この記事はエムスリーキャリア FY22 AdventCalendar20日目の記事です。
はじめに
突然ですが、RailsエンジニアをしているとActiveRecordモデルを継承しないフォームオブジェクトで一対多、しかも子要素をクライアント上で動的に追加・削除するようなフォームを実装したい時もあるかと思います(あるのかな?)
調べてみた所そのような事例が見当たらなかったので(やっぱりなさそう)、自分が見つけた実装方法を記事に残したいと思います。
要件
- クライアント(ブラウザ上)で子要素となるフォーム部分を動的に追加削除できること。
- フォームオブジェクトはActiveRecordのモデルを継承しないこと。
- バリデーションをフォームオブジェクトで実施して、入力値がバリデーションに引っかかった場合は子要素ごとにバリデーションエラーのメッセージが表示できること。(子要素ごとに状態を保持できること)
- フォームの登録時にコントローラーでストロングパラメーターを使用できること。
動的なネストしたフォームといえばcocoonですが、cocoonはActiveRecordで関連付けられたモデルで使用する事を前提としているため、今回のケースでは使用できません。
実装の概要
下記のフォームオブジェクトの値を、アソシエーションにより一体多で関連づけられた別のモデルに移し替えて保存するというシナリオで実装してみました。
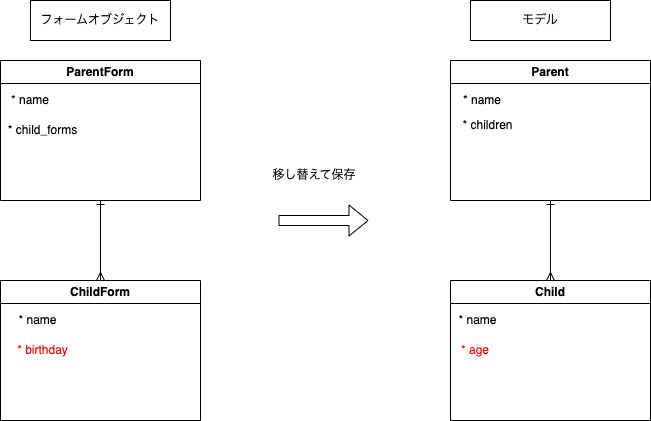
ChildFormがbirthdayとして受け取った値をChildでageとして永続化したいのでフォームオブジェクトはActiveRecordを継承できない。という体です。
Childにbirthdayの属性をもたせてageメソッドとして都度導出すれば良いのですが、あまり良いシチュエーションが思い浮かばず。。。サンプルということでご容赦ください😇
モデル
Parentモデル
class Parent < ApplicationRecord
has_many :children, dependent: :destroy, autosave: true
CHILDREN_MAX_SIZE = 5
end
本筋ではないのですがhas_manyのアソシエーションにautosave: trueを追加して、Parentが保存されたときにChildモデルも保存できるようにしています。
Childモデル
class Child < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :parent
end
belongs_toでアソシエーションを定義しているだけです。
フォームオブジェクト
ParentForm(ネストする側)
module Forms
class ParentForm
include ActiveModel::Model
include ActiveModel::Attributes
attribute :name
attribute :child_forms
validate :presence_name
def initialize(*args)
super(*args)
self.child_forms = [ChildForm.new] if child_forms.blank?
end
def child_forms_attributes=(attributes)
self.child_forms = attributes.map { |_k, v| ChildForm.new(v) }
end
def presence_name
return true if name.present?
errors.add(:presence_name, '名前の入力は必須です')
false
end
def to_parent
parent = Parent.new(name: self.name)
child_forms.each do |child_form|
parent.children.build(name: child_form.name, age: child_form.age)
end
parent
end
end
end
initializeの時にデフォルトのChildFormをセットしています。
これはビュー側の都合で予めChildFormを一つもっておく必要があるからです。
また、child_forms_attributes=メソッドを定義する必要があります。
これもビュー側の都合なのですがParentFormのフォームから受け取ったChildFormの属性値を元にParentFormの属性値としてChildFormのインスタンスを生成しています。
ChildForm(ネストされる側)
module Forms
class ChildForm
include ActiveModel::Model
include ActiveModel::Attributes
attribute :name
attribute :birthday
validate :presence_name
validate :presence_birthday
validate :correct_birthday, if: :presence_birthday
def age
date_format = '%Y%m%d'
(Time.current.strftime(date_format).to_i - Time.zone.parse(birthday).strftime(date_format).to_i) / 10000
end
def presence_name
return true if name.present?
errors.add(:presence_name, '名前の入力は必須です')
false
end
def presence_birthday
return true if birthday.present?
errors.add(:presence_birthday, '生年月日は入力必須です')
false
end
def correct_birthday
return true if Time.zone.parse(birthday) <= Time.current
errors.add(:correct_birthday, '未来の日付は入力できません')
false
end
end
end
特筆すべき所はありません。
強いてあげればbirthdayをageに変換するためのメソッドを定義しているくらいです。
ビュー
新規作成フォーム
%script{ src: 'https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.2.slim.js' }
%h1 新規作成フォーム
= form_with model: @parent_form,
method: :create,
local: true,
url: parents_path,
data: { turbo: false } do |f|
%div{ style: 'margin-bottom: 30px;' }
= f.label :name, '親の名前'
= f.text_field :name
%span= @parent_form.errors[:presence_name].first
#child-forms{ data: { 'max-size' => Parent::CHILDREN_MAX_SIZE, 'initial-size' => @parent_form.child_forms.size } }
= f.fields_for :child_forms do |cf|
.child-form{ style: 'margin-bottom: 30px;' }
%div{ style: 'margin-bottom: 10px;' }
= cf.label :name, '子の名前'
= cf.text_field :name,
value: cf.object.name
%span.child-form-error= cf.object.errors[:presence_name].first
%div{ style: 'margin-bottom: 10px;' }
= cf.label :name, '子の生年月日'
= cf.date_field :birthday,
value: cf.object.birthday
%span.child-form-error= cf.object.errors[:presence_birthday].first
%span.child-form-error= cf.object.errors[:correct_birthday].first
%div.child-form-buttons{ style: 'margin-bottom: 10px;' }
%span.add-form-button 日程を追加
%span.delete-form-button 日程を削除
%div
= f.submit '登録',
data: { disable_with: '送信中です' }
%div
= link_to '戻る', parents_path, data: { turbo: false }
:javascript
$(function () {
let currentIndex = $('#child-forms').data('initial-size') - 1;
const maxIndex = $('#child-forms').data('max-size') - 1;
const minIndex = 0;
const allChildForms = () => { return $('#child-forms').find('.child-form') }
function setIndex(index, element) {
['name', 'id'].forEach(attribute => {
element.attr(attribute, element.attr('name').replace(/\d{1}/, index))
})
}
function newChildForm(index) {
const newForm = allChildForms().last().clone()
$('input', newForm).each((i, element) => {
setIndex(index, $(element))
$(element).val('')
})
$('.child-form-error', newForm).text('')
return newForm
}
function resetButton() {
const forms = allChildForms()
forms.each((index, form) => {
// フォームがひとつだけ
if(forms.length === 1) {
$('.add-form-button', form).show()
$('.delete-form-button', form).hide()
}
// フォームが複数、かつフォームの要素ではない
if(forms.length > 1 && index < currentIndex) {
$('.add-form-button', form).hide()
$('.delete-form-button', form).show()
}
// 最後のフォーム、かつフォームの数が上限値未満
if(forms.length > 1 && index === currentIndex && currentIndex < maxIndex) {
$('.add-form-button', form).show()
$('.delete-form-button', form).show()
}
// 要素数が上限値、かつ最後のフォーム
if(index === maxIndex) {
$('.add-form-button', form).hide()
$('.delete-form-button', form).show()
}
})
}
function alignmentIndex() {
const forms = allChildForms()
forms.each((index, form) => {
$('input', form).each((i, element) => {
setIndex(index, $(element))
})
})
}
$(document).on('click', '.add-form-button', function() {
if(currentIndex >= maxIndex) return;
currentIndex++
$('#child-forms').append(newChildForm(currentIndex))
resetButton()
})
$(document).on('click', '.delete-form-button', function() {
if(currentIndex <= minIndex) return
currentIndex--
$(this).closest('.child-form').remove()
alignmentIndex()
resetButton()
})
// 初期表示、ブラウザバック
$(window).on('pageshow', function(){
resetButton()
})
})
今回はHamlとJQueryで簡単に実装しました。
form_withのf.fields_for :child_formsを用いてParentForm経由でChildFormの属性値を入力します。
#child-forms{ data: { 'max-size' => Parent::CHILDREN_MAX_SIZE, 'initial-size' => @parent_form.child_forms.size } }
= f.fields_for :child_forms do |cf|
ParentFormインスタンスのchild_formsの要素数だけ子要素のフォームを表示するため、初期化の段階でChildFormのインスタンスを保持しておく必要がありました。
また、バリデーションに引っかかった時に前回入力時の値の保持とエラーメッセージを表示する必要があるのですがcf.object.XXXとすることでChildFormインスタンスの値にアクセスしています。
動的な子要素の追加・削除の処理は泥臭くJQueryで実装しています😇
function setIndex(index, element) {
['name', 'id'].forEach(attribute => {
element.attr(attribute, element.attr('name').replace(/\d{1}/, index))
})
}
ブラウザの操作で生成したフォームの値をPOSTした時に、フォームオブジェクトの子要素として認識してもらうために、
フォームの追加処理では元のフォームをコピーしてインデックスの部分を置換しています。
コントローラー
class ParentsController < ApplicationController
skip_before_action :verify_authenticity_token
def index
@parents = Parent.all
end
def show
@parent = Parent.find(params[:id])
end
def new
@parent_form = Forms::ParentForm.new
end
def create
@parent_form = Forms::ParentForm.new(parent_form_params)
@child_forms = @parent_form.child_forms
unless[@parent_form, *@child_forms].map(&:valid?).all?
return render({ action: :new, status: :unprocessable_entity }, notice: '登録できませんでした')
end
parent = @parent_form.to_parent
parent.save!
redirect_to action: :show, id: parent.id
end
def destroy
parent = Parent.find(params[:id])
parent.destroy!
redirect_to action: :index
end
private
def parent_form_params
params.require(:forms_parent_form).permit(:name, child_forms_attributes: [:name, :birthday])
end
end
ストロングパラメーターを使用する時にChildFormの属性値をchild_forms_attributes: [:name, :birthday]として定義してあげる必要があります。
例えば子要素のフォームを3つにして、すべて空で送信した場合のパラメーターは下記のようになります。
{
"authenticity_token"=>"[FILTERED]",
"forms_parent_form"=>{
"name"=>"",
"child_forms_attributes"=>{
"0"=>{
"name"=>"",
"birthday"=>""
},
"1"=>{
"name"=>"",
"birthday"=>""
},
"2"=>{
"name"=>"",
"birthday"=>""
}
}
},
"commit"=>"登録"
}
これによりコントローラーに送信された子要素のフォームの入力値をもとにParentForm.child_formsとしてChildFormのインスタンスが生成され、要素ごとにバリデーションのエラーメッセージが表示される様になります。

ActiveRecordモデルとして保存ができるようになりました!

簡素ですが今回のサンプルコードのGithubリポジトリ公開しておきます。
https://github.com/AkitoShiga/rails_sample_nested_form
まとめ
結構手間だったので使えるならcocoon使った方がよいです。
