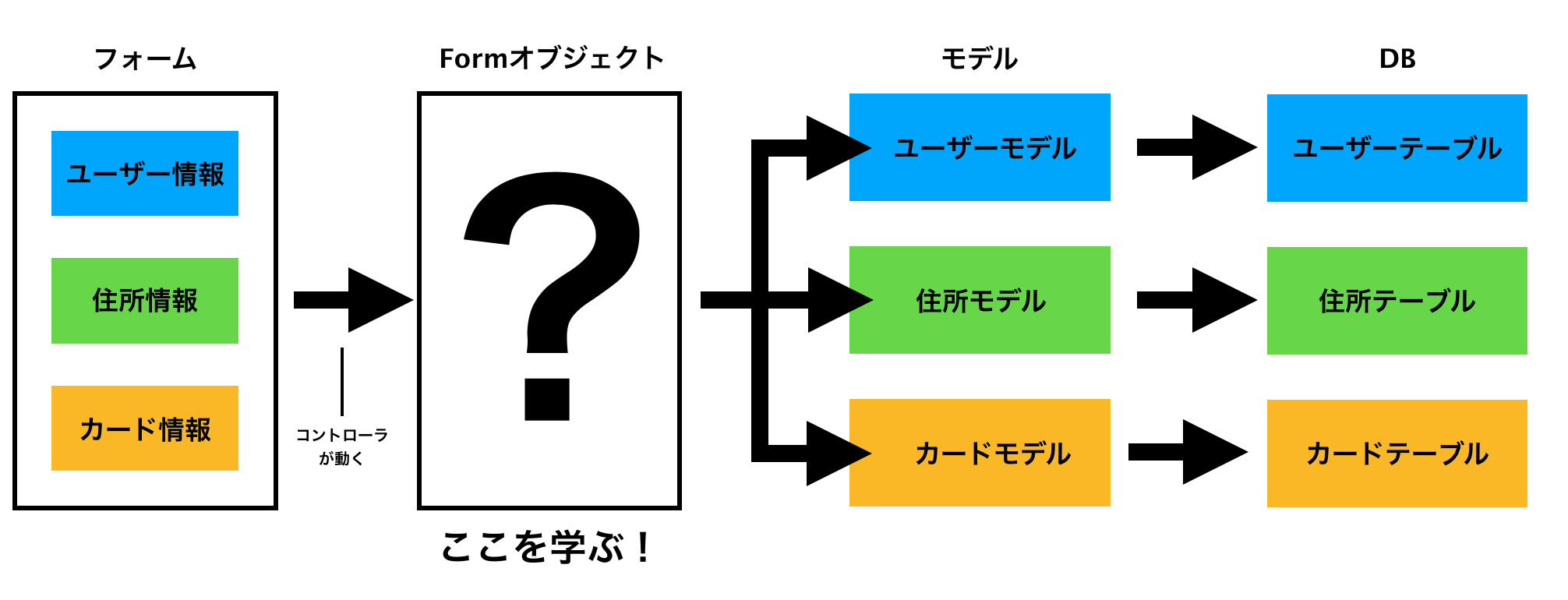
理解するのになかなか苦労しましたがタイトルでも書いてあるとおり、formオブジェクトは複数モデルにまとめて情報の保存・更新などを行う際に用いられるものです。
このように複数モデルを介す必要のあるフォーマットを実装するのにformオブジェクトを使います。
では具体的にformオブジェクト内にはどのような記述が必要か考えていきましょう。
・formオブジェクトを使用するモデルに設定していたバリデーションの移行
・コントローラでformオブジェクトを使えるようにする記述
・モデルを介すための記述
大まかにこの3つが必要になりますね!
では今回はユーザー情報と住所情報を同時に登録するフォーマットを作成していきます。
※deviseを使用しないため、簡易的になっておりますのでご了承を
1-アプリの骨格を作る
1. アプリの骨格を作る
以下コマンドを実行% rails _6.0.0_ new format_app -d mysql
% cd format_app
% rails db:create
その後、ローカルホストに接続してrails初期画面に接続できるかチェックしておきましょう
MVCなどの設定・作成
コントローラの作成とルーティングの設定
コントローラの作成 % rails g controller formats index
ルーティングの設定
Rails.application.routes.draw do
root 'formats#index'
resources :formats, only: [:index, :new, :create]
end
コントローラのアクション設定
まずはユーザー登録・閲覧だけできるようにします
class FormatsController < ApplicationController
def index
@formats = User.all
end
def new
@format = User.new
end
def create
@format = User.create(format_params)
redirect_to root_path
end
private
def format_params
params.require(:user).permit(:name, :name_kana, :nickname)
end
end
モデル・マイグレーションの作成
% rails g model user
% rails g model address
マイグレーションファイルの設定
XXXXXXXXXX_create_user.rb
class CreateUsers < ActiveRecord::Migration[6.0]
def change
create_table :users do |t|
t.string :name, null: false
t.string :name_kana, null: false
t.string :nickname, null: false
t.timestamps
end
end
end
XXXXXXXXXX_create_address.rb
class CreateAddresses < ActiveRecord::Migration[6.0]
def change
create_table :addresses do |t|
t.string :postal_code, default: "", null: false
t.integer :prefecture_id, null: false
t.string :city, default: ""
t.string :house_number, default: ""
t.string :building_name, default: ""
t.references :user, null: false, foreign_key: true
t.timestamps
end
end
end
モデルの設定
user.rb
・アソシエーションの設定
-> userモデル親にして、addressモデルを子にする
・バリデーションの設定
-> 値が空になるのを防ぐ
-> 名前は漢字・ひらがな・カタカナのみ
-> フリガナはカタカナのみ
-> ニックネームは半角英数字のみ
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_one :address
with_options presence: true do
validates :name, format: {with:/\A[ぁ-んァ-ン一-龥]/, message: "is invalid. Please input full-width characters."}
validates :name_kana, format: {with:/\A[ァ-ヶー-]+\z/, message: "is invalid. Please input full-width katakana characters."}
validates :nickname, format: {with:/\A[a-z0-9]+\z/i, message: "is invalid. Please input half-width characters."}
end
end
address.rb
・アソシエーションの設定
-> userモデル親にして、addressモデルを子にする
class Address < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :user
end
ビューファイルの作成
まずはユーザ情報だけ登録・閲覧できるようにします。<div class="wrapper">
<div class="btn">
<%= link_to '登録する', new_format_path %>
</div>
<div class="formats">
<% @formats.each do |format| %>
<div class="format">
<div class="format-name"><%= format.name %>/<%= format.name_kana %>/<%= format.nickname %></div>
</div>
<% end %>
</div>
</div>
ユーザー情報だけ登録できるようなフォーマットを作成する
<%= form_with(model: @format, url: formats_path, local: true) do |form| %>
<h1>ユーザー名を入力</h1>
<div class="field">
<%= form.label :name, "名前(全角)" %>
<%= form.text_field :name %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= form.label :name_kana, "フリカナ(全角カタカナ)" %>
<%= form.text_field :name_kana %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= form.label :nickname, "ニックネーム(半角英数)" %>
<%= form.text_field :nickname %>
</div>
<div class="actions">
<%= form.submit "登録する" %>
</div>
<% end %>
2. formオブジェクト着手
# 2-formオブジェクト着手 さて本題はここからですね。まずは必要なファイルなどの作成をしていきましょう。 app内にformsディレクトリーを作り、その中にuser_address.rbを生成します% mkdir app/forms
% touch app/forms/user_address.rb
その後ファイル名と同じクラス名を中に定義します
class UserAddress
end
formオブジェクトを利用する際は、上記で生成したファイル内にActiveModel::Modelという記述を組み込みます。これにより、user_address.rbがモデルのような働きをしてくれるようになります。以下参照。
class UserAddress
include ActiveModel::Model
end
これでこのファイルが擬似的なモデルとなりました。
続いてこのファイルで参照・更新がかけられる値を設定していきます。
先ほどのユーザー登録時に必要だった値は
:name, :name_kana, :nickname でした。
そして、さらに住所登録も行いたいため以下の値を追加します。
郵便番号(:postal_code), 都道府県(:prefecture_id), 市町村(:city), 番地(:house_number), 建物名(:building_name)
ということでattr_accessorを使ってインスタンス変数の中身を参照・変更できるような記述をします。
class UserAddress
include ActiveModel::Model
attr_accessor :name, :name_kana, :nickname, :postal_code, :prefecture_id, :city, :house_number, :building_name
end
続いてはformオブジェクト(user_address.rb)内にユーザーモデルと住所モデルのバリデーションをまとめてしまいます。これを行う理由は管理のしやすさや可読性を上げるためです。
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_one :address
# ---------- ここから -------------
with_options presence: true do
validates :name, format: {with:/\A[ぁ-んァ-ン一-龥]/, message: "is invalid. Please input full-width characters."}
validates :name_kana, format: {with:/\A[ァ-ヶー-]+\z/, message: "is invalid. Please input full-width katakana characters."}
validates :nickname, format: {with:/\A[a-z0-9]+\z/i, message: "is invalid. Input half-width characters."}
end
# ------- ここまで切り取り ----------
end
class UserAddress
include ActiveModel::Model
attr_accessor :name, :name_kana, :nickname, :postal_code, :prefecture_id, :city, :house_number, :building_name
# ----- 切り取った部分の貼り付け ここから -----
with_options presence: true do
validates :name, format: {with:/\A[ぁ-んァ-ン一-龥]/, message: "is invalid. Please input full-width characters."}
validates :name_kana, format: {with:/\A[ァ-ヶー-]+\z/, message: "is invalid. Please input full-width katakana characters."}
validates :nickname, format: {with:/\A[a-z0-9]+\z/i, message: "is invalid. Input half-width characters."}
end
# ----- 切り取った部分の貼り付け ここまで -----
end
そしてさらに住所モデルのバリデーションを追記していきます。
今回の注意点は
・ 郵便番号は数字のみ、3桁、ハイフン、4桁の順でのみ登録ができる仕様にする
・ 都道府県はactive_hashを使って、都道府県を選択しないと登録できないようにする
active_hashについてはあまり触れないので、他の記事など参考ください。
class UserAddress
include ActiveModel::Model
attr_accessor :name, :name_kana, :nickname, :postal_code, :prefecture_id, :city, :house_number, :building_name
with_options presence: true do
validates :name, format: {with:/\A[ぁ-んァ-ン一-龥]/, message: "is invalid. Please input full-width characters."}
validates :name_kana, format: {with:/\A[ァ-ヶー-]+\z/, message: "is invalid. Please input full-width katakana characters."}
validates :nickname, format: {with:/\A[a-z0-9]+\z/i, message: "is invalid. Please input half-width characters."}
# ----- ここから 住所モデルのバリデーション -----
validates :postal_code, format: {with: /\A[0-9]+\z/, message: "is invalid. Please input half-width characters."}
validates :prefecture_id, numericality: { other_than: 0, message: "can't be blank" }
# ----- ここまで 住所モデルのバリデーション -----
end
end
これでユーザーモデルと住所モデルのバリデーションの統合は完了したので、次はコントローラの仕組みを編集していきます。
コントローラで行いたいことはまず値の登録です。
そのため、formオブジェクト内に2つのモデルを介して値が登録できるメソッドを生み出す必要があります。今回は分かりやすくsaveとしましょう。
class UserAddress
include ActiveModel::Model
attr_accessor :name, :name_kana, :nickname, :postal_code, :prefecture_id, :city, :house_number, :building_name
# ----- バリデーションの記述は割愛 -----
def save
# ここにモデル2つを介して値を保存する記述を施す
end
end
今回介したいモデルはUser.rbとAddress.rbですので以下のようになります。
class UserAddress.rb
include ActiveModel::Model
attr_accessor :name, :name_kana, :nickname, :postal_code, :prefecture_id, :city, :house_number, :building_name
# ----- バリデーションの記述は割愛 -----
def save
user = User.create(name: name, name_kana: name_kana, nickname: nickname)
Address.create(postal_code: postal_code, prefecture_id: prefecture_id, city: city, house_number: house_number, building_name: building_name, user_id: user.id)
end
end
これによりコントローラの記述もformオブジェクトを経由させる記述に変更します。
class FormatsController < ApplicationController
def index
@formats = User.includes(:address) # ここを変更
end
def new
# @format = User.new ここを削除
@format = UserAddress.new # ここを追記
end
def create
# @format = User.create(format_params) ここを削除
@format = UserAddress.new(format_params) # ここを追記
@format.save # user_addres.rbで定義したメソッドをここで使用する
redirect_to root_path
end
private
def format_params
# permit内に住所登録に必要な値を追加する
params.require(:user_address).permit(:name, :name_kana, :nickname, :postal_code, :prefecture_id, :city, :house_number, :building_name)
end
end
ビューファイルを編集して、住所項目登録欄を作ります。
Gemfileにactive_hashを追加
gem 'active_hash'
以下のファイルを作成して記述を行う
class Prefecture < ActiveHash::Base
self.data = [
{id: 0, name: '--'}, {id: 1, name: '北海道'}, {id: 2, name: '青森県'},
{id: 3, name: '岩手県'}, {id: 4, name: '宮城県'}, {id: 5, name: '秋田県'},
{id: 6, name: '山形県'}, {id: 7, name: '福島県'}, {id: 8, name: '茨城県'},
{id: 9, name: '栃木県'}, {id: 10, name: '群馬県'}, {id: 11, name: '埼玉県'},
{id: 12, name: '千葉県'}, {id: 13, name: '東京都'}, {id: 14, name: '神奈川県'},
{id: 15, name: '新潟県'}, {id: 16, name: '富山県'}, {id: 17, name: '石川県'},
{id: 18, name: '福井県'}, {id: 19, name: '山梨県'}, {id: 20, name: '長野県'},
{id: 21, name: '岐阜県'}, {id: 22, name: '静岡県'}, {id: 23, name: '愛知県'},
{id: 24, name: '三重県'}, {id: 25, name: '滋賀県'}, {id: 26, name: '京都府'},
{id: 27, name: '大阪府'}, {id: 28, name: '兵庫県'}, {id: 29, name: '奈良県'},
{id: 30, name: '和歌山県'}, {id: 31, name: '鳥取県'}, {id: 32, name: '島根県'},
{id: 33, name: '岡山県'}, {id: 34, name: '広島県'}, {id: 35, name: '山口県'},
{id: 36, name: '徳島県'}, {id: 37, name: '香川県'}, {id: 38, name: '愛媛県'},
{id: 39, name: '高知県'}, {id: 40, name: '福岡県'}, {id: 41, name: '佐賀県'},
{id: 42, name: '長崎県'}, {id: 43, name: '熊本県'}, {id: 44, name: '大分県'},
{id: 45, name: '宮崎県'}, {id: 46, name: '鹿児島県'}, {id: 47, name: '沖縄県'}
]
end
モデルにアソシエーションを追加
class Address < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :user
extend ActiveHash::Associations::ActiveRecordExtensions
belongs_to_active_hash :prefecture
end
ビューを以下のように編集
<%= form_with(model: @format, url: formats_path, local: true) do |form| %>
<h1>ユーザー名を入力</h1>
<div class="field">
<%= form.label :name, "名前(全角)" %>
<%= form.text_field :name %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= form.label :name_kana, "フリカナ(全角カタカナ)" %>
<%= form.text_field :name_kana %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= form.label :nickname, "ニックネーム(半角英数)" %>
<%= form.text_field :nickname %>
</div>
<%# ここから 追加 %>
<h1>住所を入力</h1>
<div class="field">
<%= form.label :postal_code, "郵便番号(ハイフンを含む)" %>
<%= form.text_field :postal_code %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= form.label :prefecture_id, "都道府県" %>
<%= form.collection_select :prefecture_id, Prefecture.all, :id, :name, {} %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= form.label :city, "市町村(任意)" %>
<%= form.text_field :city %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= form.label :house_number, "番地(任意)" %>
<%= form.text_field :house_number %>
</div>
<div class="field">
<%= form.label :building_name, "建物名(任意)" %>
<%= form.text_field :building_name %>
</div>
<%# ここまで 追加 %>
<div class="actions">
<%= form.submit "登録する" %>
</div>
<% end %>
登録できた値を表示させてみましょう。
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="btn">
<%= link_to '登録する', new_format_path %>
</div>
<div class="formats">
<% @formats.each do |format| %>
<div class="format">
<div class="format-name">ユーザー情報:<%= format.name %>/<%= format.name_kana %>/<%= format.nickname %></div>
<div class="format-name">住所情報:<%= format.address.postal_code%>/<%= format.address.prefecture.name%>/<%= format.address.city%>/<%= format.address.house_number%>/<%= format.address.building_name%></div>
</div>
<% end %>
</div>
</div>
これで完成です!