Field with Bokeh Rendering by Charles de Rousiers and Matt Pettineo)に出てくる手法であるが、説明が少ないわりにかなり特殊に見える描画方法だったので、概要を調べて、一般的な利用に落とし込めるようにまとめることとした。機能自体は2011年にはリリースされているので全く目新しくはない。にもかかわらず日本語情報は稀なので、習作の延長のような記事ではあるが参考になれば幸いだ。
Atomic Counter
OpenGL 4.2からの機能で、GPU上で一意な数えあげができる。"Atomic"とは不可分操作という意味合いで、並列処理の中でも、一意なデータ操作を実現すること。公式ドキュメントの説明はこちら。
具体的な例をあげると、画像の中に特定の輝度以上のピクセルがいくつあるかを、ピクセル毎の並列処理で走査確認し総数を数えあげることができる。ピクセル毎の計算単位(Compute ShaderもしくはFragment Shader)の中で、並列にカウントアップしてやれば同期される。実体は、GPU上のバッファ(1つの符号なし整数、いわゆるGLuint)であり、これを不可分操作することで実現している。Atomic Counterの実体もGPU上で結果が計算・格納されるゆえ、Buffer Object の1つとなる。
利用の仕方の概要は以下。その他のBuffer Object同様にidを用いて初期化し、それにGL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFERのenum値とともに、GLuint一つ分のデータとしてバインディングする。Compute ShaderでもVertex-Fragment shaderパイプラインの任意のステージでも同じように数え上げをすることができる。
// Atomic Counterの生成
glGenBuffers(1, &counterId);
glBindBuffer(GL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFER, counterId);
glBufferData(GL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFER, sizeof(GLuint), nullptr, GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFER, 0); // コンテキストからアンバインド
...
// Atomic Counterの利用。Shader上で数え上げるためにbindする。
// indexを0に指定することで、layout(binding=0)でアクセスできる
glBindBufferBase(GL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFER, 0, counterId);
shader.begin();
shader.dispatchCompute(w, h, 1);
shader.end();
// 任意でアンバインド
glBindBufferBase(GL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFER, 0, 0);
例としてCompute Shader内でアトミックな数え上げを実行する。glBindBufferBaseでバインドされているバッファは任意のステージでロードできる。
# version 440
layout(binding = 0, offset = 0) uniform atomic_uint counter;
layout(rgba32f, binding = 0) uniform writeonly image2D brightPixBuffer;
...
layout(local_size_x = 1, local_size_y = 1, local_size_z = 1) in;
void main() {
...
float difLum = dot(vec3(1.), color);
if (difLum > lumThres) {
// インクリメントを実行。返り値に現在の値が戻る。
int current = int(atomicCounterIncrement(counter));
// 現在のカウンタの値をキーとしてピクセルデータを更新したりできる。
imageStore(brightPixBuffer, ivec2(current, 0), vec4(uv, depth, farCoc));
}
}
数え上げられたデータはこちらの記事にあるように、glMapBufferなどでGPUからCPUに読み出せる。
CPUロードすることもできるが、CPU-GPUの同期待ちが長いため、リアルタイムの毎フレーム処理となると利用が難しいかもしれない。この長いロードを回避するために、GPU内で更新および利用(読み出し)を完結させることができる。
レンダリングのプロセスは通常、CPUでコマンドを呼び出しするためCPU-GPUの同期は待つ必要があるが、この同期をスキップできるレンダリング手順が存在する。それが以下の間接レンダリングだ。
Indirect Rendering - 間接レンダリング
間接レンダリングは、可変長のインスタンシング(Instanced Rendering)のような用途でつかわれるが、描画用のデータ転送をCPUから都度おこなう通常のインスタンシングよりも効率が良い代替案となる。なぜなら、描画のためのデータをほぼすべてGPU上でバッファするからだ。
頂点情報などはVertex Buffer Objectとして送信するなど、通常のエレメント描画やインスタンシング描画を踏襲する前提ではあるが、さらに必要となる単純な整数型などの些細なデータ、例えばインスタンシングするVBOの頂点数や、インスタンシングする回数などがこのバッファで扱われる。このコマンドバッファ的なものは Buffer Object の中のGL_DRAW_INDIRECT_BUFFERとして定義されている。
頂点数やインスタンシングの個数などを格納したコマンドバッファを利用して、特定の頂点配列の描画を効率化する。コマンドバッファは、静的利用(GL_STATIC_DRAW:一度だけコマンドバッファをGPU転送しあとから変更させない)か、動的利用(GL_DYTNAMIC_DRAW:都度コマンドバッファの値を動的に変えることを許す)を選択できる。静的利用でも、単純なインスタンシングよりも良い代替案である。
// コマンドバッファとなる構造体を自前で定義
struct DrawElementsIndirectCommand {
GLuint count;
GLuint primCount;
GLuint firstIndex;
GLuint baseVertex;
GLuint baseInstance;
};
DrawElementsIndirectCommand cmd;
// Indirect Bufferの生成
glGenBuffers(1, &indirectBufferId);
glBindBuffer(GL_DRAW_INDIRECT_BUFFER, indirectBufferId);
glBufferData(GL_DRAW_INDIRECT_BUFFER, sizeof(DrawElementsIndirectCommand), &cmd, GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_DRAW_INDIRECT_BUFFER, 0);
...
// Indirect Renderingのドローコールの前に必ずメモリバリアを呼んで同期を終わらせることを保証させる。
glMemoryBarrier(GL_COMMAND_BARRIER_BIT);
// 頂点配列(VAO)をバインドして、Indirect Renderingを実行
glBindVertexArray(vaoID);
glBindBuffer(GL_DRAW_INDIRECT_BUFFER, indirectBufferId);
glDrawElementsIndirect(drawMode, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, NULL);
glBindBuffer(GL_DRAW_INDIRECT_BUFFER, 0);
glBindVertexArray(0);
さらに強力な道具だと感じるのは、「GPU上で」コマンドバッファを書き換えて利用する動的な手法だ。例えば上記のアトミックカウンタをGPU上で計算し、そのデータをプロキシを通して(ここではバッファ間のデータコピーぐらいの意味)間接レンダリングのデータとして利用する。これは、CPU-GPU同期を減らせるためレンダリングの効率の改善が見込める手法となる。
用途としては、Shaderの高度な並列計算によって得られた特定のバッファデータのみをもちいてインスタンシグしたりできる。例えばリアルタイムのカメラから検出した特定のピクセルデータのみを用いてインスタンシング(例えばボクセルパーティクルなど)するということが実現できる。図にすると以下のような感じ。
Atomic Counter + Indirect Rendering のサンプルプログラム
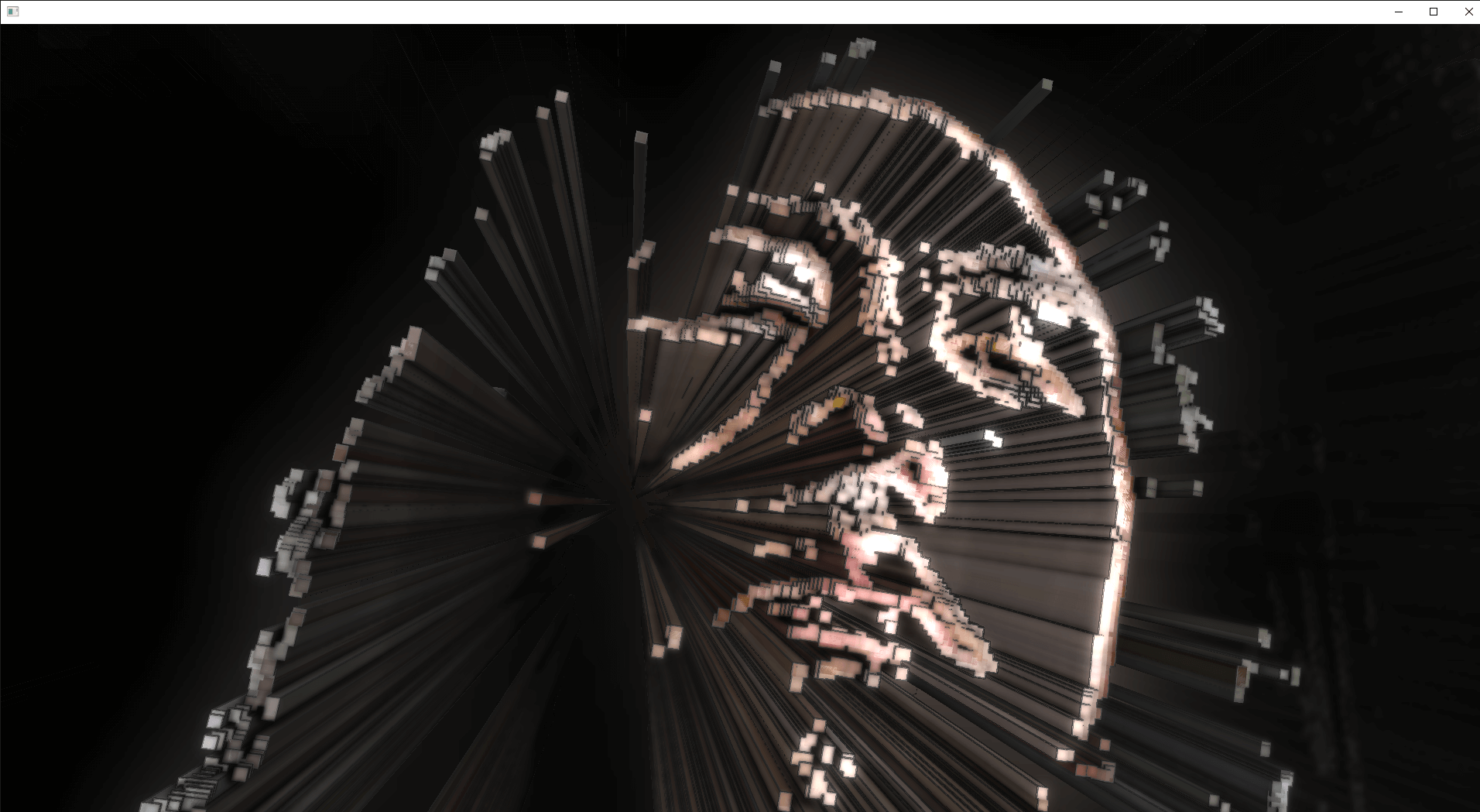
上記の「リアルタイムのカメラから検出した特定のピクセルデータのみを用いてインスタンシング(例えばボクセルパーティクルなど)する」ことをやってみる。ここでは、このAtomic Counter + Indirect Renderingの手法で、RealSenseからボクセルのインスタンシングを間接レンダリングを用いて行う。
デプスセンサーの入力にコンピュートシェーダでフィルタしてボクセルインスタンシング。可変長のインスタンシングでも効率よく描画できる方法やってみた(Indirect Rendering) #openFrameworks pic.twitter.com/4ON0SfAFhp
— Ayumu Nagamatsu (@ayumu_naga) September 12, 2019
輝度でフィルタした場合
ソベルフィルタで境界抽出したとき
前提条件 / 外部依存
- openFrameworks 0.10.1
- Windows 10
- Realsense & librealsense
- addons
コード
Github repoはこちら | FilterInstancingExample
C++
# include "ofMain.h"
# include "ofApp.h"
int main( ){
ofGLFWWindowSettings s;
s.setGLVersion(4, 5);
s.setSize(1920, 1080);
ofCreateWindow(s);
ofRunApp(new ofApp());
}
# pragma once
# include "ofMain.h"
# include "ofxRealSenseUtil.h"
# include "ofxDeferredHelper.h"
class ofApp : public ofBaseApp{
public:
ofApp() : ofBaseApp(), acb(36), isDebug(false) {}
void setup();
void update();
void draw();
void exit();
void keyPressed(int key);
private:
ofxPanel paramPanel;
ofParameter<float> depthThres, lumThres, voxelSize;
ofxRealSenseUtil::Interface rs;
ofxPanel rsPanel;
ofxDeferred::AtomicCounterBuffer acb;
ofShader detectShader;
ofShader instancingShader;
ofTexture posTex, colorTex;
ofVboMesh box;
ofEasyCam cam;
ofxDeferred::Helper helper;
bool isDebug;
bool hasTex;
};
# include "ofApp.h"
void ofApp::setup(){
detectShader.loadCompute("shader/detect.glsl");
instancingShader.load("shader/instancing");
paramPanel.setup();
paramPanel.add(lumThres.set("lumThres", 0.5, 0., 1.));
paramPanel.add(voxelSize.set("voxelSize", 20., 0., 50.));
box = ofMesh::box(1, 1, 300, 1, 1, 1);
rs.enableFlags(
ofxRealSenseUtil::USE_DEPTH_MESH_POINTCLOUD |
ofxRealSenseUtil::USE_COLOR_TEXTURE
);
rsPanel.setup(rs.getParameters());
const glm::vec2 s(ofxRealSenseUtil::rsColorRes);
posTex.allocate(s.x, s.y, GL_RGBA32F);
posTex.setTextureMinMagFilter(GL_NEAREST, GL_NEAREST);
colorTex.allocate(s.x, s.y, GL_RGBA8);
colorTex.setTextureMinMagFilter(GL_NEAREST, GL_NEAREST);
acb.setMaxCount(s.x * s.y);
helper.init();
cam.setFarClip(1500);
}
void ofApp::update(){
rs.update();
hasTex = rs.getColorImage().isAllocated() && rs.getPointCloud().hasVertices();
const auto pointCloud = rs.getPointCloud().getVbo();
const auto& vertexBuffer = pointCloud.getVertexBuffer();
const auto& texCoordBuffer = pointCloud.getTexCoordBuffer();
if (hasTex) {
/*float t = ofGetElapsedTimef() * 0.6;
cam.setPosition(300. * cos(t), 0., 600. * sin(t));
cam.lookAt(glm::vec3(0));*/
vertexBuffer.bind(GL_SHADER_STORAGE_BUFFER);
vertexBuffer.bindBase(GL_SHADER_STORAGE_BUFFER, 0);
texCoordBuffer.bind(GL_SHADER_STORAGE_BUFFER);
texCoordBuffer.bindBase(GL_SHADER_STORAGE_BUFFER, 1);
posTex.bindAsImage(0, GL_WRITE_ONLY);
colorTex.bindAsImage(1, GL_WRITE_ONLY);
acb.bind();
detectShader.begin();
detectShader.setUniform1f("lumThres", lumThres.get());
detectShader.setUniformTexture("colorImage", rs.getColorImage().getTexture(), 0);
detectShader.dispatchCompute(pointCloud.getVertexBuffer().size() / 3, 1, 1);
detectShader.end();
acb.unbind();
colorTex.unbind();
posTex.unbind();
texCoordBuffer.unbindBase(GL_SHADER_STORAGE_BUFFER, 1);
texCoordBuffer.unbind(GL_SHADER_STORAGE_BUFFER);
vertexBuffer.unbindBase(GL_SHADER_STORAGE_BUFFER, 0);
vertexBuffer.unbind(GL_SHADER_STORAGE_BUFFER);
helper.render([&](float lds, bool isShadow) {
ofTranslate(0, 0, 600.);
instancingShader.begin();
instancingShader.setUniform1f("lds", lds);
instancingShader.setUniform1i("isShadow", isShadow ? 1 : 0);
instancingShader.setUniform1f("voxelSize", voxelSize);
instancingShader.setUniform1f("time", ofGetElapsedTimef());
instancingShader.setUniformTexture("posTex", posTex, 1);
instancingShader.setUniformTexture("colorTex", colorTex, 2);
acb.drawIndirect(box.getVbo(), GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP);
instancingShader.end();
}, cam);
}
}
void ofApp::draw(){
if (hasTex) helper.getRenderedImage().draw(0, 0, ofGetWidth(), ofGetHeight());
if (isDebug) {
//helper.debugDraw();
helper.drawGui();
rsPanel.draw();
paramPanel.draw();
float w = ofGetViewportWidth() * 0.25;
float h = ofGetViewportHeight() * 0.25;
float y = ofGetHeight() - h;
float x = 0;
//posTex.draw(x, y, w, h); x += w;
//colorTex.draw(x, y, w, h); x += w;
//rs.getColorImage().draw(x + w * 3., y, w, h); // x += w;
//rs.getDepthImage().draw(x, y, w, h);
}
}
void ofApp::exit() {
rs.stopThread();
}
void ofApp::keyPressed(int key){
if (key == 's') {
isDebug = !isDebug;
}
}
# pragma once
# include "ofVboMesh.h"
# include "ofBufferObject.h"
# include "ofGLProgrammableRenderer.h"
namespace ofxDeferred {
class AtomicCounterBuffer {
public:
AtomicCounterBuffer(int indirectVertCount) : maxCount(500) {
// Create atomic counter buffer
// and define its initial storage capacity
glGenBuffers(1, &counterId);
glBindBuffer(GL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFER, counterId);
glBufferData(GL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFER, sizeof(GLuint), nullptr, GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFER, 0);
// Indirect command
DrawElementsIndirectCommand cmd{ indirectVertCount, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
// Create buffer storage for indirect buffer
// Setup the indirect buffer
glGenBuffers(1, &indirectBufferId);
glBindBuffer(GL_DRAW_INDIRECT_BUFFER, indirectBufferId);
glBufferData(GL_DRAW_INDIRECT_BUFFER, sizeof(DrawElementsIndirectCommand), &cmd, GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_DRAW_INDIRECT_BUFFER, 0);
// Create the texture proxy for the indirect buffer
glGenTextures(1, &indirectBufferTex);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_BUFFER, indirectBufferTex);
glTexBuffer(GL_TEXTURE_BUFFER, GL_R32UI, indirectBufferId);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_BUFFER, 0);
synchIndirect.loadCompute(shaderPath + "bokeh/bokehSync.glsl");
}
~AtomicCounterBuffer() {
glDeleteBuffers(1, &counterId);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &indirectBufferId);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &indirectBufferTex);
}
void bind() {
glBindBufferBase(GL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFER, 0, counterId);
// Clear atomic counter buffer
glm::uint32* bokehCounterValue = (glm::uint32*)glMapBufferRange(
GL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFER, 0, sizeof(glm::uint32),
GL_MAP_WRITE_BIT | GL_MAP_INVALIDATE_BUFFER_BIT | GL_MAP_UNSYNCHRONIZED_BIT
);
*bokehCounterValue = 0;
glUnmapBuffer(GL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFER);
}
void setMaxCount(int maxCount) {
this->maxCount = maxCount;
}
void unbind() {
// Synch the atomic counter with the indirect texture for indirect instanced-rendering
synchIndirect.begin();
synchIndirect.setUniform1i("maxCount", maxCount);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0 + synchIndirect.getUniformLocation("indirectBufferTex"));
glBindImageTexture(synchIndirect.getUniformLocation("indirectBufferTex"), indirectBufferTex, 0, false, 0, GL_WRITE_ONLY, GL_R32UI);
synchIndirect.dispatchCompute(1, 1, 1);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
synchIndirect.end();
// unbind atomic counter buffer
glBindBufferBase(GL_ATOMIC_COUNTER_BUFFER, 0, 0);
}
void drawIndirect(ofVbo& vbo, GLenum drawMode) {
glMemoryBarrier(GL_ALL_BARRIER_BITS);
vbo.bind();
glBindBuffer(GL_DRAW_INDIRECT_BUFFER, indirectBufferId);
glDrawElementsIndirect(drawMode, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, NULL);
glBindBuffer(GL_DRAW_INDIRECT_BUFFER, 0);
vbo.unbind();
}
private:
struct DrawElementsIndirectCommand {
GLuint count;
GLuint primCount;
GLuint firstIndex;
GLuint baseVertex;
GLuint baseInstance;
};
// Atomic Counter Buffer ID
GLuint counterId;
// Texture buffer ID for indirect rendering
GLuint indirectBufferId;
GLuint indirectBufferTex;
ofShader synchIndirect;
int maxCount;
};
}
GLSL
# version 440
layout(binding = 0, offset = 0) uniform atomic_uint counter;
layout(rgba32f, binding = 0) uniform writeonly image2D posTex;
layout(rgba8, binding = 1) uniform writeonly image2D colorTex;
uniform sampler2DRect colorImage;
uniform float lumThres;
layout(std430, binding = 0) buffer vertices{
float position[];
};
layout(std430, binding = 1) buffer texCoords{
float texcoord[];
};
vec3 sobelFilter(in sampler2DRect img, in vec2 uv) {
const vec2 offset[9] = vec2[](
vec2(-1.0, -1.0), vec2( 0.0, -1.0), vec2( 1.0, -1.0),
vec2(-1.0, 0.0), vec2( 0.0, 0.0), vec2( 1.0, 0.0),
vec2(-1.0, 1.0), vec2( 0.0, 1.0), vec2( 1.0, 1.0)
);
const float hCoef[9] = float[](
1.0, 0.0, -1.0,
2.0, 0.0, -2.0,
1.0, 0.0, -1.0
);
const float vCoef[9] = float[](
1.0, 2.0, 1.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
-1.0, -2.0, -1.0
);
vec3 horizonColor = vec3(0.0);
vec3 verticalColor = vec3(0.0);
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
vec3 c = texture(img, uv + offset[i]).rgb;
horizonColor += c * hCoef[i];
verticalColor += c * vCoef[i];
}
return vec3(sqrt(horizonColor * horizonColor + verticalColor * verticalColor));
}
layout(local_size_x = 1, local_size_y = 1, local_size_z = 1) in;
void main() {
vec2 size = textureSize(colorImage);
int index = int(gl_GlobalInvocationID.x);
vec3 pos = vec3(position[index * 3], position[index * 3 + 1], position[index * 3 + 2]);
if (all(equal(pos, vec3(0)))) return;
// Let's filter depth buffer
vec2 uv = vec2(texcoord[index * 2], texcoord[index * 2 + 1]) * size;
// Apply Sobel filter
vec3 color = sobelFilter(colorImage, uv);
//vec3 color = texture(colorImage, uv).rgb;
float depth = - pos.z;
float lum = dot(vec3(1.), color) / 3.;
float depthLimit = 2.0;
if (lum > lumThres && depth < depthLimit) {
// Atomic Operation!
int current = int(atomicCounterIncrement(counter));
int x = int(mod(float(current), size.x));
int y = int(floor(current / size.x));
imageStore(posTex, ivec2(x, y), vec4(pos, depth / depthLimit));
imageStore(colorTex, ivec2(x, y), vec4(texture(colorImage, uv).rgb, 1.0));
}
}
# version 400
uniform mat4 modelViewMatrix; // oF Default
uniform mat4 modelViewProjectionMatrix; // oF Default
in vec4 position; // oF Default
in vec2 texcoord; // oF Default
uniform sampler2DRect posTex;
uniform sampler2DRect colorTex;
uniform float voxelSize;
uniform float lds;
uniform float time;
out vec3 vColor;
out vec4 vPos;
out float vDepth;
void main() {
// Instanced rendering
vec2 size = textureSize(colorTex);
ivec2 uv = ivec2(
mod(float(gl_InstanceID), size.x),
floor(float(gl_InstanceID) / size.x)
);
vec4 s = texelFetch(posTex, uv);
vec3 p = s.xyz * 1000.;
//float factor = ((clamp(sin(-time * 4. + p.y * 0.03), -1.0, -0.8) + 0.8) * 2.0 + 1.0);
float factor = 1.;
p += position.xyz * voxelSize * s.a * factor;
p.z -= factor * 10.;
vec3 color = pow(texelFetch(colorTex, uv).rgb, vec3(0.5));
vPos = modelViewMatrix * vec4(p, 1.);
vDepth = - vPos.z * lds;
vColor = mix(mix(color, vec3(0), s.a), vec3(0.9, 0.9, 1.2), 1. - factor);
gl_Position = modelViewProjectionMatrix * vec4(p, 1.);
}
# version 400
in vec3 vColor;
in vec4 vPos;
in float vDepth;
uniform int isShadow;
out vec4 outputColor0;
out vec4 outputColor1;
out vec4 outputColor2;
vec3 calcFlatNormal(vec3 posInViewSpace){
vec3 dx = dFdx(posInViewSpace);
vec3 dy = dFdy(posInViewSpace);
vec3 n = normalize(cross(normalize(dx), normalize(dy)));
return - n;
}
void main(){
if (isShadow == 1) {
outputColor0.r = vDepth;
outputColor0.a = 1.0;
} else {
outputColor0 = vec4(vColor, 1.);
outputColor1 = vPos;
outputColor2 = vec4(calcFlatNormal(vPos.xyz), vDepth);
}
}