はじめに
詳しいことや他のパターンは**デザインパターンをJavaScriptとJavaでの実装を比較して理解する**に書いていきます。
JavaScriptの例はJavaのを見て書きました。
クラス型・プロトタイプ型、型付の強弱、アクセス修飾子など特徴の違いなどは活かしていません。
ご了承ください。
Stateパターン
「状態」というものをクラスとして表現する
stateとは「状態(ものごとのありさま)」を意味する
Javaでの実装例
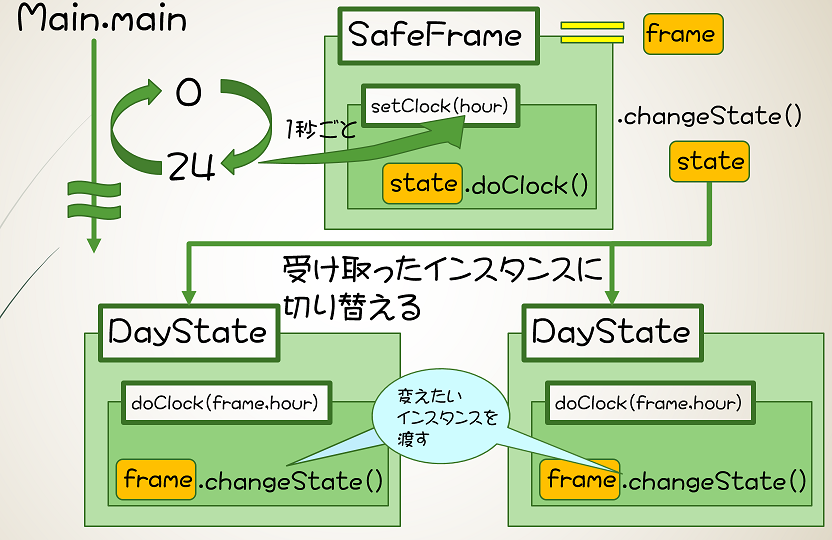
時刻ごとに警備の状態が変化する金庫警備システムを考えてみる
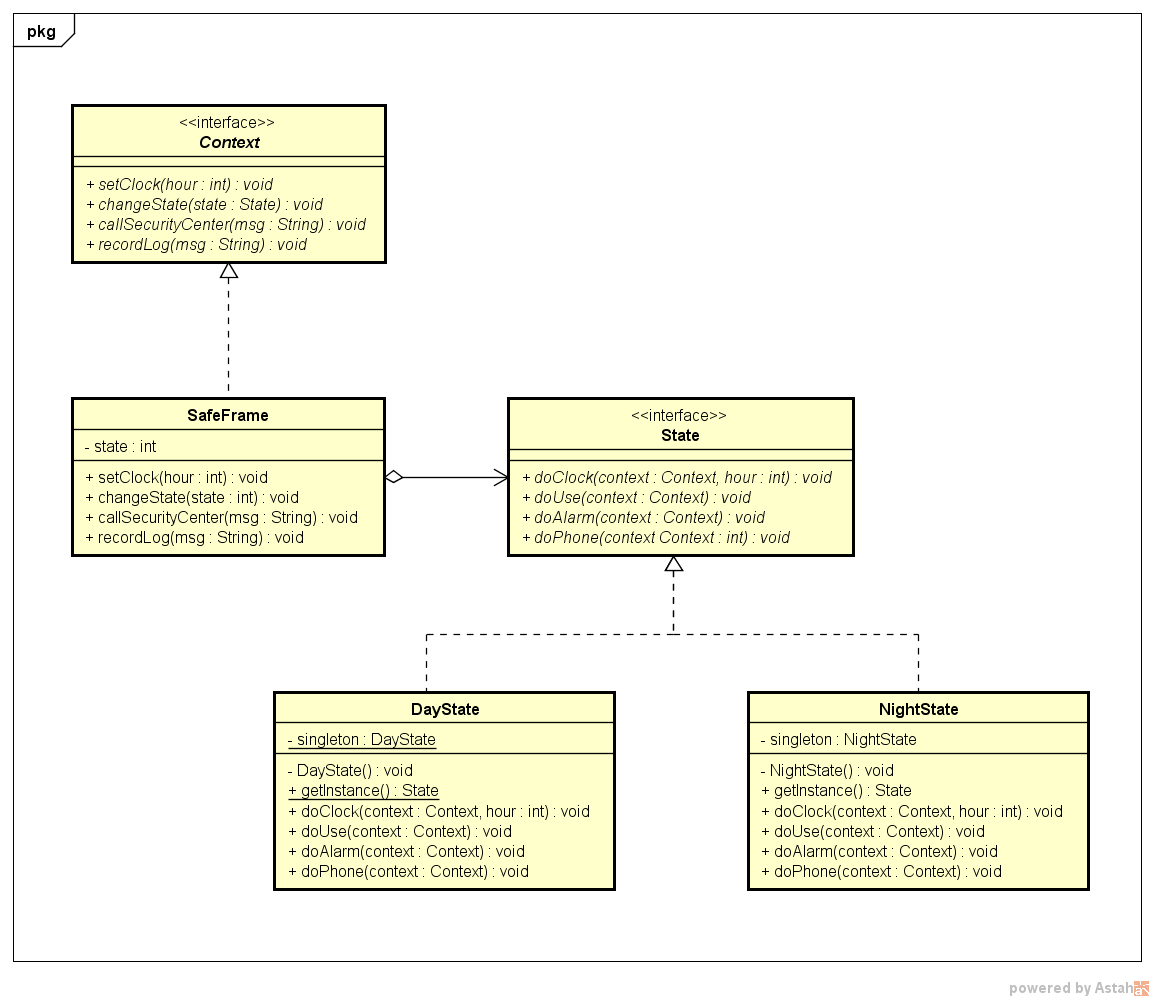
クラス図
コード
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SafeFrame frame = new SafeFrame("State Sample");
while (true) {
for (int hour = 0; hour < 24; hour++) {
frame.setClock(hour);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
}
}
public interface Context {
public abstract void setClock(int hour);
public abstract void changeState(State state);
public abstract void callSecurityCenter(String msg);
public abstract void recordLog(String msg);
}
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.Label;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.TextField;
import java.awt.TextArea;
import java.awt.Panel;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
public class SafeFrame extends Frame implements ActionListener, Context {
private TextField textClock = new TextField(60);
private TextArea textScreen = new TextArea(10, 60);
private Button buttonUse = new Button("金庫使用");
private Button buttonAlarm = new Button("非常ベル");
private Button buttonPhone = new Button("通所通話");
private Button buttonExit = new Button("終了");
private State state = DayState.getInstance();
public SafeFrame(String title) {
super(title);
setBackground(Color.lightGray);
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add(textClock, BorderLayout.NORTH);
textClock.setEditable(false);
add(textScreen, BorderLayout.CENTER);
textScreen.setEditable(false);
Panel panel = new Panel();
panel.add(buttonUse);
panel.add(buttonAlarm);
panel.add(buttonPhone);
panel.add(buttonExit);
add(panel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
pack();
setVisible(true);
buttonUse.addActionListener(this);
buttonAlarm.addActionListener(this);
buttonPhone.addActionListener(this);
buttonExit.addActionListener(this);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println(e.toString());
if (e.getSource() == buttonUse) {
state.doUse(this);
} else if (e.getSource() == buttonAlarm) {
state.doAlarm(this);
} else if (e.getSource() == buttonPhone) {
state.doPhone(this);
} else if (e.getSource() == buttonExit) {
System.exit(0);
} else {
System.out.println("?");
}
}
public void setClock(int hour) {
String clockstring = "現在時刻は";
if (hour < 10) {
clockstring += "0" + hour + ":00";
} else {
clockstring += hour + ":00";
}
System.out.println(clockstring);
textClock.setText(clockstring);
state.doClock(this, hour);
}
public void changeState(State state) {
System.out.println(this.state + "から" + state + "へ状態が変化しました。");
this.state = state;
}
public void callSecurityCenter(String msg) {
textScreen.append("call! " + msg + "\n");
}
public void recordLog(String msg) {
textScreen.append("record ... " + msg + "\n");
}
}
public interface State {
public abstract void doClock(Context context, int hour);
public abstract void doUse(Context context);
public abstract void doAlarm(Context context);
public abstract void doPhone(Context context);
}
public class DayState implements State {
private static DayState singleton = new DayState();
private DayState() {
}
public static State getInstance() {
return singleton;
}
public void doClock(Context context, int hour) {
if (hour < 9 || 17 <= hour) {
context.changeState(NightState.getInstance());
}
}
public void doUse(Context context) {
context.recordLog("金庫使用(昼間)");
}
public void doAlarm(Context context) {
context.callSecurityCenter("非常ベル(昼間)");
}
public void doPhone(Context context) {
context.callSecurityCenter("通常の通話(昼間)");
}
public String toString() {
return "[昼間]";
}
}
public class NightState implements State {
private static NightState singleton = new NightState();
private NightState() {
}
public static State getInstance() {
return singleton;
}
public void doClock(Context context, int hour) {
if (9 <= hour && hour < 17) {
context.changeState(DayState.getInstance());
}
}
public void doUse(Context context) {
context.callSecurityCenter("非常:夜間の金庫使用!");
}
public void doAlarm(Context context) {
context.callSecurityCenter("非常ベル(夜間)");
}
public void doPhone(Context context) {
context.recordLog("夜間の通話録音");
}
public String toString() {
return "[夜間]";
}
}
JavaScriptでの実装例
コード
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Stateパターン</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="main container flex">
<input type="text" name="output" disabled="disabled">
<textarea disabled="disabled"></textarea>
<div class="button_area flex">
<button>金庫使用</button>
<button>非常ベル</button>
<button>通常電話</button>
<button>終了</button>
</div>
</div>
<script src="Main.js"></script>
<script src="Context.js"></script>
<script src="DayState.js"></script>
<script src="NightState.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
/****************************************************************
共通部分
****************************************************************/
/*reset*/
body, div, dl, dt, dd, ul, ol, li, h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6, pre, form,
fieldset, input, textarea, p, blockquote, th, td{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html{
}
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6{
font-size: 100%;
font-weight: normal;
}
ol, ul{
list-style:none;
}
fieldset, img{
border:0;
}
table{
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing:0;
}
caption, th{
text-align: left;
}
address, caption, cite, code, dfn, em, strong, th, var{
font-style: normal;
font-weight: normal;
}
img {
vertical-align: bottom;
}
html {
font-size: 10px;
font-size: 62.5%;
}
a {
color: #000;
text-decoration: none;
}
/*setting*/
body {
font-size: 10px;
font-size: 1rem;
background-color: #dbdbdb;
}
.container {
width: 490px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.flex {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
}
/*main*/
.main {
margin-top: 20px;
flex-direction: column;
}
.main input {
width: 100%;
height: 25px;
border: 1px solid #000;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.main textarea {
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
box-sizing: border-box;
border: 1px solid #000;
border-top: 0;
overflow: scroll;
}
.main textarea:focus {
outline: 0;
}
.main .button_area {
width: 100%;
border:1px solid #000;
border-top: 0;
justify-content: center;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.button_area button {
margin: 5px;
}
MAIN = {};
MAIN.context;
MAIN.timer;
MAIN.hour;
MAIN.init = function() {
MAIN.context = new Context();
MAIN.hour = 0;
MAIN.timer = setInterval(MAIN.mainLoop, 500);
};
MAIN.mainLoop = function() {
MAIN.context.setClock(MAIN.hour);
MAIN.hour += 1;
if (MAIN.hour === 25) {
MAIN.hour = 0;
}
};
window.addEventListener("load", MAIN.init);
var Context = function() {
this.state = DAY_STATE.dayState.getInstance();
this.textFieldElm = document.querySelector(".main input[type='text']");
this.textAreaElm = document.querySelector(".main textarea");
document.querySelectorAll(".main .button_area button").forEach(function(b) {
switch (b.innerText) {
case "金庫使用":
b.addEventListener("click", function() {
MAIN.context.state.doUse(MAIN.context);
});
break;
case "非常ベル":
b.addEventListener("click", function() {
MAIN.context.state.doAlarm(MAIN.context);
});
break;
case "通常電話":
b.addEventListener("click", function() {
MAIN.context.state.doPhone(MAIN.context);
});
break;
case "終了":
b.addEventListener("click", function() {
window.close();
});
break;
}
});
};
Context.prototype = {
constructor: Context,
setClock: function(hour) {
var clockString = "現在時刻は";
if (hour < 10) {
clockString += "0" + hour + ":00";
} else {
clockString += hour + ":00";
}
console.log(clockString);
this.textFieldElm.value = clockString;
this.state.doClock(this, hour);
},
changeState: function(state) {
console.log(this.state.getName() + "からk" + state.getName() + "へ状態が変化しました。");
this.state = state;
},
callSecurityCenter: function(msg) {
this.textAreaElm.value += msg + "\n";
this.textAreaElm.scrollTop = this.textAreaElm.scrollHeight;
},
recordLog: function(msg) {
this.textAreaElm.value += msg + "\n";
this.textAreaElm.scrollTop = this.textAreaElm.scrollHeight;
}
};
DAY_STATE = {};
DAY_STATE.dayState = (function() {
var singleton;
var name;
var init = function() {
name = "[昼間]"
return {
doClock: function(context, hour) {
if (hour < 9 || 17 <= hour) {
context.changeState(NIGHT_STATE.nightState.getInstance());
}
},
doUse: function(context) {
context.recordLog("金庫使用(昼間)");
},
doAlarm: function(context) {
context.callSecurityCenter("非常ベル(昼間)");
},
doPhone(context) {
context.callSecurityCenter("通常の通話(昼間)");
},
getName: function() {
return name;
}
};
};
return {
getInstance: function() {
if (!singleton) {
singleton = init();
}
return singleton;
}
}
})();
NIGHT_STATE = {};
NIGHT_STATE.nightState = (function() {
var singleton;
var name;
var init = function() {
name = "[夜間]";
return {
doClock: function(context, hour) {
if (9 <= hour && hour < 17) {
context.changeState(DAY_STATE.dayState.getInstance());
}
},
doUse: function(context) {
context.recordLog("非常:夜間の金庫使用!")
},
doAlarm: function(context) {
context.callSecurityCenter("非常ベル(夜間)");
},
doPhone: function(context) {
context.callSecurityCenter("夜間の通話録音");
},
getName: function() {
return name;
}
};
};
return {
getInstance: function() {
if (!singleton) {
singleton = init();
}
return singleton;
}
};
})();
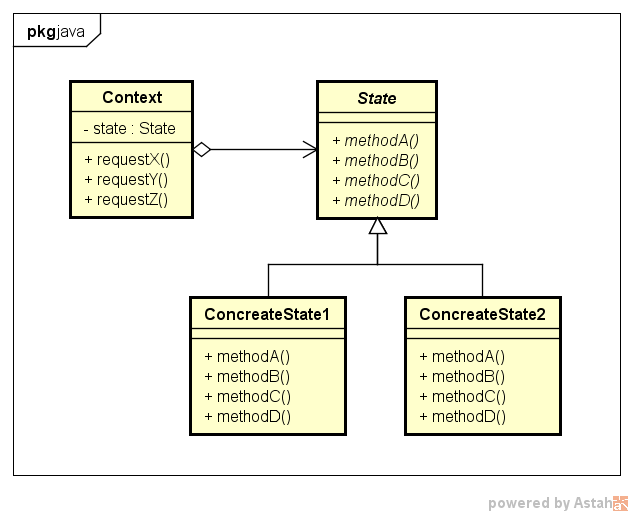
Stateパターンの登場人物
State(状態)の役
状態を表す
状態に依存した振る舞いをするメソッドの集まり
サンプルプログラム⇒State(interface)
ConcreateState(具体的な状態)の役
具体的な個々の状態を表現する
サンプルプログラム⇒DayState(class), NightState(class)
Context(状況、前後関係、文脈)の役
現在の状態を表す
サンプルプログラム⇒Context(interface)
Stateパターンのクラス図
Stateパターンの必要性
if文やswitch文で状態の変化を見て、動きを変えることもできる
public void method1(状態) {
if (状態A) {
System.out.println("状態Aなのでこんにちは");
}
if (状態B) {
System.out.println("状態Bなのでこんばんは");
}
}
public void method2(状態) {
if (状態A) {
System.out.println("状態AなのでHello");
}
if (状態B) {
System.out.println("状態BなのでGood evening");
}
}
だが、プログラマは毎回状態の違いを意識しなければならない
状態が追加された時も、多くの場所を編集しないといけない
状態をクラスとして表現していれば、クラスを切り替えることによって「状態の変化」を表せる
新しい状態を追加するときにConcreateState役を追加すれば良いだけなのでわかりやすい
Stateパターンの使い時
関連しているパターン
- Singletonパターン
- Flyweightパターン