今回は、エンドポイントのURLにアクセスしたらローカルのMySQLから情報をとってきてJSON形式で返すシンプルなAPIサーバーを作って行きたいと思います。
データベースは、MySQLを使用して、GoとDBの連携には、GORMを利用します。
GORMの詳細は、公式ドキュメントが詳しいです。
http://doc.gorm.io/
Goのwebフレームワークは、revelを使います。
installなどの初期設定は公式が良いです。
https://revel.github.io/tutorial/gettingstarted.html
実行環境
Mac OS Mojave 10.14
go version go1.11.1 darwin/amd64
Revel Version = "0.20.0"
revelを使って新規プロジェクトの生成
$ revel new api-server #$GOPATH内でディレクトリが生成されます
$ revel run -a api-server
ブラウザでlocalhost:9000にアクセスすると、ちゃんとサーバーが起動していることが確認できます。IPアドレスの設定やport番号を変えたいときは、conf/app.confで変更することが可能です。
DBとの接続
revel内では、appフォルダ下にmoldesフォルダを生成して、その中でデータ構造の定義をしていきます。構造体の中の要素は大文字で始めることと、gorm:"column:Description"のようにMySQLにおいて対応するcolumn名を書いておくことに注意します。また、フィールドの型とMySQLのデータの型が一致するようにします。json.RawMessageで型を定義することでjson形式のデータも扱うことができます。
package models
import "encoding/json"
type User struct {
Id int `gorm:"column:Id"`
Age int `gorm:"column:Age"`
Name string `gorm:"column:Name"`
Description string `gorm:"column:Description"`
SiblingInfo json.RawMessage `gorm:"column:SiblingInfo"`
}
デフォルトでは、構造体名の複数形がDB側のtable名になるので、MySQL側でデータを作るときは気をつけてください。MySQLでのDB構造は次の通りです。
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Users;
CREATE TABLE Users (
Id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment,
Age INT,
Name VARCHAR (255),
Description VARCHAR(255),
SiblingInfo json
);
INSERT Users (Age, Name, Description, SiblingInfo) values (22, "suzuki", "ダミーデータ1", '[{"sibling":"brother", "name":"akito"},{"sibling":"sister", "name":"ayaka"}, {"sibling":"brother", "name":"taro"}]');
INSERT Users (Age, Name, Description, SiblingInfo) values (34, "sato", "ダミーデータ2", '[{"sibling":"sister", "name":"kana"},{"sibling":"brother", "name":"ken"}]');
INSERT Users (Age, Name, Description, SiblingInfo) values (45, "kobayashi", "ダミーデータ3", '[{"sibling":"brother", "name":"ryo"}]');
DBとの接続には、gormのパッケージを利用しています。
package controllers
import (
"github.com/jinzhu/gorm"
_ "github.com/jinzhu/gorm/dialects/mysql"
)
var DB *gorm.DB
func InitDB() {
DBMS := "mysql"
USER := "root"
PASS := ""
PROTOCOL := "tcp(localhost)" //tcp(##.###.##.###:3306)
DBNAME := "GoApiServer"
CONNECT := USER+":"+PASS+"@"+PROTOCOL+"/"+DBNAME + "?charset=utf8&parseTime=True&loc=Local"
db,err := gorm.Open(DBMS, CONNECT)
if err != nil {
panic(err.Error())
}
db.DB()
DB = db
}
init.goに追記します。
func init() {
revel.Filters = []revel.Filter{
...省略...
}
revel.OnAppStart(controllers.InitDB) // 追記
}
apiをjsonで返す関数を作る
package controllers
import (
"github.com/revel/revel"
"go-api-server/app/models"
)
type UserApi struct {
*revel.Controller
}
type JsonResponse struct {
Response interface{} `json:"response"`
}
func (c UserApi) GetUsers() revel.Result {
Users := []models.User{}
DB.Find(&Users)
response := JsonResponse{}
response.Response = Users
return c.RenderJSON(response)
}
エンドポイントの設定
# UserのAPI
GET /api/v1/users UserApi.GetUsers
エンドポイントにアクセスしてみる
ここまでできたらブラウザでlocalhost:9000/api/v1/usersにアクセスしてみるとjson形式でリスポンスが返ってくると思います。
{
"response": [
{
"Id": 1,
"Age": 22,
"Name": "suzuki",
"Description": "ダミーデータ1",
"SiblingInfo": [
{
"name": "akito",
"sibling": "brother"
},
{
"name": "ayaka",
"sibling": "sister"
},
{
"name": "taro",
"sibling": "brother"
}
]
},
{
"Id": 2,
"Age": 34,
"Name": "sato",
"Description": "ダミーデータ2",
"SiblingInfo": [
{
"name": "kana",
"sibling": "sister"
},
{
"name": "ken",
"sibling": "brother"
}
]
},
{
"Id": 3,
"Age": 45,
"Name": "kobayashi",
"Description": "ダミーデータ3",
"SiblingInfo": [
{
"name": "ryo",
"sibling": "brother"
}
]
}
]
}
特定のIDのユーザー情報をGETする
次に、特定のIDのユーザーを指定して情報を取ってこれるようにしましょう。
新しい関数GetUserを追加します。
func (c UserApi) GetUser() revel.Result {
//int型に変換する
number , _ := strconv.Atoi(c.Params.Get("number"))
Users := []models.User{}
DB.Find(&Users)
response := JsonResponse{}
response.Response = Users[number]
return c.RenderJSON(response)
}
また、confファイルもにエンドポイントを設定します。
# UserのAPI
GET /api/v1/users UserApi.GetUsers
GET /api/v1/user/:number UserApi.GetUser #追加
以上で、URLでIDを指定するとそのユーザーの情報だけをGETすることができます。
ブラウザでlocalhost:9000/api/v1/user/1にアクセスします。
{
"response": {
"Id": 2,
"Age": 34,
"Name": "sato",
"Description": "ダミーデータ2",
"SiblingInfo": [
{
"name": "kana",
"sibling": "sister"
},
{
"name": "ken",
"sibling": "brother"
}
]
}
}
ちゃんとユーザー情報を取れてきていることが確認できます。
ユーザー情報をURLに乗せてGETする
DBにアクセスしてデータを追加できるようにしていきます。
まずは、json型のデータをDBに渡すために、新しくstructを定義します。
type SiblingInfo struct {
Sibling string `json:"sibling"`
Name string `json:"name"`
}
次に、新しいメソッドを追加します。
json.Marshalを使って、struct型のデータ構造をjson.RawMessage型に直します。
func (c UserApi) PostUser(age int, name string, description string, info [][]string) revel.Result {
var TotalNewData = []models.SiblingInfo{}
length := len(info)
fmt.Println(length)
for i := 0; i < length; i++ {
NewData := models.SiblingInfo{
Sibling:info[i][0],
Name:info[i][1],
}
TotalNewData = append(TotalNewData, NewData)
}
//structからjson.RawMessage型に変換
RawData, err := json.Marshal(TotalNewData)
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
}
//挿入するデータの生成
User := models.User{
Age: age,
Name: name,
Description: description,
SiblingInfo: RawData,
}
//DBに追加
DB.NewRecord(User)
DB.Create(&User)
//結果表示用
response := JsonResponse{}
response.Response = User
return c.RenderJSON(response)
}
また、confファイルもにエンドポイントを設定します。
# UserのAPI
GET /api/v1/users UserApi.GetUsers
GET /api/v1/user/:number UserApi.GetUser
GET /api/v1/createUser UserApi.PostUser #追加
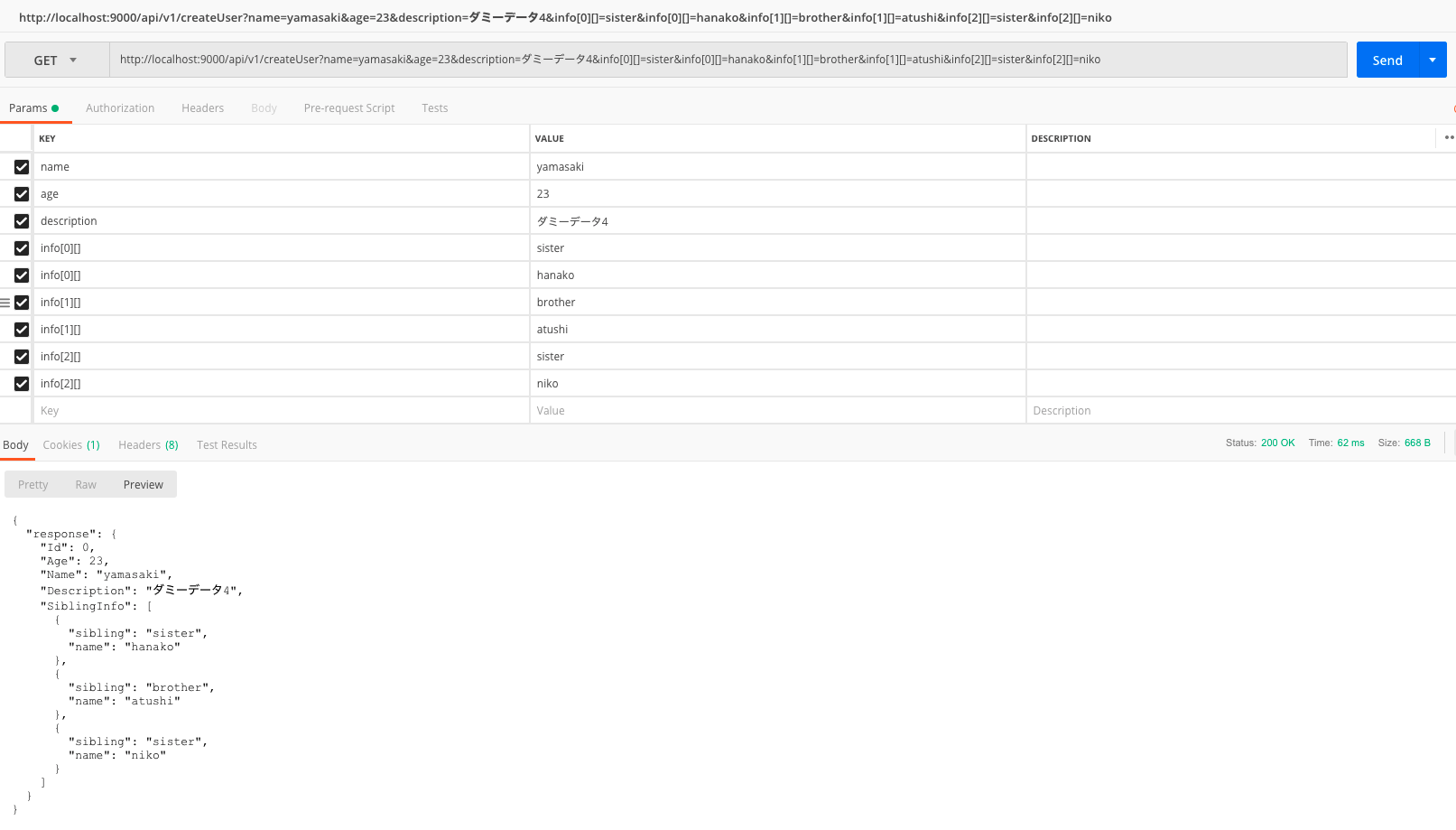
以上で、URLにユーザー情報を乗せて、DB上に新しいデータを追加することができます。
ブラウザでhttp://localhost:9000/api/v1/createUser?name=yamasaki&age=23&description=ダミーデータ4&info[0][]=sister&info[0][]=hanako&info[1][]=brother&info[1][]=atushi&info[2][]=sister&info[2][]=nikoにアクセスします。