Your Spark Tutorial
Why Apache Spark ?
"Apache Spark is a fast and general-purpose cluster computing system. It provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, Python and R, and an optimized engine that supports general execution graphs. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and structured data processing, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Spark Streaming." (Apache Software Foundation)
Brief Explanation
The main objective of this tutorial is to demonstrate some basic configurations and implementations of Apache Spark 2.4.5 to those who are puzzled and don't know where to start off from. You don't need any language proficiency apart from very little Linux knowledge to proceed with this tutorial. However, a certain level of proficiency in at least one or more languages from Python, Scala, and R, is recommended in understanding Spark in depth. The standard go-to language for Spark is Scala, the language of which Spark is built on.
Jargons
Cluster
A collection of master and slave nodes of one-to-many relationship in general.
Node
A node can be a computing device or a dispatcher.
Master Node
A node primarily used for distributing or assigning tasks and managing computational resources.
Slave Node / Worker
A node that offers solely its computational resources.
Configuration
- Ubuntu 18.04
- Apache Spark 2.4.5
- Java SDK (Open JDK 11 in our case)
- One master node and one slave node
Installing
TLDR;
Here's a summary or reminder for those who know what they are doing.
- Configure your environment
- Install JDK
- Set up your Spark package
- Configure
spark-env.shandslaves - Distribute your configured Spark package to other nodes
- Run it
Download
Download the corresponding Spark package from here.
Unzip
mv path/to/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz path/to/your/spark
tar -zxvf path/to/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz -C path/to/your/spark
Configure the Templates
Go to Spark's configuration directory and make copies of spark-env.sh.template and slaves.templates.
cd path/to/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7/conf
cp spark-env.sh.template spark-env.sh
cp slaves.templates slaves
When you run path/to/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7/bin/spark-shell without a Java SDK, you'll get an error saying
This is asking you to set JAVA_HOME to the Java SDK that Spark would be using since Spark runs on Scala and Scala runs on Java. This is what we'll be doing soon. Some people might ask if they have to set that of Scala as well, and the answer is no. If you look carefully,
you may see that the SDK needed for Scala is downloaded along with the Spark package.
sudo apt-get install default-jre
java -version gives the following; we're using OpenJDK 11.

The default path of OpenJDK 11 is /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/ for Ubuntu 18.04, and we'll add this to our Spark's configuration.
nano path/to/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7/conf/spark-env.sh
Add the following line to your configuration.
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64
If you go back and run path/to/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7/bin/spark-shell.sh, you should now get something resembling the following.
Now let's return to path/to/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7/conf/spark-env.sh and add the master host and port number. The master host can be in the form of your IP-address or simply your host's name. We'll go with IP-address for its uniqueness. For those that don't know the IP-address of their host, run ifconfig. The port can simply be any available ports of your device and your choice, but we'll stick with the default port number, 7077.
This is what your spark-env.sh should look like now.

Let's configure our slaves file.
nano path/to/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7/conf/slaves
Similarly, add the IP-address or the host name to the file.
We will then have to maintain the consistency of our configuration throughout our nodes. To do this, we'll simply copy the exact Spark package that we have configured to all devices that will be participating in this Spark trial.
Run
sudo apt-get install openssh-server
on the device of destination. This opens up ports needed for file transfer, and you will understand in a minute that this will be convenient when we later start up the slave nodes from your master.
Proceed with
scp -r path/to/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7 hostname@ip.address:~/destination
to copy your package. You might want to use an iteration when you have multiple devices.
A great habit is to keep the absolute path of your Spark package the same across all your devices. This is because Spark from your master node uses the same absolute path to find your Spark packages in your slave nodes by default. If would be harder to manage, or even to use, Spark across multiple devices if the absolute path of your Spark packages are located arbitrarily.
Spark-env.sh
This configures all your environmental variables that Spark would use. For example, the IP address of your master node can be set in this file.
Slaves
This tells Spark what your slave nodes are and allows your slave nodes to register and know their masters.
Playing Around
Quick Start
We now can run
path/to/your/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7/sbin/start-all.sh
to activate all your nodes. What that bash command essentially does is configure your devices and run path/to/your/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7/sbin/start-master.sh and path/to/your/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7/sbin/start-slaves.sh at one go. To stop the process, we can simply run
path/to/your/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7/sbin/stop-all.sh
.
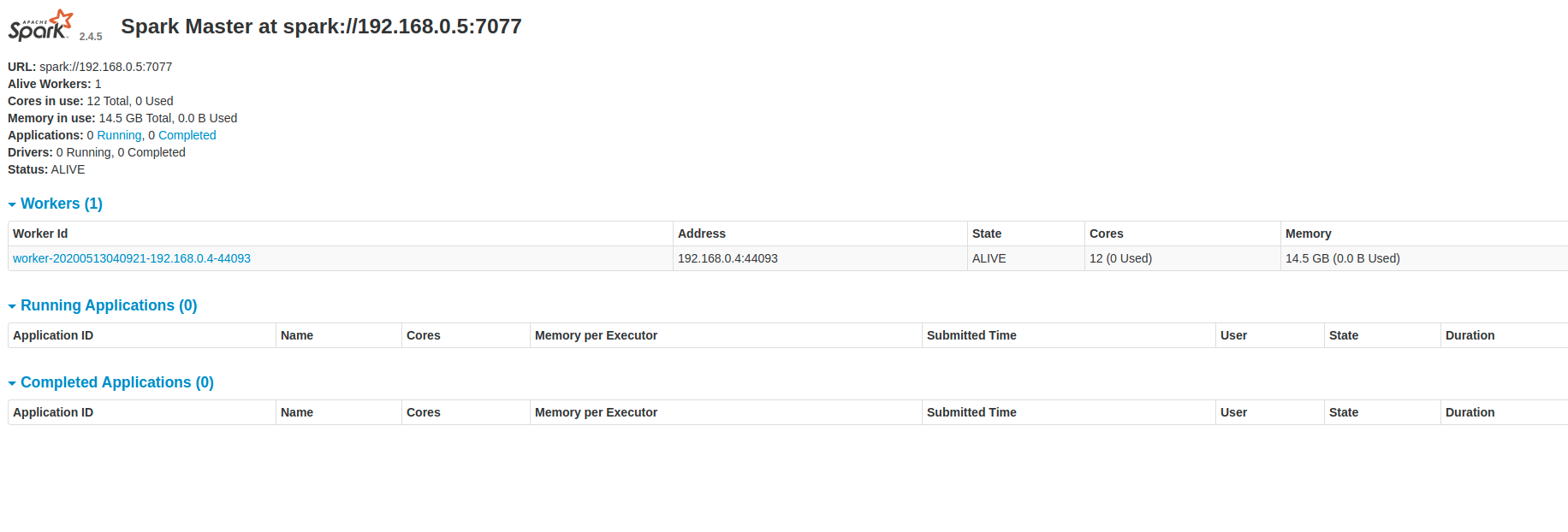
If we go to localhost:8080, we should expect the following WebUI to appear.
Remember that Port 7077 is used for the communications between devices and Port 8080 is used solely for the WebUI. Please make sure that Port 8080 is not used by other applications, say Apache Airflow or Django, owing to its popularity, else you may find difficulties in navigating to your WebUI.
Your First Spark-Submit
We can try submitting example tasks that are pre-written to see our Spark is working or not.
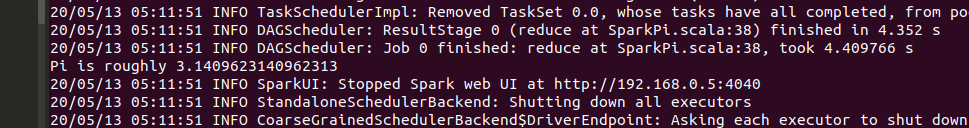
This following command submits a task to your master node. The task involves a calculation of Pi using 2GB of memory and 4 cpu cores(threads to be precise) on each slave node.
./bin/spark-submit --master spark://master.ip.address:7077 --executor-memory 2048mb --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi --total-executor-cores 4 examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.4.5.jar 100
We can monitor this on the WebUI given.
Using Spark-Shell
There are two modes of Spark-Shell, local and remote.
Running
path/to/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7/bin/spark-shell
brings you to the local Spark. If you check your WebUI you should see no applications running.
To use the environment that we have just created, we have to specify the master node and its address. Which should look something like this
path/to/spark-2.4.5-bin-hadoop2.7/bin/spark-shell -- master spark://master.ip.address:7077
.
You should now see your application running via the WebUI.

Reference
- Apache Software Foundation, "Overview", Apache Software Foundation. https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/index.html. 11 May 2020.