こんにちは、Hamee株式会社でSREとして働いています。大嶋です。
普段はNextEngineのクラウド化案件を担当しています。
この記事はHamee Advent Calendar 2020の9日目になります。
また、前職でテックブログ執筆のために準備していた記事を修正し公開しています。
(公開のタイミングを見失っていたためこのタイミングで公開させてください)
そのためやってみた記事と、今後弊社で個人的に取り入れていきたい仕組みの紹介(提案)となります。
それではAWSマルチアカウント運用時の脅威検出の導入の取り組みについて、紹介させて頂きます。
目次
-
概要
- 課題
- 利用AWSサービス説明
- CloudFormationStackSets
- GuardDuty
- 全体イメージ
-
CloudFormationStackSets
- 必要なリソース、用途
- 構築手順
-
GuardDuty
- 必要なリソース、用途
- 構築手順
-
Slack通知
- 必要なリソース、用途
- 構築手順
- AWS Chatbotとの比較
-
まとめ
概要
AWSアカウントを複数所有していて、プロダクト、組織、用途(Dev、Stg、Prod)などで分割され、AWS Organizationsを利用しマルチアカウントを管理しています。
以下の図はre:invent2018での資料(日本語版)ですが、用途ごとにアカウントを分割し管理することをベストプラクティスとしています。
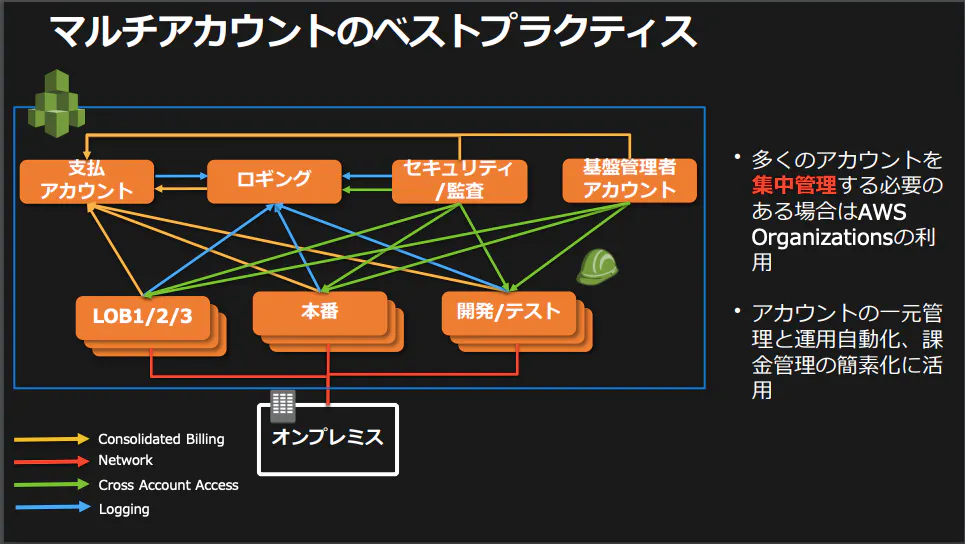
https://d0.awsstatic.com/events/jp/2017/summit/slide/D4T2-2.pdf
今後更にアカウントが増加していく可能性がある中で、いくつか課題がありました。
課題
1. すべてのアカウントの設定が必要な場合はそれぞれのアカウントに都度ログインする必要があり大変
2. アカウント担当者が適切に外部からの脅威を防げているのか不明であり、セキュリティホールが存在or今後発生する可能性がある
使用AWSサービス概要
今回利用したサービスを紹介させていただきます
CloudFormation StackSets
AWS CloudFormationは弊社でもデフォルトで使われるサービスですが、CloudFormation StackSetsは複数のアカウント及びリージョンに対してスタックを作成、更新、削除できるサービスです。
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/ja_jp/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/what-is-cfnstacksets.html
今回は大規模マルチアカウントを運用することになり、一つ一つのアカウントに対してCloudFormationを実施する必要があることが今後現実的に厳しいことからCloudFormation StackSetsを採用することにしました。
GuardDuty
悪意のある操作、不正な動作について脅威検出するサービスです。機械学習、異常検出等を利用し、潜在的な脅威なども識別することができます。AWSの複数のサービスを利用しイベントを分析することが可能です。
https://aws.amazon.com/jp/guardduty/
CloudTrail、CloudWatchなどを利用し独自カスタマイズし脅威検出を導入することもできるのですが、今回は以下2つの理由からAWSのマネージド脅威検出サービスであるGuardDutyを採用しました。
- 脅威検出の初手ということでなるべく早く導入したかった
- アカウント数が多くすべてのユースケースに対応したカスタマイズすることが困難であった
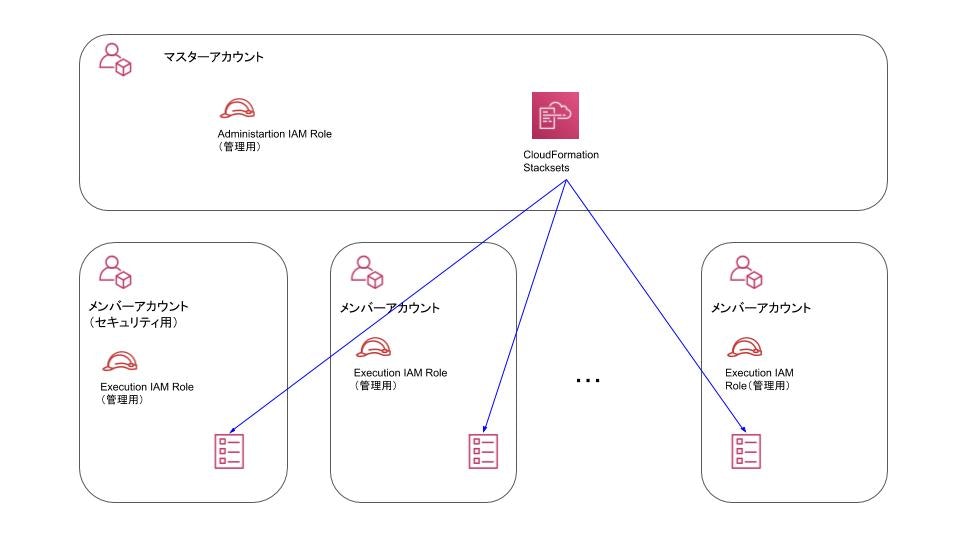
全体イメージ
上記サービスを利用し、今回どのような仕組みを構築したのか紹介させて頂きます。
全体イメージとしては以下のようになります
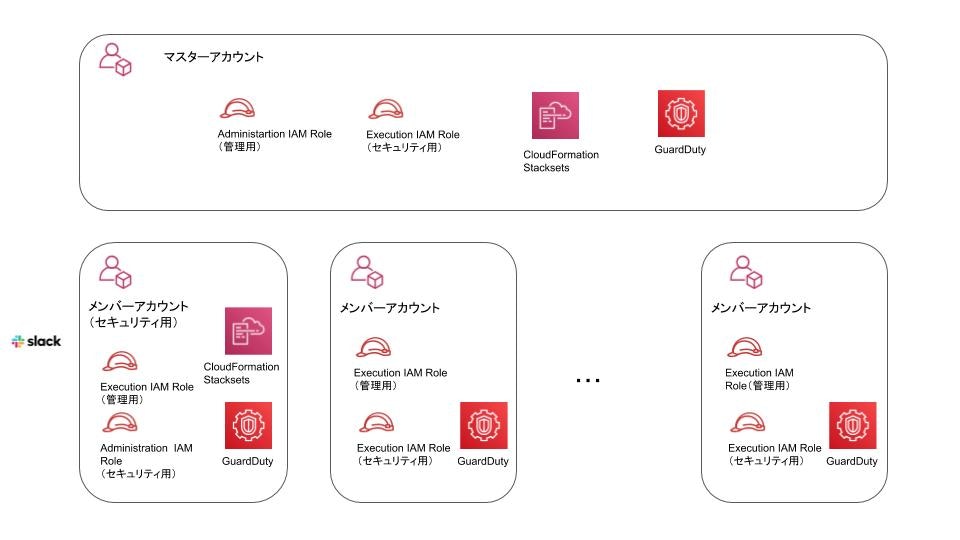
今回はAWSアカウントを3パターンに分けています
- マスターアカウント
AWS Organizationsを管理しているマスターアカウントです。 - メンバーアカウント(セキュリティ用)
マスターアカウントに管理されているメンバーアカウントの中でセキュリティに関することを取り扱うアカウントです。
今回はGuardDutyのログ集約やSlack通知を実行します。 - メンバー(一般)
マスターアカウントに管理されているメンバーアカウントです。
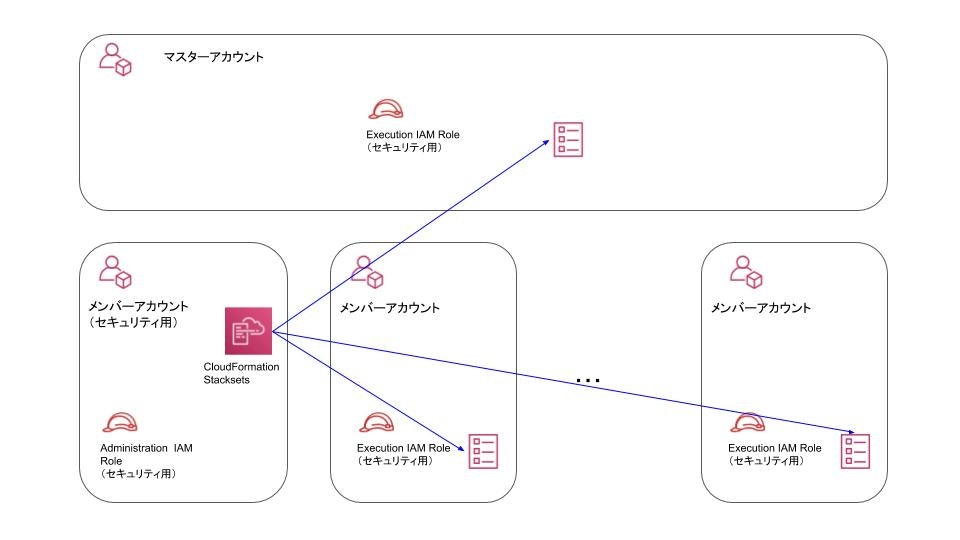
また今回はマスターアカウントからCloudFormation StackSetsを実行できるようにするだけでなく、セキュリティに関するCloudFormation StackSetsはメンバーアカウント(セキュリティ用)から実行できる設計にしました。
そうすることでセキュリティ担当者がマスターアカウントにログインする権限が不要になり、マスターアカウントにIAMユーザーを作成する必要がなくなります。
特にマスターアカウントにはセキュリティ担当者など不要なIAMユーザーを作成することは避けたかったことが理由になります。
次からは構築手順を順を追って紹介させて頂きます。
CloudFormationStackSets
必要なリソース、用途
- Administration IAM Role(管理用)
- マスターアカウントからExecution IAM Role(管理用)を保持しているアカウントに対してCloudFormationStackSetsを実行できるようにするRole
- Execution IAM Role(管理用)
- メンバーアカウント(セキュリティ用、一般)がCloudFormationStackSetsを実行できるようにするRole
- Administration IAM Role(セキュリティ用)
- メンバーアカウント(セキュリティ用)からExecution IAM Role(セキュリティ用)を保持しているアカウントに対してCloudFormationStackSetsを実行できるようにするRole
- Execution IAM Role(セキュリティ用)
- マスターアカウント、メンバーアカウント(一般)がCloudFormationStackSetsを実行できるようにするRole
先程の3パターンのアカウントに配置する各リソースの表はこちらです。
| Administration IAM Role(管理用) | Execution IAM Role(管理用) | Administration IAM Role(セキュリティ用) | Execution IAM Role(セキュリティ用) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| マスターアカウント | ◯ | ◯ | ||
| メンバーアカウント(セキュリティ用) | ◯ | ◯ | ||
| メンバーアカウント(一般) | ◯ | ◯ |
このように配置することで、先程記述したマスターアカウントからもメンバーアカウント(セキュリティ用)どちらからもCloudFormationStackSetsが実行できるようになります。
それぞれリソースのコードは以下です。
Administration IAM Role(管理用)
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: Configure the AWSCloudFormationStackSetAdministrationRole to enable use of AWS CloudFormation StackSets.
Resources:
AdministrationRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
RoleName: AWSCloudFormationStackSetAdministrationRole
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service: cloudformation.amazonaws.com
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Path: /
Policies:
- PolicyName: AssumeRole-AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRole
PolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Resource:
- "arn:aws:iam::*:role/AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRole"
Execution IAM Role(管理用)
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: Configure the AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRole to enable use of your account as a target account in AWS CloudFormation StackSets.
Parameters:
AdministratorAccountId:
Type: String
Description: AWS Account Id of the administrator account (the account in which StackSets will be created).
MaxLength: 12
MinLength: 12
Resources:
ExecutionRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
RoleName: AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRole
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS:
- !Ref AdministratorAccountId
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Path: /
ManagedPolicyArns:
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess
Administration IAM Role(セキュリティ用)
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: Configure the AWSCloudFormationStackSetAdministrationRole to enable use of AWS CloudFormation StackSets.
Parameters:
RoleSuffix:
Type: String
Description: IAM Role Suffix.CamelCase highly reccomend. ex) When RoleSuffix is SecurityAccount, AWSCloudFormationStackSetAdministrationRoleForSecurityAccount
Resources:
AdministrationRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
RoleName: !Sub AWSCloudFormationStackSetAdministrationRoleFor${RoleSuffix}
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service: cloudformation.amazonaws.com
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Path: /
Policies:
- PolicyName: !Sub AssumeRole-AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRoleFor${RoleSuffix}
PolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Resource:
- !Sub "arn:aws:iam::*:role/AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRoleFor${RoleSuffix}"
Execution IAM Role(セキュリティ用)
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: Configure the AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRole to enable use of your account as a target account in AWS CloudFormation StackSets.
Parameters:
AdministratorAccountId:
Type: String
Description: AWS Account Id of the administrator account (the account in which StackSets will be created).
MaxLength: 12
MinLength: 12
RoleSuffix:
Type: String
Description: IAM Role Suffix.CamelCase highly reccomend. ex) When RoleSuffix is SecurityAccount, AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRoleForSecurityAccount
Resources:
ExecutionRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
RoleName: !Sub AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRoleFor${RoleSuffix}
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS:
- !Ref AdministratorAccountId
Action:
- sts:AssumeRole
Path: /
ManagedPolicyArns:
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess
構築手順
マルチアカウントを運用している方に読んで頂いていると思うので、具体的なAWSの操作は省略させていただきます。
手順1
| 概要 | 操作アカウント |
|---|---|
| Administration IAM Role(管理用)を作成 | マスターアカウント |
手順2
| 概要 | 操作アカウント |
|---|---|
| Exection IAM Role(管理用)を作成 | メンバーアカウント(セキュリティ用、一般) |
| (今回のみすべてのアカウントにログインが必要になります) |
以下リンクから作成
※AdministratorAccountIdには親アカウントのアカウントIDを記入
(アカウントが多い場合はURLのXXX部分を修正すると楽になります)
手順3
| 概要 | 操作アカウント |
|---|---|
| Administration IAM Role(セキュリティ用)を作成 | メンバーアカウント(セキュリティ用) |
CloudFormationにて必要なリソースで紹介したAdministration IAM Role(セキュリティ用)のAWSCloudFormationStackSetAdministrationRoleForOtherAccount.ymlを実行し、メンバーアカウント(セキュリティ)にIAM Roleを作成
※RoleSuffixには任意で記入 例)SecurityAccount
手順4
| 概要 | 操作アカウント |
|---|---|
| Exection IAM Role(セキュリティ用)を作成 | マスターアカウント |
CloudFormation StackSetsにて必要なリソースで紹介したExecution IAM Role(セキュリティ用)AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRoleForOtherAccount.ymlを実行し、マスターアカウントとメンバーアカウント(一般)にIAM Roleを作成
※ AdministratorAccountIdには子アカウント(セキュリティ)のアカウントIDを記入
※ RoleSuffixには任意で記入 例)SecurityAccount
※ StackSetsの対象はメンバーアカウント(セキュリティ用)を除くすべてアカウントを指定してください、任意のOUを作成しメンバーアカウント(セキュリティ用)以外を参加させるか、後述するstacksets_accounts.csvを利用
次にGuarDutyを設定していきます
GuardDuty
必要なリソース、用途
- マスターアカウント、メンバーアカウント(一般)のアカウントID一覧
- CloudFormation StackSets実行時に対象を指定するために利用します
123456789012,123456789013,・・・・123456789099
- マスターアカウント、メンバーアカウント(一般)のアカウントID、メールアドレス一覧
- GuardDutyのメンバー招待用のAWSアカウントIDとルートユーザのメールアドレスのcsvファイルです。
※GuardDutyのメンバーアカウントとStackSetsのメンバーアカウントが混同しやすいので注意してください
123456789012,aws+123456789012@example.com
123456789013,aws+123456789013@example.com
・・・・
123456789099,aws+123456789099@example.com
構築手順
こちらも同様に具体的な操作は省略させて頂きます。
手順1
| 概要 | 操作アカウント |
|---|---|
| セキュリティアカウントでGuardDuty有効化 | セキュリティアカウント |
| コンソールにログインしサービスからGuardDutyを選択し、有効化します |
手順2
| 概要 | 操作アカウント |
|---|---|
| GuardDutyメンバー招待 | セキュリティアカウント |
準備しておいたguardduty_member_accounts.csvを利用しメンバーに招待します。 |
手順3
| 概要 | 操作アカウント |
|---|---|
| Stacksetsですべてアカウント、リージョンでGuardDuty有効化 | セキュリティアカウント |
次にSlackに通知を設定していきます。
Slack通知
必要なリソース、用途
- Slack通知用リソース
- CloudWatchEventRuleにて制御を入れることで脅威レベルがミディアム、高いものに絞って通知するようにしました。現時点で脅威レベルが低いを含めてしまうと通知が多く重要な脅威検出ができない可能性があったためです。今後少しずつ脅威レベルが低いものを修正した段階で脅威レベルが低いものも通知しようと思ってます。
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description:
'enable guardduty and set alert'
Parameters:
SlackWebhookUrl:
Type: String
Default: 'https://hooks.slack.com/services/XXXXXXXXX/XXXXXXXX/XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX'
SlackMentionId:
Type: String
SlackMentionName:
Type: String
Resources:
LambdaFunctionNotifyAlertFromGuardDuty:
Type: 'AWS::Lambda::Function'
Properties:
Handler: 'index.lambda_handler'
Runtime: 'python3.7'
Code:
ZipFile: |
import json
import os
import urllib.request
def get_severity_level(severity, sre_mention):
# ref: http://docs.aws.amazon.com/guardduty/latest/ug/guardduty_findings.html#guardduty_findings-severity
if severity == 0.0:
level = {'label': 'Information', 'color': 'good', 'mention': ''}
elif 0.1 <= severity <= 3.9:
level = {'label': 'Low', 'color': 'warning', 'mention': ''}
elif 4.0 <= severity <= 6.9:
level = {'label': 'Medium', 'color': 'warning', 'mention': sre_mention}
elif 7.0 <= severity <= 8.9:
level = {'label': 'High', 'color': 'danger', 'mention': sre_mention}
elif 9.0 <= severity <= 10.0:
level = {'label': 'Critical', 'color': 'danger', 'mention': sre_mention}
else:
level = {'label': 'Unknown', 'color': '#666666', 'mention': ''}
return level
def format_message(data, sre_mention):
account_id = data['detail']['accountId']
region = data['detail']['region']
severity = data['detail']['severity']
title = data['detail']['title']
description = data['detail']['description']
type = data['detail']['type']
severity_level = get_severity_level(severity, sre_mention)
payload = {
'username': 'GuardDuty',
'text': '{} GuardDuty Finding in {}'.format(severity_level['mention'], region),
'icon_emoji': ':aws:',
'attachments': [
{
'fallback': 'Detailed information on GuardDuty Finding.',
'color': severity_level['color'],
'title': title,
'text': description,
'fields': [
{
'title': 'Account ID',
'value': account_id,
'short': True
},
{
'title': 'Severity',
'value': severity_level['label'],
'short': True
},
{
'title': 'Type',
'value': type,
'short': False
}
]
}
]
}
return payload
def notify_slack(url, payload):
data = json.dumps(payload).encode('utf-8')
method = 'POST'
headers = {'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
request = urllib.request.Request(url, data = data, method = method, headers = headers)
with urllib.request.urlopen(request) as response:
return response.read().decode('utf-8')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
slack_webhook_url = os.getenv('SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL')
slack_mention_id = os.getenv('SLACK_MENTION_ID')
slack_mention_name = os.getenv('SLACK_MENTION_NAME')
sre_mention = '<!subteam^%s|%s>' % (slack_mention_id, slack_mention_name)
payload = format_message(event, sre_mention)
response = notify_slack(slack_webhook_url, payload)
return response
MemorySize: 128
Timeout: 60
Environment:
Variables:
SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL: !Ref SlackWebhookUrl
SLACK_MENTION_ID: !Ref SlackMentionId
SLACK_MENTION_NAME: !Ref SlackMentionName
Role: !GetAtt IAMRoleNotifyAlertFromGuardDuty.Arn
IAMRoleNotifyAlertFromGuardDuty:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::Role'
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: '2008-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: 'Allow'
Principal:
Service: 'lambda.amazonaws.com'
Action: 'sts:AssumeRole'
ManagedPolicyArns:
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/CloudWatchAgentServerPolicy
LambdaPermissionNotifyAlertFromGuardDuty:
Type: 'AWS::Lambda::Permission'
Properties:
FunctionName: !Ref LambdaFunctionNotifyAlertFromGuardDuty
Action: 'lambda:InvokeFunction'
Principal: 'events.amazonaws.com'
SourceArn: !GetAtt EventsRuleNotifyAlertFromGuardDutySchedule.Arn
EventsRuleNotifyAlertFromGuardDutySchedule:
Type: 'AWS::Events::Rule'
Properties:
Description: 'Alert to slack when find threats by GuardDuty'
EventPattern: |
{
'source': [
'aws.guardduty'
],
'detail-type': [
'GuardDuty Finding'
],
'detail': {
'severity': [4.0,4.1,4.2,4.3,4.4,4.5,4.6,4.7,4.8,4.9,5.0,5.1,5.2,5.3,5.4,5.5,5.6,5.7,5.8,5.9,6.0,6.1,6.2,6.3,6.4,6.5,6.6,6.7,6.8,6.9,7.0,7.1,7.2,7.3,7.4,7.5,7.6,7.7,7.8,7.9,8.0,8.1,8.2,8.3,8.4,8.5,8.6,8.7,8.8,8.9,9.0,9.1,9.2,9.3,9.4,9.5,9.6,9.7,9.8,9.9,10.0,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
}
}
Targets:
- Arn: !GetAtt LambdaFunctionNotifyAlertFromGuardDuty.Arn
Id: 'Slackbot'
IAMRoleLambdaExecutionNotifyAlertFromGuardDuty:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::Role'
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: 'Allow'
Principal:
Service: 'events.amazonaws.com'
Action: 'sts:AssumeRole'
構築手順
こちらも同様に具体的な操作は省略させて頂きます。
手順1
| 概要 | 操作アカウント |
|---|---|
| SlackにてWebフックURLの取得 | - |
手順2
| 概要 | 操作アカウント |
|---|---|
| Slack通知を設定 | セキュリティアカウント |
CloudFormationにて必要なリソースで紹介したnotify-guardduty-alert.ymlを実行し、Slack通知を設定 |
AWS Chatbotとの比較
今回はLambdaにてSlack通知を実施しましたが、AWS Chatbotも利用を検討しました。
簡単にLambdaを選択した理由をまとめておきます。
| Lambda | AWS Chatbot | |
|---|---|---|
| Slack対応 | 可能 | 可能 |
| GuarDuty対応 | 可能 | 可能 |
| 脅威レベル絞り込み | 可能 | 可能 |
| メンション | 可能 | 不可能 |
| 表示アカウントID | 問題のアカウント | セキュリティ用アカウント(セキュリティアカウントにログインして詳細を確認することで問題のアカウントを特定する) |
| 通知例 |  |
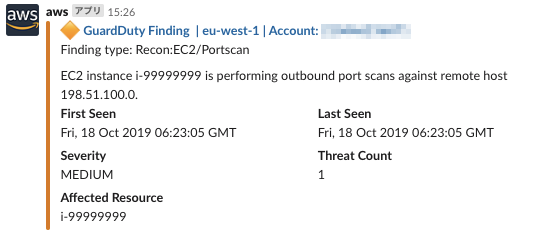 |
以上より、メンション可能であること、Slack通知を見た時にどのアカウントで脅威が検出されたのかわかるの2点から今回はLambdaにてSlack通知することとしました。
まとめ
今回は以上の手順にて、AWSマルチアカウント運用時の脅威検出の導入の取り組みについて紹介させて頂きました。
大量のAWSアカウントを運用している場合に、一つ一つのアカウントにログインして設定することは想像以上に大変のため、今回のCloudFormationStackSetsを利用することにより運用の負荷を下げることが可能です。
またGuardDutyを利用し脅威検出を可能にしたため、アカウント運用チームの知らないところでセキュリティインシデント発生も抑制することが可能になるのではと思っております。
参考
https://dev.classmethod.jp/cloud/aws/create-stacksets-iam-role/
https://dev.classmethod.jp/cloud/aws/set-guardduty-all-region/
https://dev.classmethod.jp/cloud/aws/introducing-cloudformation-stacksets/