はじめに
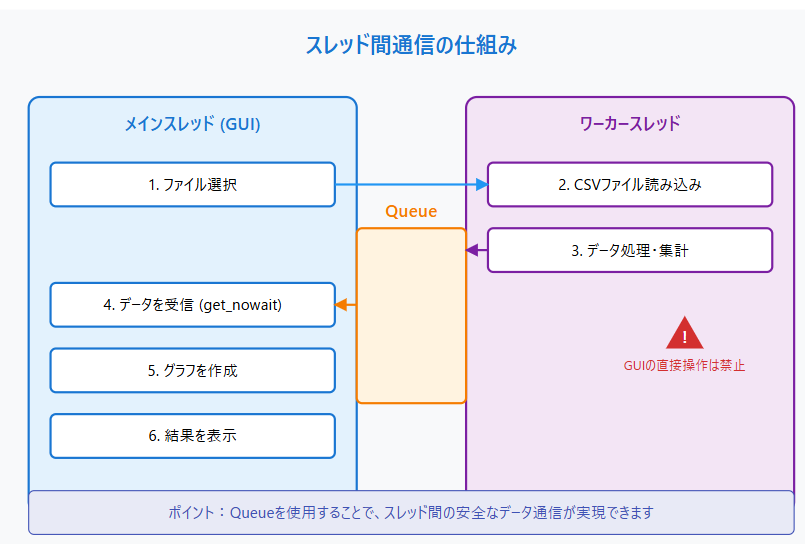
GUIアプリケーションで重い処理を行う際、メインスレッドがフリーズしないようにするには非同期処理が必要です。
本記事では、Queueを使って安全にデータを受け渡す方法を、実践的なCSVデータ可視化アプリケーションの実装を通じて解説します。
よくある問題点と解決策
問題1: UIのフリーズ
# 悪い例
def button_click():
result = heavy_process() # UIがフリーズ
show_result(result)
# 良い例
def button_click():
thread = threading.Thread(target=process_in_background)
thread.start()
def process_in_background():
result = heavy_process()
result_queue.put(result) # Queueで安全に結果を送信
問題2: スレッドからのGUI操作
# 悪い例
def background_thread():
result = process_data()
label.config(text=result) # 危険!
# 良い例
def background_thread():
result = process_data()
queue.put(result)
def check_queue(): # メインスレッドで実行
try:
result = queue.get_nowait()
label.config(text=result) # 安全
except Queue.Empty:
pass
root.after(100, check_queue)
サンプルアプリケーション
CSVデータを読み込んでグラフ表示するアプリケーションを実装してみましょう。
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk, filedialog
import threading
import queue
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.backends.backend_tkagg import FigureCanvasTkAgg
class DataProcessWindow:
def __init__(self, master, file_path, result_queue):
self.top = tk.Toplevel(master)
self.top.title("データ処理中")
self.top.geometry("300x150")
self.file_path = file_path
self.result_queue = result_queue
self.progress = ttk.Progressbar(
self.top,
mode='indeterminate',
length=200
)
self.progress.pack(pady=20)
self.progress.start()
# 処理スレッドの開始
self.thread = threading.Thread(target=self.process_data)
self.thread.daemon = True
self.thread.start()
def create_figures(self, data):
"""メインスレッドでグラフを作成(重要)"""
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
data.plot(kind='bar', ax=ax)
plt.tight_layout()
return fig
def process_data(self):
try:
# CSVファイルの読み込みと処理
df = pd.read_csv(self.file_path)
monthly_sum = df.groupby('month')['value'].sum()
# 集計結果をキューに送信
self.result_queue.put(('data', monthly_sum))
except Exception as e:
self.result_queue.put(('error', str(e)))
finally:
self.result_queue.put(('close_window', None))
class MainWindow:
def __init__(self):
self.root = tk.Tk()
self.root.title("データ分析")
self.root.geometry("400x300")
self.file_button = ttk.Button(
self.root,
text="ファイルを選択",
command=self.select_file
)
self.file_button.pack(pady=20)
self.result_queue = queue.Queue()
self.check_queue()
def select_file(self):
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(
filetypes=[("CSV files", "*.csv")]
)
if file_path:
self.file_button.config(state='disabled')
self.process_window = DataProcessWindow(
self.root, file_path, self.result_queue
)
def check_queue(self):
try:
while True:
status, data = self.result_queue.get_nowait()
if status == 'data':
# メインスレッドでグラフを作成
fig = self.process_window.create_figures(data)
self.show_result(fig)
self.file_button.config(state='normal')
elif status == 'close_window':
if self.process_window:
self.process_window.top.destroy()
except queue.Empty:
pass
finally:
self.root.after(100, self.check_queue)
def show_result(self, figure):
window = tk.Toplevel(self.root)
window.title("分析結果")
window.geometry("800x600")
canvas = FigureCanvasTkAgg(figure, master=window)
canvas.draw()
canvas.get_tk_widget().pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
# マウスイベントによるエラーを回避
canvas.mpl_connect('motion_notify_event', lambda event: None)
def run(self):
self.root.mainloop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = MainWindow()
app.run()
動作確認用のサンプルデータ
以下の内容をsample_data.csvとして保存してください:
month,value,category
2023-01,1250000,A
2023-02,1380000,A
2023-03,1420000,A
2023-04,1580000,A
2023-05,1680000,A
2023-06,1720000,A
動作例
ファイル選択を押下するとファイルダイアログが開く。
入力するCSVをファイルを選択すると、読み込みのプログレスバーが表示される。
読み込みが完了すると分析結果のグラフがの画面が出力される。
実装のポイント
-
スレッド間通信は必ずQueueを使用
- バックグラウンドスレッドからGUIを直接操作しない
- データやステータスはすべてQueueを介して送受信
-
Matplotlibの操作はメインスレッドで
- グラフの作成や更新は必ずメインスレッドで行う
- バックグラウンドスレッドではデータ処理のみを実施
-
例外処理を忘れずに
- バックグラウンドスレッドでの例外はキューで通知
- メインスレッドで適切にエラーハンドリング
まとめ
-
Queueを使用することで、スレッド間の安全なデータ通信が実現できます - GUIの操作は必ずメインスレッドで行うことで、予期せぬエラーを防げます
- 適切な非同期処理により、レスポンシブなGUIアプリケーションが実装できます