やったこと
- One Class SVM を使った外れ値検知
- 乱数使って生成したサンプルデータ(正規分布、混合正規分布)を使用
- Scikit-learnのユーザーガイドにある2.7. Novelty and Outlier Detectionを参考
なお、上記のユーザーガイドのページでは、Robust Covariance Estimator (マハラノビス距離を使った外れ値検知手法、正常データが正規分布に従うことが前提)も紹介されているが今回は割愛。
One-Class SVM
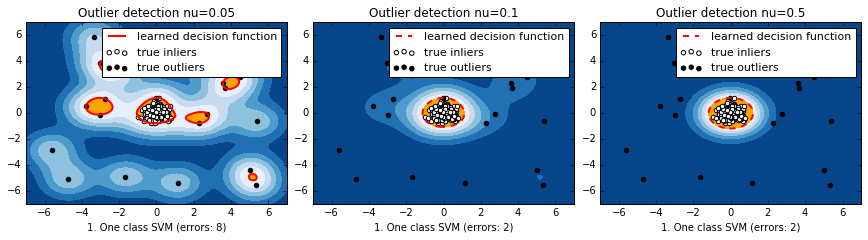
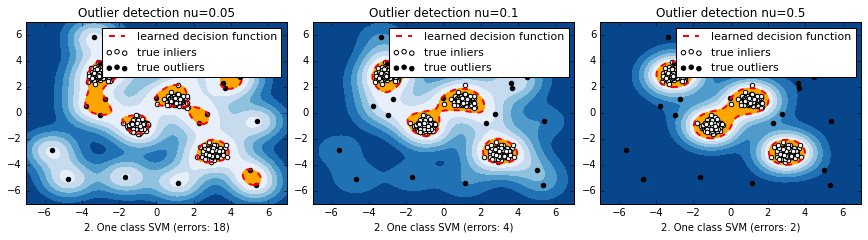
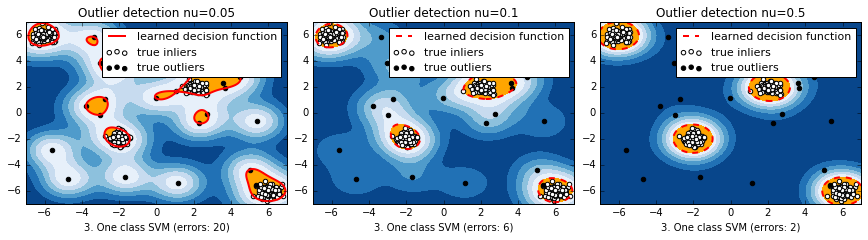
SVM を利用した外れ値検知手法。カーネルを使って特徴空間に写像、元空間上で孤立した点は、特徴空間では原点付近に分布。Kernelはデフォルトのrbfで、異常データの割合を決めるnu(0~1の範囲、def.= 0.5)を変更してみる。
Scikit-learn One Class SVMのObjectのページ
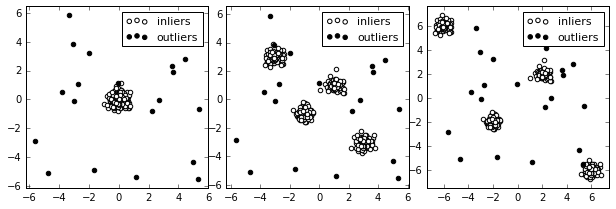
サンプルデータ
正常データが混合正規分布で表されるの3種類のデータセットを用意。一番左は単独の正規分布、右の2つは4つの正規分布の重ねあわせ。異常データは一様分布とした。
結果
マハラノビス距離と違って、元の空間上で離れている分布のそれぞれの塊に対して、識別境界ができている。nuが小さいほど、一つ一つのデータに感度が高くて複雑に、デフォルトの0.5だと非常に単純。
サンプルコード
ユーザーガイドを参考に。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.font_manager
from scipy import stats
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.covariance import EllipticEnvelope
# Example settings
n_samples = 400 # 標本数
outliers_fraction = 0.05 # 全標本数のうち、異常データの割合
clusters_separation = [0, 1, 2]
# 2次元作図用格子状データの生成
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-7, 7, 500), np.linspace(-7, 7, 500))
# 正常データと異常データの生成
n_inliers = int((1. - outliers_fraction) * n_samples) # 正常データの標本数
n_outliers = int(outliers_fraction * n_samples) # 異常データの標本数
ground_truth = np.ones(n_samples, dtype=int) # ラベルデータ
ground_truth[-n_outliers:] = 0
# Fit the problem with varying cluster separation
# [enumerate関数](http://python.civic-apps.com/zip-enumerate/)はインデックスとともにループする
for i, offset in enumerate(clusters_separation):
np.random.seed(42)
# 正常データ生成
X1 = 0.3 * np.random.randn(0.25 * n_inliers, 2) - offset # 正規分布 N(μ= -offset, σ=0.3)
X2 = 0.3 * np.random.randn(0.25 * n_inliers, 2) + offset # 正規分布 N(μ= +offset, σ=0.3)
X3 = np.c_[
0.3 * np.random.randn(0.25 * n_inliers, 1) - 3*offset, # 正規分布 N(μ= -3*offset, σ=0.3)
0.3 * np.random.randn(0.25 * n_inliers, 1) + 3*offset # 正規分布 N(μ= +3*offset, σ=0.3)
]
X4 = np.c_[
0.3 * np.random.randn(0.25 * n_inliers, 1) + 3*offset, # 正規分布 N(μ= +3*offset, σ=0.3)
0.3 * np.random.randn(0.25 * n_inliers, 1) - 3*offset # 正規分布 N(μ= -3*offset, σ=0.3)
]
X = np.r_[X1, X2, X3, X4] # 行で結合
# 外れ値データ生成
X = np.r_[X, np.random.uniform(low=-6, high=6, size=(n_outliers, 2))] # 一様分布 -6 <= X <= +6
# Fit the model with the One-Class SVM
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 12))
# 外れ値検知のツール、1クラスSVMとRobust Covariance Estimator
# classifiers = {
# "One-Class SVM": svm.OneClassSVM(nu=0.95 * outliers_fraction + 0.05,
# kernel="rbf", gamma=0.1),
# "robust covariance estimator": EllipticEnvelope(contamination=.1)} # 共分散推定
nu_l = [0.05, 0.1, 0.5]
for j, nu in enumerate(nu_l):
# clf = svm.OneClassSVM(nu=0.95 * outliers_fraction + 0.05, kernel="rbf", gamma=0.1)
clf = svm.OneClassSVM(nu=nu, kernel="rbf", gamma='auto')
clf.fit(X)
y_pred = clf.decision_function(X).ravel() # 各データの超平面との距離、ravel()で配列を1D化
threshold = stats.scoreatpercentile(y_pred, 100 * outliers_fraction) # パーセンタイルで異常判定の閾値設定
y_pred = y_pred > threshold
n_errors = (y_pred != ground_truth).sum() # 誤判定の数
# plot the levels lines and the points
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) # 格子状に超平面との距離を出力
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
subplot = plt.subplot(3, 3,i*3+j+1)
subplot.set_title("Outlier detection nu=%s" % nu)
# 予測結果
subplot.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=np.linspace(Z.min(), threshold, 7), cmap=plt.cm.Blues_r)
# 超平面
a = subplot.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[threshold], linewidths=2, colors='red')
# 正常範囲
subplot.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=[threshold, Z.max()], colors='orange')
# 正常データ
b = subplot.scatter(X[:-n_outliers, 0], X[:-n_outliers, 1], c='white')
# 異常データ
c = subplot.scatter(X[-n_outliers:, 0], X[-n_outliers:, 1], c='black')
subplot.axis('tight')
subplot.legend(
[a.collections[0], b, c],
['learned decision function', 'true inliers', 'true outliers'],
prop=matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties(size=11))
# subplot.set_xlabel("%d. %s (errors: %d)" % (i + 1, clf_name, n_errors))
subplot.set_xlabel("%d. One class SVM (errors: %d)" % (i+1, n_errors))
subplot.set_xlim((-7, 7))
subplot.set_ylim((-7, 7))
plt.subplots_adjust(0.04, 0.1, 1.2, 0.84, 0.1, 0.26)
plt.show()