はじめに
クォータニオン(Quatenion, 四元数)は、ゲーム開発プログラミングにおいて、オブジェクトの姿勢や回転を表す1つの手段です。Unityにおいても例えば、transform.rotationがクォータニオンで実装されています。
この記事では、Unityにおけるクォータニオンの構造体(UnityEngine.Quaternion)を理解するために、内部実装を再現・実装します。また、数学に関しては解説記事の紹介に留めます。
UnityのC#部分の実装に関しては、一部のソースコードが公開されていますが、クォータニオンに関しては、dll呼び出しがあるために、内部実装が確認できない箇所もあるので、それを補完しつつ実装していきます。
参考:UnityEngine.QuaternionのC#の実装コード - Unity-Technologies/GitHub
実装するにあたって、UnityEngine.QuaternionのUnity公式ドキュメントを参考にしつつ、メソッドを順に実装していきます。
この記事の貢献としては、UnityのクォータニオンのAPIをC#で完全に再現した日本語記事は確認できなかった[1]ので、その点で有益であると思われます。
最後に、実装した構造体についてのソースコードとテストに用いたUnityプロジェクトはGitHubにて公開しておきます。また、数学に精通しているわけではないので、一部不完全な記述があります。誤りがあった場合は修正依頼・コメントお願いします。
実装したQuaternion構造体のソースコード全文
using System;
using UnityEngine;
namespace FThingSoftware
{
[Serializable]
public struct Quaternion
{
// ===============================
// メンバー変数
// ===============================
public float x;
public float y;
public float z;
public float w;
// ===============================
// コンストラクタ
// ===============================
public Quaternion(float x, float y, float z, float w)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
this.w = w;
}
// ===============================
// static変数
// ===============================
// 無回転のクォータニオン(単位回転)
public static readonly Quaternion identity = new Quaternion(0f, 0f, 0f, 1f);
// ===============================
// 変数
// ===============================
// オイラー角表現を返したり、代入できるようにする
public Vector3 eulerAngles
{
get
{
// Unityなので、z-x-y系のオイラー各に変換する
// x/y/z軸の回転量
float angle_x, angle_y, angle_z = 0;
// 角度が90度のときの誤差を補正する
float theta_x = (2 * (y * z + x * w) >= 0.9999999f) ? 1.0f : 2 * (y * z + x * w);
angle_x = Mathf.Asin(theta_x) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
if (Mathf.Cos(angle_x * Mathf.Deg2Rad) != 0)
{
float y_top = 2 * (x * z - y * w);
float y_bottom = 2 * (w * w + z * z) - 1;
angle_y = Mathf.Atan2(-y_top, y_bottom) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
float z_top = 2 * (x * y - z * w);
float z_bottom = 2 * (w * w + y * y) - 1;
angle_z = Mathf.Atan2(-z_top, z_bottom) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
}
else
{
angle_y = 0;
float z_top = 2 * (x * y + z * w);
float z_bottom = 2 * (w * w + x * x) - 1;
angle_z = Mathf.Atan2(z_top, z_bottom) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
}
// 角度の範囲を0~360の範囲に補正する
return MakePositive(new Vector3(angle_x, angle_y, angle_z));
}
// オイラー角を代入して回転できるようにする
set
{
this = Euler(value.x, value.y, value.z);
}
}
// 0 ~ 360度の範囲に補正する
private static Vector3 MakePositive(Vector3 euler)
{
float min = 0f;
float max = 360f;
if (euler.x < min) { euler.x += 360f; }
else if (euler.x > max) { euler.x -= 360f; }
if (euler.y < min) { euler.y += 360f; }
else if (euler.y > max) { euler.y -= 360f; }
if (euler.z < min) { euler.z += 360f; }
else if (euler.z > max) { euler.z -= 360f; }
return euler;
}
// 正規化したクォータニオンを返す
public Quaternion normalized
{
get
{
return Normalize(this);
}
}
// ===============================
// public関数
// ===============================
public void Set(float x, float y, float z, float w)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
this.w = w;
}
// fromDirectionからtoDirectionへの回転を作成して代入する
public void SetFromToRotation(Vector3 fromDirection, Vector3 toDirection)
{
this = FromToRotation(fromDirection, toDirection);
}
// 指定した forward と upwards 方向に回転する
public void SetLookRotation(Vector3 view)
{
this = LookRotation(view);
}
// 回転を座標に対する角度の値(AngleAxis)に変換する
public void ToAngleAxis(out float angle, out Vector3 axis)
{
// クォータニオンの定義より求める
// cos(rad/2) = w より
float rad = Mathf.Acos(w) * 2.0f;
angle = rad * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
// x = axis.x * sin(rad/2), y = axis.y * sin(rad/2), z = axis.z * sin(rad/2)より
axis = new Vector3(this.x / Mathf.Sin(rad / 2), this.y / Mathf.Sin(rad / 2), this.z / Mathf.Sin(rad / 2));
}
// クォータニオンの値を見やすくした文字列を返す
// ToStringメソッドをオーバーライドする
public override string ToString()
{
string format = "F5";
return $"({x.ToString(format)}, {y.ToString(format)}, {z.ToString(format)}, {w.ToString(format)})";
}
// ===============================
// static関数
// ===============================
// 2つの回転aとb間の角度を返す(Unityの実装を引用)
public static float Angle(Quaternion a, Quaternion b)
{
// a・b = cos(θ/2) となることを利用する
float dot = Mathf.Min(Mathf.Abs(Dot(a, b)), 1f);
return IsEqualUsingDot(dot) ? 0f : (Mathf.Acos(dot) * 2f * Mathf.Rad2Deg);
}
private static bool IsEqualUsingDot(float dot)
{
return dot > 0.999999f;
}
// axisの周りをangle度回転する回転を生成して返す
public static Quaternion AngleAxis(float angle, Vector3 axis)
{
// クォータニオンの定義
// 正規化された軸ベクトルλ(x, y, z)と回転量Θのとき
// (x, y, z, w) = ( λx * sin(Θ/2), λy * sin(Θ/2), λz * sin(Θ/2), cos(Θ/2) )
// ベクトルの正規化
axis.Normalize();
// degree から radian への変換
float rad = angle * Mathf.Deg2Rad;
// 定義に従って成分を設定する
return new Quaternion(
axis.x * Mathf.Sin(rad / 2),
axis.y * Mathf.Sin(rad / 2),
axis.z * Mathf.Sin(rad / 2),
Mathf.Cos(rad / 2)
);
}
// 2つの回転の内積を返す(Unityの実装を引用)
public static float Dot(Quaternion a, Quaternion b)
{
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y + a.z * b.z + a.w * b.w;
}
// z軸を中心にz度、x軸を中心にx度、y軸を中心にy度回転する回転を返す。回転はこの順序で適用される
public static Quaternion Euler(float x, float y, float z)
{
// それぞれの軸を中心とした回転を生成
Quaternion qua_x = AngleAxis(x, Vector3.right);
Quaternion qua_y = AngleAxis(y, Vector3.up);
Quaternion qua_z = AngleAxis(z, Vector3.forward);
// z-x-y系なので、z-x-yの順番で回転させる
// クォータニオンの乗算を行う(右から掛けていく)
return qua_y * qua_x * qua_z;
}
// fromDirection から toDirection への回転を作成して返す
public static Quaternion FromToRotation(Vector3 fromDirection, Vector3 toDirection)
{
// 外積を用いて、軸ベクトルを求める
Vector3 axis = Vector3.Cross(fromDirection, toDirection);
// 外積が(0,0,0)の時は、無回転のクォータニオン(0,0,0,1)にする
if (axis == Vector3.zero) { return identity; }
// 内積の定義から回転量を求める a・b = |a||b|cosθ なので
float rad = Mathf.Acos(Vector3.Dot(fromDirection, toDirection) / (fromDirection.magnitude * toDirection.magnitude));
// 求めた軸と回転量でクォータニオンの生成
return AngleAxis(Mathf.Rad2Deg * rad, axis);
}
// rotationの逆(共役)クォータニオンを返す
public static Quaternion Inverse(Quaternion rotation)
{
return new Quaternion(-rotation.x, -rotation.y, -rotation.z, rotation.w);
}
// aとbの間をtで補間して正規化する、tは[0,1]の範囲
public static Quaternion Lerp(Quaternion a, Quaternion b, float t)
{
// tの範囲の制限
t = Mathf.Clamp01(t);
return LerpUnclamped(a, b, t);
}
// aとbの間をtで補間して正規化する、tは[0,1]の範囲にクランプされない
public static Quaternion LerpUnclamped(Quaternion a, Quaternion b, float t)
{
// 2つの回転の内積を求める
float dot = Dot(a, b);
// 内積が負の時、最短距離での補間を得るために片方を負にする
if (dot < 0)
{
b = new Quaternion(-b.x, -b.y, -b.z, -b.w);
dot = -dot;
}
// 直線経路で補完する a*(1-t) + b*t
Quaternion lerp = new Quaternion(
a.x + (-a.x + b.x) * t,
a.y + (-a.y + b.y) * t,
a.z + (-a.z + b.z) * t,
a.w + (-a.w + b.w) * t
);
return lerp.normalized;
}
// 引数のupwardsを省略した場合に、Vector3.upがデフォルト引数となるようにオーバーロード
public static Quaternion LookRotation(Vector3 forward)
{
return LookRotation(forward, Vector3.up);
}
// オブジェクトの正面(forward)を引数のforwardの向きに回転させる回転を生成する
public static Quaternion LookRotation(Vector3 forward, Vector3 upwards)
{
// オブジェクトの正面からforwardに向ける回転を取得
Quaternion lookRotation = FromToRotation(Vector3.forward, forward);
// 外積を用いてupwardsとforwardに垂直なベクトル(赤軸)を得る
Vector3 xAxisHorizontal = Vector3.Cross(upwards, forward);
// 回転後のy軸(緑軸)を求める
Vector3 yAxisAfterRotate = Vector3.Cross(forward, xAxisHorizontal);
// Look後のy軸(緑) から 回転後のy軸(緑) へ修正する回転を求める
Vector3 yAxisBeforeModify = lookRotation * Vector3.up;
Quaternion modifyRotation = FromToRotation(yAxisBeforeModify, yAxisAfterRotate);
// 回転を合成して返す
return modifyRotation * lookRotation;
}
// 正規化を行ったものを返す(Unityの実装を引用)
public static Quaternion Normalize(Quaternion q)
{
float num = Mathf.Sqrt(Dot(q, q));
if (num < Mathf.Epsilon)
{
return identity;
}
return new Quaternion(q.x / num, q.y / num, q.z / num, q.w / num);
}
public void Normalize()
{
this = Normalize(this);
}
// fromからtoへの回転を得る(Unityの実装を引用)
public static Quaternion RotateTowards(Quaternion from, Quaternion to, float maxDegreesDelta)
{
float num = Angle(from, to);
if (num == 0f)
{
return to;
}
return Slerp(from, to, Mathf.Min(1f, maxDegreesDelta / num));
}
// 球面線形補完を得る、tは[0,1]の範囲
public static Quaternion Slerp(Quaternion a, Quaternion b, float t)
{
// tの範囲の制限
t = Mathf.Clamp01(t);
return SlerpUnclamped(a, b, t);
}
// 球面線形補完を得る、tは[0,1]の範囲にクランプされない
public static Quaternion SlerpUnclamped(Quaternion a, Quaternion b, float t)
{
// 2つの回転の内積を求める
float dot = Dot(a, b);
// 内積が負の時、最短距離での補間を得るために
// 片方の回転を負にして、内積を正の値にする
if (dot < 0)
{
b = new Quaternion(-b.x, -b.y, -b.z, -b.w);
dot = -dot;
}
// 2つの回転の角度を求める
float rad = IsEqualUsingDot(dot) ? 0f : Mathf.Acos(dot);
// 球面線形補完
float bottom = Mathf.Sin(rad);
float a_rate = Mathf.Sin((1 - t) * rad) / bottom;
float b_rate = Mathf.Sin(t * rad) / bottom;
Quaternion slerp = new Quaternion(
a.x * a_rate + b.x * b_rate,
a.y * a_rate + b.y * b_rate,
a.z * a_rate + b.z * b_rate,
a.w * a_rate + b.w * b_rate
);
return slerp.normalized;
}
// ===============================
// Operator
// ===============================
// 暗黙的な型変換演算子の定義
// UnityEngine.Quaternionに自動的に変換して
// transform.rotation = Quaternion; ができるようにする
public static implicit operator UnityEngine.Quaternion(Quaternion q)
{
return new UnityEngine.Quaternion(q.x, q.y, q.z, q.w);
}
// 演算子オーバーロードを用いて
// クォータニオン同士の乗算ができるようにする
public static Quaternion operator * (Quaternion a, Quaternion b)
{
return new Quaternion(
a.w*b.x - a.z*b.y + a.y*b.z + a.x*b.w,
a.z*b.x + a.w*b.y - a.x*b.z + a.y*b.w,
-a.y*b.x + a.x*b.y + a.w*b.z + a.z*b.w,
-a.x*b.x - a.y*b.y - a.z*b.z + a.w*b.w
);
}
// 演算子オーバーロードを用いて
// Quaternion * Vector3 が計算できるようにする
public static Vector3 operator * (Quaternion q, Vector3 v)
{
// 回転後のベクトルv'について
// v' = q * v * q_inverse となる
// 3次元座標をクォータニオンで表す
Quaternion vecQuaternion = new Quaternion(v.x, v.y, v.z, 0);
// ベクトルに回転を施す
Quaternion vecAfterRotate = q * vecQuaternion * Quaternion.Inverse(q);
// クォータニオンを3次元座標に変換する
return new Vector3(vecAfterRotate.x, vecAfterRotate.y, vecAfterRotate.z);
}
// 比較(Unityの実装を引用)
public override bool Equals(object other)
{
if (!(other is Quaternion))
{
return false;
}
return Equals((Quaternion)other);
}
public bool Equals(Quaternion other)
{
return x.Equals(other.x) && y.Equals(other.y) && z.Equals(other.z) && w.Equals(other.w);
}
// Hash値を計算できるようにする(Unityの実装を引用)
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return x.GetHashCode() ^ (y.GetHashCode() << 2) ^ (z.GetHashCode() >> 2) ^ (w.GetHashCode() >> 1);
}
}
}
テストに用いたUnityプロジェクトを格納したGitHubのリポジトリ
対象読者
- クォータニオンを学習したい人
- クォータニオンの内部実装を知っておきたい人
この記事の構成
まずクォータニオンを理解する上で、基礎的な事項をはじめに実装します。その後、Unityドキュメントにあるメソッドを順に実装していきます。
基礎的なメソッド
構造体の作成
Unityではクォータニオンをクラスではなく構造体として定義しています。
まず、クォータニオンをx,y,z,wの4つの成分を持つベクトルとして定義しましょう。
using System;
using UnityEngine;
namespace FThingSoftware
{
public struct Quaternion
{
public float x;
public float y;
public float z;
public float w;
public Quaternion(float x, float y, float z, float w)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
this.w = w;
}
}
}
自作する場合は、UnityEngine.Quaternionと名前空間が重複してしまうので、適宜namespaceをつけておくと良いです。
AngleAxis()メソッド
Unityドキュメントには、「軸 axis の周りを angle 度回転する回転を作成します」と記述があります。
方向ベクトル $(\lambda _x, \lambda _y, \lambda _z)$ を回転軸として
$\theta$ だけ回転を表すクォータニオン $q$ は以下の数式で表せます。
$q(x,y,z,w) = (\lambda_x\sin(\theta/2), \lambda_y\sin(\theta/2), \lambda_z\sin(\theta/2), \cos(\theta/2))$
参考1:
クォータニオン (Quaternion) を総整理! ~ 三次元物体の回転と姿勢を鮮やかに扱う ~
参考2:高校生でもわかりそうだけど、ちゃんと理解もするUnityでのクォータニオン運用法|MetaFormingPro
この定義より実装を行うと次のようになります。
// axisの周りをangle度回転する回転を生成して返す
public static Quaternion AngleAxis(float angle, Vector3 axis)
{
// ベクトルの正規化
axis.Normalize();
// degree から radian への変換
float rad = angle * Mathf.Deg2Rad;
// 定義に従って成分を設定する
return new Quaternion(
axis.x * MathF.Sin(rad / 2),
axis.y * MathF.Sin(rad / 2),
axis.z * MathF.Sin(rad / 2),
MathF.Cos(rad / 2)
);
}
Unityでは常に正規化した状態でクォータニオンを保持しているため、先に軸ベクトルの正規化を行っています。
Euler()メソッド
Unityドキュメントには、オイラー角で、「z軸を中心にz度、x軸を中心にx度、y軸を中心にy度回転する回転を返す。回転はこの順序で適用される」と記述があります。
クォータニオンでは、回転を適用する順序が重要となってきます。複数回の回転を行う場合、回転の適用順によって、回転後の姿勢が変わります。Unityでは、回転の中心とする軸をz軸, x軸, y軸の順で適用して回転を行います。これを、z-x-y系といいます。
Euler()メソッドの実装では、与えられたオイラー角 $(\theta_x,\theta_y,\theta_z)$ を元に、x軸,y軸,z軸を中心に回転するクォータニオンを3つ作成して、z-x-yの順で適用した回転を返してあげれば良さそうです。
ここで、ある回転 $q1$ をさらに $q2$ 回転させた回転 $q3$ を求めるために、クォータニオン同士の乗算(回転の合成)を行います。クォータニオンの乗算では、$q3 = q2 \times q1$ というように、先に適用する回転を右側から掛けることで行います。
(クォータニオンの乗算は、次の項目で実装を行います。)
// z軸を中心にz度、x軸を中心にx度、y軸を中心にy度回転する回転を返す。回転はこの順序で適用される
public static Quaternion Euler(float x, float y, float z)
{
// それぞれの軸を中心とした回転を生成
Quaternion qua_x = AngleAxis(x, Vector3.right);
Quaternion qua_y = AngleAxis(y, Vector3.up);
Quaternion qua_z = AngleAxis(z, Vector3.forward);
// z-x-y系なので、z-x-yの順番で回転させる
// クォータニオンの乗算を行う(右から掛けていく)
return qua_y * qua_x * qua_z;
}
クォータニオン同士の乗算(operator *)
はじめに$q_b$回転させた後に、$q_a$回転させたクォータニオン$q_c$は、
$q_c = q_a \times q_b$ という式で表されます。(最初に適用する回転を右側から掛けることに注意)ここで、クォータニオンの乗算(合成)は、次のような式で定義できます。
{\begin{eqnarray}
a \times b =
( a_w b_x - a_z b_y + a_y b_z + a_x b_w, \\
a_z b_x + a_w b_y - a_x b_z + a_y b_w, \\
-a_y b_x + a_x b_y + a_w b_z + a_z b_w, \\
-a_x b_x - a_y b_y - a_z b_z + a_w b_w) \\
\end{eqnarray}}
この定義より演算子オーバーロードを用いて実装します。
public static Quaternion operator * (Quaternion a, Quaternion b)
{
return new Quaternion(
a.w*b.x - a.z*b.y + a.y*b.z + a.x*b.w,
a.z*b.x + a.w*b.y - a.x*b.z + a.y*b.w,
-a.y*b.x + a.x*b.y + a.w*b.z + a.z*b.w,
-a.x*b.x - a.y*b.y - a.z*b.z + a.w*b.w
);
}
余談ですが、Unityドキュメントでは「lhsを最初に、rhsを次に回転させる」と記述がありますが、誤訳です。正しくは、rhs -> lhs の順で回転が行われます。
【Unity】 Quaternionの回転順の話 - エフアンダーバー
こちらの記事でも指摘されていましたが、注意しましょう。実際にUnityのQuaternion.csのソースコードを見ても上記と同じような実装がされています。
eulerAngles
クォータニオンに対して、get/setアクセサーを用いて、直接オイラー角表現を代入したり取得できるようにします。getに関して、クォータニオン$q(x,y,z,w)$からオイラー角$(\theta_x, \theta_y, \theta_z)$への変換は以下の記事を参考にして実装を行います。
{\begin{eqnarray}
\theta_x &=& \arcsin(2q_yq_z + 2q_xq_w) \\
\theta_y &=& \left\{ \begin{array}{ll}
\arctan(-\frac{2q_xq_z - 2q_yq_w}{2q_w^2 + 2q_z^2 - 1}) & (cos\theta_x \neq 0) \\
0 & (otherwise)
\end{array} \right. \\
\theta_z &=& \left\{ \begin{array}{ll}
\arctan(-\frac{2q_xq_y - 2q_zq_w}{2q_w^2 + 2q_y^2 - 1}) & (cos\theta_x \neq 0) \\
\arctan(\frac{2q_xq_y + 2q_zq_w}{2q_w^2 + 2q_x^2 - 1}) & (otherwise)
\end{array} \right. \\
\end{eqnarray}
}
回転行列、クォータニオン(四元数)、オイラー角の相互変換 #数学 - Qiita より引用
ここでも、z-x-y系を考慮して変換を行います。また、setに関しては、先ほど実装したEuler()メソッドを用いることでそのまま実装できます。
// オイラー角表現を返したり、代入できるようにする
public Vector3 eulerAngles
{
get
{
// Unityなので、z-x-y系のオイラー角に変換する
// x/y/z軸の回転量
float angle_x, angle_y, angle_z = 0;
// 角度が90度のときの誤差を補正する
float theta_x = (2 * (y * z + x * w) >= 0.9999999f) ? 1.0f : 2 * (y * z + x * w);
angle_x = MathF.Asin(theta_x) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
if (MathF.Cos(angle_x * Mathf.Deg2Rad) != 0)
{
float y_top = 2 * (x * z - y * w);
float y_bottom = 2 * (w * w + z * z) - 1;
angle_y = MathF.Atan2(-y_top, y_bottom) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
float z_top = 2 * (x * y - z * w);
float z_bottom = 2 * (w * w + y * y) - 1;
angle_z = Mathf.Atan2(-z_top, z_bottom) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
}
else
{
angle_y = 0;
float z_top = 2 * (x * y + z * w);
float z_bottom = 2 * (w * w + x * x) - 1;
angle_z = Mathf.Atan2(z_top, z_bottom) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
}
// 角度の範囲を0~360の範囲に補正する
return MakePositive(new Vector3(angle_x, angle_y, angle_z));
}
// オイラー角を代入して回転できるようにする
set
{
this = Euler(value.x, value.y, value.z);
}
}
MakePositive()メソッドについて
Unityのオイラー角表現では、θは0〜360度の範囲で表示されます。クォータニオンをオイラー角に変換する際に、$θ$が範囲外になってしまうことがあるので、それを補正する関数になります。
// 0 ~ 360度の範囲に補正する
private static Vector3 MakePositive(Vector3 euler)
{
float min = 0f;
float max = 360f;
if (euler.x < min) { euler.x += 360f; }
else if (euler.x > max) { euler.x -= 360f; }
if (euler.y < min) { euler.y += 360f; }
else if (euler.y > max) { euler.y -= 360f; }
if (euler.z < min) { euler.z += 360f; }
else if (euler.z > max) { euler.z -= 360f; }
return euler;
}
UnityのC#のソースコードでは、Internal_MakePositive()というメソッド名で実装されており、計算時の数値誤差を補正していましたが、今回は行っていません。
Dot()メソッド
クォータニオンの内積を計算します。3次元ベクトルの内積の定義にそのまま$w$を加えて4次元に拡張しただけになります。
// 2つの回転の内積を返す(Unityの実装を引用)
public static float Dot(Quaternion a, Quaternion b)
{
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y + a.z * b.z + a.w * b.w;
}
Angle()メソッド
2つの回転の間の角度を返します。
クォータニオンの内積と角度には、以下の関係があります。
$q_a \cdot q_b = cos(\theta/2)$
これより、cosの逆関数を用いて2つの回転の間の角度を求めることができます。
参考:四元数(クォータニオン)の応用 - EMANの物理数学
// 2つの回転aとb間の角度を返す(Unityの実装を引用)
public static float Angle(Quaternion a, Quaternion b)
{
// a・b = cos(θ/2) となることを利用する
float dot = Mathf.Min(Mathf.Abs(Dot(a, b)), 1f);
return IsEqualUsingDot(dot) ? 0f : (Mathf.Acos(dot) * 2f * Mathf.Rad2Deg);
}
private static bool IsEqualUsingDot(float dot)
{
return dot > 0.999999f;
}
Unityの実装では、誤差の修正のために、IsEqualUsingDot()メソッドが入っているようですね。
その他のメソッド
基礎的な事柄は実装できたと思うので、これ以降はUnityドキュメントに従ってメソッドを上から順に実装していきます。
static変数
identity
単位クォータニオン(無回転, 恒等クォータニオン)を意味します。回転していないので、$\theta = 0$、軸を$\lambda=(0,0,0)$とするクォータニオンを求めてあげれば良さそうですね。
{\begin{eqnarray}
q(x,y,z,w)
= (\lambda_x\sin(\theta/2), \lambda_y\sin(\theta/2), \lambda_z\sin(\theta/2), \cos(\theta/2))
= (0, 0, 0 ,1)
\end{eqnarray}}
定義より、(0,0,0,1)となることがわかるので、以下のように記述すれば良さそうです。
// 無回転のクォータニオン(単位回転)
public static readonly Quaternion identity = new Quaternion(0f, 0f, 0f, 1f);
変数
normalized / Normalize() メソッド
クォータニオンの正規化を行います。自身を正規化して返す変数です。クォータニオンの正規化を行う関数(Normalizeメソッド)を呼んでいます。
// 正規化したクォータニオンを返す
public Quaternion normalized
{
get
{
return Normalize(this);
}
}
正規化自体はUnityEngine.Vector3と同じように、
それぞれの成分をベクトルの大きさで割ったものという定義になります。
// 正規化を行ったものを返す(Unityの実装を引用)
public static Quaternion Normalize(Quaternion q)
{
float num = Mathf.Sqrt(Dot(q, q));
if (num < Mathf.Epsilon)
{
return identity;
}
return new Quaternion(q.x / num, q.y / num, q.z / num, q.w / num);
}
0除算を防ぐために、クォータニオンの大きさが0に限りなく近い時を判別してその場合は単位クォータニオンを返すようにしているみたいです。ちなみに、Mathf.Epsilonは0との差分を持つ最小のfloatの値を返します。
Public関数
Set()メソッド
x、y、z、w の成分を設定します。説明するまでもありませんね。
public void Set(float x, float y, float z, float w)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
this.w = w;
}
SetFromToRotation() / FromToRotation()メソッド
ある向きから別の向きへの回転を生成するメソッドです。
// fromDirectionからtoDirectionへの回転を作成して代入する
public void SetFromToRotation(Vector3 fromDirection, Vector3 toDirection)
{
this = FromToRotation(fromDirection, toDirection);
}
FromToRotationメソッドの実装は以下になります。
// fromDirection から toDirection への回転を作成して返す
public static Quaternion FromToRotation(Vector3 fromDirection, Vector3 toDirection)
{
// 外積を用いて、軸ベクトルを求める
Vector3 axis = Vector3.Cross(fromDirection, toDirection);
// 外積が(0,0,0)の時は、無回転のクォータニオン(0,0,0,1)にする
if (axis == Vector3.zero) { return identity; }
// 内積の定義から回転量を求める a・b = |a||b|cosθ なので
float rad = MathF.Acos(Vector3.Dot(fromDirection, toDirection) / (fromDirection.magnitude * toDirection.magnitude));
// 求めた軸と回転量でクォータニオンの生成
return AngleAxis(Mathf.Rad2Deg * rad, axis);
}
軸ベクトルを外積を使って求めて、回転量を内積の定義から求めることで、目的のクォータニオンを生成できます。
SetLookRotation() / LookRotation()メソッド
FromToRotationに加えて、ある向きを向きつつ、指定した方向を上方向とする回転を求めます。
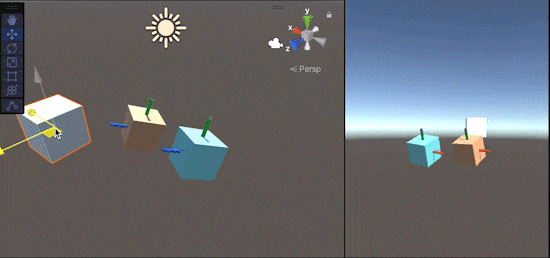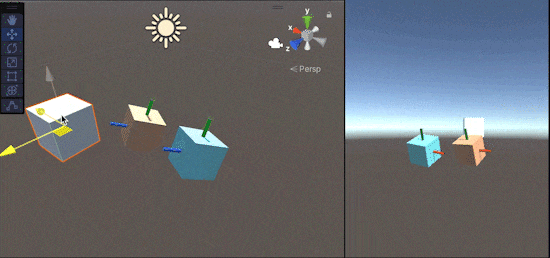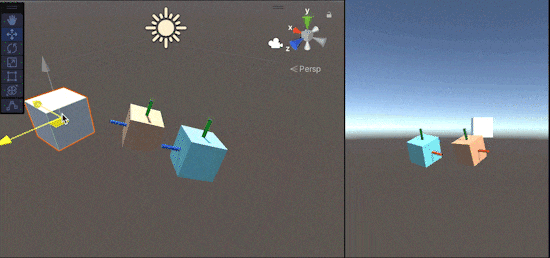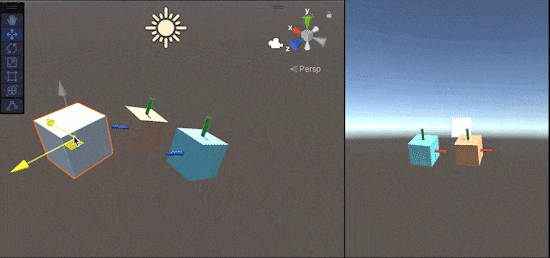
文章の説明では分かりにくいため、gif画像で説明をします。
例えば、あるオブジェクトを向き続けるカメラを実装したいとします。FromToRotationを使って、LookRotationを以下のように実装してみます。
public static Quaternion LookRotation(Vector3 forward)
{
return FromToRotation(Vector3.forward, forward);
}
あるオブジェクトを向き続けるコードを以下のように実装して実験してみます。
void Update()
{
// 目的のオブジェクトまでの向きを求める
Vector3 lookDirection = targetObj.transform.position - this.transform.position;
// UnityのLookRotationを使って求めた回転を適用
var unityQuaternion = Quaternion.LookRotation(lookDirection);
unityObj.transform.rotation = unityQuaternion;
// 自前実装のLookRotationを使って求めた回転を適用
var originalQuaternion = FThingSoftware.Quaternion.LookRotation(lookDirection);
originalObj.transform.rotation = originalQuaternion;
}
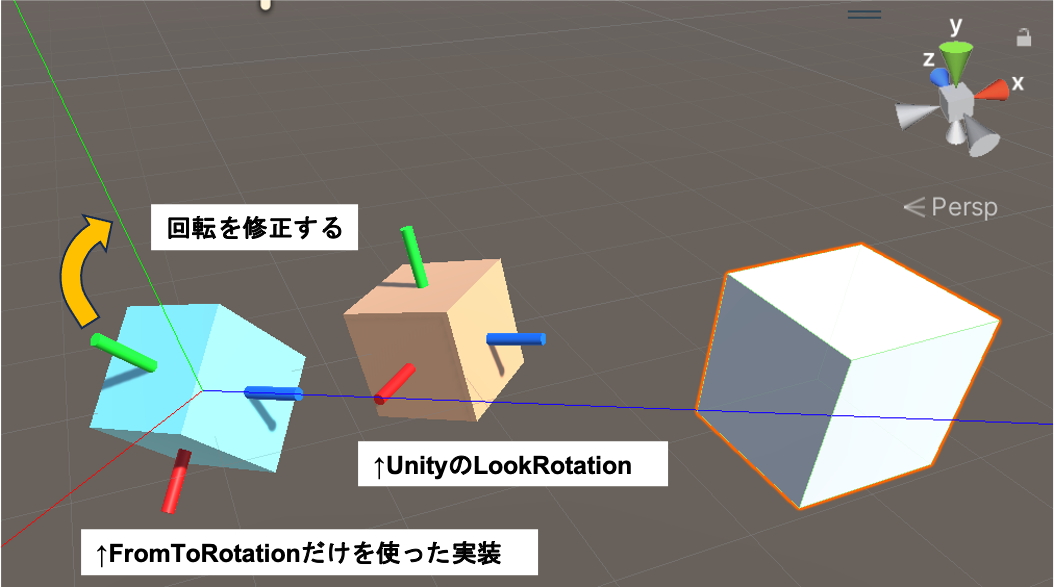
これを用いて実験した図が以下になります。
(白色Cubeがtarget、
水色Cubeが自前実装のLookRotation(FromToRotationでの実装)、
オレンジ色CubeがUnityのLookRotationです)
水色のCube(FromToRotationでの実装)に着目すると、青軸(forward)は常に白いCubeを向いていますが、それ以外の軸が回転してしまっていますね。このように、ただ単にあるオブジェクトを向き続ける回転を作成してしまうと、部分的に視点が回転してしまう現象が発生します。
これを防ぎつつ、オブジェクトを向き続ける回転を得られるようにしたのがLookRotationになります。(Transform.LookAtも同様の処理をします。)
修正したLookRotationの実装を先に記載します。
// 指定した forward と upwards 方向に回転する
public void SetLookRotation(Vector3 view)
{
this = LookRotation(view);
}
// 引数のupwardsを省略した場合に、Vector3.upがデフォルト引数となるようにオーバーロード
public static Quaternion LookRotation(Vector3 forward)
{
return LookRotation(forward, Vector3.up);
}
// オブジェクトの正面(forward)を引数のforwardの向きに回転させる回転を生成する
public static Quaternion LookRotation(Vector3 forward, Vector3 upwards)
{
// オブジェクトの正面からforwardに向ける回転を取得
Quaternion lookRotation = FromToRotation(Vector3.forward, forward);
// 外積を用いてupwardsとforwardに垂直なベクトル(赤軸)を得る
Vector3 xAxisHorizontal = Vector3.Cross(upwards, forward);
// 回転後のy軸(緑軸)を求める
Vector3 yAxisAfterRotate = Vector3.Cross(forward, xAxisHorizontal);
// Look後のy軸(緑) から 回転後のy軸(緑) へ修正する回転を求める
Vector3 yAxisBeforeModify = lookRotation * Vector3.up;
Quaternion modifyRotation = FromToRotation(yAxisBeforeModify, yAxisAfterRotate);
// 回転を合成して返す
return modifyRotation * lookRotation;
}
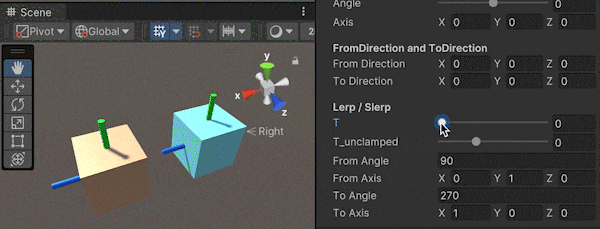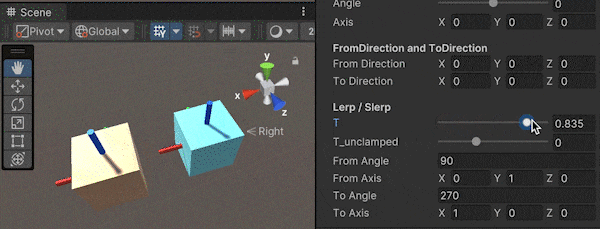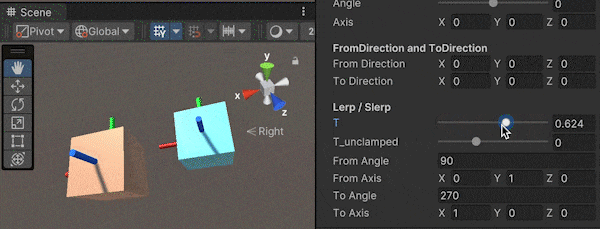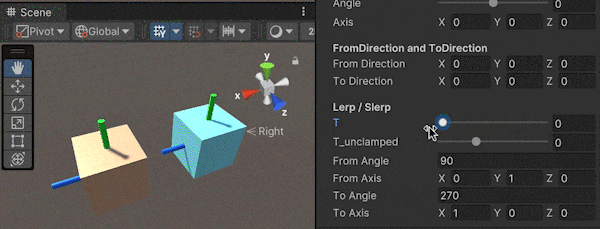
この実装の説明を行います。最終的に行いたいこととしては、下図のように緑軸を修正する回転$q_{modify}$を求めて、現在の回転に合成することですね。
画像と同じく、上方向をVector3.upとしたときの説明を行います。
まず、上方向ベクトル(Vector3.up)に直行するベクトル(図の細い赤線)を求めます。これは上方向ベクトルと向きたい方向のベクトル(図の細い青線)の外積を用いることで、求められます。
次に、回転後の緑軸(図の細い緑線)を求めます。これも同様に、外積を用いることで計算できます。先ほど求めた上方向ベクトルに直行するベクトル(図の細い赤線)と、向きたい方向のベクトル(図の細い青線)の外積を計算すれば求められますね。
最後に、FromToRotationを用いた回転後の緑軸から、今求めた細い緑線への回転を求めて、回転を合成することで目的の処理の実装ができます。
(実装には、Quaternion × Vector3 の乗算と、QuaternionをUnityEngine.Quaternionへ暗黙的に変換する処理を用いています。この2つは、operatorの項目で実装します。)
ToAngleAxis()メソッド
クォータニオンから、軸ベクトルと回転量を取り出す関数になります。AngleAxisと逆の動作ですね。
実装としては、現在のクォータニオンの成分から、最初に回転量 $θ$ を求めてから、定義に従って計算してあげれば良さそうですね。
// 回転を座標に対する角度の値(AngleAxis)に変換する
public void ToAngleAxis(out float angle, out Vector3 axis)
{
// クォータニオンの定義, cos(rad/2) = w より
float rad = Mathf.Acos(w) * 2.0f;
angle = rad * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
// x = axis.x * sin(rad/2),
// y = axis.y * sin(rad/2),
// z = axis.z * sin(rad/2) より
axis = new Vector3(
this.x / Mathf.Sin(rad / 2),
this.y / Mathf.Sin(rad / 2),
this.z / Mathf.Sin(rad / 2));
}
ToString()メソッド
クォータニオンの値を見やすくした文字列を返します。
ToStringメソッドをオーバーライドすることで実装します。
public override string ToString()
{
string format = "F5";
return $"({x.ToString(format)}, {y.ToString(format)}, {z.ToString(format)}, {w.ToString(format)})";
}
Static関数
Inverse()メソッド
逆の回転を意味する逆(共役)クォータニオンを求めます。
回転の中心となる軸を反転させることで、回転を逆にできます。軸ベクトルを表す成分である$(x,y,z)$に対して、マイナスをかけてあげれば良さそうですね。
// rotationの逆(共役)クォータニオンを返す
public static Quaternion Inverse(Quaternion rotation)
{
return new Quaternion(-rotation.x, -rotation.y, -rotation.z, rotation.w);
}
RotateTowards()メソッド
FromToRotationとは違って、第3引数に最大回転角度(maxDegreesDelta)を持ちます。
// fromからtoへの回転を得る(Unityの実装を引用)
public static Quaternion RotateTowards(Quaternion from, Quaternion to, float maxDegreesDelta)
{
float num = Angle(from, to);
if (num == 0f)
{
return to;
}
return Slerp(from, to, Mathf.Min(1f, maxDegreesDelta / num));
}
2つのクォータニオンの間の角度が0度ならば、すでに目的の回転$q_{to}$に到達しているので$q_{to}$を返します。
Slerpメソッド(球面線形補間)については以降で実装をしています。
Lerp() / LerpUnclamped()メソッド
2つのクォータニオンを直線経路で線形補間するのがLerpメソッドになります。回転$q_a$から回転$q_b$に移動させたい時、移動の割合$t$を[0, 1]の範囲で指定して、その時点での回転を返してくれます。以下のように、2つのクォータニオンの間の回転を補間して、計算することができます。
直線での線形補間については、
(1-t)q_a + tq_b
という式で実装できます。これは、$θ$が非常に小さい時の近似式なので、$θ$が大きい場合は後述のSlerpを用いた方が高い精度で補間できます。しかしながら、Slerpよりも計算量が少なくて済むという利点もあります。
実装してみましょう。
// aとbの間をtで補間して正規化する、tは[0,1]の範囲
public static Quaternion Lerp(Quaternion a, Quaternion b, float t)
{
// tの範囲の制限
t = Mathf.Clamp01(t);
return LerpUnclamped(a, b, t);
}
// aとbの間をtで補間して正規化する、tは[0,1]の範囲にクランプされない
public static Quaternion LerpUnclamped(Quaternion a, Quaternion b, float t)
{
// 2つの回転の内積を求める
float dot = Dot(a, b);
// 内積が負の時、最短距離での補間を得るために片方を負にする
if (dot < 0)
{
b = new Quaternion(-b.x, -b.y, -b.z, -b.w);
dot = -dot;
}
// 直線経路で補完する a*(1-t) + b*t
Quaternion lerp = new Quaternion(
a.x + (-a.x + b.x) * t,
a.y + (-a.y + b.y) * t,
a.z + (-a.z + b.z) * t,
a.w + (-a.w + b.w) * t
);
return lerp.normalized;
}
2つの回転を補間する経路は2つ存在するので、回転の内積が負の時には、最短経路での補間をするために片方のクォータニオンを負にして、内積が正の値になるようにしています。
参考:四元数を用いて方向や回転の補間を行う際の注意点 - yuki-koyama's blog
Slerp() / SlerpUnclamped()メソッド
球面線形補間を行うので、前述のLerpよりも精度の高い補間ができます。
Slerpは、以下の式を用いて実装することができます。
{\begin{array}{c}
\mathbf q =
\frac{\sin (1-t) \theta}{\sin \theta} \mathbf q_a +
\frac{\sin t \theta}{\sin \theta} \mathbf q_b \\
\theta = \cos ^{-1} (\mathbf q_1 \cdotp \mathbf q_2 )
\end{array}}
参考:Quaternionによる3次元の回転変換 #数学 - Qiita
これを用いて実装を行います。
// 球面線形補完を得る、tは[0,1]の範囲
public static Quaternion Slerp(Quaternion a, Quaternion b, float t)
{
// tの範囲の制限
t = Mathf.Clamp01(t);
return SlerpUnclamped(a, b, t);
}
// 球面線形補完を得る、tは[0,1]の範囲にクランプされない
public static Quaternion SlerpUnclamped(Quaternion a, Quaternion b, float t)
{
// 2つの回転の内積を求める
float dot = Dot(a, b);
// 内積が負の時、最短距離での補間を得るために
// 片方の回転を負にして、内積を正の値にする
if (dot < 0)
{
b = new Quaternion(-b.x, -b.y, -b.z, -b.w);
dot = -dot;
}
// 2つの回転の角度を求める
float rad = IsEqualUsingDot(dot) ? 0f : Mathf.Acos(dot);
// 球面線形補完
float bottom = Mathf.Sin(rad);
float a_rate = Mathf.Sin((1 - t) * rad) / bottom;
float b_rate = Mathf.Sin(t * rad) / bottom;
Quaternion slerp = new Quaternion(
a.x * a_rate + b.x * b_rate,
a.y * a_rate + b.y * b_rate,
a.z * a_rate + b.z * b_rate,
a.w * a_rate + b.w * b_rate
);
return slerp.normalized;
}
Lerpの実装と同様に、最短距離での補間を得るために2つのクォータニオンの内積が負の場合には、片方のクォータニオンを負にして、内積が正の値になるようにします。
SlerpとLerpの違い
箇条書きにするとおおよそこのような違いがあると思われます。
Lerp
- 計算量が少なくて済む
- Slerpに比べて精度は劣る($\theta$が非常に小さい場合を除く)
- $t$が1を超えた場合に、同じ回転量で回らない
Slerp
- Lerpに比べて計算量は多い
- 球面補間なので、精度の高い補間ができる
- $t$が1を超えた場合に、同じ回転量で回る
LerpとSlerpの動きの違いについては、下記のサイトで比較してくれているので参考になるかと思います。
キャラの回転の動きを作る【ゲーム開発日記】 - Overtop
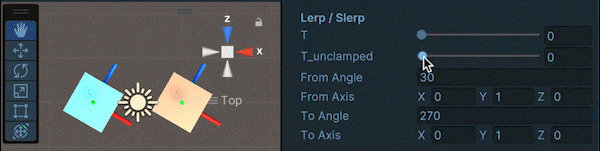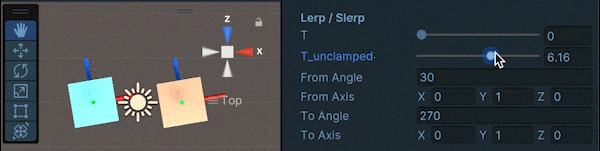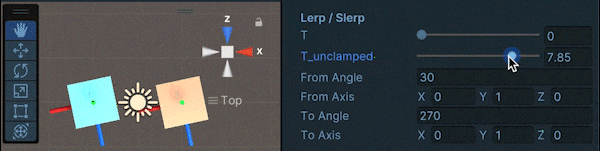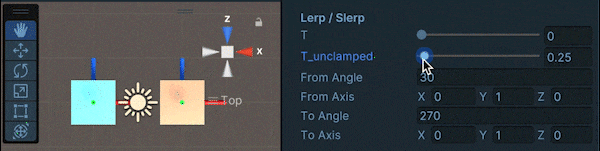
また、Lerpに関して、$t$を[0,1]の範囲に制限しない場合(LerpUnclamped)は以下のように、$t$が1を超えてからはあまり回転しません。

$t$を増加させ続けて、同じような角速度で回転させ続けたい、というような場合はSlerpUnclampedを用いるのが良いです。
Operator
演算子オーバーロードを用いて、クォータニオンを便利に記述できるようにしていきます。
operator ==
4つの成分がそれぞれ等しいかどうかを判定するように実装します。
// 比較(Unityの実装を引用)
public override bool Equals(object other)
{
if (!(other is Quaternion))
{
return false;
}
return Equals((Quaternion)other);
}
public bool Equals(Quaternion other)
{
return x.Equals(other.x) && y.Equals(other.y) && z.Equals(other.z) && w.Equals(other.w);
}
Quaternion × Vector3
クォータニオンを用いると、向きベクトルを回転させることができます。
向きベクトル$v$に対して、回転$q$を適用した後のベクトル$v'$は
$v'=q \times v \times q^{-1}$ となります。これを元に実装を行います。
参考:Quaternion を完全に理解した | VirtualCast Blog
// 演算子オーバーロードを用いて
// Quaternion * Vector3 が計算できるようにする
public static Vector3 operator * (Quaternion q, Vector3 v)
{
// 回転後のベクトルv'について
// v' = q * v * q_inverse となる
// 3次元座標をクォータニオンで表す
Quaternion vecQuaternion = new Quaternion(v.x, v.y, v.z, 0);
// ベクトルに回転を施す
Quaternion vecAfterRotate = q * vecQuaternion * Quaternion.Inverse(q);
// クォータニオンを3次元座標に変換する
return new Vector3(vecAfterRotate.x, vecAfterRotate.y, vecAfterRotate.z);
}
UnityEngine.Quaternionへの暗黙的な変換
自作したQuaternionをUnityのtransform.rotationなどにそのまま代入できるようにします。詳細はC#の暗黒的な型変換を参照してください。
// 暗黙的な型変換演算子の定義
// UnityEngine.Quaternionに自動的に変換して
// transform.rotation = Quaternion; ができるようにする
public static implicit operator UnityEngine.Quaternion(Quaternion q)
{
return new UnityEngine.Quaternion(q.x, q.y, q.z, q.w);
}
まとめ
この記事では、クォータニオンに関して以下の実装を行いました。
- 中心軸と回転量を用いたクォータニオンの定義
- クォータニオンから中心軸と回転量を取り出す
- オイラー角とクォータニオンの相互変換
- クォータニオン同士の乗算
- クォータニオンの内積
- 逆クォータニオン、単位(恒等)クォータニオン
- 2つのクォータニオン間の角度を求める
- 1つのVector3からもう1つのVector3への回転を求める
- クォータニオンを用いた3次元ベクトルの回転
- 2つのクォータニオンの線形補間、球面線形補間
その他参考記事
クォータニオンの概要を理解する際に参考になった記事を貼っておきます。
高校生でもわかりそうだけど、ちゃんと理解もするUnityでのクォータニオン運用法|MetaFormingPro
ゆるめのクォータニオン入門 | NEXTSCAPE with MR
追記
[1]JavaScriptでUnityEngine.Quaternionを実装・再現している方がいらっしゃいました。
こちらも確認しながら学習を進めると参考になるかもしれません。
【四元数】フルスクラッチで実装して分かったクォータニオンのお気持ち #JavaScript - Qiita
[2]書籍 ゲームプログラミングC++ に付属のコード(GitHubにて公開されています)においてもクォータニオンの実装コードがありました.この書籍も参考にすることでより理解が深まるかもしれません.