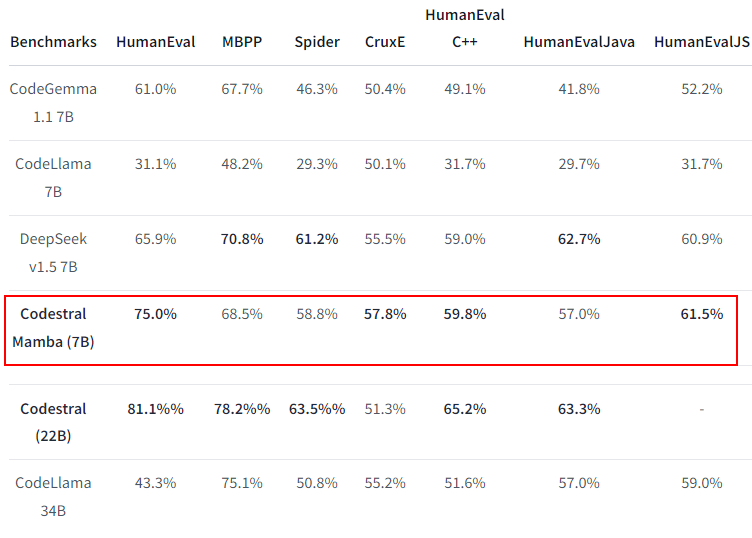
やばいコード生成LLMでてきた
なにがやばいって、7Bクラスで HumanEval 75% ですよ。これは相当な高得点じゃないでしょうか。
このモデルは Transformer モデルではなく Mamba モデルを採用していて、
Transformer ベースの SOTA モデルと同等のパフォーマンスが可能になってそうです。
ということでお試ししてみました。
お試しした環境
CPU: 12世代 i7
RAM: 64GB
OS: Windows(WSL Ubuntu)
GPU:A5000
動画にもまとめました
お試しした内容を動画にもまとめています
パッケージのインストール
pip install mistral_inference
pip install packaging mamba-ssm causal-conv1d transformers
モデルのダウンロード
まずモデルのページにいって、Permissionを得ます
次に以下のように、コードをつかってダウンロードします。
ここでは Windows PC の Dドライブに落としました。
WSLを使っているので /mnt のように指定しています。
mistral_models_path = Path.home().joinpath('/mnt/d/mistral_models', 'mamba-codestral-7B-v0.1')
mistral_models_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
snapshot_download(
repo_id="mistralai/mamba-codestral-7B-v0.1",
local_dir=mistral_models_path,
token="ダウンロード許可を得たユーザーのHuggingFaceのトークンをここにいれる"
)
コンソールチャットを実行
mistral_inference パッケージが仮想環境にインストールされていると、以下のように mistral-chat コマンドが使えるようになります。
モデル名を指定して起動します。
mistral-chat /mnt/d/mistral_models/mamba-codestral-7B-v0.1 --instruct --max_tokens 1024
私の環境では、モデル読み込んでプロンプトでるまで 5分くらいかかりました。
お試しした内容
Pythonプログラムを書くよう命令する
「1から1000までのすべての数の和を計算するPythonプログラムを書きなさい。」
mistral-chat /mnt/d/mistral_models/mamba-codestral-7B-v0.1 --instruct --max_tokens 1024
Prompt: Write a Python program to calculate the sum of all numbers from 1 to 1000.
Here is a simple Python program that calculates the sum of all numbers from 1 to 1000:
```python
sum = 0
for i in range(1, 1001):
sum += i
print(sum)
```
This program uses a for loop to iterate over each number from 1 to 1000. In each iteration, it adds the current number to the sum. After the loop finishes, it prints the sum.
=====================
1から100までのすべての偶数を表示するPython関数を作りなさい
Prompt: Create a Python function that prints all even numbers between 1 and 100.
def print_even_numbers():
for i in range(1, 101):
if i % 2 == 0:
print(i)
=====================
「第10項までのフィボナッチ数列を生成するPythonスクリプトを書きなさい。」
Prompt: Write a Python script to generate the Fibonacci sequence up to the 10th term.
def fibonacci(n):
a, b = 0, 1
for i in range(n):
print(a, end=' ')
a, b = b, a + b
fibonacci(10)
=====================
「セ氏から華氏への変換」
Prompt: Create a Python function that converts Celsius to Fahrenheit.
def celsius_to_fahrenheit(celsius):
return (celsius * 9/5) + 32
=====================
「指定された長さのランダムなパスワードを生成するPythonプログラムを書きなさい。」
Prompt: Write a Python program that generates a random password of a specified length.
import string
import random
def generate_password(length):
characters = string.ascii_letters + string.digits + string.punctuation
password = ''.join(random.choice(characters) for _ in range(length))
return password
length = int(input("Enter the length of the password: "))
password = generate_password(length)
print("Generated password:", password)
=====================
「リストの中にある2番目におおきな数字」
Prompt: Implement a Python function that finds the second largest number in a list.
def second_largest(numbers):
numbers = list(set(numbers))
numbers.sort()
return numbers[-2]
# Example usage:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 9]
print(second_largest(numbers)) # Output: 8
=====================
コードを補完させる
Prompt: def reverse_string(s):
def reverse_string(s):
return s[::-1]
# Example usage:
s = "Hello, World!"
print(reverse_string(s)) # Output: "!dlroW ,olleH"
=====================
Prompt: def calculate_average(numbers):
def calculate_average(numbers):
return sum(numbers) / len(numbers)
# Example usage:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print(calculate_average(numbers)) # Output: 3.0
=====================
Prompt: def flatten_list(nested_list):
def flatten_list(nested_list):
flat_list = []
for sublist in nested_list:
for item in sublist:
flat_list.append(item)
return flat_list
# Example usage:
nested_list = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
print(flatten_list(nested_list)) # Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
=====================
Prompt: def calculate_bmi(weight,height):
def calculate_bmi(weight, height):
bmi = weight / (height ** 2)
return bmi
# Example usage:
weight = 70
height = 1.75
print(calculate_bmi(weight, height)) # Output: 23.157894736842106
=====================
Prompt: Write Python code to create an interactive chat using the Mistral LLM. The code should allow users to input messages and receive responses from the Mistral model in a continuous conversation loop.
To create an interactive chat using the Mistral LLM, you will need to install the `mistralai` package and provide your API key. You can install the package using pip:
```
pip install mistralai
```
Then, you can use the following Python code to create an interactive chat:
```python
import os
from mistralai.client import MistralClient
from mistralai.models.chat_completion import ChatMessage
# Set your Mistral API key as an environment variable
os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"] = "your_api_key_here"
# Initialize the Mistral client
client = MistralClient()
# Define the model to use
model = "mistral-medium"
# Initialize an empty list to store the chat history
chat_history = []
# Start the conversation loop
while True:
# Get user input
user_message = input("You: ")
# Add the user message to the chat history
chat_history.append(ChatMessage(role="user", content=user_message))
# Generate the assistant response
response = client.chat(
model=model,
messages=chat_history,
)
# Get the assistant message from the response
assistant_message = response.choices[0].message.content
# Print the assistant message
print("Assistant:", assistant_message)
# Add the assistant message to the chat history
chat_history.append(ChatMessage(role="assistant", content=assistant_message))
```
まとめ
mamba-codestral-7B をファーストルック的にさわってみました。
また分かったことを順次追記していきたいとおもいます。
ひとまず次は、 ChatStream.net にのせて、みんなにさわってもらえるようにしたいな~