VSCode Remote Containersで.NET Core + MySQL + Elasticsearchの開発環境構築 の続きです。
今回はアプリケーションコードの開発についてご紹介しようと思います。
はじめに
まず、今回構成するアプリケーションについてですが、最小限の構成で作るので要件は以下とします。
- データの一覧が表示可能
- データの登録が可能
- データの全文検索が可能
以上の要件を満たすアプリケーションを作りたいので、今回はエンティティを本と定義し、本棚アプリケーションを作成していきたいと思います。
また、今回デフォルトでDIコンテナをサポートしている.NET Coreを採用しているということで、バックエンドの部分に関してクリーンアーキテクチャライクに作ってみました。
環境
- MacBook Pro 10.15.7
- VSCode 1.50.1
- Docker 19.03.13
- Docker For Mac 2.4.0.0
- Docker image version
- mysql:8.0
- sebp/elk:oss-792
- mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/core/sdk:3.1
あと、VSCodeのExtensionであるRemote-Containersを使用しています
ソースコード
大雑把なディレクトリ構成
root/
├ .devcontainer/
└ 省略
├ app/
├ Lib/
├ Books/
├ Entity / BookOverview.cs
├ Repository
├ BookRepository.cs
└ BookSearchRepository.cs
└ UseCase / BookInteractor.cs
└ Infrastructure/
├ DBContext.cs
└ ESContext.cs
├ Web/
├ Controllers/
├ BooksController.cs
└ 省略
├ Filters / DataAccessFilter.cs
├ 省略
└ Startup.cs
Entity
namespace Lib.Books.Entity
{
public class BookOverview
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; }
public string Description { get; }
public string Category { get; }
public BookOverview(int id, string name, string description, string category)
{
this.Id = id;
this.Name = name;
this.Description = description;
this.Category = category;
}
}
}
なにはともあれEntityの定義です。
今回はサンプルアプリケーションの意味合いが強いのでElasticsearchとDBの両方に同じ形式のデータを登録することを念頭にこの構成としました。
こちらはあくまで本の概要を表すオブジェクトとして作成したので、おそらくDBには他にも以下のような本に対する詳細が存在しているのが自然だと思います。
・著者情報
・価格
・表紙画像を表すCDNパス
理想は全文検索で引っ掛けたい内容のみのElasticsearch用オブジェクトと、詳細を詰め込んだDB用オブジェクトを作ることかなと考えてます。
Repository 1.MySQL
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Lib.Books.Entity;
using Lib.Infrastructure;
namespace Lib.Books.Repository
{
public interface IBookRepository
{
void Init();
IEnumerable<BookOverview> GetBookOverviews();
void Register(BookOverview book);
}
public class BookRepository : IBookRepository
{
private readonly DBContext _ctx;
public BookRepository(DBContext ctx)
{
this._ctx = ctx;
}
public void Init()
{
this._ctx.Command.CommandText = $@"
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS books;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS books (
`id` MEDIUMINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
`description` TEXT NOT NULL,
`category` TEXT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);";
this._ctx.Command.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
public IEnumerable<BookOverview> GetBookOverviews()
{
var result = new List<BookOverview>();
this._ctx.Command.CommandText = "SELECT * FROM books";
using (var reader = this._ctx.Command.ExecuteReader())
{
while (reader.Read())
{
var id = int.Parse(reader["id"].ToString());
var name = reader["name"].ToString();
var description = reader["description"].ToString();
var category = reader["category"].ToString();
result.Add(new BookOverview(id, name, description, category));
}
}
return result;
}
public void Register(BookOverview book)
{
this._ctx.Command.CommandText = $@"
INSERT INTO books
(
`name`,
`description`,
`category`
)
VALUES
(
@name,
@description,
@category
)";
this._ctx.Command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@name", book.Name);
this._ctx.Command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@description", book.Description);
this._ctx.Command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@category", book.Category);
this._ctx.Command.ExecuteNonQuery();
this._ctx.Command.Parameters.Clear();
this._ctx.Command.CommandText = "SELECT last_insert_id();";
book.Id = int.Parse(this._ctx.Command.ExecuteScalar().ToString());
}
}
}
次にMySQLに関するRepositoryのクラスです。
こちらはDBアクセスを想定して作成されたRepositoryで、主に永続化されたデータへの操作に対する責務を担っています。
UseCaseの部分でも紹介しますが、IBookRepositoryを定義し参照をそこに限定することでDIP(依存関係逆転の法則)に従います。
また、他の特徴としてはコネクションのオープン・クローズをRepositoryの責務としていません。そこについては以下に記事を書いたので疑問を感じた方はご覧いただければと思います。
【ASP.NET】マルチテナントサービスにおけるデータベースアクセスのDI
Repository 2.Elasticsearch
using System.Linq;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Lib.Books.Entity;
using Lib.Infrastructure;
namespace Lib.Books.Repository
{
public interface IBookSearchRepository
{
void Init();
IEnumerable<BookOverview> Search(string word);
void Register(BookOverview book);
}
public class BookSearchRepository : IBookSearchRepository
{
private readonly ESContext _ctx;
public BookSearchRepository(ESContext ctx)
{
this._ctx = ctx;
}
public void Init()
{
var name = "books";
if (this._ctx.Client.Indices.Exists(name).Exists)
{
this._ctx.Client.Indices.Delete(name);
}
this._ctx.Client.Indices.Create("books", index => index.Map<BookOverview>(m => m.AutoMap()));
}
public IEnumerable<BookOverview> Search(string word)
{
var res = this._ctx.Client.Search<BookOverview>((s => s
.Query(q => q
.Bool(b => b
.Should(
s => s.Match(m => m
.Field(f => f.Name)
.Query(word)
),
s => s.Match(m => m
.Field(f => f.Description)
.Query(word)
),
s => s.Match(m => m
.Field(f => f.Category)
.Query(word)
)
)
.MinimumShouldMatch(1)
)
)
));
return res.Hits.Select(_ => _.Source);
}
public void Register(BookOverview book)
{
this._ctx.Client.IndexDocument(book);
}
}
}
次にElasticsearchに関するRepositoryのクラスです。
こちらは全文検索データに対する操作の責務を担います。
Searchメソッドについてですが、今回は検索語が名前、説明、分類のいずれかにヒットした場合はその検索結果全てを返却するような実装になっています。
また、こちらもIBookSearchRepositoryを定義し参照をそこに限定する構成にしているので、後で「やっぱCloudsearch使いたいなぁ」というときなどにBookSearchRepositoryの内容のみ変更すれば対応できるわけです。
UseCase
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Lib.Books.Entity;
using Lib.Books.Repository;
namespace Lib.Books.UseCase
{
public interface IBookInteractor
{
IEnumerable<BookOverview> Init();
IEnumerable<BookOverview> GetBookOverviews();
IEnumerable<BookOverview> Search(string word);
IEnumerable<BookOverview> Add(string name, string description, string category);
}
public class BookInteractor : IBookInteractor
{
private readonly IBookRepository _repo;
private readonly IBookSearchRepository _searchRepository;
public BookInteractor(IBookRepository repo, IBookSearchRepository search)
{
this._repo = repo;
this._searchRepository = search;
}
public IEnumerable<BookOverview> Init()
{
this._repo.Init();
this._searchRepository.Init();
var initialData = new List<BookOverview>(){
new BookOverview(1, "book1", "test book", "category1"),
new BookOverview(2, "book2", "test book2", "分類2"),
new BookOverview(3, "本3", "テスト用の本", "category1")
};
initialData.ForEach(b =>
{
this._repo.Register(b);
this._searchRepository.Register(b);
});
return initialData;
}
public IEnumerable<BookOverview> GetBookOverviews()
{
return this._repo.GetBookOverviews();
}
public IEnumerable<BookOverview> Search(string word)
{
return this._searchRepository.Search(word);
}
public IEnumerable<BookOverview> Add(string name, string description, string category)
{
var entity = new BookOverview(-1, name, description, category);
this._repo.Register(entity);
this._searchRepository.Register(entity);
return this._repo.GetBookOverviews();
}
}
}
次はUseCase部分のクラスです。主にビジネスロジックを形成する責務を担います。
実はこの部分の実装については自分でもやや懐疑的で、開発チームで意見を交わしながら構築していくことが求められるのではないかと思っています。
理由は主に以下です。
- .NET Core MVCにおいてプレゼンターは必要か?
- 凝集性を高めるためにはInteractorで纏めず、メソッド単位でクラスを作成する必要があるのでは?
- インターフェースを定義しているが、Interactorを参照するのはControllerであり、同心円で考えた場合、依存関係的に必要ないのでは?
Infrastructure 1.DBContext.cs
using System;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;
namespace Lib.Infrastructure
{
public class DBContext
{
private string _connectionString;
public MySqlConnection Connection { get; private set; }
public MySqlCommand Command { get; private set; }
public DBContext(string connectionString)
{
this._connectionString = connectionString;
}
public void Open()
{
try
{
this.Connection = new MySqlConnection()
{
ConnectionString = this._connectionString
};
this.Connection.Open();
this.Command = this.Connection.CreateCommand();
}
catch
{
this.Close();
throw;
}
}
public void Close()
{
if (this.Command != null)
{
this.Command.Dispose();
}
if (this.Connection != null)
{
this.Connection.Dispose();
}
}
}
}
次はMySQLへの接続に使用するクラスです。ライブラリにはMySql.Data(version = 8.0.21)を使用しています。
この部分は直接外部サービスとのやり取りを行うため、別オブジェクトとして定義しています。
また、理由はそれ以外にも、複数レポジトリにまたがるビジネスロジックの存在や、トランザクションに対応するため等様々あり、クリーンアーキテクチャのようなデータ永続化とビジネスロジックを切り分ける実装にする場合はおそらく後悔の少ない実装方法であると思います。
Infrastructure 2.ESContext.cs
using System;
using Nest;
namespace Lib.Infrastructure
{
public class ESContext
{
public ElasticClient Client { get; }
public ESContext(string url)
{
var uri = new Uri(url);
var setting = new ConnectionSettings(uri)
.DefaultMappingFor<Lib.Books.Entity.BookOverview>(map => map.IndexName("books"));
this.Client = new ElasticClient(setting);
}
}
}
次はElasticsearchへの接続に使用するクラスです。ライブラリにはNEST(version = 7.9.0)を使用しています。
実装をRepositoryから切り離した理由としては上記のDBContext.csの説明と同様です。
コンストラクタ内でElasticClientオブジェクトを生成していますが、APIを叩く処理がなければ通信は発生せず、生成コストも高くない認識なのでそうしています。
Controller
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Lib.Books.UseCase;
using Web.Filters;
namespace Web.Controllers
{
public class BooksController : Controller
{
private readonly ILogger<HomeController> _logger;
private readonly IBookInteractor _interactor;
public BooksController(ILogger<HomeController> logger, IBookInteractor interactor)
{
this._logger = logger;
this._interactor = interactor;
}
[HttpPost]
[ServiceFilter(typeof(DataAccessFilterBase))]
public IActionResult Init()
{
var books = this._interactor.Init();
return new JsonResult(books);
}
[HttpGet]
[ServiceFilter(typeof(DataAccessFilterBase))]
public IActionResult Get()
{
var books = this._interactor.GetBookOverviews();
return new JsonResult(books);
}
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Search(string word)
{
var books = this._interactor.Search(word);
this._logger.LogInformation($"検索結果 Search word:{word}");
return new JsonResult(books);
}
[HttpPost]
[ServiceFilter(typeof(DataAccessFilterBase))]
public IActionResult Add(string name, string description, string category)
{
var books = this._interactor.Add(name, description, category);
return new JsonResult(books);
}
}
}
次はBookユースケースに対するControllerクラスです。
受け取った要求をinteractorに流し、JSON形式でのレスポンスを返却すること、また、ロギングの責務を担います。
[ServiceFilter(typeof(DataAccessFilterBase))]がついているメソッドに関しては、DBアクセスを使用することを意味しています。ここの実装に関してはFilterで説明します。
Filter
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Filters;
using Lib.Infrastructure;
namespace Web.Filters
{
public abstract class DataAccessFilterBase : ActionFilterAttribute
{
}
public class DataAccessFilter : DataAccessFilterBase
{
private readonly DBContext _ctx;
public DataAccessFilter(DBContext ctx)
{
this._ctx = ctx;
}
public override void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext context)
{
this._ctx.Open();
}
public override void OnActionExecuted(ActionExecutedContext context)
{
this._ctx.Close();
}
}
}
次はControllerに干渉するFilterクラスです。
今回定義したのはMySQLへの接続が必要な場合に関する処理で、.NET Coreのリクエストライフサイクルに直接干渉するコードをFilterで提供することによって、同じコードを複数書くことを避けています。
Controllerに直接記述することも可能ですが、そうした場合はControllerが増えた際に同じコードを書かなければならなくなります。
EntryPoint 1.StartUp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.HttpsPolicy;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
namespace Web
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllersWithViews();
var connectionString = this.Configuration.GetValue<string>("DB_CONNECTION_STRING");
var searchUrl = this.Configuration.GetValue<string>("ELASTIC_SEARCH_SERVER");
services.AddScoped<Lib.Infrastructure.DBContext>((s) => new Lib.Infrastructure.DBContext(connectionString));
services.AddScoped<Lib.Infrastructure.ESContext>((s) => new Lib.Infrastructure.ESContext(searchUrl));
services.AddScoped<Lib.Books.Repository.IBookRepository, Lib.Books.Repository.BookRepository>();
services.AddScoped<Lib.Books.Repository.IBookSearchRepository, Lib.Books.Repository.BookSearchRepository>();
services.AddScoped<Lib.Books.UseCase.IBookInteractor, Lib.Books.UseCase.BookInteractor>();
services.AddScoped<Filters.DataAccessFilterBase, Filters.DataAccessFilter>();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
}
}
次に、アプリケーションのセットアップを担当するStartupクラスです。
Twelve-Factor Appに習って各接続情報などを環境変数から呼び出し、これまでご紹介したContext、Repository、Interactor、FilterをDIしていきます。
Configureに関しては開発環境で動けば良いので最小構成にしました。
EntryPoint 2.Program
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using NLog.Web;
namespace Web
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
}
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureAppConfiguration(cfg =>
{
cfg.AddEnvironmentVariables();
})
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>();
})
.UseNLog();
}
}
最後に、今回のアプリケーションのエントリーポイントであるProgramクラスです。
特徴としてはConfigureAppConfigurationをcallし、その中でcfg.AddEnvironmentVariables()を実行しています。
今回のアプリケーションでは環境変数を使用してDBやESへの接続情報を制御しているので必要な実装となっています。
実行
$ cd /root/app/Web
$ dotnet run
こんな感じのサイトが出来上がりました。
一応本の追加と検索を実行してますがめちゃくちゃわかりづらい個性的なgifですね。
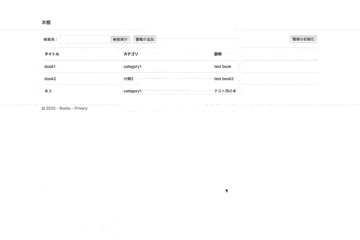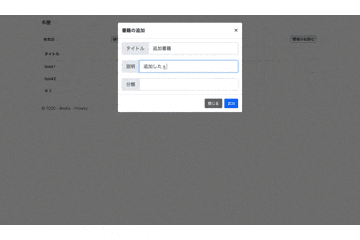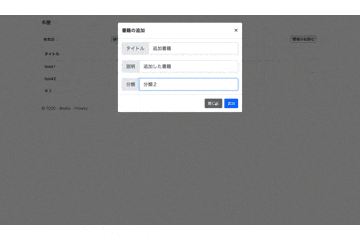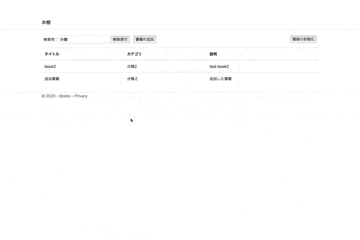
link
公式ドキュメント
ASP.NET Core MVC の概要
Elasticsearch.Net and NEST