For those who seek efficiency and ease in everything they do.
So here is one solution for you. Today we are talking about, how to make a APIs call from the your favourite IDE, i.e., Visual Studio Code.
Developers use a lot of URLs: your app URLs, URLs for consumed services, etc. These URLs, and sometimes their payloads may differ per environment. And as a dev you are going to constantly hit them. Developers have relied on utilities outside the IDE to track the URLs, send test payloads to the URLs, and inspect the response. Now you can do all of that from your IDE!
To do this we’ll use the REST Client extension for Visual Studio Code and Dummy Rest API.
Get Started
If you haven't installed the Visual Studio Code then please install.
If you already have Visual Studio Code installed then
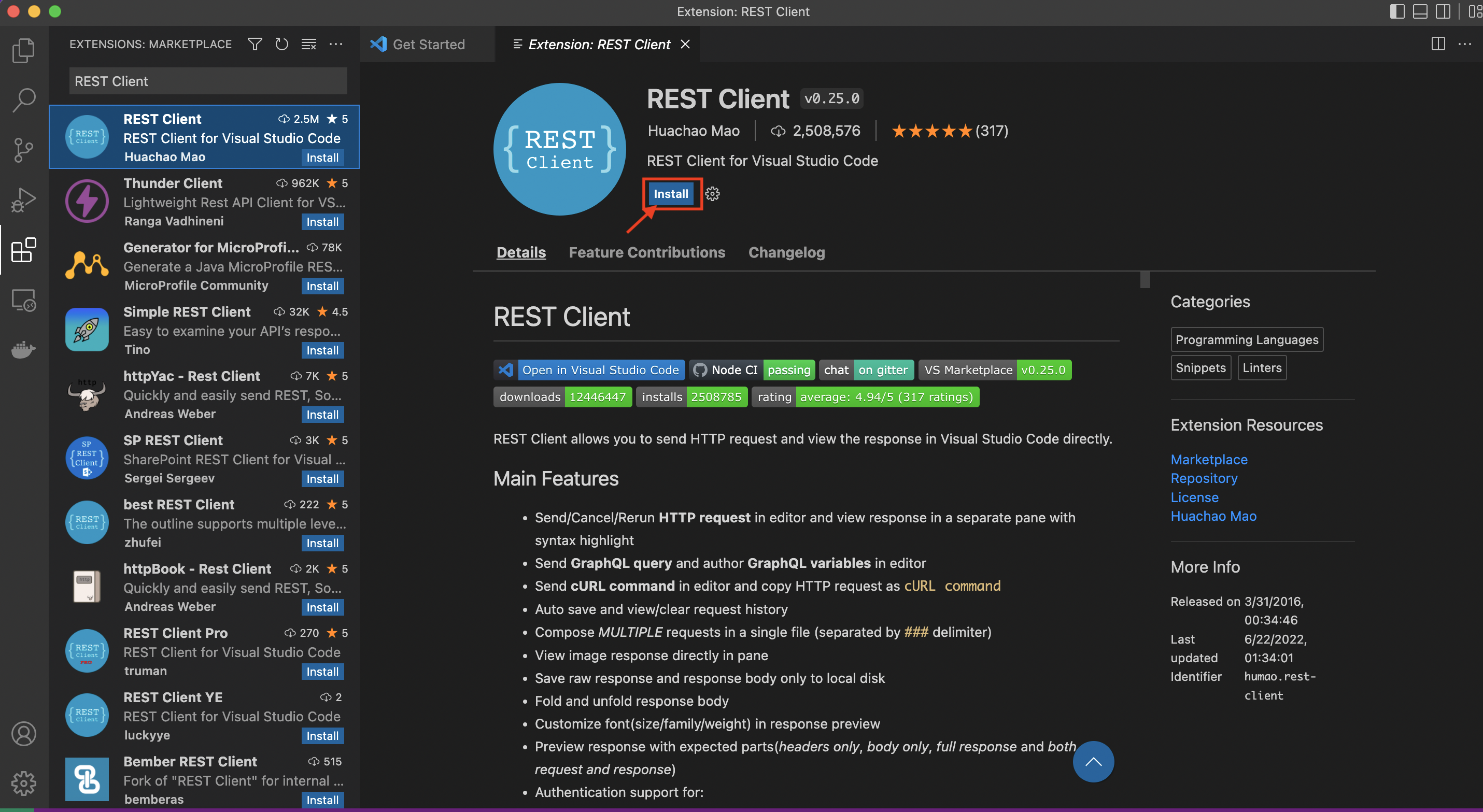
Install the REST Client extension for Visual Studio Code.
Open your VS Code and search for "REST Client".

Click here to Install the extension.
After successfully installed, it looks like below.
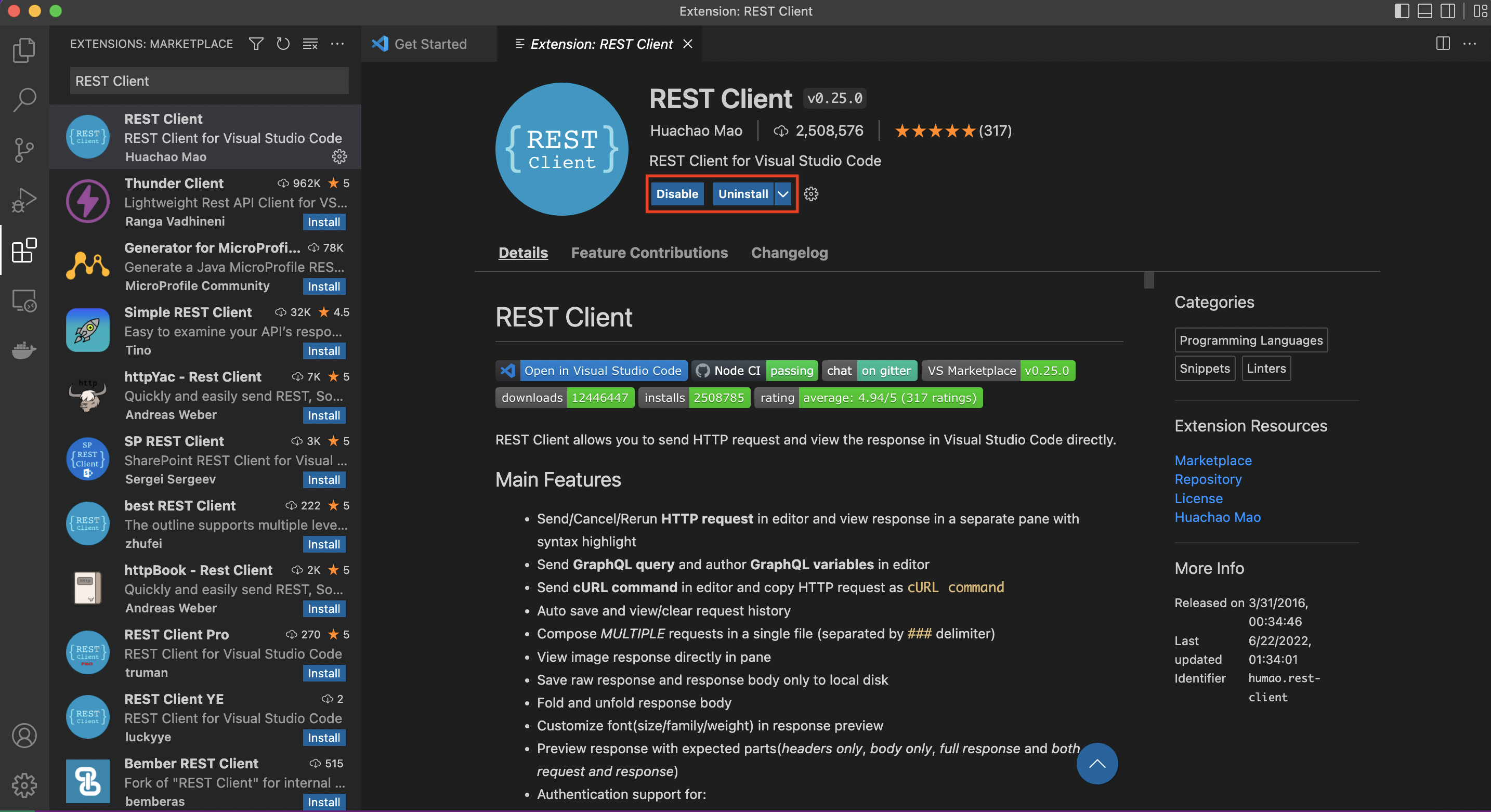
So, you have done with your ENV setup. Great Job![]()
![]()
How to Use 
1st, let's create a new file with the extension ".http" or ".rest". Here I used ".http".
GET
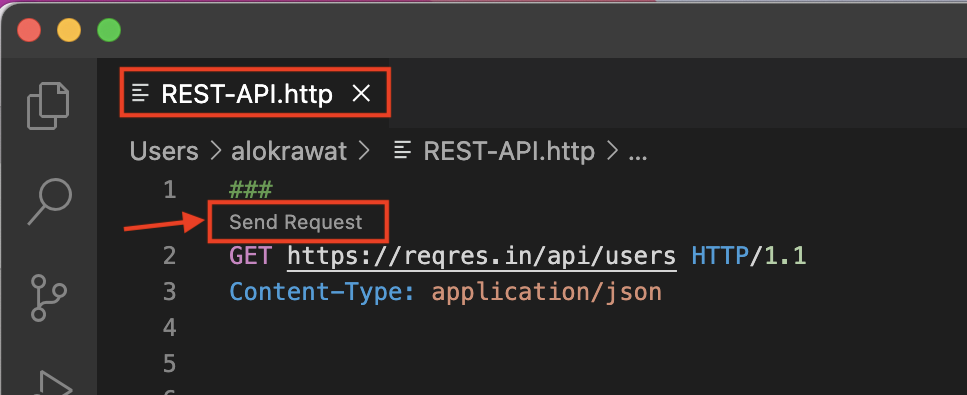
Let's make our first call.
As soon as you save, you’ll see a Send Request button appear right after the ###.
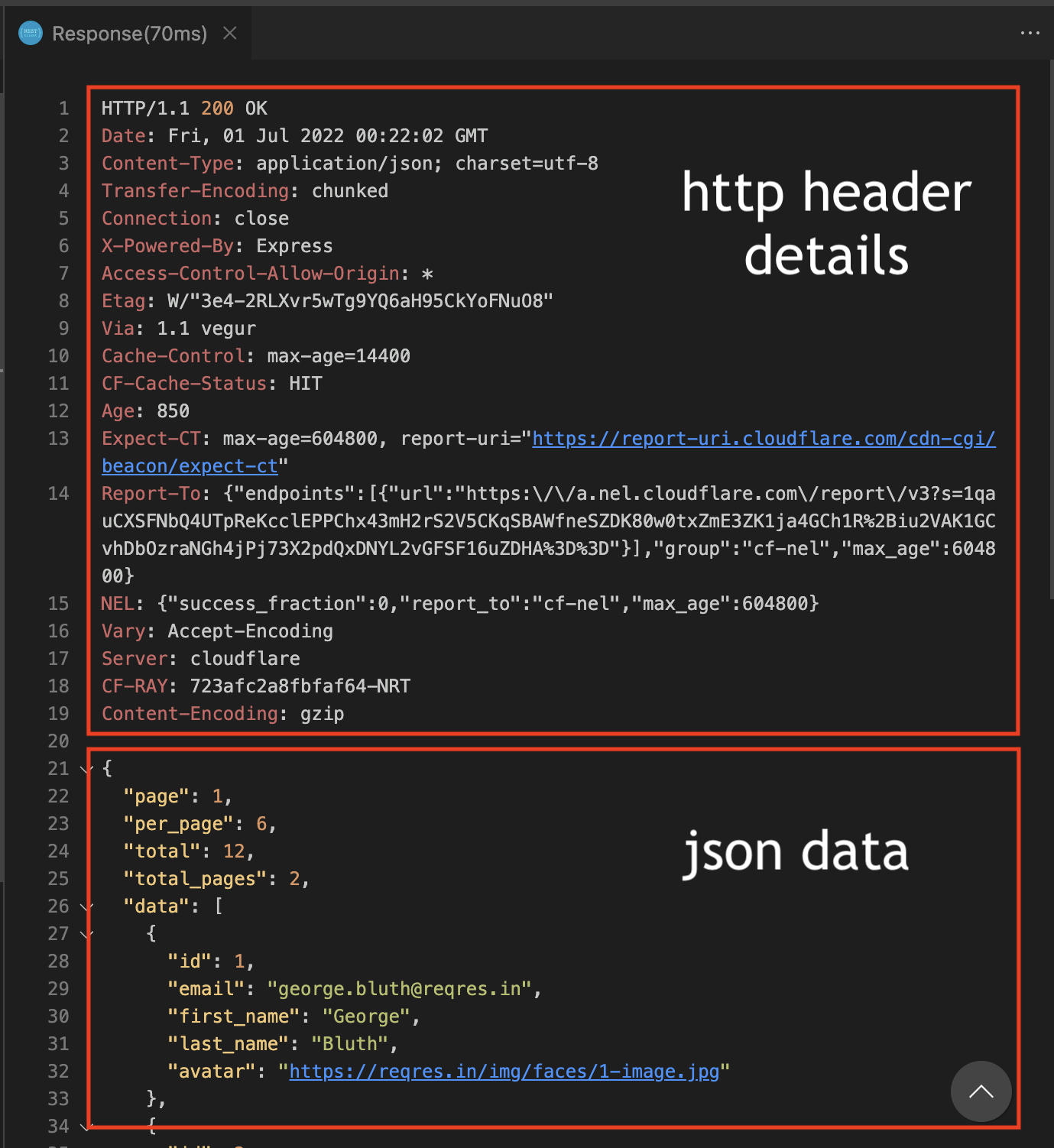
That’s it!![]() No need to open a web browser, debug tools, networking, and then inspect responses- it’s all right there!
No need to open a web browser, debug tools, networking, and then inspect responses- it’s all right there!
Code:
###
Send Request
GET https://reqres.in/api/users/ HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
What is the HTTP 1.1?
HTTP 1.1 is the latest version of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), the World Wide Web application protocol that runs on top of the Internet's TCP/IP suite of protocols. HTTP 1.1 provides faster delivery of Web pages than the original HTTP and reduces Web traffic.
For more details, please visit here
POST
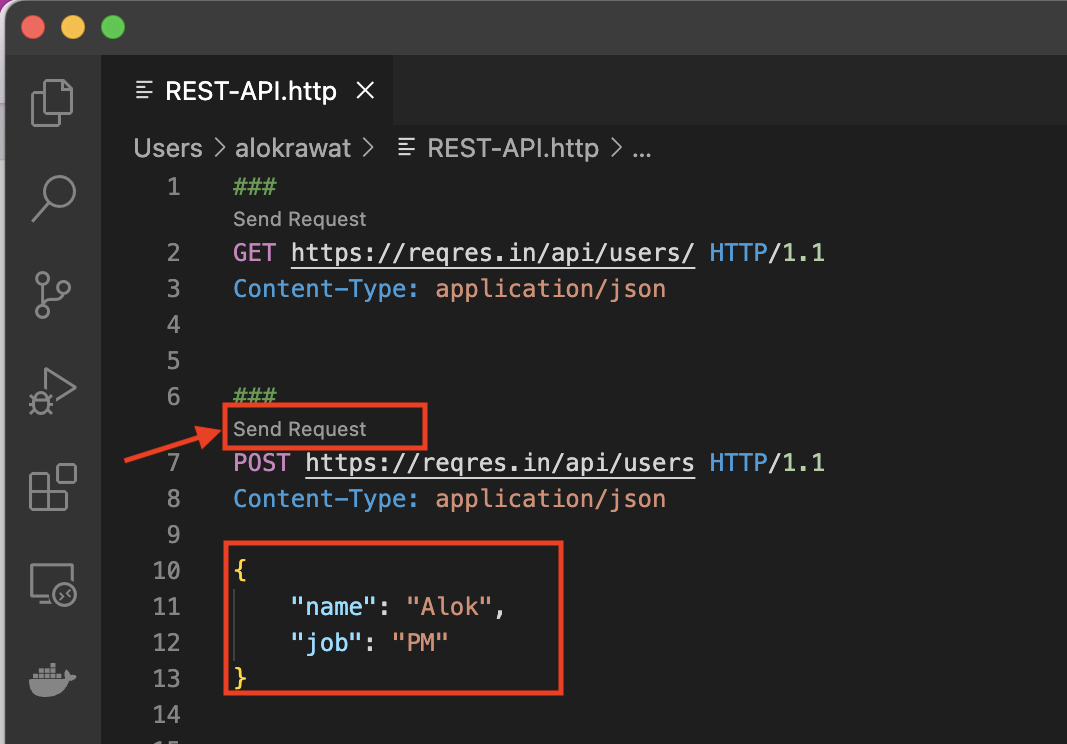
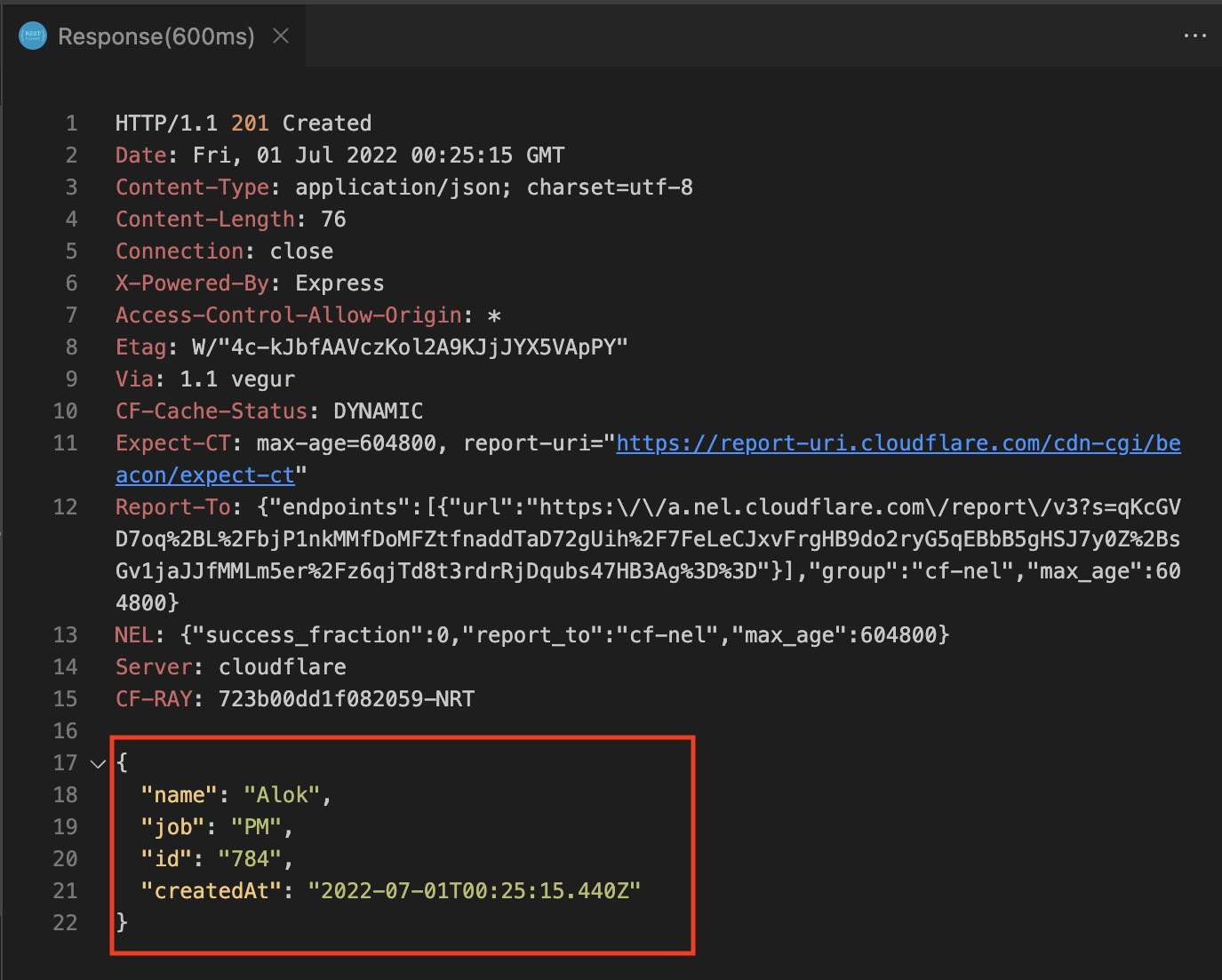
Doing a POST request follows the same pattern but its slightly different as you need to provide the payload and optionally the content-type (along many options in the docs of REST Client like authentication).
Code:
###
Send Request
POST https://reqres.in/api/users HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
{
"name": "Alok",
"job": "PM"
}
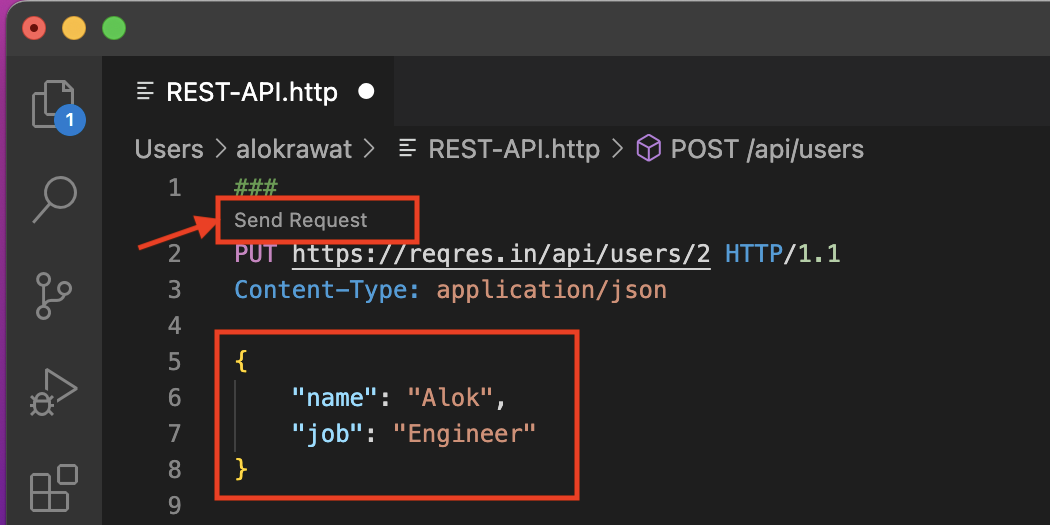
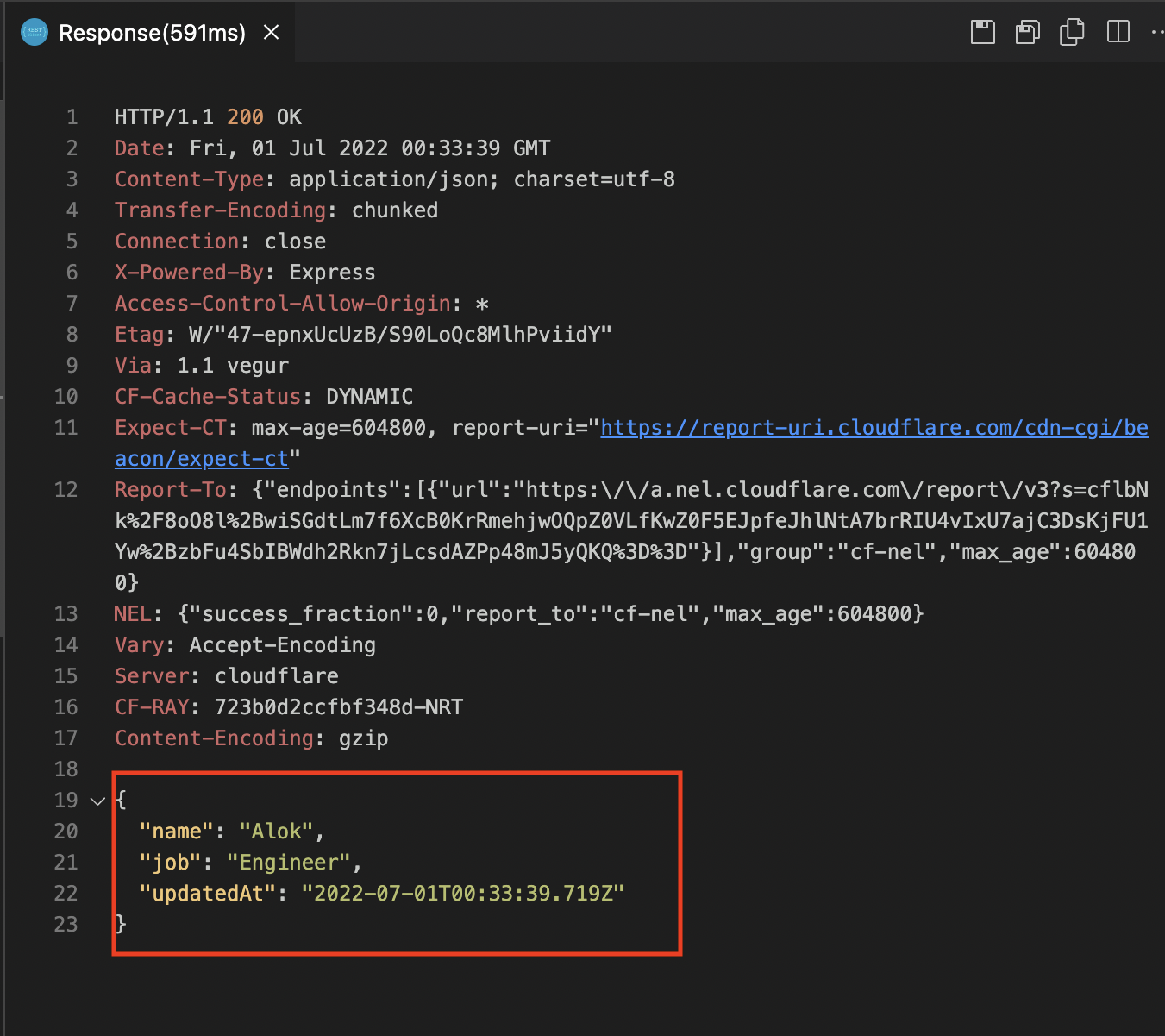
PUT
Code:
###
Send Request
PUT https://reqres.in/api/users/2 HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
{
"name": "Alok",
"job": "Engineer"
}
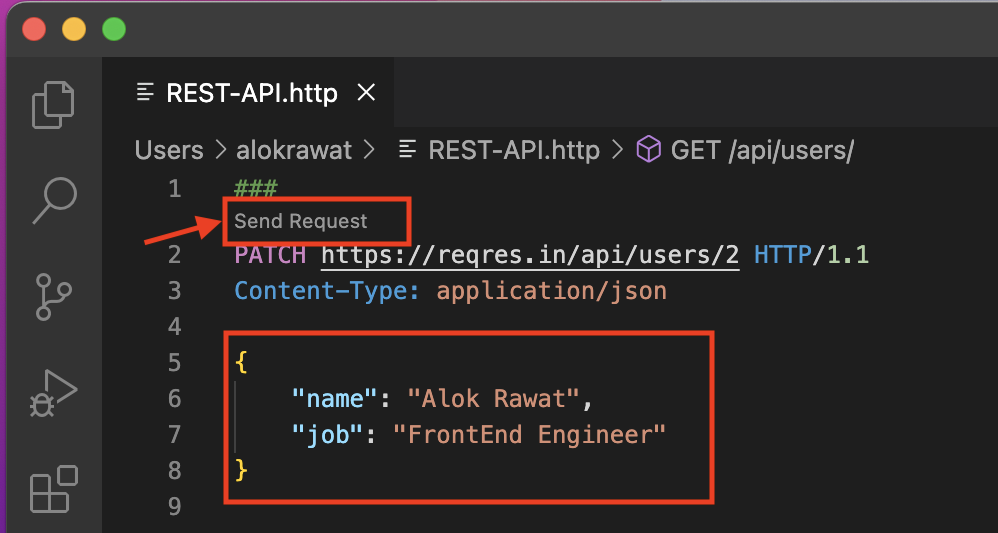
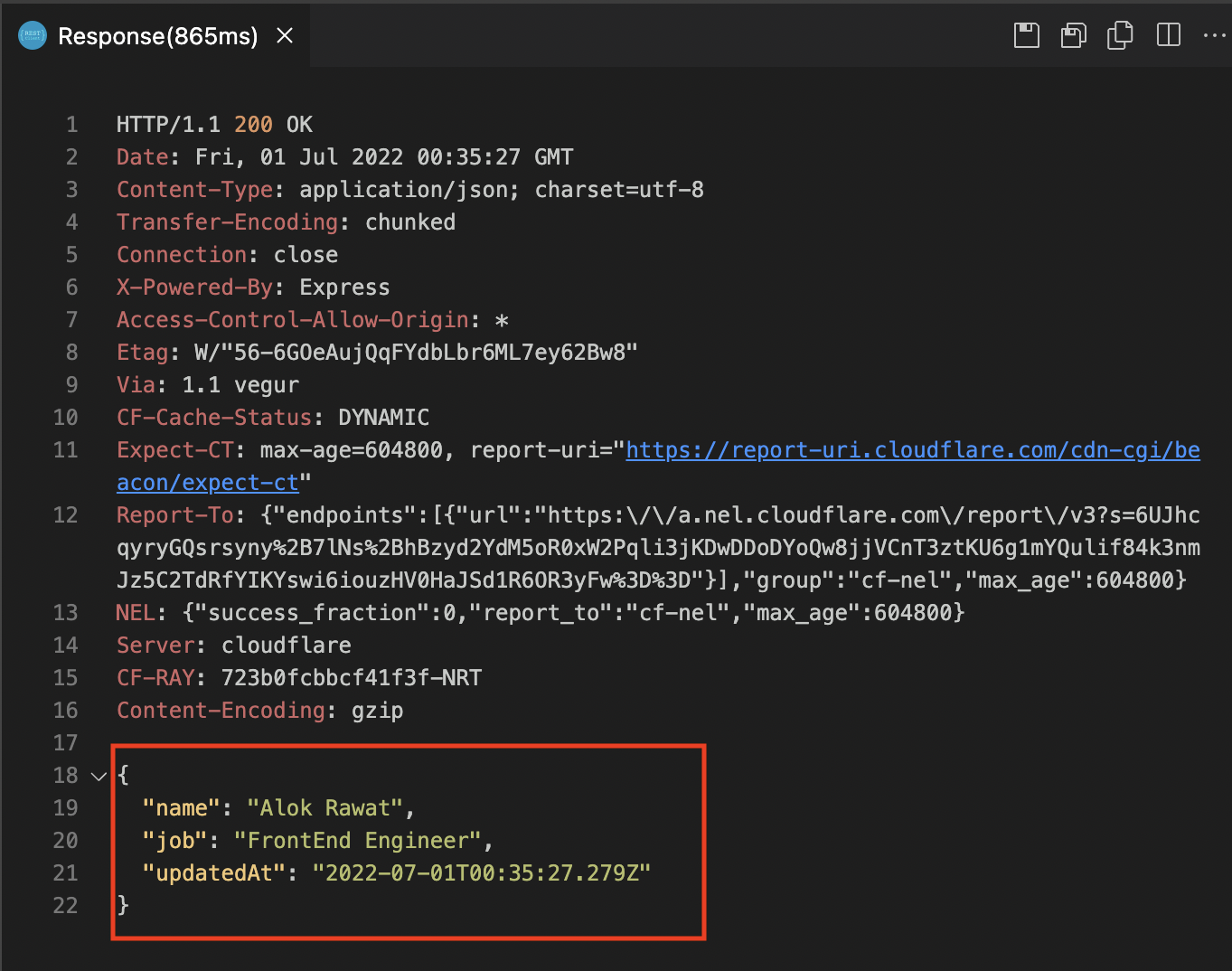
PATCH
Code:
###
Send Request
PATCH https://reqres.in/api/users/2 HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
{
"name": "Alok Rawat",
"job": "FrontEnd Engineer"
}
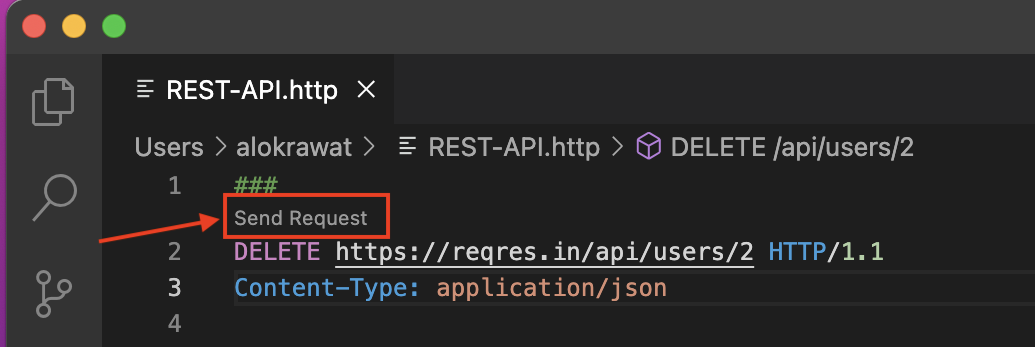
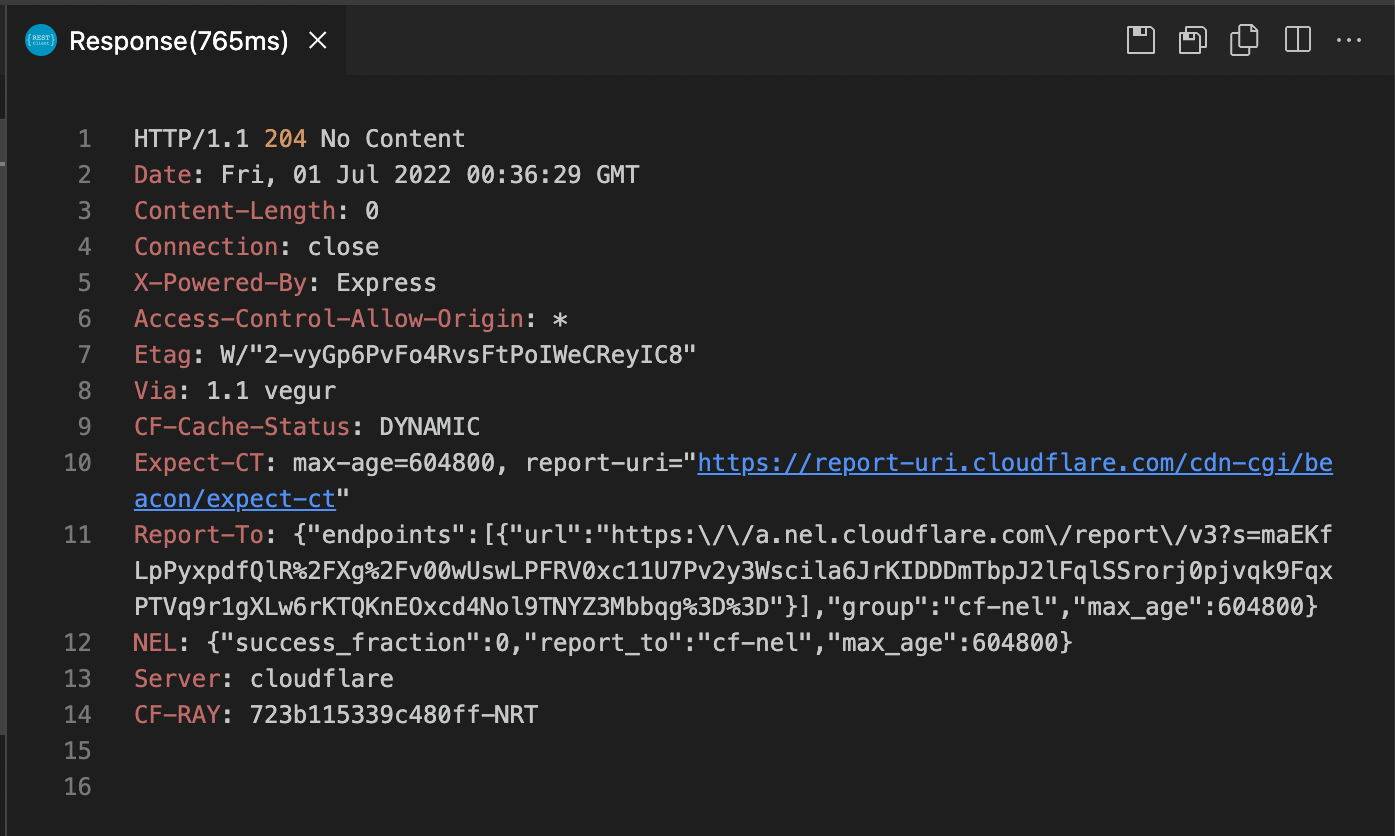
DELETE
Code:
###
Send Request
DELETE https://reqres.in/api/users/2 HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
Final
Why should you use a REST client extension?
In the current time, what we need to keep in mind i.e., speed and ease. Both the things you can find in REST Client Extension.
Besides, if you use an external tool, you will have to alt-tab to it while you develop and any other method you prefer. But with REST Client you only need to know how to use the same IDE you already know and use a lot!
- Stay in the your favorite IDE – stop the context switching.
- Document All URLs your app uses - No more bookmarks or comments in code.
- Store URLs next to your code – Since everything is in simple plain text files, as you change and modify your .http files you’ll be able to easily track the differences.
- Quickly Test URLs – even after a year, you do not need to import/setting up the ENV to send the request. You can simply open the text file and “send request”.
- Inspect Responses As Text Files – use all the tools of VS Code to look through the response: collapse/expand, find, regex.
- Save/Share Responses – No more screenshots of browser dev tools- simply send others the entire response payload.
Enjoy Coding and Happy Learning.
Reference: