ベイズ最適化の概説
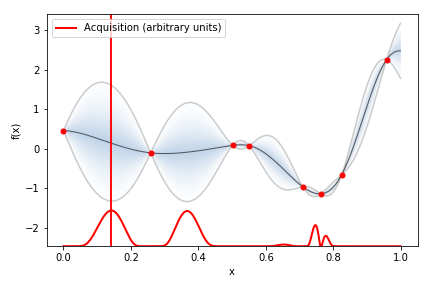
ガウス過程により平均と分散を考慮した回帰式について、最小となりうる可能性のある部分に実験点を追加し、回帰式を更新するとともに最小値を探す手法
上図において、最小値はx=0.75付近であるがx=0.15付近の回帰式の予測精度が悪く(事後分布の幅が大きい)、最小値を持ちうる可能性がある。ベイズ最適化では最小値を持ちうる可能性のある0.15付近を次の実験点とし、最小値付近の回帰式の精度を向上させつつ最小値を探す。
- 効率的な動的実験計画
- 多峰性に強い
以上からベイズ最適化は、一回の計算時間がかかり、設計空間の非常に広いパラメトリックなCAEの最適化に有効と思われる。
使用するパッケージ
GPyOpt
ベイズ最適化のパッケージ
ガウス過程のGPyが必要な他、初期の計算にラテン超方格サンプリングを利用する場合はpyDOEも必要
インストール
conda update scipy
pip install GPy
pip install gpyopt
pip install pyDOE
パッケージ情報
Name: GPy
Version: 1.9.2
Summary: The Gaussian Process Toolbox
Home-page: http://sheffieldml.github.com/GPy/
Author: GPy Authors: https://github.com/SheffieldML/GPy/graphs/contributors
Author-email: gpy.authors@gmail.com
License: BSD 3-clause
Location: /home/ubuntu/.pyenv/versions/anaconda3-5.0.1/envs/py35/lib/python3.5/site-packages
Requires: numpy, paramz, scipy, six
Required-by: GPyOpt
---
Name: GPyOpt
Version: 1.2.1
Summary: The Bayesian Optimization Toolbox
Home-page: http://sheffieldml.github.io/GPyOpt/
Author: -Aki Vehtari
Author-email: None
License: None
Location: /home/ubuntu/.pyenv/versions/anaconda3-5.0.1/envs/py35/lib/python3.5/site-packages
Requires: numpy, scipy, GPy
Required-by:
---
Name: pyDOE
Version: 0.3.8
Summary: Design of experiments for Python
Home-page: https://github.com/tisimst/pyDOE
Author: Abraham Lee
Author-email: tisimst@gmail.com
License: BSD License (3-Clause)
Location: /home/ubuntu/.pyenv/versions/anaconda3-5.0.1/envs/py35/lib/python3.5/site-packages
Requires: numpy, scipy
Required-by:
PyGEM
メッシュモーフィングのパッケージ
Stl形式のサーフェイスデータやOpenFOAMなどのメッシュのモーフィングが可能
Python2系で提供されているが2to3で3系でも利用可能
インストール
いろいろ試したので下記でよかったのか自信なし。
あとUbuntu-16.04.3 LTSにおける説明です。
sudo apt install -y libxt6
sudo apt install -y libsm6
pip install numpy scipy matplotlib vtk nose coveralls coverage
conda install -c conda-forge -c dlr-sc -c pythonocc -c oce pythonocc-core==0.17.3
git clone https://github.com/mathLab/PyGeM.git
cd PyGeM
2to3 -w ./
python3 setup.py install
パッケージ情報
Name: pygem
Version: 1.1
Summary: Tools for gemetrical morphing.
Home-page: https://github.com/mathLab/PyGeM
Author: Marco Tezzele, Nicola Demo
Author-email: marcotez@gmail.com, demo.nicola@gmail.com
License: MIT
Location: /home/ubuntu/.pyenv/versions/anaconda3-5.0.1/envs/py35/lib/python3.5/site-packages/pygem-1.1-py3.5.egg
Requires: numpy, numpy-stl, enum34, scipy, matplotlib, vtk, Sphinx, sphinx-rtd-theme
Required-by:
PyFoam
OpenFOAMに関するユーティリティを提供するパッケージ
今回はOpenFOAMのコントロールに利用する
インストール
pip install PyFoam
パッケージ情報
Name: PyFoam
Version: 0.6.9
Summary: Python Utilities for OpenFOAM
Home-page: http://openfoamwiki.net/index.php/Contrib/PyFoam
Author: Bernhard F.W. Gschaider
Author-email: bgschaid@ice-sf.at
License: GPL
Location: /home/ubuntu/.pyenv/versions/anaconda3-5.0.1/envs/py35/lib/python3.5/site-packages
Requires: numpy
Required-by:
OpenFOAMのバージョン
今回はOpenFOAM-v1712を使っている。
(別途インストールしてください-->OpenFOAMの環境構築2018
OpenFOAMの設定($FOAM_ETC/bashrc)を読み込んだ状態で起動したPythonで下記を実行。
import PyFoam
PyFoam.foamVersionString()
# -->'v1712'
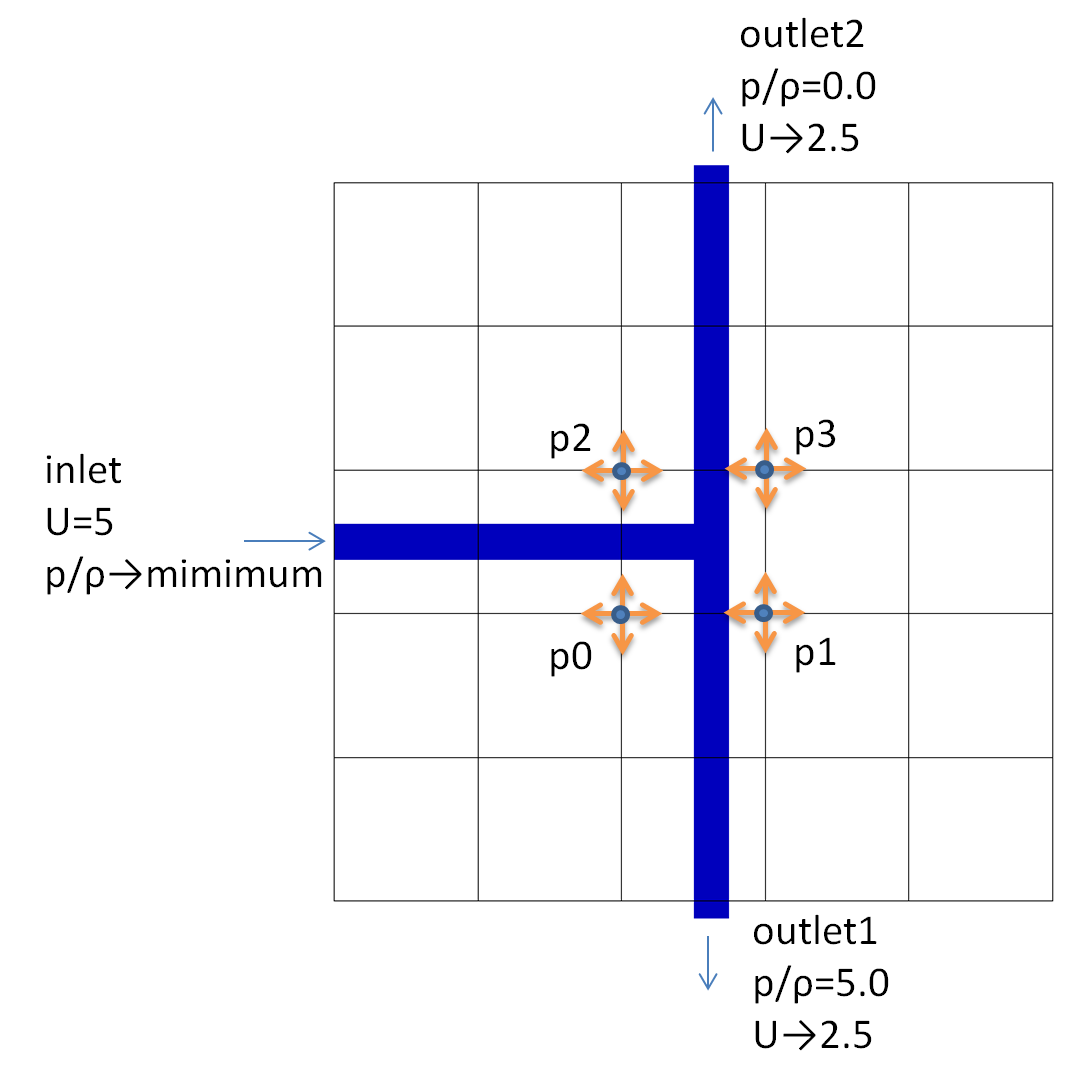
流路の最適化問題
OpenFOAMのTutorialにあるTJunctionを下記のように改造(定常計算化+境界条件変更)
outlet1, outlet2から流出する流量(流速)を等しくした上で、inletの圧力を最小化する
設計変数はモーフィンググリッドのp0~p3のxy座標とする
OpenFOAMをPythonで動かす準備
基本的にPyFoamからOpenFOAMを動かす。
下記の関数を定義しておく
import shlex, os
from PyFoam.RunDictionary.SolutionDirectory import SolutionDirectory
from PyFoam.RunDictionary.ParsedParameterFile import ParsedParameterFile
from PyFoam.Basics.DataStructures import Vector
from PyFoam.Execution.BasicRunner import BasicRunner
from PyFoam.LogAnalysis.UtilityAnalyzer import UtilityAnalyzer
from PyFoam.LogAnalysis.LogAnalyzerApplication import LogAnalyzerApplication
from PyFoam.Applications.ClearCase import ClearCase
def ofExec(cmd, case_path):
cmds = shlex.split("{} -case {}".format(cmd, case_path))
runner = BasicRunner(cmds, silent=True)
state = runner.start()
return state
def getValueFromLog(re, logfile, rmLog=True):
ua = UtilityAnalyzer()
ua.addExpression("val",re)
logApp = LogAnalyzerApplication(ua)
logApp.run(logfile)
if rmLog:
shutil.rmtree(logfile,ignore_errors=True)
return np.array(ua.getData("val"),dtype=float)
解析ケースの準備
チュートリアルケースのコピーする
その後、blockMeshを実行し、polyMeshディレクトリ内のpointsファイルをpoints_orgとしてコピーしておく
from PyFoam.IPythonHelpers.Case import Case
tut_TJunc=Case(
"{}/tutorials/incompressible/pimpleFoam/RAS/TJunction/".format(
PyFoam.FoamInformation.findInstallationDir(PyFoam.foamVersionString())[-1]
))
TJunc = tut_TJunc.sol.cloneCase("./TJunction")
points_path ="{}/points".format(TJunc.polyMeshDir())
org_points_path = "{}_org".format(points_path)
res_blockMesh = ofExec("blockMesh", TJunc.name)
shutil.move(points_path, org_points_path)
あと、境界条件などの変更を行っておく
diff --git a/0/U b/0/U
index d0660ba..8f0b2c9 100644
--- a/0/U
+++ b/0/U
@@ -22,7 +22,8 @@ boundaryField
{
inlet
{
- type pressureInletOutletVelocity;
+ type flowRateInletVelocity;
+ volumetricFlowRate constant 0.002; //[m3/s]
value uniform (0 0 0);
}
diff --git a/0/p b/0/p
index 807e4dc..97397a9 100644
--- a/0/p
+++ b/0/p
@@ -22,18 +22,13 @@ boundaryField
{
inlet
{
- type uniformTotalPressure;
- p0 table
- (
- (0 10)
- (1 40)
- );
+ type zeroGradient;
}
outlet1
{
type fixedValue;
- value uniform 10;
+ value uniform 5;
}
outlet2
diff --git a/system/controlDict b/system/controlDict
index 78cd543..cbf36ec 100644
--- a/system/controlDict
+++ b/system/controlDict
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ FoamFile
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
-application pimpleFoam;
+application simpleFoam;
startFrom startTime;
@@ -23,13 +23,13 @@ startTime 0;
stopAt endTime;
-endTime 1.5;
+endTime 1000;
-deltaT 0.001;
+deltaT 1;
-writeControl adjustableRunTime;
+writeControl timeStep;
-writeInterval 0.1;
+writeInterval 1000;
purgeWrite 0;
@@ -45,75 +45,12 @@ timePrecision 6;
runTimeModifiable true;
-adjustTimeStep yes;
+adjustTimeStep no;
maxCo 5;
functions
{
- probes
- {
- // Where to load it from
- libs ("libsampling.so");
-
- type probes;
-
- // Name of the directory for probe data
- name probes;
-
- // Write at same frequency as fields
- writeControl writeTime;
- writeInterval 1;
-
- // Fields to be probed
- fields
- (
- p U
- );
-
- probeLocations
- (
- ( 1e-06 0 0.01 ) // at inlet
- (0.21 -0.20999 0.01) // at outlet1
- (0.21 0.20999 0.01) // at outlet2
- (0.21 0 0.01) // at central block
- );
- }
-
- sTransport
- {
- type scalarTransport;
- libs ("libsolverFunctionObjects.so");
-
- enabled true;
- writeControl outputTime;
- writeInterval 1;
-
- field s;
-
- write true;
-
- fvOptions
- {
- unitySource
- {
- type scalarSemiImplicitSource;
- enabled true;
-
- scalarSemiImplicitSourceCoeffs
- {
- selectionMode all;
- volumeMode specific;
- injectionRateSuSp
- {
- s (1 0);
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- resetOnStartUp false;
- }
}
// ************************************************************************* //
diff --git a/system/fvSchemes b/system/fvSchemes
index 45b7880..9724934 100644
--- a/system/fvSchemes
+++ b/system/fvSchemes
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ FoamFile
ddtSchemes
{
- default Euler;
+ default steadyState;
}
gradSchemes
@@ -28,14 +28,13 @@ gradSchemes
divSchemes
{
default none;
- div(phi,U) Gauss limitedLinearV 1;
- div(phi,k) Gauss limitedLinear 1;
- div(phi,epsilon) Gauss limitedLinear 1;
- div(phi,R) Gauss limitedLinear 1;
- div(phi,s) Gauss limitedLinear 1;
- div(R) Gauss linear;
- div(phi,nuTilda) Gauss limitedLinear 1;
+ div(phi,U) bounded Gauss linearUpwind grad(U);
+ div(phi,k) bounded Gauss limitedLinear 1;
+ div(phi,epsilon) bounded Gauss limitedLinear 1;
+ div(phi,omega) bounded Gauss limitedLinear 1;
+ div(phi,v2) bounded Gauss limitedLinear 1;
div((nuEff*dev2(T(grad(U))))) Gauss linear;
+ div(nonlinearStress) Gauss linear;
}
laplacianSchemes
@@ -53,5 +52,10 @@ snGradSchemes
default corrected;
}
+wallDist
+{
+ method meshWave;
+}
+
// ************************************************************************* //
diff --git a/system/fvSolution b/system/fvSolution
index da1a955..a014d3d 100644
--- a/system/fvSolution
+++ b/system/fvSolution
@@ -21,51 +21,38 @@ solvers
{
solver GAMG;
tolerance 1e-06;
- relTol 0.01;
- smoother GaussSeidel;
- }
-
- pFinal
- {
- solver GAMG;
- tolerance 1e-06;
- relTol 0;
+ relTol 0.1;
smoother GaussSeidel;
}
- "(U|k|epsilon|s)"
+ "(U|k|epsilon|omega|f|v2)"
{
solver smoothSolver;
smoother symGaussSeidel;
tolerance 1e-05;
relTol 0.1;
}
-
- "(U|k|epsilon|s)Final"
- {
- $U;
- tolerance 1e-05;
- relTol 0;
- }
}
-PIMPLE
+SIMPLE
{
- nOuterCorrectors 1;
- nCorrectors 2;
nNonOrthogonalCorrectors 0;
- pRefCell 0;
- pRefValue 0;
+ consistent yes;
+
+ residualControl
+ {
+ p 1e-2;
+ U 1e-3;
+ "(k|epsilon|omega|f|v2)" 1e-3;
+ }
}
relaxationFactors
{
equations
{
- "U.*" 1;
- "k.*" 1;
- "epsilon.*" 1;
- "s.*" 1;
+ U 0.9; // 0.9 is more stable but 0.95 more convergent
+ ".*" 0.9; // 0.9 is more stable but 0.95 more convergent
}
}
モーフィングの準備
モーフィングの設定をparamsで行う。
xyz方向にそれぞれ6,6,2のグリッドで分割し、中央のp0~p3のグリッドを動かす。
下記ではp0~p3のグリッドを時計方向に回転させたときのメッシュモーフィング例である
import pygem as pg
e =1.e-6
l = 0.2-e
c = np.array([0.2, 0.0, 0.01])
params = pg.params.FFDParameters()
params.rot_angle = np.array([0,0,0])
params.origin_box = np.array([c[0] - l, c[1] - l ,c[2] - l])
params.lenght_box = np.array([2*l, 2*l, 2*l])
params.n_control_points = np.array([6,6,2])
params.array_mu_x = np.zeros(params.n_control_points.cumprod()[-1]).reshape(params.n_control_points)
params.array_mu_y = np.zeros(params.n_control_points.cumprod()[-1]).reshape(params.n_control_points)
params.array_mu_z = np.zeros(params.n_control_points.cumprod()[-1]).reshape(params.n_control_points)
# moving grid
params.array_mu_x[2,2,:] = -1. #p0x
params.array_mu_y[2,2,:] = 1. #p0y
params.array_mu_x[3,2,:] = -1. #p1x
params.array_mu_y[3,2,:] = -1. #p1y
params.array_mu_x[2,3,:] = 1. #p2x
params.array_mu_y[2,3,:] = 1. #p2y
params.array_mu_x[3,3,:] = 1. #p3x
params.array_mu_y[3,3,:] = -1. #p3y
of_handler = pg.openfhandler.OpenFoamHandler()
points = of_handler.parse(org_points_path)
# morphing
free_form = pg.freeform.FFD(params, points)
free_form.perform()
new_points = free_form.modified_mesh_points
shutil.rmtree(points_path,ignore_errors=True)
of_handler.write(new_points, points_path)
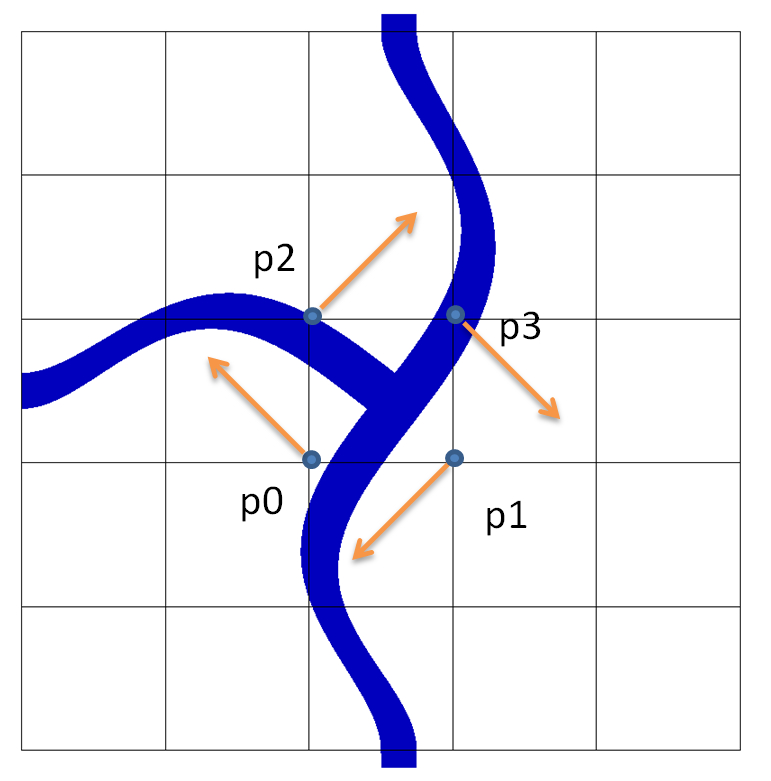
これをParaViewで確認すると下図のように中心部が回転しているような変形を実現できてる
モーフィング部分のみ関数化しておく
def morph_mesh(x, polyMeshDir):
x=x.reshape(-1,1)
params.array_mu_x[2,2,:] = x[0]
params.array_mu_y[2,2,:] = x[1]
params.array_mu_x[3,2,:] = x[2]
params.array_mu_y[3,2,:] = x[3]
params.array_mu_x[2,3,:] = x[4]
params.array_mu_y[2,3,:] = x[5]
params.array_mu_x[3,3,:] = x[6]
params.array_mu_y[3,3,:] = x[7]
org_points_path = "{}/points_org".format(polyMeshDir)
points_path ="{}/points".format(polyMeshDir)
of_handler = pg.openfhandler.OpenFoamHandler()
points = of_handler.parse(org_points_path)
free_form = pg.freeform.FFD(params, points)
free_form.perform()
new_points = free_form.modified_mesh_points
shutil.rmtree(points_path,ignore_errors=True)
of_handler.write(new_points, points_path)
目的関数の定義
先に記した通り、最小化したい関数は下記のとおりである。
\begin{align}
min: & p_{inlet} \\
const: & - U_{y_{outlet1}} = U_{y_{outlet2}} = 2.5
\end{align}
ベイズ最適化で制約条件を扱うことは可能であるが、今回制約条件の計算にもCFDの計算が必要であるので計算時間がかかりそう(うまく実装すればそうでもないはず…)
今回ラグランジェ未定定数のような形で、制約条件を満たさない場合にペナルティを課す目的関数に変更する。
min: p_{inlet} + 1000 \cdot (2.5 -U_{y_{outlet2}})^2
OpenFOAMの計算処理も含めてコード化すると下記のようになる
def objectFunc(x):
#clean case
TJunc.clearResults()
TJunc.clearPattern("PyFoam*")
# check points_org in polyMeshDir
points_path ="{}/points".format(TJunc.polyMeshDir())
org_points_path = "{}_org".format(points_path)
if not os.path.exists(org_points_path):
res_blockMesh = ofExec("blockMesh", TJunc.name)
shutil.move(points_path, org_points_path)
# morphing mesh
morph_mesh(x,TJunc.polyMeshDir())
# solve simpleFoam
res_simpleFoam = ofExec("simpleFoam", TJunc.name)
# get U_outlet2
res_pathAveU = ofExec(
'postProcess -func "patchAverage\(name=outlet2,U\)" -latestTime', TJunc.name)
U_outlet2 =getValueFromLog(
"average\(outlet2\) of U = \((%f%) (%f%) (%f%)\)", res_pathAveU["logfile"])
# get p_inlet
res_pathAvep = ofExec(
'postProcess -func "patchAverage\(name=inlet,p\)" -latestTime', TJunc.name)
p_inlet= getValueFromLog(
"average\(inlet\) of p = (%f%)", res_pathAvep["logfile"])
#print("Uy:{}".format(U_outlet2[1]))
#print("p:{}".format(p_inlet[0]))
if np.abs(2.5 - U_outlet2[1]) < 0.001:
Uy = 2.5
else:
Uy = U_outlet2[1]
p = p_inlet[0]
return p + 1000. *(2.5 - Uy)**2
内容は、「モーフィング → simpleFoam → patchAverage U → ログ分析(Uy_outlet2) → patchAverage p → ログ分析(p) → 目的関数の値計算」を実施している
Uy_outlet2が多少ずれても(2.5±0.001)ペナルティをかけないようにしてみた。
ベイズ最適化
設計変数は先述の通りp0~p3のxy座標である。変数の範囲などを定めてベイズ最適化モデルを作成する。
初期実験点は50点のラテン超方格計画で定めている
import GPy
import GPyOpt
bounds = [
{'name': 'p0x', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (-1,1)},
{'name': 'p0y', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (-1,1)},
{'name': 'p1x', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (-1,1)},
{'name': 'p1y', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (-1,1)},
{'name': 'p2x', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (-1,1)},
{'name': 'p2y', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (-1,1)},
{'name': 'p3x', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (-1,1)},
{'name': 'p3y', 'type': 'continuous', 'domain': (-1,1)},
]
myBopt = GPyOpt.methods.BayesianOptimization(
f=objectFunc,
domain=bounds,
initial_design_numdata=50,
initial_design_type="latin",
acquisition_type='LCB')
最適化を行う。
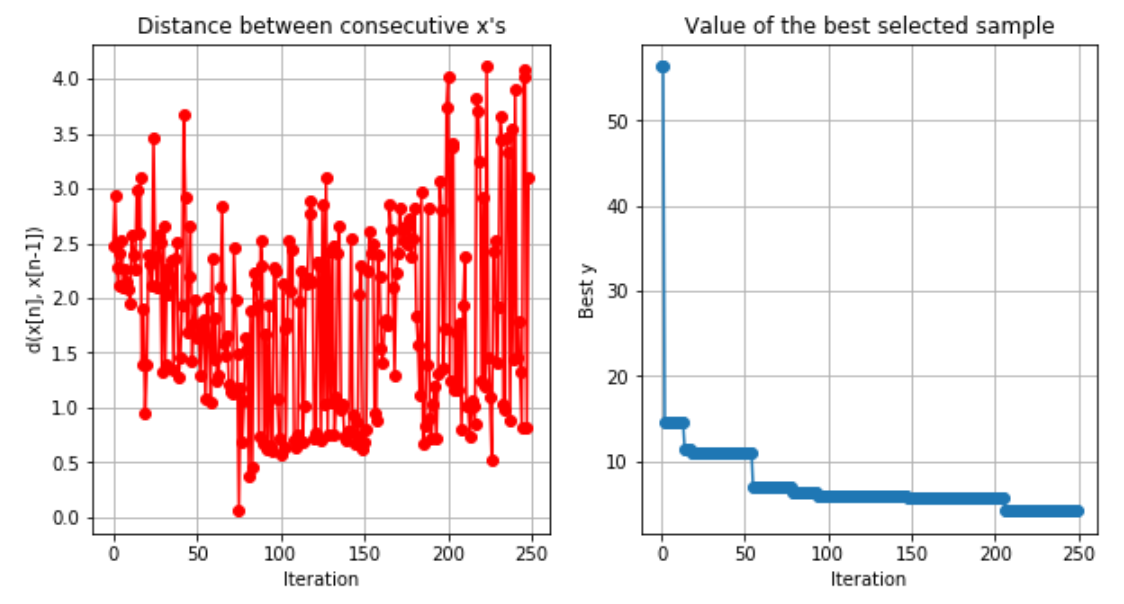
myBopt.run_optimization(max_iter=200)
計算完了後、最適解の履歴を表示する
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
myBopt.plot_convergence()
初期計算50回 + max_iter 200回 合計250回の計算が実施されている。
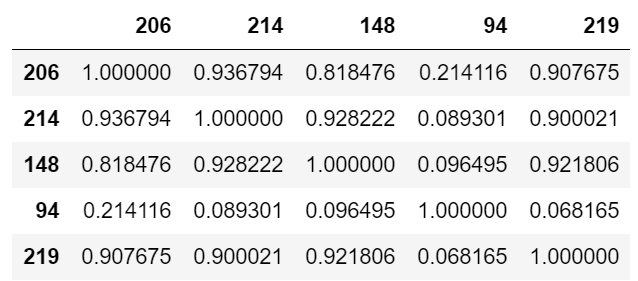
計算の履歴から最適解のベスト5を確認する
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(np.c_[myBopt.X,myBopt.Y])
df.columns = ["p0x", "p0y", "p1x", "p1y", "p2x", "p2y", "p3x", "p3y", "f"]
df.sort_values("f").head()
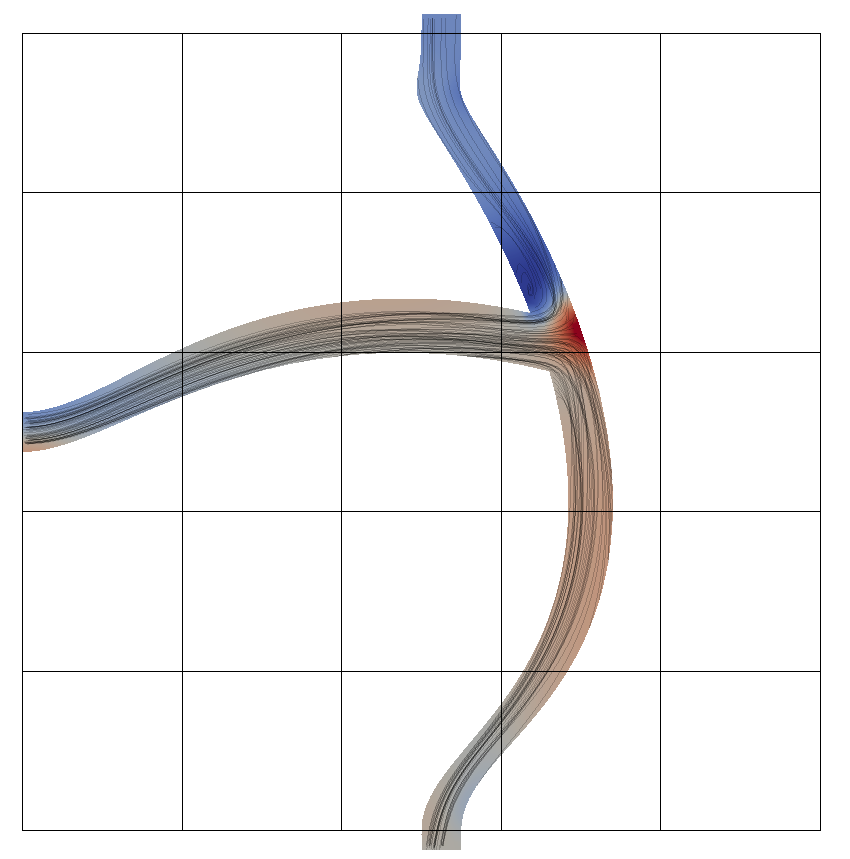
最適解は206回目の結果であることがわかる。
実際206回目の最適化結果をParaViewで確認する
x_opt1 = df.iloc[206,:].values[:-1]
objectFunc(x_opt1)
最適化結果の理解としては、圧力が高いOutlet1(下側)に積極的に流すために「つ」の形になめらかな流路を目指すべきで、一方圧力の低いOutlet2側へは圧損をつけて
流れにくくすべきだと、最適解が語っていると思われる。言われれば当たり前な気がする。
ちなみに最適解における、p_inlet:3.93941,Uy_outlet2:2.48509でほぼ求める解となっている
準最適解の確認
他の最適解も確認する。
最適解のベスト5の設計変数の相関行列を確認する
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(np.c_[myBopt.X,myBopt.Y])
df.columns = ["p0x", "p0y", "p1x", "p1y", "p2x", "p2y", "p3x", "p3y", "f"]
df.sort_values("f").head().T.corr()
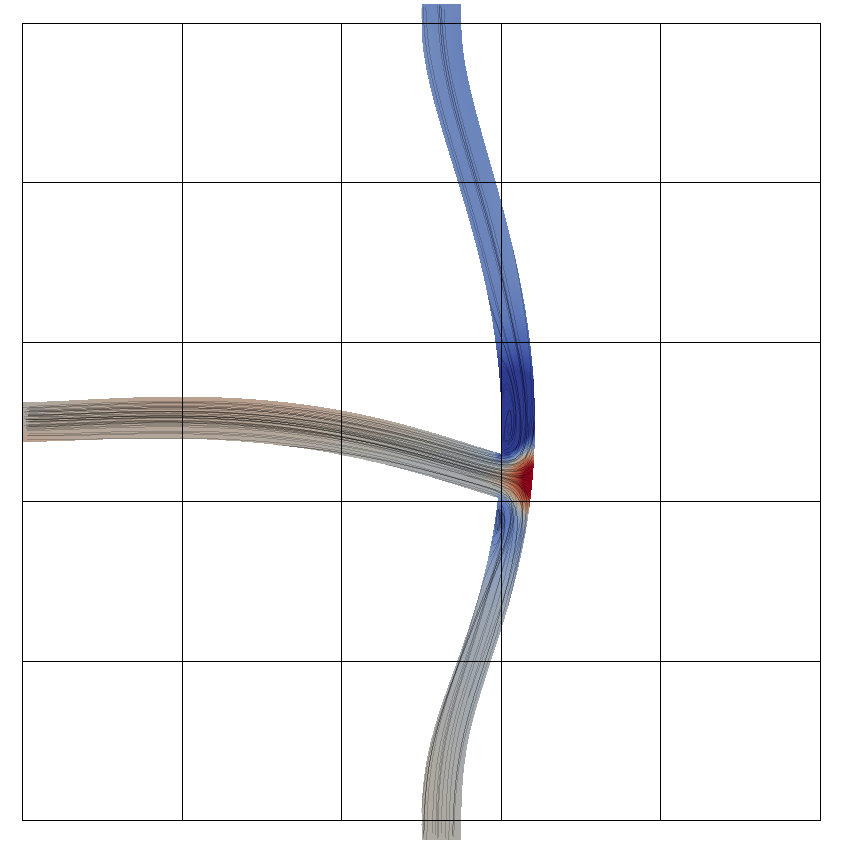
ほとんど206回目の解と相関性が高いが、94回目の解は相関性が低い。つまり別の峰の解であると思われる。
x_opt1 = df.iloc[94,:].values[:-1]
objectFunc(x_opt1)
ParaViewで確認すると下図の通りである
最適解の理解としては206回目の最適解と比べて交差点がoutlet1に近い。できるだけinletとoutlet1を直線的につないで圧損をつけずに流したいいう思想と思わる。
尚、この解のp_inlet:5.85746, Uy_outlet2:2.4938である。
まとめ
- メッシュモーフィングによる流路の最適化をベイズ最適化を用いて行った
- 最適解の履歴にある準最適解の相関を確認することで、別の峰の最適解を確認できた